
Hamlet's Mill
An essay on myth and the frame of time
GIORGIO de SANTILLANA
Professor of the History and Philosophy of Science
M.l.T.
and
HERTHA von DECHEND
apl. Professor fur Geschichte der Naturivissenschaften
]. W. Goethe-Universitat Frankfurt
Preface
ASthe senior, if least deserving, of the authors, I shall open the
narrative.
Over many years I have searched for the point where myth and
science join. It was clear to me for a long time that the origins of
science had their deep roots in a particular myth, that of invariance.
The Greeks, as early as the 7th century B.C., spoke of the quest of
their first sages as the Problem of the One and the Many, sometimes
describing the wild fecundity of nature as the way in which the
Many could be deduced from the One, sometimes seeing the Many
as unsubstantial variations being played on the One. The oracular
sayings of Heraclitus the Obscure do nothing but illustrate with
shimmering paradoxes the illusory quality of "things" in flux as
they were wrung from the central intuition of unity. Before him
Anaximander had announced, also oracularly, that the cause of
things being born and perishing is their mutual injustice to each
other in the order of time, "as is meet," he said, for they are bound
to atone forever for their mutual injustice. This was enough to
make of Anaximander the acknowledged father of physical science,
for the accent is on the real "Many." But it was true science after
a fashion.
Soon after, Pythagoras taught, no less oracularly, that "things
are numbers." Thus mathematics was born. The problem of the ori-
gin of mathematics has remained with us to this day. In his high old
age, Bertrand Russell has been driven to avow: "I have wished to
know how the stars shine. I have tried to apprehend the Pytha-
gorean power by which number holds sway above the flux. A little
of this, but not much, I have achieved." The answers that he found,
very great answers, concern the nature of logical clarity, but not
of philosophy proper. The problem of number remains to perplex
Preface
Vlll
us, and from it all of metaphysics was born. As a historian, I went
on investigating the "gray origins" of science, far into its pre-Greek
beginnings, and how philosophy was born of it, to go on puzzling
us. [ condensed it into a small book, The Origins of Scientific
Thought. For both philosophy and science came from that foun-
tainhead; and it is clear that both were children of the same myth.1
In a number of studies, I continued to pursue it under the name of
"scientific rationalism"; and I tried to show that through all the
immense developments, the "Mirror of Being" is always the object
of true science, a metaphor which still attempts to reduce the
Many to the One. We now make many clear distinctions, and have
come to separate science from philosophy utterly, but what remains
at the core is still the old myth of eternal invariance, ever more
remotely and subtly articulated, and what lies beyond it is a multi-
tude of procedures and technologies, great enough to have changed
the face of the world and to have posed terrible questions. But they
have not answered a single philosophical question, which is what
myth once used to do.
If we come to think of it, we have been living in the age of
Astronomical Myth until yesterday. The careful and rigorous edi-
fice of Ptolemy's Almagest is only window dressing for Plato's
theology, disguised as elaborate science. The heavenly bodies are
moving in "cycle and epicycle, orb in orb" of a mysterious motion
according to the divine decree that circular motions ever more
intricate would account for the universe. And Newton himself,
once he had accounted for it, simply replaced the orbs with the
understandable force of gravitation, for which he "would feign no
hypotheses." The hand of God was still the true motive force;
God's will and God's own mathematics went on, another name for
Aristotle's Prime Mover. And shall we deny that Einstein's space-
time is nothing other than a pure pan-mathematical myth, openly
acknowledged at last as such?
I was at this point, lost between science and myth, when, on the
occasion of a meeting in Frankfurt in 1959,I met Dr. von Dechend,
1 The Pythagorean problem is at the core of my Origins, My efforts came even-
lually to fruition in my Prologue to Parmenides, 1964. (reprinted in Reflections
on Men and Ideas [1968], p. 80).
ix • Preface
one of the last pupils of the great Frobenius, whom I had.known;
and with her I recalled his favorite saying: "What the hell should I
care for my silly notions of yesterday?" We were friends from the
start. She was then Assistant to the Chair of the History of Science,
but she had pursued her lonely way into cultural ethnology, starting
in West Africa on the tracks of her "Chef," which were being
opened up again at the time by that splendid French ethnologist,
the late Marcel Griaule. She too had a sense that the essence of myth
should be sought somewhere in Plato rather than in psychology,
but as yet she had no clue.
By the time of our meeting she had shifted her attention to Poly-
nesia, and soon she hit pay dirt. As she looked into the archaeologi-
cal remains on many islands, a clue was given to her. The moment
of grace came when, on looking (on a map) at two little islands,
mere flyspecks on the waters of the Pacific, she found that a strange
accumulation of maraes or cult places could be explained only one
way: they, and only they, were both exactly sited on two neat
celestial coordinates: the Tropics of Cancer and of Capricorn.
Now let Dechend take over the narrative:
"To start from sheer opposition to ruling opinions is not likely to
lead to sensible insight, at least so we think. But anyhow, I did not
start from there, although there is no denying that my growing
wrath about the current interpretations (based upon discouraging
translations) was a helpful spur now and then. In fact, there was
nothing that could be called a 'start,' least of all the intention to
explore the astronomical nature of myth. To the contrary, on my
side, having come from ethnology to the history of science, there
existed 'in the beginning' only the firm decision never to become
involved in astronomical matters, under any condition. In order to
keep safely away from this frightening field, my subject of inquiry
was meant to be the mythical figure of the craftsman god, the
Demiurge in his many aspects (Hephaistos, Tvashtri, Wayland the
Smith, Goibniu, Ilmarinen, Ptah, Khnum, Kothar-wa-Hasis, Enki/
Ea, Tane, Viracocha, etc.). Not even a whiff of suspicion came
to me during the investigation of Mesopotamian myths—of all cul-
tures!—everything looked so very terrestrial, though slightly pe-
culiar. It was after having spent more than a year over at least
Preface • x
[0,000 pages of Polynesian myths—collected in the 19th century
(there are many more pages available than these)—that the anni-
hilating recognition of our complete ignorance came down upon me
like a sledge hammer: there was no single sentence that could be
understood. But then, if anybody was entitled to be taken seriously,
it had to be the Polynesians guiding their ships securely over the
largest ocean of our globe, navigators to whom our much praised
discoverers from Magellan to Captain Cook confided the steering
of their ships more than once. Thus, the fault had to rest with us,
not with Polynesian myth. Still, I did not then 'try astronomy for a
change'—there was a strict determination on my part to avoid this
field. I looked into the archaeological remains of the many islands,
and there a clue was given to me (to call it being struck by light-
ning would be more correct) which I duly followed up, and then
there was no salvation anymore: astronomy could not be escaped.
First it was still 'simple' geometry—the orbit of the sun, the Trop-
ics, the seasons—and the adventures of gods and heroes did not make
much more sense even then. Maybe one should count, for a change?
What could it mean, when a hero was on his way slightly more
than two years, 'returning' at intervals, 'falling into space,' coming
off the 'right' route? There remained, indeed, not many possible
solutions: it had to be planets (in the particular case of Aukele-nui-
a-iku, Mars). If so, planets had to be constitutive members of every
mythical personnel; the Polynesians did not invent this trait by
themselves."
This text of Professor von Dechend, in its intellectual freedom
and audacity, bears the stamp of her inheritance from the heroic
and innocent and cosmopolitan age of German science around the
eighteen-thirties. Its heroes, Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Woeh-
ler, were the objects of her work done before 1953. Another of
those virtues, scornful indignation, will come to the fore in the
appendices, which are so largely the product of her efforts.
Now I resume:
Years before, I had once looked at Dupuis' L'Origine de tons les
cultes, lost in the stacks of Widener Library, never again consulted.
It was a book in the 18th-century style, dated "An III de la Repu-
xi • Preface
blique." The title was enough to make one distrustful—one of those
"enthusiastic" titles which abounded in the 18th century and prom-
ised far too much. How could it explain the Egyptian system, I
thought, since hieroglyphics had not yet been deciphered? (Atha-
nasius Kircher was later to show us how it was done out of Coptic
tradition.) I had dropped the forbidding tome, only jotting down
a sentence: "Le mythe est ne de la science; la science seule l'expli-
quera." I had the answer there, but I was not ready to understand.
This time I was able to grasp the idea at a glance, because I was
ready for it. Many, many years before, I had questioned myself, in
a note, about the meaning of fact in the crude empirical sense, as
applied to the ancients. It represents, I thought, not the intellectual
surprise, not the direct wonder and astonishment, but first of all an
immense, steady, minute attention to the seasons. What is a solstice
or an equinox? It stands for the capacity of coherence, deduction,
imaginative intention and reconstruction with which we could
hardly credit our forefathers. And yet there it was. I saw.
Mathematics was moving up to me from the depth of centuries;
not after myth, but before it. Not armed with Greek rigor, but with
the imagination of astrological power, with the understanding of
astronomy. Number gave the key. Way back in time, before writ-
ing was even invented, it was measures and counting that provided
the armature, the frame on which the rich texture of real myth was
to grow.
Thus we had returned to the true beginnings, in the Neolithic
Revolution. We agreed that revolution was essentially technologi-
cal. The earliest social scientist, Democritus of Abdera, put it in
one striking sentence: men's progress was the work not of the mind
but of the hand. His late successors have taken him too literally,
and concentrated on artifacts. They have been unaware of the
enormous intellectual effort involved, from metallurgy to the arts,
but especially in astronomy. The effort of sorting out and identify-
ing the only presences which totally eluded the action of our hands
led to those pure objects of contemplation, the stars in their courses.
The Greeks would not have misapprehended that effort: they
called astronomy the Royal Science. The effort at organizing the
Preface
xii
cosmos took shape from the supernal presences, those alone which
thought might put in control of reality, those from which all arts
look their meaning.
But nothing is so easy to ignore as something that does not yield
freely to understanding. Our science of the past flowered in the
fullness of time into philology and archaeology, as learned volumes
on ancient philosophy have continued to pour forth, to little avail.
A few masters of our own time have rediscovered these "prelit-
crate" accomplishments. Now Dupuis, Kircher and Boll are gone
like those archaic figures, and are equally forgotten. That is the de-
vouring way of time. The iniquity of oblivion blindly scattereth her
poppies.
It is well known how many images of the gods have to do with
the making of fire, and an American engineer, J. D. McGuire, dis-
covered that also certain Egyptian images, until then unsuspected,
presented deities handling a fire drill. Simple enough: fire itself was
the link between what the gods did and what man could do. But
from there, the mind had once been able to move on to prodigious
feats of intellect. That world of the mind was fully worthy of those
Newtons and Einsteins long forgotten—those masters, as d'Alem-
bert put it, of whom we know nothing, and to whom we owe
everything.
We had the idea. It was simple and clear. But we realized that we
would run into formidable difficulties, both from the point of view
of modern, current scholarship and from the no less unfamiliar ap-
proach needed for method. I called it playfully, for short, "the
cat on the keyboard," for reasons that will appear presently. For
how can one catch time on the wing? And yet the flow of time,
the time of music, was of the essence, inescapable, baffling to the
systematic mind. I searched at length for an inductive way of pre-
sentation. It was like piling Pelion upon Ossa. And yet this "was the
least of our difficulties. For we also had to face a wall, a veritable
Berlin Wall, made of indifference, ignorance, and hostility. Hum-
boldt, that wise master, said it long ago: First, people will deny
a thing; then they will belittle it; then they will decide that it
had been known long ago. Could we embark upon an enormous
xiii • Preface
task of detailed scholarship on the basis of this more than dubious
prospect? But our own task was set: to rescue those intellects of
the past, distant and recent, from oblivion. "Thus saith the Lord
God: 'Come from the four winds, O breath, and breathe upon these
slain, that they may live.' " Such poor scattered bones, ossa vehe-
menter sicca, we had to revive.
This book reflects the gradually deepening conviction that, first
of all, respect is due these fathers of ours. The early chapters will
make, I think, for easy reading. Gradually, as we move above tim-
berline, the reader will find himself beset by difficulties which are
not of our making. They are the inherent difficulties of a science
which was fundamentally reserved, beyond our conception. Most
frustrating, we could not use our good old simple catenary logic,
in which principles come first and deduction follows. This was not
the way of the archaic thinkers. They thought rather in terms of
what we might call a fugue, in which all notes cannot be constrained
into a single melodic scale, in which one is plunged directly into the
midst of things and must follow the temporal order created by their
thoughts. It is, after all, in the nature of music that the notes cannot
all be played at once. The order and sequence, the very meaning, of
the composition will reveal themselves—with patience—in due time.
The reader, I suggest, will have to place himself in the ancient
"Order of Time."
Troilus expressed the same idea in a different image: "He that
will have a cake out of the wheat must needs tarry the grinding."
Giorgio de Santillana
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Illustration from a postcard. Copyright 1962 by Verlag Karl Alber.
Reprinted by permission of Verlag Karl Alber, Freiburg im Breisgau.
Figures 1 and 2 on page 21 in "Etudes sur la cosmologie des Dogon et
des Bambara du Soudan Franjais" by D. Zahan and S. de Ganay, Africa,
vol. 21, 1951, copyright 1951 by D. Zahan, S. de Ganay, and the Inter-
national African Institute. Reprinted by permission of the International
African Inst itute, London.
Figure 6 on page 21 in The Catta Marina of Olaus Magnus: Venice
1539 and Rome 1572 by Edward Lynam, Tall Tree Library Publication
12, 1941. Reprinted by permission of Tall Tree Library, Jenkintown, pa.
Illustrations on page 26 and facing page 48 in Gesammelte, Werke, vol.
8, by Johannes Kepler, cd. Franz Hammer, 1963. Reprinted by permis-
sion of C. H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Munich.
Illustration on page 179 in Gesammelte Werke, vol. 1, by Johannes
Kepler, ed. Max Caspar, 1938. Reprinted by permission of C. H. Beck'-
sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Munich.
Figures 63 and 64 on pages 44 and 45 in The Flammarion Book of As-
tronomy, ed. Camille Flammarion, Simon and Schuster, 1964. Copy-
right 1955 by Librairie Flammarion. Reprinted by permission of Flam-
marion Publishers, Paris.
Figure 177 on page 742 in "Primitive Methods of Drilling" by J. D.
McGuire, Annual Report of the U.S. National Museum, 1894. Re-
printed by permission of the Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington,
D.C.
Figures 724 and 970 on pages 663 and 748 in Gesammelte Abhandlungen,
vol. 4, by E. Seler, i960. Copyright 1960 by Akademische Druck- und
Verlagsanstalt. Reprinted by permission of Akademische Druck- und
Verlagsanstalt, Graz.
xv • Acknowledgments
Illustration on page 96 of the Codices Selecti Phototypice Impressi, vol.
8, ed. Dr. F. Anders, 1967. Copyright 1952 by Akademische Druck-
und Verlagsanstalt. Reprinted by permission of Akademische Druck-
und Verlagsanstalt, Graz.
Illustration on page 434 in L'Uranographie Chinoise by G. Schlegel,
1875. Reprinted by permission of Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague.
Figure 104 on page 377 in Science and Civilisation in China, vol. 3, by
J. Needham, 1959. Copyright 1959 by Cambridge University Press.
Reprinted by permission of Cambridge University Press, New York.
Plate II facing page 22 in Die Geschichte der Sternkunde by E. Zinner,
1931. Reprinted by permission of Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Figures 36, 70, 71, and 75 on pages 91, 117, and 120 in Die Erscheinun-
gen am Sternenhimmel by H. v. Baravalle, 1962. Copyright 1962 by
Verlag Freies Geistesleben. Reprinted by permission of Verlag Freies
Geistesleben, Stuttgart.
Illustration on page 289 in The Dawn of Astronomy by J. N. Lockyer,
1894. Reprinted by permission of the Massachusetts Institute of Tech-
nology Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Figure 15 on plate IV in Catalogue of Engraved Gems, Greek, Etruscan
and Roman by G. M. A. Richter, 1956. Reprinted by permission of the
Metropolitan Museum of Art, Fletcher Fund, 31.11.14, New York.
Figure 70 on page 540 in "Animal Figures on Prehistoric Pottery from
Mimbres Valley, New Mexico" by J. W. Fewkes. Reprinted by permis-
sion of the American Anthropological Association from the American
Anthropologist, vol. 18, 1916, Washington, D.C.
Figures 1427 and 1444 on plates 107 and 109 in La Glyptique Mesopo-
tamienne Archaique by P. Amiet, 1961. Reprinted by permission of the
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Paris.
Figures 7 and 9 on pages 66 and 69 in Anfange der Astronomie by B. L.
van der Waerden, 1965. Copyright 1965 by N. V. Erben P. Noordhoff's
Uitgcverszaak, renewed 1968 by Birkhauser Verlag. Reprinted by per-
mission of Birkhauser Verlag, Basel.
Acknowledgments
xvi
Figure 17 on page 99 in L'Arbre Cosmique dans la Pensee populaire et
dans la Vie quotidienne du Nord-Ouest Africain by Viviana Paques,
1964, Copyright 1965 by Institut d'Ethnologie. Reprinted by permis-
sion of Institut d'Ethnologie, Paris.
illustrations on pages 67 and 68 in "Ein zweites Goldland Salomos" by
by J. Dahse, Zeitschrift fur Ethnologie, vol. 43, 1911. Reprinted by per-
mission of Dr. Gunther Hartmann.
Drawing of the Precession of the Equinoxes by Stefan Fuchs. Reprinted
by permission of Stefan Fuchs, University of Frankfurt, Germany.
We are indebted to Mrs. Katharina Lommel, Staatliches Museum fur
Volkerkunde, Munchen, for obtaining most of the illustrations used in
our book.
CONTENTS
Preface
Acknowledgments
Introduction
i. The Chronicler's Tale
ii. The Figure in Finland
iii. The Iranian Parallel
iv. History, Myth and Reality
Intermezzo: A Guide for the Perplexed
v. The Unfolding in India
vi. Amlodhi's Quern
vii. The Many-Colored Cover
vin. Shamans and Smiths
ix. Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
X. The Twilight of the Gods
xi. Samson Under Many Skies
xii. Socrates' Last Tale
xiii. Of Time and the Rivers
xiv. The Whirlpool
xv. The Waters from the Deep
xvi. The Stone and the Tree
xvii. The Frame of the Cosmos
xviii. The Galaxy
xix. The Fall of Phaethon
xx. The Depths of the Sea
xxi. The Great Pan Is Dead
xxii. The Adventure and the Quest
xxiii. Gilgamesh and Prometheus
Epilogue: The Lost Treasure
Conclusion
Appendices
Bibliography
Index
Vll
xiv
1
12
26
36
43
56
76
86
96
113
137
149
165
179
192
204
213
225
230
242
250
263
275
288
317
326
344
351
453
485
ABBREVIATIONS
|
ABAW |
Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Aka- |
|
demie der Wissenschaften |
|
|
AEG. WB. |
Worterbuch der Aegyptischen |
|
Sprache |
|
|
AEG. Z. |
Zeitschrift fur Aegyptische Sprache |
|
und Altertumskunde |
|
|
AFO |
Archiv fur Orientforschung |
|
AJSL |
American Journal of Semitic Lan- |
|
guages and Literature |
|
|
ANET |
Ancient Near Eastern Texts relating |
|
to the Old Testament |
|
|
AN. OR. |
Analecta Orientalia (Roma) |
|
AOTAT |
Altorientalische Texte zum Alten |
|
Testament |
|
|
APAW |
Abhandlungen der Preussischen Aka- |
|
demie der Wissenschaften |
|
|
AR |
Annual Report |
|
ARBAE |
Annual Report of the Bureau of |
|
American Ethnology (Washington) |
|
|
ARW |
Archiv fur Religionswissenschaft |
|
ATAO |
A. Jeremias: Das Alte Testament im |
|
Lichte des Alten Orients |
|
|
AV |
Atharva Veda |
|
BA |
Baessler Archiv (Berlin) |
|
BAE |
Bureau of American Ethnology |
|
BASOR |
Bulletin of the American Schools of |
|
Oriental Research |
|
|
BIFAO |
Bulletin de l'lnstitut Francais d'Arche- |
|
ologie Orientale (Cairo) |
|
|
BPB MUS. |
Bernice Pauahi Bishop |
|
Museum (Honolulu) |
|
|
BVSGW |
Berichte iiber die Verhandlungen der |
|
Sachsischen Gesellschaft der Wissen- |
|
|
schaften (Leipzig) |
|
|
BT |
Bibliotheca Teubneriana |
|
EE |
Enuma elish, the Babylonian Creation |
|
Epic |
|
|
ERE |
Encyclopaedia of Religion and Ethics |
|
(ed. James Hastings) |
Abbreviations
FFC Folklore Fellows Communications
(Helsinki)
FUF Finnisch-Ugrische Forschungen
GE Gilgamesh Epic
11 AOG A. Jeremias: Handbuch der Altorien-
talischen Geisteskultur
IIUCA Hebrew Union College Annual (Cin-
cinnati)
IAFE Internationales Archiv fur Ethnogra-
phie (Leiden)
JAOS Journal of the American Oriental So-
ciety
JCS Journal of Cuneiform Studies
JNES Journal of Near Eastern Studies
JRAS Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society
JSA Journal de la Societe des Africanistes
LCL Loeb Classical Library
MAGW Mitteilungen der Anthropologischen
Gesellschaft Wien
MAR Mythology of All Races (Boston)
MBH. Mahabharata
MVAG Mitteilungen der Vorderasiatischen
Gesellschaft
OLZ Orientalistische Literaturzeitung
OR. Orientalia, New Series (Roma)
PB A. Deimel: Pantheon Babylonicum
RA Revue d'Assyriologie et d'Archeologie
Orientale
RC Revue Celtique
RE Realencyclopaedie der Klassischen
Altertumswissenschaften (ed. Pauly-
Wissowa)
RH. MUS. Rheinisches Museum fur Philologie
RLA Reallexikon der Assyriologie
ROSCHER Ausfiihrliches Lexikon der griechis-
chen und romischen Mythologie
RV Rigveda
SBAW Sitzungsberichte der Bayerischen Aka-
demie der Wissenschaften
SBF, Sacred Books of the East
XXIV
xxv • Abbreviations
SHAW
SOAW
SPAW
TM
WB. MYTH.
WZKM
ZA
ZDMG
ZFE
ZVV
Sitzungsberichte der Heidelberger
Akademie der Wissenschaften
Sitzungsberichte der Oesterreichischen
Akademie der Wissenschaften
Sitzungsberichte der Preussischen
Akademie der Wissenschaften
J. Grimm: Teutonic Mythology
Worterbuch der Mythologie
Wiener Zeitschrift fur die Kunde des
Morgenlandes
Zeitschrift fur Assyriologie und vor-
derasiatische Archaeologie
Zeitschrift der Deutschen Morgen-
landischen Gesellschaft
Zeitschrift fiir Ethnologie
Zeitschrift des Vereins fiir Volkskunde
ILLUSTRATIONS
The Precession of the Equinoxes, shown in the order of
signs, with the dates marked on the left. endpaper
R. Eisler, The Royal Art of Astronomy, Herbert Joseph Ltd., London, 1946.
frontispiece
God creating the stars.
Courtesy Verlag Karl Alber, Freiburg im Breisgau.
The Precession of the Equinoxes.
Courtesy Stefan Fuchs, University of Frankfurt.
"The internal motion of the cosmic tree," according to
North-West Africans.
Courtesy Institut d'Ethnologie, Paris.
The ways of the Demiurge during creation.
Courtesy International African Institute, London.
Mount Meru, the world mountain, rising from the sea.
A. Qruenwedel, Altbuddhistische Kultstaetten in Chinesisch Turkestan, D.
Reitner, Berlin,
between
60-61
The collapse of the hourglass-shaped Meru.
A. Gruenwedel, Altbuddhistische Kultstaetten in Chinesisch Turkestan, D.
Reimer, Berlin, 1912.
The Carta Marina of Olaus Magnus.
Courtesy Tall Tree Library, Jenkintoivn, Pa.
The whirlpool, here called "Norvegianus Vortex."
Athanasius Kircher, Mundus Subterraneus, 1665.
The subterranean flow of rivers.
Athanasius Kircher, Mundus Subterraneus, 1665.
How Kronos continually gives to Zeus "all the measures of
the whole creation."
Courtesy C. H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Munich.
between
90-91
between
I34~I35
Illustrations
xx
The Precession of the Poles.
Courtesy Flammarion Publishers, Paris.
Horus and Seth in the act of drilling or churning.
Egyptian Mythology, The Hamlyn Group, Middlesex,
. between
142-143
between
162-163
The "incomparably mighty churn" of the Sea of Milk.
A. B. Keith, Indian Mythology, MAR 6, 1917.
The simplified version of the Amritamanthana.
Courtesy Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C.
The Maya Codex Tro-Cortesianus presents the same event.
Courtesy Akademische Druck- und Verlagsanstalt, Graz.
The Mesopotamian constellation of Bow and Arrow. between
Courtesy Birkhduser Verlag, Basel.
The Chinese constellation of Bow and Arrow.
Courtesy Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague.
The star maps for the celestial globe.
Courtesy Cambridge University Press, New York.
Drawing the bow at Sirius, the celestial jackal.
J. C. Ferguson, Chinese Mythology, MAR 8, 1917.
The so-called "Round Zodiac" of Dendera.
Courtesy Springer Verlag, Berlin.
The Polyhedra inscribed into the planetary orbits.
Courtesy C. H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Munich.
A detailed illustration of the motions of the Trigon of Great
between
222-223
between
268-269
Conjunctions.
Courtesy C. H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Munich.
"The shepherd is shown on the left sighting first the pole star." between
R. Eisler, The Royal Art of Astronomy, Herbert Joseph Ltd., London,
1946. .
xxi • Illustrations
The Chinese picture illustrates the surveying of the universe.
Sir Aurel Stein, Innermost Asia, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1928.
A terra-cotta mask of Humbaba/Huwawa. between
290—291
S. Langdon, Semitic Mythology, MAR 5, 1931.
Tlaloc, the so-called "rain-god" of Mexico.
Courtesy Akademische Druck- und Verlagsanstalt, Graz.
The movements of the planets Mercury and Saturn.
Courtesy Verlag Freies Geistesleben, Stuttgart.
The Egyptian goddess Serqet, or Selket.
Courtesy Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Cambridge.
A green jasper scarab of Greco-Phoenician origin shows the
Scorpion lady.
Courtesy Metropolitan Museum of Art, Fletcher Fund, 31.11.14, New York
The Scorpion goddess in the Maya Codex Tro-Cortesianus.
Courtesy Akademische Druck- und Verlagsanstalt, Graz.
The Mesopotamian cylinder seal shows in the upper part the
"God Boat." between
Courtesy Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Paris.
The "God Boat" surrounded by the crescent moon, three
single stars, and constellations.
Courtesy Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Paris.
The "God Boat" in the Maya Codex Tro-Cortesianus.
Courtesy Akademische Druck- und Verlagsanstalt, Graz.
The "God Boat" on the Arabian celestial globe made by Tabari.
P. Casanova, Bulletin of the Institut Frangais d'Archeologie Orientale 2,
Editions A. & J. Picard et Cie., Paris, 1902.
The Pegasus-square, called "I-Iku," with the circumjacent
constellations. between
Courtesy Birkhauscr Verlag, Basel.
Illustrations • xxii
The same Babylonian constellation, according to A. Ungnad.
A. Ungnad, Das wiedergefundene Paradies, 1923.
The same square in the round and rectangular zodiacs of Dendera.
A. Ungnad, Das wiedergefundene Paradies, 1923.
A calabash from the Guinea Coast, Africa.
Courtesy Zeitschrift fur Ethnologie, Muenster/Westfalen.
Another calabash from the Guinea Coast.
Courtesy "Leitschrift fur Ethnologie, Muenster/Westfalen.
The zodiacal Pisces, as drawn by the Toba Batak of Sumatra.
A. Maass, Tijdschrift voor Indische Taal-, Land-, en Volkenkunde 64, 66,
1924-26.
A New World picture, described as "composite animal."
Courtesy American Anthropological Association, Washington, D.C.
Introduction
The unbreakable fetters which
bound down the Great Wolf
Fenrir had been cunningly
forged by Loki from these: the
footfall of a cat, the roots of a
rock, the beard of a woman, the
breath of a fish, the spittle of a
bird.
The Edda
Toute vue des choses qui n'est
pas etrange est fausse.
Valery
This is meant to be only an essay. It is a first reconnaissance of a
realm well-nigh unexplored and uncharted. From whichever way
one enters it, one is caught in the same bewildering circular com-
plexity, as in a labyrinth, for it has no deductive order in the
abstract sense, but instead resembles an organism tightly closed in
itself, or even better, a monumental "Art of the Fugue."
The figure of Hamlet as a favorable starting point came by
chance. Many other avenues offered themselves, rich in strange
symbols and beckoning with great images, but the choice went to
Hamlet because he led the mind on a truly inductive quest through
a familiar landscape—and one which has the merit of its literary
setting. Here is a character deeply present to our awareness, in
whom ambiguities and uncertainties, tormented self-questioning and
dispassionate insight give a presentiment of the modern mind. His
personal drama was that he had to be a hero, but still try to avoid
the role Destiny assigned him. His lucid intellect remained above
the conflict of motives—in other words, his was and is a truly con-
Hamlet's Mill • 2
temporary consciousness. And yet this character whom the poet
made one of us, the first unhappy intellectual, concealed a past as
a legendary being, his features predetermined, preshaped by long-
standing myth. There was a numinous aura around him, and many
clues led up to him. But it was a surprise to find behind the mask
an ancient and all-embracing cosmic power—the original master of
the dreamed-of first age of the world.
Yet in all his guises he remained strangely himself. The original
Amlodhi,* as his name was in Icelandic legend, shows the same
characteristics of melancholy and high intellect. He, too, is a son
dedicated to avenge his father, a speaker of cryptic but inescapable
truths, an elusive carrier of Fate who must yield once his mission is
accomplished and sink once more into concealment in the depths of
time to which he belongs: Lord of the Golden Age, the Once and
Future King.
This essay will follow the figure farther and farther afield, from
the Northland to Rome, from there to Finland, Iran, and India;
he will appear again unmistakably in Polynesian legend. Many
other Dominations and Powers will materialize to frame him
within the proper order.
Amlodhi was identified, in the crude and vivid imagery of the
Norse, by the ownership of a fabled mill which, in his own time,
ground out peace and plenty. Later, in decaying times, it ground
out salt; and now finally, having landed at the bottom of the sea, it
is grinding rock and sand, creating a vast whirlpool, the Mael-
strom (i.e., the grinding stream, from the verb mala, "to grind"),
which is supposed to be a way to the land of the dead. This imagery
stands, as the evidence develops, for an astronomical process, the
secular shifting of the sun through the signs of the zodiac which
determines world-ages, each numbering thousands of years. Each
age brings a World Era, a Twilight of the Gods. Great structures
collapse; pillars topple "which supported the great fabric; floods and
cataclysms herald the shaping of a new world.
The image of the mill and its owner yielded elsewhere to more
* The indulgence of specialist's is asked for the form of certain transliterations
throughout the text; for example, Amlodhi instead of Amlodi, Grotte instead of
Grotti, etc. (Ed.)
3
Introduction
sophisticated ones, more adherent to celestial events. In Plato's pow-
erful mind, the figure stood out as the Craftsman God, the Demi-
urge, who shaped the heavens; but even Plato did not escape the
idea he had inherited, of catastrophes and the periodic rebuilding
of the world.
Tradition will show that the measures of a new world had to be
procured from the depths of the celestial ocean and tuned with the
measures from above, dictated by the "Seven Sages," as they are
often cryptically mentioned in India and elsewhere. They turn out
to be the Seven Stars of Ursa, which are normative in all cosmo-
logical alignments on the starry sphere. These dominant stars of the
Far North are peculiarly but systematically linked with those which
are considered the operative powers of the cosmos, that is, the
planets as they move in different placements and configurations
along the zodiac. The ancient Pythagoreans, in their conventional
language, called the two Bears the Hands of Rhea (the Lady of
Turning Heaven), and called the planets the Hounds of Per-
sephone, Queen of the Underworld. Far away to the south, the
mysterious ship Argo with its Pilot star held the depths of the past;
and the Galaxy was the Bridge out of Time. These notions appear
to have been common doctrine in the age before history—all over
the belt of high civilizations around our globe. They also seem to
have been born of the great intellectual and technological revolu-
tion of the late Neolithic period.
The intensity and richness, the coincidence of details, in this
cumulative thought have led to the conclusion that it all had its
origin in the Near East. It is evident that this indicates a diffusion
of ideas to an extent hardly countenanced by current anthropology.
But this science, although it has dug up a marvelous wealth of de-
tails, has been led by its modern evolutionary and psychological
bent to forget about the main source of myth, which was astronomy
—the Royal Science. This obliviousness is itself a recent turn of
events—barely a century old. Today expert philologists tell us that
Saturn and Jupiter are names of vague deities, subterranean or at-
mospheric, superimposed on the planets at a "late" period; they
neatly sort out folk origins and "late" derivations, all unaware that
planetary periods, sidereal and synodic, were known and rehearsed
Hamlet's Mill • 4
in numerous ways by celebrations already traditional in archaic
times. If a scholar has never known those periods even from elemen-
tary science, he is not in the best position to recognize them when
they come up in his material.
Ancient historians would have been aghast had they been told
that obvious things were to become unnoticeable. Aristotle was
proud to state it as known that the gods were originally stars, even
if popular fantasy had later obscured this truth. Little as he believed
in progress, he felt this much had been secured for the future. He
could not guess that W. D. Ross, his modern editor, would conde-
SCendingly annotate: "This is historically untrue." Yet we know
that Saturday and Sabbath had to do with Saturn, just as Wednes-
day and Mercredi had to do with Mercury. Such names are as old
as time; as old, certainly, as the planetary heptagram of the Har-
ranians. They go back far before Professor Ross' Greek philology.
The inquiries of great and meticulous scholars such as Ideler, Lep-
sius, Chwolson, Boll and, to go farther back, of Athanasius Kircher
and Petavius, had they only been read carefully, and noted, would
have taught several relevant lessons to the historians of culture, but
interest shifted to other goals, as can be seen from current anthro-
pology, which has built up its own idea of the "primitive" and what
came after.
One still reads in that most unscientific of records, the Bible, that
God disposed all things by number, weight and measure; ancient
Chinese texts say that "the calendar and the pitch pipes have such
a close fit, that you could not slip a hair between them." People read
it, and think nothing of it. Yet such hints might reveal a world of
vast and firmly established complexity, infinitely different from
ours. But the experts now are benighted by the current folk fantasy,
which is the belief that they are beyond all this—critics without
nonsense and extremely wise.
In 1959 I wrote:
The dust of centuries had settled upon the remains of this great
world-wide archaic construction when the Greeks came upon the
scene.Yet something of it survived in traditional rites, in myths and
fairy tales no longer understood. Taken verbally, it matured the
5 • Introduction
bloody cults intended to procure fertility, Based on the belief in a
dark universal force of an ambivalent nature, which seems now to
monopolize our interest. Yet its original themes could flash out again,
preserved almost intact, in the later thought of the Pythagoreans and
of Plato.
But they are tantalizing fragments of a lost whole. They make one
think of those "mist landscapes" of which Chinese painters are mas-
ters, which show here a rock, here a gable, there the tip of a tree, and
leave the rest to imagination. Even when the code shall have yielded,
when the techniques shall be known, we cannot expect to gauge the
thought of those remote ancestors of ours, wrapped as it is in its
symbols.
Their words are no more heard again
Through lapse of many ages ...
We think we have now broken part of that code. The thought
behind these constructions of the high and far-off times is also lofty,
even if its forms are strange. The theory about "how the world
began" seems to involve the breaking asunder of a harmony, a kind
of cosmogonic "original sin" whereby the circle of the ecliptic
(with the zodiac) was tilted up at an angle with respect to the
equator, and the cycles of change came into being.
This is not to suggest that this archaic cosmology will show any
great physical discoveries, although it required prodigious feats of
concentration and computing. What it did was to mark out the
unity of the universe, and of man's mind, reaching out to its farthest
limits. Truly, man is doing the same today.
Einstein said: "What is inconceivable about the universe, is that
it should be at all conceivable." Man is not giving up. When he
discovers remote galaxies by the million, and then those quasi-stellar
radio sources billions of light-years away which confound his specu-
lation, he is happy that he can reach out to those depths. But he
pays a terrible price for his achievement. The science of astro-
physics reaches out on a grander and grander scale without losing its
footing. Man as man cannot do this. In the depths of space he loses
himself and all notion of his significance. He is unable to fit himself
into the concepts of today's astrophysics short of schizophrenia.
Modern man is facing the nonconceivable. Archaic man, however,
kept a firm grip on the conceivable by framing within his cosmos
Hamlet's Mill • 6
an order of time and an eschatology that made sense to him and
reserved a fate for his soul. Yet it was a prodigiously vast theory,
with no concessions to merely human sentiments. It, too, dilated
the mind beyond the bearable, although without destroying man's
role in the cosmos. It was a ruthless metaphysics.
Not a forgiving universe, not a world of mercy. That surely not.
Inexorable as the stars in their courses, miserationis parcissimae, the
Romans used to say. Yet it was a world somehow not unmindful of
man, one in which there was an accepted place for everything,
rightfully and not only statistically, where no sparrow could fall
unnoted, and where even what was rejected through its own error
would not go down to eternal perdition; for the order of Number
and Time was a total order preserving all, of which all were mem-
bers, gods and men and animals, trees and crystals and even absurd
errant stars, all subject to law and measure.
This is what Plato knew, who could still speak the language of
archaic myth. He made myth consonant with his thought, as he
built the first modern philosophy. We have trusted his clues as
landmarks even on occasions when he professes to speak "not quite
seriously." He gave us a first rule of thumb; he knew what he was
talking about.
Behind Plato there stands the imposing body of doctrine attrib-
uted to Pythagoras, some of its formulation uncouth, but rich with
the prodigious content of early mathematics, pregnant with a sci-
ence and a metaphysics that were to flower in Plato's time. From it
come such words as "theorem," "theory," and "philosophy." This
in its turn rests on what might be called a proto-Pythagorean phase,
spread all over the East but with a focus in Susa. And then there
was something else again, the stark numerical computing of Baby-
lon. From it all came that strange principle: "Things are numbers."
Once having grasped a thread going back in time, then the test
of later doctrines with their own historical developments lies in
their congruence with tradition preserved intact even if half under-
stood. For there are seeds which propagate themselves along the
jetstream of time.
Introduction
And universality is in itself a test when coupled with a firm de-
sign. When something found, say, in China turns up also in Baby-
lonian astrological texts, then it must be assumed to be relevant, for
it reveals a complex of uncommon images which nobody could
claim had risen independently by spontaneous generation.
Take the origin of music. Orpheus and his harrowing death may
be a poetic creation born in more than one instance in diverse
places. But when characters who do not play the lyre but blow
pipes get themselves flayed alive for various absurd reasons, and
their identical end is rehearsed on several continents, then we feel
we have got hold of something, for such stories cannot be linked by
internal sequence. And when the Pied Piper turns up both in the
medieval German myth of Hamelin and in Mexico long before
Columbus, and is linked in both places with certain attributes like
the color red, it can hardly be a coincidence. Generally, there is
little that finds its way into music by chance.
Again, when one finds numbers like 108, or 9 X 13, reappearing
under several multiples in the Vedas, in the temples of Angkor, in
Babylon, in Heraclitus' dark utterances, and also in the Norse Val-
halla, it is not accident.
There is one way of checking signals thus scattered in early data,
in lore, fables and sacred texts. What we have used for sources may
seem strange and disparate, but the sifting was considered, and it
had its reasons. Those reasons will be given later in the chapter
on method. I might call it comparative morphology. The reservoir
of myth and fable is great, but there are morphological "markers"
for what is not mere storytelling of the kind that comes naturally.
There is also wonderfully preserved archaic material in "secondary"
primitives, like American Indians and West Africans. Then there
are courtly stories and annals of dynasties which look like novels:
the Feng Shen Yen I, the Japanese Nihongi, the Hawaiian Kumu-
lipo. These are not merely fantasy-ridden fables.
In hard and perilous ages, what information should a well-born
man entrust to his eldest son? Lines of descent surely, but what else?
The memory of an ancient nobility is the means of preserving the
Hamlet's Mill
8
arcana imperil, the arcana legis and the arcana mundi, just as it was
in ancient Rome. This is the wisdom of a ruling class. The Poly-
nesian chants taught in the severely rest restricted Whare-wananga were
mostly astronomy. That is what a liberal education meant then.
Sacred texts are another great source. In our age of print one is
tempted to dismiss these as religious excursions into homiletics, but
originally they represented a great concentration of attention on
material which had been distilled for relevancy through a long pe-
riod of time and which was considered worthy of being committed
to memory generation after generation. The tradition of Celtic
Druidism was delivered not only in songs, but also in tree-lore
which "was much like a code. And in the East, out of complicated
games based on astronomy, there developed a kind of shorthand
which became the alphabet.
As we follow the clues—stars, numbers, colors, plants, forms,
verse, music, structures—a huge framework of connections re-
vealed at many levels. One is inside an echoing manifold where
everything responds and everything has a place and a time assigned
to it. This is a true edifice, something like a mathematical matrix, a
World-Image that fits the many levels, and all of it kept in order
by strict measure. It is measure that provides the countercheck, for
there is much that can be identified and re-disposed from rules like
the old Chinese saying about the pitch pipes and the calendar.
When we speak of measures, it is always some form of Time that
provides them, starting from two basic ones, the solar year and the
octave, and going down from there in many periods and intervals,
to actual weights and sizes. What modern man attempted in the
merely conventional metric system has archaic precedents of great
complexity. Down the centuries there comes an echo of Al-Biruni's
wondering a thousand years ago, when that prince of scientists dis-
covered that the Indians, by then miserable astronomers, calculated
aspects and events by means of stars—and were not able to show
him any one star that he asked for. Stars had become items for them,
as they were to become again for Leverrier and Adams, who never
troubled to look at Neptune in their life although they had com-
puted and discovered it in 1847. The Mayas and the Aztecs in their
9 • Introduction
unending calculations seem to have had similar attitudes. The con-
nections were what counted. Ultimately so it was in the archaic
universe, where all things were signs and signatures of each other,
inscribed in the hologram, to be divined subtly. And Number ,
dominated them all (appendix # 1).
This ancient world moves a little closer if one recalls two great
transitional figures who were simultaneously archaic and modern in
their habits of thought. The first is Johannes Kepler, who was of
the old order in his unremitting calculations and his passionate de-
votion to the dream of rediscovering the "Harmony of the Spheres."
But he was a man of his own time, and also of ours, when this dream
began to prefigure the polyphony that led up to Bach. In somewhat
the same way, our strictly scientific world view has its counterpart
in what John Hollander, the historian of music, has described as
"The Untuning of the Sky." The second transitional figure is no
less a man than Sir Isaac Newton, the very inceptor of the rigor-
ously scientific view. There is no real paradox in mentioning New-
ton in this connection. John Maynard Keynes, who knew Newton
as well as many of our time, said of him:
Newton was not the first of the Age of Reason. He was the last of the
magicians, the last of the Babylonians and Sumerians, the last great
mind which looked out on the visible and intellectual world with the
same eyes as those who began to build our intellectual world rather
less than 10,000 years ago .. . Why do I call him a magician? Because
he looked on the whole universe and all that is in it as a riddle, as a
secret which could be read by applying pure thought to certain evi-
dence, certain mystic clues which God had laid about the world to
allow a sort of philosopher's treasure hunt to the esoteric brother-
hood. He believed that these clues were to be found partly in the
evidence of the heavens and in the constitution of elements (and that
is what gives the false suggestion of his being an experimental natural
philosopher), but also partly in certain papers and traditions handed
down by the brethren in an unbroken chain back to the original
cryptic revelation in Babylonia. He regarded the universe as a crypto-
gram set by the Almighty—just as he himself wrapt the discovery of
the calculus in a cryptogram when he communicated with Leibniz.
By pure thought, by concentration of mind, the riddle, he believed,
would be revealed to the initiate.1
1 "Newton the Man," in The Royal Society. Newton Tercentenary Celebrations (1947), p. 29.
Hamlet's Mill
10
Lord Keynes' appraisal, written ca. 1942, remains both uncon-
ventional and profound. He knew, we all know, that Newton
failed. Newton was led astray by his dour sectarian preconceptions.
But his undertaking was truly in the archaic spirit, as it begins to
appear now after two centuries of scholarly search into many cul-
tures of which he could have had no idea. To the few clues he
found with rigorous method, a vast number have been added. Still,
the wonder remains, the same that was expressed by his great
predecessor Galileo:
But of all other stupendous inventions, what sublimity of mind must
have been his who conceived how to communicate his most secret
thoughts to any other person, though very far distant either in time
or place, speaking with those who are in the Indies, speaking to those
who are not yet born, nor shall be this thousand or ten thousand
yean? And with no greater difficulty than the various arrangement
of two dozen Little signs upon paper? Let this be the seal of all the
admirable inventions of man.
Way back in the 6th century a.d., Gregoire de Tours was writ-
ing: "The mind has lost its cutting edge, we hardly understand the
Ancients." So much more today, despite our wallowing in mathe-
matics for the million and in sophisticated technology.
It is undeniable that, notwithstanding our Classics Departments'
labors, the wilting away of classical studies, the abandonment of
any living familiarity with Greek and Latin has cut the ompha-
loessa, the umbilical cord which connected our culture—at least at
its top level—with Greece, in the same manner in which men of the
Pythagorean and Orphic tradition were tied up through Plato and
a few others with the most ancient Near East. It is beginning to
appear that this destruction is leading into a very up-to-date Middle
Ages, much worse than the first. People will sneer: "Stop the
World, I want to get off." It cannot be changed, however; this is
the way it goes when someone or other tampers with the reserved
knowledge that science is, and was meant to represent.
But, as Goethe said at the very onset of the Progressive Age,
"Noch ist es Tag, da ruhre sich der Mann! Die Nacht tritt ein,
wo nicmand wirken kann." ("It is still day, let men get up and
11
Introduction
going—the night creeps in, when there is nothing doing.") There
light come once more some kind of "Renaissance" out of the
hopelessly condemned and trampled past, when certain ideas come
to life again, and we should not deprive our grandchildren of a last
chance at the heritage of the highest and farthest-off times. And if,
as looks infinitely probable, even that last chance is passed up in
the turmoil of progress, why then one can still think with Poli-
ziano, who was himself a master humanist, that there will be men
whose minds find a refuge in poetry and art and the holy tradition
"which alone make men free from death and turn them to eternity,
so long as the stars will go on, still shining over a world made for-
ever silent." Right now, there is still left some daylight in which to
undertake this first quick reconnaissance. It will necessarily leave
out great and significant areas of material, but even so, it will in-
vestigate many unexpected byways and crannies of the past.
Chapter I
The Chronicler's Tale
. . . you of changeful counsel,
undefiled Titan of exceeding
strength, you who consume all
and increase it again, you who
hold the indestructible bond by
the unlimited order of the Aeon,
wily-minded, originator of gen-
eration, you of crooked coun-
sel ...
From the Orphic Hymns
The proper gate through which to enter the realm of pre-
Shakespearean Hamlet is the artless account given by Saxo Gram-
maticus (c. 1150-c. 1216) in books III and IV of his Gesta Dano-
rum. What follows is the relevant part of book III in Elton's
translation, only slightly shortened.
The story begins with the feats of Orvendel, Amlethus' father-
especially his victory over King Koll of Norway—which drove
Orvendel's brother Fengo, "stung with jealousy," to murder him
(appendix #2). "Then he took the wife of the brother he had
butchered, capping unnatural murder with incest." (So Saxo
qualifies it.)
Amleth beheld all this, but feared lest too shrewd a behaviour
might make his uncle suspect him. So he chose to feign dullness, and
pretend an utter lack of wits. This cunning course not only con-
cealed his intelligence, but ensured his safety. Every day he remained
in his mother's house utterly listless and unclean, flinging himself on
the ground and bespattering his person with foul and filthy dirt. His
13 • The Chronicler''s Tale
discoloured face and visage smutched with slime denoted foolish and
grotesque madness. All he said was of a piece with these follies; all
he did savoured of utter lethargy . . .
He used at times to sit over the fire, and, raking up the embers with
his hands, to fashion wooden crooks, and harden them in the fire,
shaping at their tips certain barbs, to make them hold more tightly
to their fastenings. When asked what he was about, he said that he
was preparing sharp javelins to avenge his father. This answer was
not a little scoffed at, all men deriding his idle and ridiculous pursuit;
but the thing helped his purpose afterwards. Now it was his craft in
this matter that first awakened in the deeper observers a suspicion of
his cunning. For his skill in a trifling art betokened the hidden talent
of a craftsman . . . Lastly, he always watched with the most punctual
care over his pile of stakes that he had pointed in the fire. Some
people, therefore, declared that his mind was quick enough, and fan-
cied that he only played the simpleton . . . His wiliness (said these)
would be most readily detected, if a fair woman were put in his way
in some secluded place, who should provoke his mind to the tempta-
tions of love . . . , if his lethargy were feigned, he would seize the
opportunity, and yield straightway to violent delights.
So men were commissioned to draw the young man in his rides into
a remote part of the forest, and there assail him with a temptation of
this nature. Among these chanced to be a foster-brother of Amleth,
who had not ceased to have regard to their common nurture . . . He
attended Amleth among his appointed train . . . and was persuaded
that he would suffer the worst if he showed the slightest glimpse of
sound reason, and above all if he did the act of love openly. This was
also plain enough to Amleth himself. For when he was bidden mount
his horse, he deliberately set himself in such a fashion that he turned
his back to the neck and faced about, fronting the tail; which he pro-
ceeded to encompass with the reins, just as if on that side he would
check the horse in its furious pace . . . The reinless steed galloping
on, with the rider directing its tail, was ludicrous enough to behold.
Amleth went on, and a wolf crossed his path amid the thicket; when
his companions told him that a young colt had met him, he retorted
that in Fengo's stud there were too few of that kind fighting. This
was a gentle but witty fashion of invoking a curse upon his uncle's
riches. When they averred that he had given a cunning answer, he
answered that he had spoken deliberately: for he was loth to be
thought prone to lying about any matter, and wished to be held a
stranger to falsehood; and accordingly he mingled craft and candour
in such wise that, though his words did lack truth, yet there was
nothing to betoken the truth and betray how far his keenness went.
Hamlet's Mill • 14
Again, as he passed along the beach, his companions found the rud-
der1 of a ship which had been wrecked, and said they had discov-
ered a huge knife. "This," said he, "was the right thing to carve such
a huge ham"; by which he really meant the sea, to whose infinitude,
he thought, this enormous rudder matched.
Also, as they passed the sandhills, and bade him look at the meal,
meaning the sand, he replied that it had been ground small by the
hoary tempests of the ocean. His companions praising his answer, he
said that he had spoken wittingly. Then they purposely left him, that
he might pluck up more courage to practice wantonness.
The woman whom his uncle had dispatched met him in a dark spot,
as though she had crossed him by chance; and he took her and would
have ravished her, had not his foster-brother, by a secret device, given
him an inkling of the trap . . . Alarmed, and fain to possess his desire
in greater safety, he caught up the woman in his arms and dragged
her off to a distant and impenetrable fen. Moreover, when they had
lain together, he conjured her earnestly to disclose the matter to none,
and the promise of silence was accorded as heartily as it was asked.
For both of them had been under the same fostering in their child-
hood; and this early rearing in common had brought Amleth and the
girl into great intimacy.
So, when he had returned home, they all jeeringly asked him whether
he had given way to love, and he avowed that he had ravished the
maid. When he was next asked where he did it, and what had been
his pillow, he said that he had rested upon the hoof of a beast of
burden, upon a cockscomb, and also upon a ceiling. For, when he was
starting into temptation, he had gathered fragments of all these things,
in order to avoid lying . . .
The maiden, too, when questioned on the matter, declared that he
had done no such thing; and her denial was the more readily credited
when it was found that the escort had not witnessed the deed.
But a friend of Fengo, gifted more with assurance than judgment,
declared that the unfathomable cunning of such a mind could not be
detected by a vulgar plot, for the man's obstinacy was so great that
it ought not to be assailed with any mild measures . . . Accordingly,
said he, his own prof ounder acuteness had hit on a more delicate way,
which was well fitted to be put in practice, and would effectually
discover what they desired to know. Fengo was purposely to absent
himself, pretending affairs of great import. Amleth should be closeted
alone with his mother in her chamber; but a man should first be com-
missioned to place himself in a concealed part of the room and listen
heedfully to what they talked about . . . The speaker, loth to seem
1Saxo, however, wrote gubernaculum, i.e., steering oar (5.6.10; Gesta Danorum,
C. Knabe and P. Herrmann, eds. [1931], p. 79).
15 • The Chronicler's Tale
readier to devise than to carry out the plot, zealously proffered him-
self as the agent of the eavesdropping. Fengo rejoiced of the scheme,
and departed on pretence of a long journey. Now he who had given
this counsel repaired privily to the room where Amleth was shut up
with his mother, and lay down skulking in the straw. But Amleth had
his antidote for the treachery.
Afraid of being overheard by some eavesdropper, he at first resorted
to his usual imbecile ways, and crowed like a noisy cock, beating his
arms together to mimic the flapping of wings. Then he mounted
the straw and began to swing his body and jump again and again,
wishing to try if aught lurked there in hiding. Feeling a lump beneath
his feet, he drove his sword into the spot, and impaled him who lay
hid. Then he dragged him from his concealment and slew him. Then,
cutting his body into morsels, he seethed it in boiling water, and
flung it through the mouth of an open sewer for the swine to eat,
bestrewing the stinking mire with his hapless limbs. Having in this
wise eluded the snare, he went back to the room. Then his mother
set up a great wailing and began to lament her son's folly to his face
but he said: "Most infamous of women! dost thou seek with such
lying lamentations to hide thy most heavy guilt? Wantoning like a
harlot, thou hast entered a wicked and abominable state of wedlock,
embracing with incestuous bosom thy husband's slayer . . ." With
such reproaches he rent the heart of his mother and redeemed her to
walk in the ways of virtue.
When Fengo returned, nowhere could he find the man who had sug-
gested the treacherous espial. . . Amleth, among others, was asked in
jest if he had come on any trace of him, and replied that the man had
gone to the sewer, but had fallen through its bottom and been stifled
by the floods of filth, and that he had then been devoured by the
swine that came up all about that place. This speech was flouted by
those who heard; for it seemed senseless, though really it expressly
avowed the truth.
Fengo now suspected that his stepson was certainly full of guile, and
desired to make away with him, but durst not do the deed for fear of
the displeasure, not only of Amleth's grandsire Rorik, but also of his
own wife. So he thought that the King of Britain should be employed
to slay him, so that another could do the deed, and he be able to feign
innocence . . .
Amleth, on departing, gave secret orders to his mother to hang the
lull with knotted tapestry, and to perform pretended obsequies for
him a year from thence; promising that he would then return.
two retainers of Fengo then accompanied him, bearing a letter
graven in wood . . . ; this letter enjoined the King of the Britons to
Hamlet's Mill • 16
put to death the youth who was sent over to him. While they were
reposing, Amleth searched their coffers, found the letter, and read
the instructions therein. Whereupon he erased all the writing on the
surface, substituted fresh characters, and so, changing the purport of
the instructions, shifted his own doom upon his companions. Nor was
he satisfied with removing from himself the sentence of death and
passing the peril on to others, but added an entreaty that the King of
Britain would grant his daughter in marriage to a youth of great
judgment whom he was sending to him. Under this was falsely marked
the signature of Fengo.
Now when they had reached Britain, the envoys went to the king and
proffered him the letter which they supposed was an implement of
destruction to another, but which really betokened death to them-
selves. The king dissembled the truth, and entreated them hospitably
and kindly. Then Amleth scouted all the splendour of the royal ban-
quet like vulgar viands, and abstaining very strangely, rejected that
plenteous feast, refraining from the drink even as from the banquet.
All marvelled that a youth and a foreigner should disdain the care-
fully cooked dainties of the royal board and the luxurious banquet
provided, as if it were some peasant's relish. So, when the, revel broke
up, and the king was dismissing his friends to rest, he had a man sent
into the sleeping room to listen secretly, in order that he might hear
the midnight conversation of his guests. Now, when Amleth's com-
panions asked him why he had refrained from the feast of yestereve,
as if it were poison, he answered that the bread was flecked with
blood and tainted; that there was a tang of iron in the liquor; while
the meats of the feast reeked the stench of a human carcase, and were
infected by a kind of smack of the odour of the charnel. He further
said that the king had the eyes of a slave, and that the queen had in
three ways shown the behaviour of a bondmaid. Thus he reviled with
insulting invective not so much the feast as its givers. And presently
his companions, taunting him with his old defect of wits, began to
flout him with many saucy jeers . . .
All this the king heard from his retainer; and declared that he who
could say such things had either more than mortal wisdom or more
than mortal folly . . . Then he summoned his steward and asked him
whence he had procured the bread . . . The king asked where the
corn had grown of which it was made, and whether any sign was to
be found there of human carnage? The other answered, that not far
off was a field, covered with the ancient bones of slaughtered men,
and still bearing plainly all the signs of ancient carnage . . . The
king . . . took the pains to learn also what had been the source of the
lard. The other declared that his hogs had, through negligence,
strayed from keeping, and battened on the rotten carcase of a robber,
17 The Chronicler's Tale
and that perchance their pork had thus come to have something of a
corrupt smack. The king, finding that Amleth's judgment was right
in this thing also, asked of what liquor the steward had mixed the
drink? Hearing that it had been brewed of water and meal, he had
the spot of the spring pointed out to him, and set to digging deep
down; and there he found rusted away, several swords, the tang
whereof it was thought had tainted the waters. Others relate that
Amleth blamed the drink because, while quaffing it, he had detected
some bees that had fed in the paunch of a dead man; and that the
taint, which had formerly been imparted to the combs, had reap-
peared in the taste. The king . . . had a secret interview with his
mother, and asked her who his father had really been. She said she
had submitted to no man but the king. But when he threatened that
he would have the truth out of her by a trial, he was told that he was
the offspring of a slave . . . Abashed as he was with shame for his low
estate, he was so ravished with the young man's cleverness that he
asked him why he had aspersed the queen with the reproach that she
had demeaned herself like a slave? But while resenting that the court-
liness of his wife had been accused in the midnight gossip of a guest,
he found that her mother had been a bondmaid . . .
Then the king adored the wisdom of Amleth as though it were in-
spired, and gave him his daughter to wife; accepting his bare word
as though it were a witness from the skies.
Moreover, in order to fulfill the bidding of his friend, he hanged
Amleth's companions on the morrow. Amleth, feigning offence,
treated this piece of kindness as a grievance, and received from the
king, as compensation, some gold which he afterwards melted in the
fire, and secretly caused to be poured into some hollowed sticks.
When he had passed a whole year with the king he obtained leave to
make a journey, and returned to his own land, carrying away of all
his princely wealth and state only the sticks which held the gold. On
reaching Jutland, he exchanged his present attire for his ancient
demeanour, which he had adopted for righteous ends . . .
Covered with filth, he entered the banquet-room where his own
obsequies were being held, and struck all men utterly aghast, rumour
having falsely noised abroad his death. At last terror melted into
mirth, and the guests jeered and taunted one another, that he, whose
last rites they were celebrating as though he were dead, should ap-
pear in the flesh. When he was asked concerning his comrades, he
pointed to the sticks he was carrying, and said, "Here is both the one
and the other." This he observed with equal truth and pleasantry . . .
for it pointed at the weregild of the slain as though it were them-
selves.
Hamlet's Mill
18
Thereon, wishing to bring the company into a gayer mood, he joined
the cupbearers, and diligently did the office of plying the drink.
Then, to prevent his loose dress hampering his walk, he girded his
sword upon his side, and purposely drawing it several times, pricked
his fingers with its point. The bystanders accordingly had both sword
and scabbard riveted across with an iron nail. Then, to smooth the
way more safely to his plot, he went to the lords and plied them
heavily with draught upon draught, and drenched them all so deep
in wine, that their feet were made feeble with drunkenness, and they
turned to rest within the palace, making their bed where they had
revelled . . .
So he took out of his bosom the stakes he had long ago prepared, and
went into the building, where the ground lay covered with the bodies
of the nobles wheezing off their sleep and their debauch. Then, cut-
ling away its Supports, he brought down the hanging his mother had
knitted, which covered the inner as well as the outer walls of the hall.
This he flung upon the snorers, and then applying the crooked stakes,
he knotted and bound them in such insoluble intricacy, that not one
of the men beneath, however hard he might struggle, could contrive
to rise. After this he set fire to the palace. The flames spread, scatter-
ing the conflagration far and wide. It enveloped the whole dwelling,
destroyed the palace, and burnt them all while they were either
buried in deep sleep or vainly striving to arise.
Then he went to the chamber of Fengo, who had before this been
conducted by his train into his pavilion; plucked up a sword that
chanced to be hanging to the bed, and planted his own in its place.
Then, awakening his uncle, he told him that his nobles were perishing
in the flames, and that Amleth was here, armed with his old crooks
to help him, and thirsting to exact the vengeance, now long overdue,
for his father's murder. Fengo, on hearing this, leapt from his couch,
but was cut down while, deprived of his own sword, he strove in
vain to draw the strange one . . . O valiant Amleth, and worthy of
immortal fame, who being shrewdly armed with a feint of folly,
covered a wisdom too high for human wit under a marvellous dis-
guise of silliness! and not only found in his subtlety means to protect
his own safety, but also by its guidance found opportunity to avenge
his father. By this skillful defence of himself, and strenuous revenge
for his parent, he has left it doubtful whether we are to think more
of his wit or his bravery.
It is a far cry from Saxo's tale and its uncouth setting to the
Renaissance refinements of Shakespeare. This is nowhere more ob-
vious than in the scene in the Queen's hall, with its heaped straw
19 . The Chronicler's Tale
on the floor, its simmering caldrons, its open sewer, and the crude
manner of disposing of "Polonius," all befitting the rude Middle
Ages. The whole sad, somber story of the lonely orphan prince is
turned by Saxo into a Narrenspiel, yet a strong tradition permeates
the artless narrative. Hamlet is the avenging power whose superior
intellect confounds evildoers, but his intellect also brings light and
strength to the helpless and ill-begotten who are made to recognize
their misery. There is nothing pleasant in the revelation brought
home to the English king, yet he humbles himself before the ruth-
less insight and "adores" Hamlet's wisdom as "though it were in-
spired." More clearly than in Shakespeare, Hamlet is the ambivalent
power dispensing good and evil. It is clear also that certain episodes,
like the exchange of swords with Fengo, are crude and pointless
devices going counter to the heroic theme. These are set dramati-
cally right only when handled by Shakespeare, but they seem to
indicate an original rigid pattern based on the Ruse of Reason, as
Hegel would say. Evil is never attacked frontally, even when con-
vention would require it. It is made to defeat itself. Hamlet must
not be conceived as a heroic misfit, but as a distributor of justice.
Shakespeare has focused exactly right. He has avoided restoring the
brutal, heroic element required by the saga, and made the drama
instead wholly one of the mind. In the light of a higher clarity, who
can 'scape whipping?
It would be pointless to compare all over again the several ver-
sions of the Hamlet scheme in the north and west of Europe, and
in ancient Rome. This has been done very effectually.2 Thus, it
is possible to rely on the "identity" of the shadowy Icelandic
Amlodhi (in a so-called fairy tale his name is Brjam), who is first
mentioned in the 10th century, and appears anew in Iceland as a
Danish reimport in the "Ambales Saga," written in the 16th or 17th
Century. Parallels to Amlethus' behavior and career have been found
' Besides F. Y. Powell's introduction and appendix to Elton's translation of Saxo
Grammaticus' The First Nine Books of the Danish History of Saxo Grammaticus
(1894), already cited at the opening of the chapter, see the following: P. Herr-
in.inn. Die Heldensagen des Saxo Grammaticus (1922); I. Gollancz, Hamlet in Ice-
land (1898); R. Zcnker, Boeve-Amlethus (1905); E. N. Setala, "Kullervo-Hamlet,"
II 'I'' (1903, 1907, 1910).
Hamlet's Mill
20
21
The Chronicler's Tale
in the Sagas of Hrolf Kraki, of Havelok the Dane, as well as in
several Celtic myths.3
In the version reported by Saxo, Hamlet goes on to reign suc-
cessfully. The sequel of his adventures is taken up in book IV of
the Chronicle, but this narrative shows a very different hand. It is
an inept job, made of several commonplaces from the repertory of
ruse and fable, badly stitched together. When Hamlet, in addition
to the English King's daughter, is made to marry the Queen of
Scotland, and bring his two wives home to live together in har-
mony, we can suspect an incompetent attempt to establish a dynas-
tic claim of the House of Denmark to the realm of Britain. Hamlet
eventually falls in battle, but there is not much in the feats re-
counted to justify Saxo's dithyrambic conclusion that if he had
lived longer he might have been another Hercules. The true per-
sonage has been overlaid beyond recognition, although there still
clings to him a numinous aura. Curiously enough, the misconstruing
of Hamlet's story in the direction of success continues today. In
the recent Russian film version of Shakespeare's play, Hamlet is
shown as a purposeful, devious and ruthless character, bent only on
•carrying off a coup d'etat. Yet, in Saxo's first part, the tragic
meaning is clearly adumbrated when Hamlet's return is timed to
coincide with his own obsequies. The logic requires that he perish
together with the tyrant.
The name Amleth, Amlodhi, Middle English Amlaghe, Irish
Amlaidhe, stands always for "simpleton," "stupid," "like unto a
dumb animal." It also remained in use as an adjective. Gollancz has
pointed out that in "The Wars of Alexander," an alliterative poem
from the north of England largely translated from the Historia de
Preliis, Alexander is twice thus mentioned contemptuously by his
(enemies:
Thou Alexander, thou ape, thou amlaghe out of Greece
Thou little thefe, thou losangere (1), thou lurkare in cities . . .
3 See, for Hrolfssaga Kraki, scil., the youth of Helgi and Hroar, and the related
story of Harald and Haldan (told in Saxo's seventh book): Zenker, Boeve-Amle-
thus, pp. 121-26; Herrmann, Die Heldensagen, pp. 271f.; Setala, "Kullervo-Hamlet,"
FUF 3 (1903), pp. 74f.
Darius, inquiring about Alexander's appearance, is shown by his
courtiers a caricature graphically described:
And thai in parchment him payntid, his person him shewid,
Ane amlaghe, ane asaleny (2), ane ape of all othire,
A wirling (3), a wayryngle (4), a waril-eghid (5) shrewe,
The caitifeste creatour, that cried (6) was evire4
This image of the "caitiffest creature" goes insistently with cer-
tain great figures of myth. With the figure of Hamlet there goes,
too, the "dog" simile. This is true in Saxo's Amlethus, in Ambales, in
the Hrolfssaga Kraki, where the endangered ones, the two princes
Helgi and Hroar (and in Saxo's seventh book Harald and Haldan),
are labeled dogs, and are called by the dog-names "Hopp and Ho."
Next comes what looks at first like the prototype of them all, the
famous Roman story of Lucius Junius Brutus, the slayer of King
Tarquin, as told first by Titus Livius. (The nickname Brutus
again connotes the likeness to dumb brutes.) Gollancz says of it:
The merest outline of the plot cannot fail to show the striking like-
ness between the tales of Hamlet and Lucius Iunius Brutus. Apart
from general resemblance (the usurping uncle; the persecuted
nephew, who escapes by feigning madness; the journey; the oracular
utterances; the outwitting of the comrades; the well-matured plans
for vengeance), there are certain points in the former story which
must have been borrowed directly from the latter. This is especially
true of Hamlet's device of hiding the gold inside the sticks. This
could not be due to mere coincidence; and moreover, the evidence
seems to show that Saxo himself borrowed this incident from the
account of Brutus in Valerius Maximus; one phrase at least from the
passage in the Memorabilia was transferred from Brutus to Hamlet
(Saxo says of Hamlet "obtusi cordis esse," Valerius "obtusi se cordis
esse simulavit"). Saxo must have also read the Brutus story as told by
' Livy, and by later historians, whose versions were ultimately based on
Dionysius of Halicarnassus.5
To juxtapose the twin brothers Hamlet and Brutus, here is the
earlier portion of the tale of Brutus as told by Livy (1.56). The
subsequent events connected with the rape of Lucrece are too well
known to need repeating.
4 (1) liar; (2) little ass; (3) dwarf; (4) little villain; (5) wall-eyed; (6) created.
3Glollancz, pp.xxi xxiv.
Hamlet's Mill
22
While Tarquin was thus employed (on certain defensive measures),
a dreadful prodigy appeared to him; a snake sliding out of a wooden
pillar, terrified the beholders, and made them fly into the palace; and
not only struck the king himself with sudden terror, but filled his
breast with anxious apprehensions: so that, whereas in the case of
public prodigies the Etrurian soothsayers only were applied to, being
thoroughly frightened at this domestic apparition, as it were, he re-
solved to send to Delphi, the most celebrated oracle in the world;
and judging it unsafe to entrust the answers of the oracle to any other
person, he sent his two sons into Greece, through lands unknown at
that time, and seas still more unknown. Titus and Aruns set out, and,
as a companion, there was sent with them Junius Brutus, son to
Tarquinia, the king's sister, a young man of a capacity widely dif-
ferent from the assumed appearance he had put on. Having heard
that the principal men in the state, and among the rest his brother,
had been put to death by his uncle, he resolved that the king should
find nothing in his capacity which he need dread, nor in his fortune
which he need covet; and he determined to find security in contempt
since in justice there was no protection. He took care, therefore, to
fashion his behaviour to the resemblance of foolishness, and submit-
ted himself and his portion to the king's rapacity. Nor did he show
any dislike of the surname Brutus, content that, under the cover of
that appellation, the genius which was to be the deliverer of the
Roman people should lie concealed, and wait the proper season for
exertion . . . He was, at this time, carried to Delphi by the Tarquinii,
rather as a subject of sport than as a companion; and is said to have
brought, as an offering to Apollo, a golden wand inclosed in a staff
of cornel wood, hollowed for the purpose, an emblem figurative of
the state of his own capacity. When they were there, and had exe-
cuted their father's commission, the young men felt a wish to enquire
to which of them the kingdom of Rome was to come; and we are told
that these words were uttered from the bottom of the cave.—"Young
men, whichever of you shall first kiss your mother, he shall possess
the sovereign power at Rome" . . . Brutus judged that the expression
of Apollo had another meaning, and as if he had accidentally stum-
bled and fallen, he touched the earth with his lips, considering that
she was the common mother of all mankind.
For most conventional-minded philologists, Brutus was the an-
swer to a prayer, even to the gold enclosed in a stick. They had the
sound classical source, from which it is reassuring to derive develop-
ments in the outlying provinces. They felt their task to be at an end.
With a few trimmings of seasonal cults and fertility rites, the whole
2 3 • The Chronicler's Tale
Amlethus package was wrapped, sealed and delivered, to join the
growing pile of settled issues.
Yet even the Roman version was not without its disturbing
peculiarities. Livy reports only the answer to the private question
of the two princes. But if Tarquin had sent them to Delphi, it
was to get an answer to his own fears. And the answer is to be
found in Zonaras' compendium of the early section of Dio Cassius'
lost Roman history. Delphic Apollo said that the king would lose
his reign "when a dog would speak with human voice."6 There is
no evidence that Saxo read Zonaras.
There is also a strange variant to Tarquin's prophetic nightmare
reported by Livy. It does not lack authority, for it is mentioned
in Cicero's De divinatione (1.22) and taken from a lost tragedy on
Brutus by Accius, an early Roman poet. Says Tarquin: "My dream
was that shepherds drove up a herd and offered me two beautiful
rams issued of the same mother. I sacrificed the best of the two, but
the other charged me with its horns. As I was lying on the ground,
gravely wounded, and looked up at heaven, I saw a great portent:
the naming orb of the sun coming from the right, took a new course
and melted." Well may the Etruscan soothsayers have been exer-
cised about the rams and the changed course of the sun in the same
image, for they were concerned with astronomy. This problem
will be dealt with later. An interesting variant of this dream is found
in the Ambales Saga, and it can hardly have come from Cicero.7
However all that may be, there is more than enough to suspect
that the story goes back even farther than the Roman kings. Ac-
cordingly scholars undertook to investigate the link with the Per-
sian legend of Kyros, which turned out not to be rewarding. But
Saxo himself, even if he read Valerius- Maximus, contains features
which are certainly outside the classical tradition, and he shows
another way.
From the Narrenspiel the account of Hamlet's ride along the
shore is worth a second look: He notices an old steering oar (guber-
6 Zenker, pp. 149f.
7Gollancz, p. 105.
Hamlet's Mill
24
naculum) left over from a shipwreck, and he asks what it might be.
"Why," they say, "it is a big knife." Then he remarks, "This is
the right thing to carve such a huge ham"—by which he really
means the sea. Then, Saxo goes on, "as they passed the sandhills
and bade him look at the meal, meaning the sand, he replied that it
had been ground small by the hoary tempests of the ocean. His
companions praising his answer, he said he had spoken wittingly."
It is clear that Saxo at this point does not know what to do with
the remarks, for he has always pointed out that Amlethus' answers
were meaningful. "For he was loth to be thought prone to lying
about any matter, and wished to be held a stranger to falsehood,
although he would never betray how far his keenness went." This
being the systematic theme of Hamlet's adventure, a theme worked
out and contrived to show him as a Sherlock Holmes in disguise,
the two remarks quoted are the only ones left to look pointlessly
silly. They do not fit.
In fact, they come from a vastly different story. Snorri Sturluson,
the learned poet of Iceland (1178-1241), in his Skaldskaparmal
("The Language of the Bards") explains many kenningar of famous
bards of the past. He quotes a verse from Snaebjorn, an Icelandic
skald who had lived long before. This kenning has been the despair
of translators, as is the case in any very ancient, partly lost poetic
language. There are no less than three terms in the nine lines that
can be considered hapax legomena, i.e., terms which occur only
once. The most authoritative translation is that of Gollancz and
here it is:
'Tis said, sang Snaebjorn, that far out, off yonder ness, the Nine Maids
of the Island Mill stir amain the host-cruel skerry-quern—they who
in ages past ground Hamlet's meal. The good chieftain furrows the
hull's lair with his ship's beaked prow. Here the sea is called Am-
lodhi's mill.8
That is enough. Whatever the obscurities and ambiguities, one
thing is clear: goodbye to Junius Brutus and the safe playgrounds
of classical derivations.
8 Gollancz, p. xi.
25 • The Chronicler's Tale
This deals with the gray, stormy ocean of the North, its huge
breakers grinding forever the granite skerries, and Amlodhi is its
king. The quern has not vanished from our language. It is still the
surf mill. Even the British Island Pilot, in its factual prose, conveys
something of the power of the Nine Maids, whose very name is
echoed in the Merry Men of Mey on Pentland Firth:
When an ordinary gale has been blowing for many days, the whole
force of the Atlantic is beating against the shores of the Orkneys;
rocks of many tons in weight are lifted from their beds, and the roar
of the surge may be heard for twenty miles; the breakers rise to the
height of 60 feet . . .
As the storm heightens, "all distinction between air and water is
lost, everything seems enveloped in a thick smoke." Pytheas, the
first explorer of the North, called it the "sea lung," and concluded
this must be the end of the earth, where sky and water rejoin each
other in the original chaos.
This introduces a much more ancient and certainly independent
tradition, whose sources are in early Norse myth—or at least run
through it from a still more ancient lineage.
Chapter II
The Figure in Finland
N.
Now the discussion leaps, without apologies, over the impas-
sable fence erected by modern philologists to protect the linguistic
family of Indo-European languages from any improper dealings
with strange outsiders. It is known that Finland, Esthonia and Lap-
land are a cultural island, ethnically related to the Hungarians and
to other faraway Asian peoples: Siryenians, Votyaks, Cheremis-
sians, Mordvinians, Voguls, Ostyaks. They speak languages which
belong to the Ugro-Finnish family, as totally unrelated to Ger-
manic as Basque would be. These languages are described as "ag-
glutinative" and often characterized by vowel harmonization, such
as is found in Turkish. These cultural traditions until quite recently
were segregated from the Scandinavian environment. Even if West-
ern culture—and Christianity with it—seeped through among the
literati from the Middle Ages on, their great epic, the Kalevala,
remained intact, entrusted as it was to oral transmission going back
in unchanged form to very early times. It shows arrestingly primi-
tive features, so primitive that they discourage any attempt at a
classical derivation. It was collected in writing only in the 19th
century by Dr. Elias Lonnrot. But even in this segregated tradi-
tion, startling parallels were found with Norse and Celtic myth,
which must go back to times before their respective recorded his-
tories. The main line of the poem will be dealt with later. Here, it
is important to look at the story of Kullervo Kalevanpoika ("the
son of Kaleva"), which has been carefully analyzed by E. N.
Setala in his masterly inquiry "Kullervo-Hamlet."1 His material is
1FUF 3 (1903). pp.- 61-9797, 188-255; 7 (1907), pp. 188-224; 10 (1910), pp. 44-127.
27 • The Figure in Finland
necessary, as well as that collected by Kaarle Krohn,2 in order
to take into account many variants (which Lonnrot has not incor-
porated into the runes 31-36 of the official Kalevala) dealing with
Kullervo.
The first event is the birth of Kullervo's father and uncle, who
are, according to rune 31, swans (or chickens), driven from one
another by a hawk. Usually it is told that a poor man, a plowman,
made furrows around a tree trunk (or on a small hill) which split
open, and out of it were born two boys. One of them, Kalervo,
grew up in Carelia, the other, Untamo, in Suomi-Finland. The
hate between the brothers arises usually in the following manner:
Kalervo sows oats before the door of Untamo, Untamo's sheep eat
them, Kalervo's dog kills the sheep; or there is a quarrel about the
fishing grounds (rune 31.19ff.). Untamo then produces the war.
In fact, he makes the war out of his fingers, the army out of his
toes, soldiers of the sinews of his heel. But there are versions where
Untamo arms trees and uses them as his army. He kills Kalervo and
all his family, except Kalervo's wife, who is brought to Untamo's
home and there gives birth to our hero, Kullervo. The little one
is rocked in the cradle for three days,
when the boy began his kicking,
and he kicked and pushed about him,
tore his swaddling clothes to pieces,
freed himself from all his clothing,
then he broke the lime-wood cradle.3
At the age of three months,
when a boy no more than knee-high,
he began to speak in this wise:
"Presently when I am bigger,
And my body shall be stronger,
I'll avenge my father's slaughter,
2 Kalevalastudien 6. Kullervo (1928).
3 Translated by W. F. Kirby (Everyman's Library). The original rough meter
has been made to sound like a poor man's Hiawatha, but it was the original metric
model for Longfellow.
Hamlet's Mill
28
And my mother's tears atone for."
This was heard by Untamoinen,
And he spoke the words which follow.
"He will bring my race to ruin,
Kalervo reborn is in him."
And the old crones all considered,
how to bring the boy to ruin,
so that death might come upon him.
Untamo tries hard to kill the child, with fire, with water, by hang-
ing. A large pyre is built, Kullervo is thrown into it. When the
servants of Untamo come after three days to look,
knee-deep sat the boy in ashes,
in the embers to his elbows,
in his hands he held a coal-rake,
and was stirring up the fire.
Setala reports a version where the child, sitting in the midst of the
fire, the (golden) hook in his hand, and stirring the fire, says to
Untamo's servants that he is going to avenge the death of his father.4
Kullervo is thrown into the sea; after three days they find him sit-
ting in a golden boat, with a golden oar, or, according to another
version, he is sitting in the sea, on the back of a wave, measuring
the waters
Which perchance might fill two/ladles,
Or if more exactly measured,
Partly was a third filled also.
Next, they hang the child on a tree, or a gallows is erected—again
with frustrating results;
Kullervo not yet has perished,
Nor has he died on the gallows.
Pictures on the tree he's carving,
4 "Kullervo-Hamlet," FUF 7, p. 192.
29 • The Figure in Finland
In his hands he holds a graver.
All the tree is filled with pictures,
All the oak-tree filled with carvings.
One tradition says that he is carving the names of his parents
with a golden stylus. After this the sequence of events is difficult
to establish. There are variants, where Kullervo performs his re-
venge very soon—he merely goes to a smithy and procures the
arms. Or he is at once sent out of the country to the smith to serve
as cowherd and shepherd. But in rune 5/, he is first given smaller
commissions: to guard and rock a child—he blinds and kills it. Then
he js sent to clear a forest, and to fell the slender birch trees.
Five large trees at length had fallen,
Eight in all he felled before him}
He sits down afterwards and speaks (31.273 ff.).
"Lempo [the Devil] may the work accomplish,
Hiisi now-may-sloape the timber!"
In a stump he struck his axe-blade,
And began to shout full loudly,
And he piped, and then he whistled,
And he said the words which follow:
"Let the woods be felled around me,
Overthrown the slender birch-trees,
Far as sounds my voice resounding,
Far as I can send my whistle.
Let no sapling here be growing,
Let no blade of grass be standing,
Never while the earth endureth,
5 There is a strange Dindsencha (this word applies to the explanations of place-
names which occur repeatedly in Irish tradition; see W. Stokes, "The Prose Tales
in the Rennes Dindsenchas," RC 16, pp. 278f.) about the felling of five giant trees
—three ash trees, one oak, one yew. "The oak fell to the south, over Mag n-Ailte,
as far as the Pillar of the Living Tree. 900 bushels was its crop of acorns, and three
crops it bore every year . . . apples, nuts, and acorns. The ash of Tortu fell to the
South-east, that from Usnach to the North. The yew north-east, as far as Druinn
Bairr it fell. The ash of Belach Dahli fell upwards as far as Cam Uachtair Bile."
Hamlet's Mill
30
Or the golden moon is shining,
Here in Kalervo's son's forest,
Here upon the good man's clearing."6
In the Kalevala, Untamo next orders Kullervo to build a fence,
and so he does, out of whole pines, firs, ash trees. But he made no
gateway into it, and announced:
He who cannot raise him birdlike,
Nor upon two wings can hover,
Never may he pass across it,
Over Kalervo's son's fencing!
Untamo is taken aback:
Here's a fence without an opening . . .
Up to heaven the fence is builded,
To the very clouds uprising."1
6 The Esthonian Kalevipoeg (= son of Kaleva, the same as Finnish Kalevan-
poika) makes the soil barren wherever he has plowed with his wooden plow
(Setala, FUF 7, p. 215), but he, too, fells trees with noise—as far as the stroke of his
axe is heard, the trees fall down (p. 203). As for Celtic tradition, one of the
Rennes Dindsenchas tells that arable land is changed into woodland because
brother had killed brother, "so that a wood and stunted bushes overspread Guaire's
country, because of the parricide which he committed" (Stokes, RC 16, p. 35).
Whereas J. Loth (Les Mabinogion du Livre Rouge de Hergest, vol. I, p. 272,
n. 6) gives the names of three heroes who make a country sterile: "Morgan
Mwynvawr, Run, son of Beli, and Llew Llaw Gyffes, who turn the ground red.
Nothing grew for a year, herb or plant, where they passed: Arthur was more
'rudvawc' than they. Where Arthur had passed, for seven years nothing would
grow." Rudvawc means "red ravager," as we learn from Rachel Bromwich
(TrioedaYnys Prydein: The Welsh Triads [1961], p. 35). Seven years was the
cycle of the German Wild Hunter; Arthur was a Wild Hunter, too. The "Waste
Land" is, moreover, a standard motif of the legends spun around the Grail and
the Fisher King. All this will make sense eventually.
7 This might originally have been the same story as the one about Romulus
drawing a furrow around the new city and killing Remus for jumping over it.
In the Roman tradition, the murder makes no sense. Without following up this
key phenomenon here, we would like to say that in Finland the stone labyrinth
(the English "Troy town") is called Giant's Fence, and also St. Peter's Game,
Ruins of Jerusalem, Giant's Street, and Stone Fence (see W. H. Matthews,
Mazes and Labyrinths, p. 150). Whereas Al-Biruni (India 1, p. 306), when dealing
with Lanka (Ceylon)—i.e., Ravana's labyrinth that was conquered by Rama and
Hanuman—remarks that in Muslim countries this "labyrinthic fortress is called
Yavana-Koti, which has been frequently explained as Rome."
31 • The Figure in Finland
Kullervo does some more mischief, threshing the grain to mere
chaff, ripping a boat asunder, feeding the cow and breaking its
horn, heating the bath hut and burning it down—these are the usual
feats of the "Strong Boy" (the "Starke Hans" of German tales,
who with us became Paul Bunyan). So, finally, he is sent out of the
country, to the house of Ilmarinen the divine smith, as a cowherd.
There is, however, a remarkable variant where it is said that he
was "sent to Esthonia to bark under the fence; he barked one year,
another one, a little from the third; three years he barked at the
smith as his uncle, at the wife [or servant] of the smith as his
daughter-in-law." This sounds strange indeed, and the translator
himself added question marks. There is a still stranger parallel in
the great Irish hero Cuchulainn, a central figure of Celtic myth,
whose name means "Dog of the Smith Culan." This persistent dog-
gishness will bear investigation at another point and so will Smith
Ilmarinen himself.
The wife of Ilmarinen (often called Elina, Helena) makes Kul-
lervo her herdsman, and maliciously bakes a stone into his lunch
bread so that he breaks his knife, the only heirloom left from his
father. A crow then advises Kullervo to drive the cattle into the
marshes and to assemble all the wolves and bears and change them
into cattle. Kullervo said:
"Wait thou, wait thou, whore of Hiisi,
For my father's knife I'm weeping,
Soon wilt thou thyself be weeping." (33.125ff.)
He acts on the crow's advice, takes a whip of juniper, drives the
cattle into the marshes, and the oxen into the thicket.
Half of these the wolves devoured,
To the bears he gave the others,
And he sang the wolves to cattle,
And he changed the bears to oxen.
Kullervo carefully instructs the wolves and the bears on what they
are expected to do, and
Hamlet's Mill
3 3 • The Figure in Finland
Then he made a pipe of cow-bone,
And a whistle made of ox-horn,
From Tuomikki's leg a cow-horn,
And a flute from heel of Kir jo,
Then upon the horn blew loudly,
And upon his pipe made music.
Thrice upon the hill he blew it,
Six times at the pathway's opening.
\
He drives the "cattle" home, Helena goes to the stables to milk,
and is torn by wolf and bear.
This fierce retaliation gives point to an event that is only a feeble
joke in Saxo's version. A wolf crosses Hamlet's path, and he is told
it is a horse. "Why," he remarks, "in Fengo's stud there are too
few of that kind fighting." Saxo tries to explain: "This was a gentle
but witty fashion of invoking a curse upon his uncle's riches." It
makes little sense. One suspects here instead an echo of the theme
revealed by Kullervo, who drives home wolves and bears in place
of cattle. The hero's mastery of wild beasts evokes memories of
classical myth. This has not escaped Karl Kerenyi,8 whose com-
ment is useful, although not his line of psychological speculation:
"It is impossible to try to derive Finnish mythology from the Greek,
or conversely. Yet it is also impossible not to notice that Kullervo,
who is the Miraculous Child and the Strong Servant in one, shows
himself at last to be Hermes and Dionysos. He appears as Hermes
in the making of musical instruments tied up with the destruction
of cattle . . . He shows himself as Dionysos in what he does with
wild beasts and with his enemy. It is Dionysos-like behavior—if we
see it through the categories of Greek myth—to make wolves and
bears appear by magic as tame animals, and it is again Dionysos-like
to use them for revenge against his enemy. We recognize with awe
the tragic-ironic tone of Euripides' Bacchae, when we read the
dramatic scene of the milking of wild beasts. An even closer analogy
is given by the fate of the Etruscan pirates, Dionysos' enemies, who
are chastised by the intervention of wild animals . . ."
8 K. Kercnyi, "Zum Urikind-Mythologen," Paideuma 1 (1940), p. 255.
In rune 55, Lonnrot makes Kullervo return to his parents and
brothers and sisters. This is unexpected inasmuch as they have been
killed a number of runes earlier, although the crux of the many
rune songs is that the names of the heroes are far from stable and,
as has already been said, the original order of things is impossible
to reconstruct. But one event stands out. A sister is not at home. On
one occasion the hero meets a maiden in the woods, gathering ber-
ries. They lie together and realize later in conversing that they are
brother and sister. The maiden drowns herself, but Kullervo's
mother dissuades him from suicide. So he goes to war, and in so
doing he fulfills his revenge. First he asks the great god Ukko for
the gift of a sword
Then the sword he asked was granted,
And a sword of all most splendid,
And he slaughtered all the people,
Untamo's whole tribe was slaughtered,
Burned the houses all to ashes,
And with flame completely burned them,
Leaving nothing but the hearthstones,
Nought but in each yard the rowan.
Returning home, Kullervo finds no living soul; all have died. When
he weeps over his mother's grave, she awakes,
And beneath the mould made answer:
"Still there lives the black dog, Musti,
Go with him into the forest,
At thy side let him attend thee."
There in the thicket reside the blue forest-maidens, and the mother
advises him to try to win their favor. Kullervo takes the black
dog and goes into the forest, but when he comes upon the spot
where he had dishonored his sister, despair overcomes him, and he
throws himself upon his own sword.
Here at last a point is made explicitly which in other stories
remains a dark hint. There is a sin that Hamlet has to atone for.
The knowledge that Kullervo and his sister killed themselves for
Hamlet's Mill
34
unwitting incest calls to mind the fact that in Saxo the adolescent
Prince is initiated to love by a girl who does not betray him "be-
cause she happened to be his foster-sister and playmate since child-
hood." This seems contrived, as if Saxo had found there a theme
he does not grasp. The theme becomes manifest in King Arthur. It
is ambiguous and elusive, but all the more inexorable in Shakespeare.
Hamlet must renounce his true love, as he has to renounce himself
in his predicament:
"Get thee to a nunnery. Why wouldst thou be a breeder of sinners?
. . . What should such fellows as I do nawling between earth and
heaven? We are arrant knaves all; believe none of us. Go thy ways
to a nunnery."
In the play-within-a-play, the Prince feels free to step out of
character:
Lady, shall I lie in your lap?
No, my lord.
1 mean, my head upon your lap?
Ay, my lord.
Do you think I meant country matters?
I think nothing, my lord.
That is a fair thought to lie between maid's legs.
What is, my lord?
Nothing.
But the die is cast. Ophelia's suicide by drowning, like Kullervo's
sister's, brings about the death of her lover—and of her brother too.
The two aspects join in the final silence. At least Hamlet, ever con-
scious, has had a chance to describe in despair the insoluble knot
of his guilt:
"I loved Ophelia; forty thousand brothers
could not with all their quantity of love
make up my sum. What wilt thou do for her?"
And now Kullervo. Setala's analysis of the whole parallel goes as
follows:
35 • The Figure in Finland
As concerns generalities: brother kills brother; one son survives,
who sets his mind on revenge from earliest childhood; the uncle
tries to kill him, but he succeeds in achieving his revenge. As con-
cerns details: Setala wants to identify the stakes and hooks, which
the hero in all northern versions shapes or carves, sitting at the
hearth—Brjam does it in a smithy—with the golden hook or rake
that little Kullervo, sitting in the middle of the fire, holds in his
hands, stirring the flames. Each hero (including Kullervo in one of
the versions found by Setala) makes it clear that he means to avenge
his father.
With some puzzlement Setala brings out one other point which
will turn out to be crucial later on. In every northern version there
is some dark utterance about the sea. The words are weird. Hamlet
wants to "cut the big ham" with the steering oar; the child Kullervo
is found measuring the depth of the sea with an oar or with a ladle.
Kalevipoeg, the Esthonian counterpart of Kullervo Kalevanpoika,
measures the depth of lakes with his height. Amlodhi-Ambales, sit-
ting by a bottomless mountain lake, says only: "Into water wind
has come, into water wind will go."
Chapter III
The Iranian Parallel
For from today new feasts and
customs date
Because tonight is born Shah Kai
Khusrau
Shahnama
T.
. he Hamlet theme moves now to Persia. Firdausi's Shahnama,
the Book of Kings, is the national epic of Iran,1 and Firdausi
(ca. a.d. 1010) is still today the national poet. At the time Firdausi
wrote, his protector, Sultan Mahmud of Ghazna, had shifted the
center of his power to India, and the Iranian empire had long been
only a memory. With prodigious scholarship, Firdausi, like Homer
before him, undertook to organize and record the Zendic tradition,
which extended back from historic times into the purely mythical.
The first section on the Pishdadian and Kaianian dynasties must be
considered mythical throughout, although it does reach into his-
toric times and encompasses four of the nine volumes of the Book
of Kings in the English translation. Khusrau (Chosroes in Greek) is
also the name of a line of historical rulers, one of whom, Khusrau
Anushirvan, gave sanctuary to the last philosophers of Greece, the
members of the Platonic Academy driven out by Justinian in
a.d. 529. But Firdausi's Kai Khusrau is the towering figure of his
own mythical age. Almost one-fifth of the whole work is allotted
to him. He is actually the Haosravah of the Zend Avesta, and also
'We cite here the English translation of Arthur and Edward Warner (1905-
1909).
3 7 • The Iranian Parallel
the Rigvedic Sushravah, an identity which raises again the much
discussed question of a common Indo-European "Urzeit," the time
of origins.
The common features of Saxo's Amlethus and Kai Khusrau are
so striking that Jiriczek, and after him Zenker, undertook detailed
comparative studies.2 But they concluded that the Greek saga of
Bellerophon might provide a common origin, and that was the end
of their quest. Classical antiquity has a magnetic quality for the
scholarly mind. It acts upon it like the Great Lodestone Mountain
in Sindbad. The frail philological bark comes apart as soon as
Greece looms over the horizon. Bellerophon's somber tale would
provide a parallel too, but does that have to be the end of the trail?
As Herodotus ruefully remarks, his own Hellenic antiquity goes
back in recorded memory but a few centuries; beyond that, it
blends with the Indo-European patrimony of legends.
In the vast flow of the Shahnama, one prominent feature is the
perpetual war between "Untamo" and "Kalervo," here the two
rival peoples of Turan and Iran. Because the vicissitudes of the
Kaianian dynasty of Iran are spread over a narrative twice as long
as both epics of Milton combined, it is necessary here to concentrate
on one essential aspect.
The Iranian plot shows some "displacement" in that Afrasiyab
the Turanian kills, instead of his brother, his nephew Siyawush who
is also His son-in-law, so that the "avenger" of this crime is bound
to come forth as the common grandson of the hostile Turanian
Shah Afrasiyab and his brother, the noble Iranian Shah Kai Ka'us
(the same one who plays no small role in the Rigveda as Kavya
Ushanas, and in the Avesta as Kavi Usan). Siyawush, as commander
of his father's army, offers peace to the Turanian Afrasiyab, who
accepts the offer because he has had a catastrophic dream.3 This
dream resembles those of Tarquin and Ambales. Kai Ka'us does not
trust Afrasiyab and declines peace. Siyawush, not wishing to break
his own treaty with Turan, goes to live with Afrasiyab.
0. L. Jiriczek, "Hamlet in Iran," ZVV 10 (1900)pp.353-64; R. Zenker, Boeve-
Amlethus (1905), pp. 207-82.
3Firdausi, Warner trans., vol. 2, pp. 232f.
Hamlet's Mill • 38
Afrasiyab honors the young man in every way, and gives him a
large province which he rules excellently, i.e., in the "Golden Age"
style of his father Kai Ka'us. Siyawush marries first a daughter of
the Turanian Piran, then Shah Afrasiyab gives him his own
daughter Farangis. But there is a serpent in that garden. Afrasiyab's
jealous brother Garsiwas, an early Polonius, plots so successfully
against Siyawush that Afrasiyab finally sends an army against the
blameless young ruler. Siyawush is captured and killed. The wid-
owed Farangis escapes, accompanied by Piran (Siyawush's first
father-in-law) to Piran's home where she gives birth to a boy of
great beauty, Kai Khusrau, Afrasiyab's and Kai Ka'us' common
grandson:
One dark and moonless night, while birds, wild beasts
And cattle slept, Piran in dream beheld
A splendour that outshone the sun itself,
While Siyawush, enthroned and sword in hand,
Called loudly to him saying: "Rest no more!
Throw off sweet sleep and think of times to come.
For from today new feasts and customs date,
Because to-night is born Shah Kai Khusrau!"
The chieftain roused him from his sweet repose:
Gulshahr the sunny-faced woke. Piran
Said unto her: "Arise, Betake thyself
To minister to Farangis, for I
Saw Siyawush in sleep a moment since,
Surpassing both the sun and moon in lustre,
And crying: ''Sleep no more, but join the feast
Of Kai Khusrau, the monarch of the world!' "
Gulshahr came hasting to the Moon and saw
The prince already born; she went with cries
Of joy that made the palace ring again
Back to Piran the chief. "Thou wouldest say"
She cried, "that king and Moon are fairly matched!"4
4 Firdausi, Warner trans., vol. 2, pp.
39
The Iranian Parallel
With this prophetic dream of a great new age begins a long time
of trials for the predestined hero. The boy grows up among the
shepherds; he becomes a great hunter with a crude bow and arrows
that he makes for himself without arrowheads or feathers, like
Hamlet whittling his stakes. Grandfather Afrasiyab, being afraid of
the boy, orders the prince brought to him so that he can convince
himself his victim is harmless. Although Afrasiyab has sworn sol-
emnly not to hurt Khusrau, Piran urges the boy to play the village
idiot for his own safety. When the tyrant questions him with
feigned benevolence, Kai Khusrau answers in the very same style as
Amlethus did, in riddles which sound senseless and indicate that
young Khusrau likens himself to a dog. The usurper feels relieved:
"The fellow is a fool!"
Now, the tale of vengeance, unduly abbreviated by Saxo's report
and in other versions, is told by Firdausi with an appropriately
majestic setting and on a grand scale. The anger of Iran and the
world, stemming from the death of Siyawush, is orchestrated apo-
calyptically into a cosmic tumult:
The world was all revenge and thou hadst said:
"It is a seething sea!" Earth had no room
For walking, air was ambushed by the spears;
The stars began to fray, and time and earth
Washed hands in mischief...5
Still, the two archcriminals manage to escape and hide with inex-
haustible resourcefulness. Afrasiyab even plays Proteus in the waters
of a deep salt lake, constantly assuming new shapes to evade cap-
ture. Finally, two volumes and a multitude of events later, Afrasiyab
and the evil counsellor are caught with a lasso or a net and both
perish.
Only by going back to the Avestan tradition can one make sense
of the many vicissitudes to which the Yashts or hymns of the
Avesta allude repeatedly.6 The Shahs Kai Khusrau and Afrasiyab
5Firdausi, Warner trans., vol. 2, p. 342.
6Vasht 5.41-49; 19.56-64,74.
Hamlet's Mill
40
were contending in a quest for the enigmatic Hvarna, rendered as
the "Glory," or the Charisma of Fortune. To obtain it the Shahs
kept sacrificing a hundred horses, a thousand oxen, ten thousand
lambs to the goddess Anahita, who is a kind of Ishtar-Artemis. Now
this Glory "that belongs to the Aryan nations, born and unborn,
and to the holy Zarathustra" was in Lake Vurukasha. Afrasiyab,
Shah of the non-Aryan Turanians, was not entitled to it. But leav-
ing his hiding place in an underground palace of iron "a thousand
times the height of man" and illuminated by artificial sun, moon
and stars, he tried three times to capture the Hvarna, plunging into
Lake Vurukasha. However, "the Glory escaped, the Glory fled
away, the Glory changed its seat." There will be more discussion
of Afrasiyab's attempts and his "horrible utterances," in the chapter
"Of Time and the Rivers." The Glory was, instead, allotted to Kai
Khusrau, and it was bestowed upon him without much ado. At this
point it is fair to say that Hvarna stands for Legitimacy, or
Heavenly Mandate, which is granted to rulers, but is also easily
withdrawn. Yima (Jamshyd), the earliest "world ruler," lost it
three times.
The story of diving Afrasiyab has had many offshoots in Eurasian
folklore. There the Turanian Shah is spelled "Devil," and God
causes him to dive to the bottom of the sea, so that in the meantime
one of the archangels, or St. Elias, can steal a valuable object which
is the legal property of the Devil. Sometimes the object is the sun,
sometimes the "divine power," or thunder and lightning, or even a
treaty between God and Devil which had turned out to be un-
profitable for God.
There remains the essential denouement. During those eventful
years, Kai Ka'us held joint rulership with his grandson, secure in
the Glory. Shortly after the victory over the upstart, Kai Ka'us dies
and Kai Khusrau ascends the Ivory Throne. For sixty years, says
the poem, "the whole world was obedient to his sway." It is strik-
ing that there is no word of any event after Kai Ka'us' death. May-
be it is because all has been achieved. Happy reigns have no history.
But it is told that Kai Khusrau falls into deep melancholy and soul-
41 . The Iranian Parallel
searching.7 He fears he may "grow arrogant in soul, corrupt in
thought" like his predecessors Yima (Jamshyd) and, among others,
Kai Ka'us himself, who had tried to get himself carried to heaven
by eagles like the Babylonian Etana. So he makes the supreme
decision:
"And now I deem it better to depart
To God in all my glory . . .
Because this Kaian crown and throne will pass."
The great Shah, then, who had once stated (at his first joint en-
thronement) :
"The whole world is my kingdom, all is mine
From Pisces downward to the Bull's head,"8
prepares his departure, takes leave of his paladins, waving aside
their supplications and those of his whole army:
A cry rose from the army of Iran:
The sun hath wandered from its way in heaven!
The dream of Tarquin finds here an early echo. The Shah appoints
as his successor Luhrasp and wanders off to a mountaintop, accom-
panied by five of his paladins, to whom he announces in the eve-
ning, before they sit down for the last time to talk of the great past
they have lived together:
"What time the radiant sun shall raise its flag,
And turn the darksome earth to liquid gold,
Then is the time when I shall pass away
And haply with Surush9 for company."
Toward dawn he addresses his friends once more:
"Farewell for ever! When the sky shall bring
The sun again ye shall not look on me
7 Firdausi, Warner trans., vol. 4, pp. 272ff.
8Firdausi, Warner trans., vol. 2, p. 407.
9Surush • Avestic Sraosha, the "angel" of Ahura Mazdah.
Hamlet's Mill • 42
Henceforth save in your dreams. Moreover be not
Here on the morrow on these arid sands,
Although the clouds rain musk, for from the Mountains
Will rise a furious blast and snap the boughs
And leafage of the trees, a storm of snow
Will shower down from heaven's louring rack,
And towards Iran ye will not find the track."
The chieftains' heads were heavy at the news.
The warriors slept in pain, and when the sun
Rose over the hills the Shah had disappeared.
The five paladins are lost and buried in the snowstorm.10
10 This theme of sleep in the "hour of Gethsemane" will occur more than once,
e.g., in Gilgamesh. The myth of Quetzalcouatl is even more circumstantial. The
exiled ruler is escorted by the dwarves and hunchbacks, who are also lost in the
snow along what is now the Cortez Pass, while their ruler goes on to the sea and
departs. But here at least he promises to come back and judge the living and the
dead.
Chapter IV
History, Myth and Reality
"Let us try, then, to set forth in
our statement what things these
are, and of what kind, and how
one should learn them ... It is,
indeed, a rather strange thing to
hear; but the name that we, at
any rate, give it—one that people
would never suppose, from inex-
perience in the matter—is astron-
omy; people are ignorant that he
who is truly an astronomer must
be wisest, not he who is an as-
tronomer in the sense understood
by Hesiod . . . ; but the man who
has studied the seven out of the
eight orbits, each travelling over
its own circuit in such a manner
as could not ever be easily ob-
served by any ordinary nature
that did not partake of a marvel-
lous nature."
Epinomis 989 E—990 b
The strange end of the Iranian tale, which concludes with an
ascent to heaven like that of Elias, leaves the reader wondering. If
this is the national epos (almost one half of it in content), where is
the epic and the tragic element? In fact, there is a full measure of
the Homeric narrative in Firdausi that had to be left aside, there are
great battles as on the windy plains of Troy, challenges and duels,
the incredible feats of heroes like Rustam and Zal, abductions and
intrigues, infinite subplots to the tale, enough for a bard to entertain
Hamlet's Mill
44
his patrons for weeks and to ensure him a durable supply of
haunches of venison. But the intervention of the gods in the tale
is not so humanized as in the Iliad, although it shows through re-
peatedly in complicated symbolism and bizarre fairy tales. The con-
flict of will and fate is not to the measure of man. What has been
traced above is a confusing story of dynastic succession under a
shadowy Glory, a Glory without high events, keyed to a Hamlet
situation and an unexplained melancholy. The essence is an unsub-
stantial pageant of ambiguous abstractions, an elusive ballet of
wildly symbolic actions tied to ritual magic and religious doctrines,
with motivations which bear no parallel to normal ones. The whole
thing is a puzzle to be interpreted through hymns—very much as
in the Rigveda.
But here at last there is given apertis verbis one key to the imag-
ery: Khusrau's crowning words:
"The whole world is my kingdom: all is mine
From Pisces downward to the Bull's head."
If a hero of the western hemisphere were to proclaim: "All of
this continent is mine, from Hatteras to Eastport," he would be
considered afflicted with a one-dimensional fancy. Does that stretch
of coast stand in his mind for a whole continent? Yet here the
words make perfect sense because Kai Khusrau does not refer to the
earth. He designates that section of the zodiac comprised between
Pisces and Aldebaran, the thirty degrees which cover the constel-
lation Aries. It means that his reign is not only of heaven, it is essen-
tially of Time. The dimension of heaven is Time. Kai Khusrau
comes in as a function of time, preordained by events in the zodiac.
"For from today new feasts and customs date .. ."
Why Aries, and what it all imports, is not relevant at this point. It
turns out that "ruler of Aries" was the established title of supreme
power in Iran,1 and it may have meant as much or as little as "Holy
1 Persia "belongs" to Aries according to Paulus Alexandrinus. See Boll's Sphaera,
pp. 296f., where it is stated that this was the oldest scheme. It is still to be found
in the Apocalypse. Moses' ram's horns stand for the same world-age.
45 • History, Myth and Reality
Roman Emperor" in the West. What counts is that Rome is a place
on earth, whose prestige is connected with a certain historical pe-
riod, whereas Aries is a zone of heaven, or rather, since heaven
keeps moving, a certain time determined by heavenly motion in
connection with that constellation. Rome is a historic fact, even
"Eternal Rome," which was once and then is left only to memory.
Aries is a labeled time, and is bound to come back within certain
cycles.
Even if Kai Khusrau is conceived as a worldly ruler in an epos
which prefaces history, it is clear that no modern historical or
naturalistic imagination can provide the key to such minds as those
of the Iranian bards out of whose rhapsodies the learned Firdausi
organized the story. No basis in history can be found, no fertility
or seasonal symbolism can be traced into it, and even the psycho-
analysts have given up trying. This type of thought can be defined
in one way: it is essentially cosmological.
This is not to make things uselessly difficult, but to outline the
real frame of mythical thought, such as is actually quite familiar
and yet by now hardly recognized. It even appears in the mode of
lyrical meditation, at least in the English of Fitzgerald:
Iram indeed is gone with all its Rose
And ]amshyd's Sev'n-ringed Cup where no one knows
But still the Vine her ancient Ruby yields
And still a Garden by the Water blows.
And look—a thousand Blossoms with the Day
Woke—and a thousand scatter'd into Clay
And the first Summer month that brings the Rose
Shall take Jamshyd and Kai Kubad away.
But come with old Khayyam, and leave the lot
Of Kai Kubad and Kai Khosrau forgot . . .
Omar Khayyam may speak as a weary skeptic or as mystical Sufi,
but all he speaks of is understood as real. The heroes of the past are
II real as the friends for whom he is writing, as the vine and the
roses and the waters, as his own direct experience of flux and im-
Hamlet's Mill • 46
permanence in life. When he makes his earthenware pots to feel
and think, it is no literary trope; it is the knowledge that all tran-
sient things are caught in the same transmutation, that all substance
is one: the stuff that pots and men and dreams are made of.
This is what could be called living reality, and it is singularly
different from ordinary or objective reality. When the poet thinks
that this brick here may be the clay that was once Kai Khusrau, he
rejoins Hamlet musing in the graveyard: "To what base uses we
return, Horatio! Why may not imagination trace the noble dust of
Alexander till'a find it stopping a bung-hole?" Here are already
four characters, two of them unreal, two lost in the haze of time,
yet all equally present in our game, whereas most concrete charac-
ters, say the Director of Internal Revenue, are not, however they
may affect us otherwise. In that realm of "true existence" we shall
find stars and vines and roses and water, the eternal forms, and it
will include also the ideas of mathematics, another form of direct
experience. The world of history is outside it as a whole. Khayyam
does not, any more than Firdausi a generation later, mention the
glories of Cyrus and Artaxerxes, but only mythical heroes, just as
our own Middle Ages ignored history and spoke of Arthur and
Gawain. It had been all "once upon a time," and if Dante brings
back myth so powerfully to life, it is because his own contempora-
ries believed themselves truly descended from Dardanus and Troy,
and wondered whether the Lord Ulysses might not still be alive;
whereas Kaiser Barbarossa, asleep in his Kyffhauser mountain—that
must surely be a fable like Snow White. Or is it? Fairy tales are
easily dismissed for their familiar sound. But it might turn out that
such great imperial figures turned into legend have a hidden life of
their own, that they follow the laws of myth laid down long before
them. Even as King Arthur did not really die but lives on in the
depth of the mystic lake, according to Merlin's prophecy, so God-
frey of Viterbo (c. 1190), who had been in Barbarossa's service,
alone brings the "true" version. It is the orthodox one in strangely
preserved archaic language: the Emperor sleeps on in the depth of
the Watery Abyss (cf. chapter XI and appendix #33) where the
retired rulers of the world are.
47 • History, Myth and Reality
Voire, ou sont de Constantinople
Uempereurs aux poings dorez . . .
A distinction begins to appear between myth and fable. Hamlet
is showing himself in the aspect of a true myth, a universal one. He
is still that now. And Khayyam was the greatest mathematician of
his time, the author of a planned calendar reform which turned out
to be even more precise than the one that was adopted later as the
Gregorian calendar, an intellect in whom trenchant skepticism
could coexist with profound Sufi intellection. He knew full well
that Jamshyd's seven-ringed cup is not lost, since it stands for the
seven planetary circles of which Jamshyd is the ruler, just as Jam-
shyd's magic mirror goes on reflecting the whole world, as it is the
sky itself. But it is natural to let them retain their iridescent mys-
tery, since they belong to the living reality, like Plato's whorls and
his Spindle of Necessity. Or like Hamlet himself.
What then were Jamshyd or Kai Khusrau? To the simple, a
magic image, a fable. To those who understood, a reflection of
Time itself, obviously one of its major aspects. They could be
recognized under many names in many places, even conflicting al-
lusions. It was always the same myth, and that was enough. It
expressed the laws of the universe, in that specific language, the
language of Time. This was the way to talk about the cosmos.
All that is living reality, sub specie transeuntis, has a tale, as it
appears in awesome, or appalling, or comforting aspects, in the
"fearful symmetry" of tigers or theorems, or stars in their courses,
but always alive to the soul. It is a play of transmutations which
include us, ruled by Time, framed in the eternal forms. A thought
ruled by Time can be expressed only in myth. When mythical
languages were universal and self-explanatory, thought was also
sef-sufficient. It could seek no explanation of itself in other terms,
for it was reality expressed as_ living. As Goethe said, "Alles Ver-
gitngliche—ist nur ein Gleichnis."
Men today are trained to think in spatial terms, to localize ob-
jicis. After childhood, the first question is "where and when did it
happen?" As science and history invade the whole landscape of
Hamlet's Mill • 48
thought, the events of myth recede into mere fable. They appear
as escape fantasies: unlocated, hardly serious, their space ubiquitous,
their time circular.
Yet some of those stories are so strong that they have lived on
vividly. These are true myths. These personages are unmistakably
identified, yet elusively fluid in outline. They tell of gigantic figures
and superhuman events which seem to occupy the whole; living
space between heaven and earth. Those figures often lend their
names to historical persons in passing and then vanish. Any attempt
to tie them down to history, even to the tradition of great and
catastrophic events, is invariably a sure way to a false trail. His-
torical happenings will never "explain" mythical events. Plutarch
already knew as much. Instead, mythical figures have invaded his-
tory under counterfeit presentments, and subtly shaped it to their
own ends. This is a ■working rule which was established long ago,
and it has proved constantly valid if one is dealing with true myth
and not with ordinary legends. To be sure, mythical figures are
born and pass on, but not quite like mortals. There have to be char-
acteristic styles for them like The Once and Future King. Were
they once? Then they have been before, or will be again, in other
names, under other aspects, even as the sky brings back forever its
configurations. Surely, if one tried to pinpoint them as persons and
things, they would melt before his eyes, like the products of sick
fantasy. But if one respects their true nature, they will reveal that
nature as junctions.
Functions of what? Of the general order of things as it could be
conceived. These figures express the behavior of that vast complex
of variables once called the cosmos. They combine in themselves
variety, eternity, and recurrence, for such is the nature of the cos-
mos itself. That the cosmos might be infinite seems to have re-
mained beyond the threshold of awareness of humankind up to the
time of Lucretius, of Bruno and Galileo. And Galileo himself, who
had serious doubts on the matter, agreed with all his predecessors
that surely the universe is eternal, and that hence all its changes
come under the law of periodicity and recurrence. "What is eter-
nal," Aristotle said, "is circular, and what is circular is eternal."
49 • History, Myth and Reality
That was the mature conclusion of human thought over millennia.
It was, as has been said, an obsession with circularity. There is
nothing new under the sun, but all things come back in ever-varying
recurrence. Even the hateful word "revolution" referred once only
to those of the celestial orbs. The cosmos was one vast system full
of gears within gears, enormously intricate in its connections, which
could be likened to a many-dialed clock. Its functions appeared and
disappeared all over the system, like strange cuckoos in the clock,
and wonderful tales were woven around them to describe their
behavior; but just as in an engine, one cannot understand each part
until one has understood the way all the parts interconnect in the
system.
Similarly, Rudyard Kipling in a droll allegory, "The Ship That
Found Herself," once explained what happens on a new ship in her
shakedown voyage. All the parts spring into clamorous being as
each plays its role for the first time, the plunging pistons, the groan-
ing cylinders, the robust propeller shaft, the straining bulkheads,
the chattering rivets, each feeling at the center of the stage, each
telling the steam about its own unique and incomparable feats, until
at last they subside into silence as a new deep voice is heard, that
of the ship, who has found her identity at last.
This is exactly what happens with the great array of myths. All
the myths presented tales, some of them weird, incoherent or out-
landish, and some epic and tragic. At last it is possible to understand
them as partial representations of a system, as functions of a whole.
The vastness and complexity of the system is only beginning to take
shape, as the parts fall into place. The only thing to do is proceed
inductively, step by step, avoiding preconceptions and letting the
argument lead toward its own conclusions.
In the simple story of Kai Khusrau, the Hamlet-like features are
curiously preordained, although it is not clear to what end. The
King's power is explicitly linked, in time and space, with the mov-
ing configurations of the heavens. It is common knowledge that
heaven in its motion does provide coordinates for time and place
on earth. The navigator's business is to operate on this connection
between above and below. But in the early centuries, the connect
Hamlet's Mill • 50
tion was infinitely richer in meaning. No historical monarch, how-
ever convinced of his charisma, could have said: "The whole world
is my kingdom, all is mine from Pisces to Aldebaran." Earthly
concepts seem to have been transferred to heaven, and inversely.
In fact, this world of myth imbricates uranography and geography
into a whole which is really one cosmography, and the "geographi-
cal" features referred to can be mystifying, as they may imply
either of these domains or both.
For instance, when the "rivers" Okeanos or Eridanos are men-
tioned, are they not conceived as being first in heaven and then
eventually on earth, too? It is as if any region beyond ancient man's
direct ken were to be found simply "upwards." True events, even
in an official epic like the Shahnama, are not "earth-directed." They
tend to move "upwards." This is the original form of astrology,
which is both vaster and less defined than the later classic form
which Ptolemy set forth. Even as the cosmos is one, so cosmogra-
phy is made up of inextricably intertwined data. To say that events
on earth reflect those in heaven is a misleading simplification to
begin with. In Aristotelian language, form is said to be metaphys-
ically prior to matter, but both go together. It is still necessary to
discover which is the focus of "true" events in heaven.
To recapitulate for clarity, whatever is true myth has no his-
torical basis, however tempting the reduction, however massive and
well armed the impact of a good deal of modern criticism on that
belief. The attempt to reduce myth to history is the so-called "eu-
hemerist" trend, from the name of Euhemeros, the first debunker.
It was a wave of fashion which is now receding, for it was too
simpleminded to last. Myth is essentially cosmological. As heaven in
the cosmos is so vastly more important than our earth, it should not
be surprising to find the main functions deriving from heaven. To
identify them under a variety of appearances is a matter of mytho-
logical judgment, of the capacity to recognize essential forms
through patient sifting of the immense amount of material.
Hamlet "is" here Kullervo, there Brutus or Kai Khusrau, but
always recognizably the same. Jamshyd reappears as Yama among
the Indo-Aryans, as Huang-ti, the Yellow Emperor, in China, and
51 • History, Myth and Reality
under many other names. There was always the tacit understanding,
for those who spoke the archaic language, who were involved in
the archaic cosmos, that he is everywhere the same function. And
who is the Demiurge? He has many names indeed. Plato does not
care to explain in our terms. Is this personage a semi-scientific fic-
tion, the manufacturer of a planetarium, just as the Lost Continent
of Atlantis is a semi-historical fiction? The author himself says only
that such stories are "not quite serious." Yet they are surely not a
spoof. Plato, who shaped what is called philosophy and its language,
who was the master of its penetrating distinctions, reverts to the
language of myth when he feels he has to; and he uses that ancient
language as if to the manner born.2
In this accounting for past myths, the heart of the problem re-
mains elusive. Kipling was a writer still marvellously attuned to the
juvenile mind that lives in most of us. But the fact is that myth it-
self, as a whole, is a lost world. The last forms—or rehearsals—of
a true myth took place in medieval culture: the Romance of Alex-
ander, and the Arthurian myth as it is found in Malory.*
There are other stories—we call them history—of man's conquest
over nature, the telling of the great adventure of mankind as a
whole. But here it is only faceless social man who is winning man's
victories. It is not the history of technology; it is, if anything,
science fiction that can bring in the adventures of the future. Science
fiction, when it is good, is a wholly valid attempt at restoring a
mythical element, with its adventures and tragedies, its meditations'"
on man's errors and man's fate. For true tragedy is an essential com-
ponent or outcome of myth. Possibly, history can be given a minute
2 In his Seventh Letter (3410-3440) he denies strongly that scientific "names" and
"sentences" (onomata, remata) could assist in obtaining essential insight. Cf. also
Clemens Alexandrinus, Stromata 5.9.58.
* Still, there have been modern attempts deserving the name of myth. One, of
course, is Sir Thomas More's Utopia, which has taken on so much meaning through
the centuries. We realize today that it, too, was partly oracular. And we should
not forget Alice in Wonderland, the perfect nonsense myth, as significant and as
nonsensical as the Kalevala itself. This parallel will appear relevant at the end of
the appendices. Today, there is Austin Wright's Islandia, which appeared in 1942,
and its present sequel, The lslar, by Mark Saxton, to be published in the autumn
of 1969.
Hamlet's Mill • 52
of timeliness and then dismissed with its load of interpretations and
apprehensions that last as long as the reading—but the real present,
the only thing that counts, is the eternal Sphinx.
Today's children, that impassive posterity to whom all reverence
is due, know where to look for myths: in animal life, in the Jungle
Books, in the stories of Lassie and Flipper, where innocence is un-
assailable, in Western adventures suitably arranged by grownups
for the protection of law and order. Much of the rest sedulously
built up by mass media is modern prejudice and delusion, like the
glamor of royalty, or the perfection of super-detergents and cos-
metics: super-stitio, leftovers. So one might feel tempted to say:
actually, however, no particle of myth today is left over, and we
have to do only with a deliberate lie about the human condition.
Tolkien's efforts at reviving the genre, whatever the talent em-
ployed, carry as much conviction as the traditional three-dollar bill.
The assumed curious child would have been pleased only if he
had been told the "story" of the engine just as Kipling tells it, which
is hardly the style of a mechanical engineer. But suppose now the
child had been confronted with the "story" of a planet (or comet) as it emerges
from the textbooks of celestial mechanics, and had been asked to
calculate its orbits and perturbations. This would be a task for a
joyless grownup, and a professional one at that. Who else could
face the pages bristling with partial differential equations, with long
series of approximations, with integrals contrived from pointless
quadratures? Truly a world of reserved knowledge. But if, on the
other hand, a person living several thousand years ago had been
confronted with cunningly built tales of Saturn's reign, and of his
exorbitant building and modeling activities—after he had "separated
Heaven and Earth" by means of that fateful sickle, that is, after he
had established the obliquity of the ecliptic ... If he had heard of
Jupiter's ways of command and his innumerable escapades, popu-
lating the earth with gentle nymphs forever crossed in their quest
for happiness, escapades that were invariably successful in spite of
the constant watchfulness of his jealous "ox-eyed" or sometimes
"dog-eyed" spouse ... If this person also learned of the fierce ad-
ventures of Mars, and the complex mutual involvement of gods
53 • History, Myth and Reality
and heroes expressing themselves in terms of action and unvarying
numbers, he would have been a participant in the process of mythi-
cal knowledge. This knowledge would have been transmitted by
his elders, confirmed by holy commands, rehearsed by symbolic
experiences in the form of musical rites and performances involving
his whole people. He would have found it easier to respect than .
comprehend, but it would have led to an idea of the overall texture
of the cosmos. In his own person, he would have been part of a
genuine theory of cosmology, one he had absorbed by heart, that
was responsive to his emotions, and one that could act on his aspira-
tions and dreams. This kind of participation in ultimate things, now
extremely difficult for anyone who has not graduated in astro-
physics, was then possible to some degree for everyone, and no-
where could it be vulgarized.
That is what is meant here by mythical knowledge. It was under-
stood only by a very few, it appealed to many, and it is forever
intractable for those who approach it through "mathematics for the
million" or by speculations on the unconscious. In other words,
this is a selective and difficult approach, employing the means at
hand and much thought, limited surely, but resistant to falsifi-
cation.
How, in former times, essential knowledge was transmitted on
two or more intellectual levels can be learned from Germaine
Dieterlen's introduction to Marcel Griaule's Conversations with
Ogotemmeli, which deals with Dogon education and with the per-
sonal experience of the members of La Mission Griaule, who had to
wait sixteen years before the sage old men of the tribe decided to
"open the door."3 The description is revealing enough to be quoted
in full:
In African societies which have preserved their traditional organiza-
tion the number of persons who are trained in this knowledge is
quite considerable. This they call "deep knowledge" in contrast with
"simple knowledge" which is regarded as "only a beginning in the
understanding of beliefs and customs" that people who are not fully
instructed in the cosmogony possess. There are various reasons for
the silence that is generally observed on this subject. To a natural
3M. Griaule, Conversations with Ogotemmeli (1965), pp. xiv-xvii.
Hamlet's Mill
54
reserve before strangers who, even when sympathetic, remain un-
consciously imbued with a feeling of superiority, one must add the
present situation of rapid change in African societies through con-
tact with mechanization and the influence of school teaching. But
among groups where tradition is still vigorous, this knowledge, which
is expressly characterized as esoteric, is only secret in the following
sense. It is in fact open to all who show a will to understand so long
as, by their social position and moral conduct, they are judged worthy
of it. Thus every family head, every priest, every grown-up person
responsible for some small fraction of social life can, as part of the
social group, acquire knowledge on condition that he has the pa-
tience and, as the African phrase has it, "he comes to sit by the side
of the competent elders" over the period and in the state of mind
necessary. Then he will receive answers to all his questions, but it
will take years. Instruction begun in childhood during assemblies
and rituals of the age-sets continues in fact throughout life.
These various aspects of African civilization gradually became clear
in the course of intensive studies undertaken among several of the
peoples of Mali and Upper Volta over more than a decade. In the
case of the Dogon, concerning whom there have already been nu-
merous publications, these studies have made possible the elaboration
of a synthesis covering the greater part of their activities.
We should now record the important occurrence during the field
expedition of 1947 which led to the writing of this particular study.
From 1931 the Dogon had answered questions and commented on
observations made during previous field trips on the basis of the in-
terpretation of facts which they call "la parole de face"; this is the
"simple knowledge" which they give in the first instance to all
enquirers. Publications of information obtained before the studies in
1948 relate to this first level of interpretation.
But the Dogon came to recognize the great perseverance of Marcel
Griaule and his team in their enquiries, and that it was becoming in-
creasingly difficult to answer the multiplicity of questions without
moving on to a different level. They appreciated our eagerness for
an understanding which earlier explanations had certainly not satis-
fied, and which was clearly more important to us than anything else.
Griaule had also shown a constant interest in the daily life of the
Dogon, appreciating their efforts to exploit a difficult country where
there was a serious lack of water in the dry season, and our relation-
ships, which had thus extended beyond those of ethnographical en-
quiry, became more and more trusting and affectionate. In the light
of all this, the Dogon took their own decision, of which we learned
only later when they told us themselves. The ciders of the lineages
55 • History, Myth and Reality
of the double village of Ogol and the most important totemic priests
of the region of Sanga met together and decided that the more eso-
teric aspects of their religion should be fully revealed to Professor
Griaule. To begin this they chose one of their best informed mem-
bers, Ogotommeli, who, as will be seen in the introduction, arranged
the first interview. This first exposition lasted exactly the number of
days recorded in Dieu d'Eau, in which the meandering flow of in-
formation is faithfully reported. Although we knew nothing of it at
the time, the progress of this instruction by Ogotemmeli was being
reported on daily to the council of elders and priests.
The seriousness and importance of providing this expose of Dogon
belief was all the greater because the Dogon elders knew perfectly
well that in doing so they were opening the door, not merely to these
thirty days of information, but to later and more intensive work
which was to extend over months and years. They never withdrew
from this decision, and we should like to express here our grateful
thanks to them. After Ogotemmeli's death, others carried on the
work. And since Professor Griaule's death they have continued with
the same patience and eagerness to complete the task they had under-
taken. These later enquiries have made possible the publication of the
many further studies cited in the bibliography, and the preparation
of a detailed treatise entitled Le Renard Pale, the first part of which
is now in press. And in 1963, as this is written, the investigation still
continues.
Intermezzo
A Guide for the Perplexed
Tout-puissants etrangers, inevitables astres . . .
Valery, La Jeune Parque
This book is highly unconventional, and often the flow of the tales
will be interrupted to put in words of guidance, in the fashion of
the Middle Ages, to emphasize salient points.
To begin with, there is no system that can be presented in mod-
ern analytical terms. There is no key, and there are no principles
from which a presentation can be deduced. The structure comes
from a time when there was no such thing as a system in our sense,
and it would be unfair to search for one. There could hardly have
been one among people who committed all their ideas to memory.
It can be considered a pure structure of numbers. From the
beginning we considered calling this essay "Art of the Fugue."
And that excludes any "world-picture," a point that cannot be
stressed strongly enough. Any effort to use a diagram is bound to
lead into contradiction. It is a matter of times and rhythms.
The subject has the nature of a hologram, something that has to
"be present as a whole to the mind.1 Archaic thought is cosmological
first and last; it faces the gravest implications of a cosmos in ways
which reverberate in later classic philosophy. The chief implication
is a profound awareness that the fabric of the cosmos is not only
determined, but overdetermined and in a way that does not permit
the simple location of any of its agents, whether simple magic or
1 In optics, "hologram" is the interference pattern of light with itself; i.e., every
part of an image is displayed at every point, as if every point looked at every
source of light.
57 • A Guide for the Perplexed '
astrology, forces, gods, numbers, planetary powers, Platonic Forms,
Aristotelian Essences or Stoic Substances. Physical reality here
cannot be analytical in the Cartesian sense; it cannot be reduced
to concreteness even if misplaced. Being is change, motion and
rhythm, the irresistible circle of time, the incidence of the "right
moment," as determined by the skies.
There are many events, described with appropriate terrestrial
imagery, that do not, however, happen on earth. In this book there
is mention of floods. In tradition, not one but three floods are
registered, one being the biblical flood, equivalents of which are
mentioned in Sumerian and Babylonian annals. The efforts of pious
archaeologists to connect the biblical narrative with geophysical
events are highly conjectural. There have been floods in Mesopo-
tamia causing grievous loss of life. There still are in the river plains
of China and elsewhere, but none of the total nature that the Bible
describes.
There are tales, too, of cataclysmic deluges throughout the great
continental masses, in Asia and America, told by peoples who have
never seen the sea, or lakes, or great rivers. The floods the Greeks
described, like the flood of Deucalion, are as "mythical" as the
narrative of Genesis. Greece is not submersible, unless by tsunamis.
Deucalion and his wife landed on Mount Parnassus, high above
Delphi, the "Navel of the Earth," and were the only survivors of
this flood, the second, sent by Zeus in order to destroy the men of
one world-age. Classical authors disagreed on the specification of
which world-age. Ovid voted for the Iron Age. Plato's Solon keeps
his conversation with the Egyptian priest on a mythical level, and
his discussion of the two types of world destruction, by fire or
water, is astronomical.
The "floods" refer to an old astronomical image, based on an ab-
stract geometry. That this is not an "easy picture" is not to be
wondered at, considering the objective difficulty of the science of
astronomy. But although a modern reader does not expect a text on
celestial mechanics to read like a lullaby, he insists on his capacity
to understand mythical "images" instantly, because he can respect
as "scientific" only page-long approximation formulas, and the like.
Hamlet's Mill • 58
He does not think of the possibility that equally relevant knowledge
might once have been expressed in everyday language. He never
suspects such a possibility, although the visible accomplishments of
ancient cultures—to mention only the pyramids, or metallurgy—
should be a cogent reason for concluding that serious and intelli-
gent men were at work behind the stage, men who were bound to
have used a technical terminology.
Thus, archaic "imagery" is strictly verbal, representing a specific
type of scientific language, which must not be taken at its face
value nor accepted as expressing more or less childish "beliefs."
Cosmic phenomena and rules were articulated in the language, or
terminology, of myth, where each key word was at least as "dark"
as the equations and convergent series by means of which our
modern scientific grammar is built up. To state it briefly, as we are
going to do, is not to explain it—far from it.
First, what was the "earth"? In the most general sense, the
"earth" was the ideal plane laid through the ecliptic. The "dry
earth," in a more specific sense, was the ideal plane going through
the celestial equator. The equator thus divided two halves of the
zodiac which ran on the ecliptic, 23.5 deg. inclined to the equator, one
half being "dry land" (the northern band of the zodiac, reaching
from the vernal to the autumnal equinox), the other representing
the "waters below" the equinoctial plane (the southern arc of the
zodiac, reaching from the autumnal equinox, via the winter solstice,
to the vernal equinox). The terms "vernal equinox," "winter
solstice," etc., are used intentionally because myth deals with time,
periods of time which correspond to angular measures, and not with
tracts in space.
This could be neglected were it not for the fact that the equi-
noctial "points"—and therefore, the solstitial ones, too—do not re-
main forever where they should in order to make celestial goings-on
easier to understand, namely, at the same spot with respect to the
sphere of the fixed stars. Instead, they stubbornly move along the
ecliptic in the opposite direction to the yearly course of the sun,
that is, against the "right" sequence of the zodiacal signs (Taurus->
Aries-»Pisces, instead of Pisces->Aries-»Taurus).
59 • A Guide for the Perplexed
This phenomenon is called the Precession of the Equinoxes, and
it was conceived as causing the rise and the cataclysmic fall of ages
of the world. Its cause is a bad habit of the axis of our globe, which
turns around in the manner of a spinning top, its tip being in the
center of our small earth-ball, whence our earth axis, prolonged to
the celestial North Pole, describes a circle around the North Pole
of the ecliptic, the true "center" of the planetary system, the radius
of this circle being of the same magnitude as the obliquity of the
ecliptic with respect to the equator: 23.5 deg.. The time which this
prolonged axis needs to circumscribe the ecliptical North Pole is
roughly 26,000 years, during which period it points to one star after
another: around 3000 b.c. the Pole star was alpha Draconis; at the
time of the Greeks it was beta Ursae Minoris; for the time being it
is alpha Ursae Minoris; in a.d. 14,000 it will be Vega. The equi-
noxes, the points of intersection of ecliptic and equator, swinging
from the spinning axis of the earth, move with the same speed of
26,000 years along the ecliptic.
The sun's position among the constellations at the vernal equinox
was the pointer that indicated the "hours" of the precessional cycle
—very long hours indeed, the equinoctial sun occupying each zodi-
acal constellation for about 2,200 years. The constellation that rose
in the east just before the sun (that is, rose heliacally) marked the
"place" where the sun rested. At this time it was known as the
sun's "carrier," and as the main "pillar" of the sky, the vernal
equinox being recognized as the fiducial point of the "system,"
determining the first degree of the sun's yearly circle, and the first
day of the year. (When we say, it was "recognized," we mean that
it was spelled "carrier" or "pillar," and the like: it must be kept in
mind that we are dealing with a specific terminology, and not
with vague and primitively rude "beliefs.") At Time Zero (say,
5000 b.c.—there are reasons for this approximate date), the sun
was in Gemini; it moved ever so slowly from Gemini into Taurus,
then Aries, then Pisces, which it still occupies and will for some
centuries more. The advent of Christ the Fish marks our age. It was
hailed by Virgil, shortly before Anno Domini: "a new great order
of centuries is now being born . . ." which earned Virgil the
Hamlet's Mill • 60
strange title of prophet of Christianity. The preceding age, that of
Aries, had been heralded by Moses coming down from Mount Sinai
as "two-horned," that is, crowned with the Ram's horns, while his
flock disobediently insisted upon dancing around the "Golden
Calf" that was, rather, a "Golden Bull," Taurus.
Thus, the revolving heavens gave the key, the events of our globe
receding into insignificance. Attention was focused on the supernal
presences, away from the phenomenal chaos around us. What
moved in heaven of its own motion, the planets in their weeks and
years, took on ever more awesome dignity. They were the Persons
of True Becoming. The zodiac was where things really happened,
for the planets, the true inhabitants, knew what they were doing,
and mankind was only passive to their behest. It is revealing to look
at the figure drawn by a West Sudanese Dogon at the request of
Professor Zahan, showing the world egg, with the "inhabited world"
between the tropics, "le cylindre ou rectangle du monde."2 The
Dogon are fully aware of the fact that the region between the ter-
restrial tropics is not the best of inhabitable quarters, and so were
their teachers of far-off times, the archaic scientists who coined the
terminology of myth. What counted was the zodiacal band be-
tween the celestial tropics, delivering the houses, and the inns, the
"masks" (prosopa), and the disguises to the much traveling and
"shape-shifting" planets.
How far this point of view was from modern indifference can
hardly be appreciated except by those who can see the dimensions
of the historical chasm that opened with the adoption of the Coper-
nican doctrine. What had been for Sir Thomas Browne an o alti-
tudo crowded with religious emotions, presences and presentiments
has become a platitude that could at best inspire a Russian cosmo-
naut with the triumphant observation: "I have been up in the sky,
and nowhere did I find God." Astronomy has come down into the
realm of exterior ballistics, a subject for the adventures of the Space
Patrol.
2 D. Zahan and S. de Ganay, "Etudes sur la cosmologie des Dogon," Africa 21
(1951), p. 14.
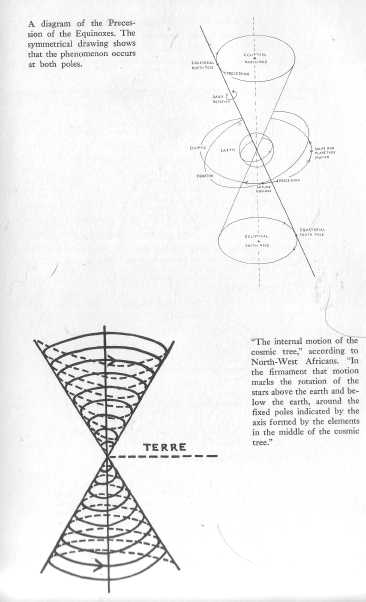
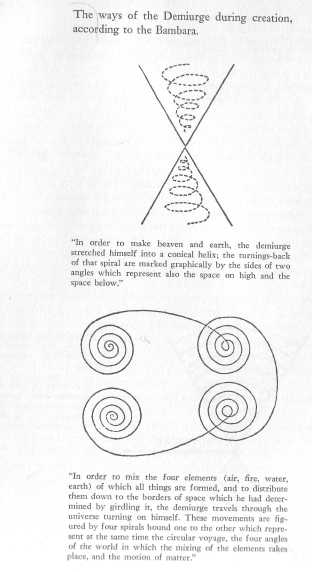


61 • A Guide for the Perplexed
One might say that it takes a wrenching effort of the imagination
to restore in us the capacity for wonder of an Aristotle. But it
would be misleading to talk of "us" generally, because the average
Babylonian or Greek showed as little inclination to wonder at order
and law in nature as our average contemporaries do. It has been and
will be the mark of a true scientific mind to search for, and to
wonder at, the invariable structure of number behind the manifold
appearances. (It needs the adequate "expectation," the firm con-
fidence in "sense"—and "sense" does mean number and order for us,
since the birth of high civilization—to discover the periodical sys-
tem of the elements or, further on, Balmer's series.) Whence it is
much easier for a great scientist—for instance, Galileo, Kepler, or
Newton—to appreciate master feats of early mathematicians than
it is for the average humanist of all ages. No professional historian
of culture is likely to understand better the intellectual frame of
mind of the Maya than the astronomer Hans Ludendorff has done.
It is not so much the enormous number of new facts established
by scientists in the many centuries between antiquity and the 20th
century which separates us from the outlook of our great scientific
ancestors but the "deteriorated" expectations ruling our time.
Kepler's quest, were he living today, would be to discover a modi-
fied perspective from which to rediscover the Harmonice Mundi
on another scale. But, after all, what else if not such a quest for the
establishment of a new kind of cosmos is the work on the "general
field formula"? This time, the cosmos, as covered by the coming
to-be formula, will be understandable and will make "sense" only
for the best mathematicians, to the complete exclusion of the com-
mon people, and it will hardly be a "meaningful" universe such as
the archaic one had been.
To come back to the key words of ancient cosmology: if the
words "flat earth" do not correspond in any way to the fancies of
the flat-earth fanatics who still infest the fringes of our society
and who in the guise of a few preacher-friars made life miserable
for Columbus, so the name of "true earth" (or of "the inhabited
world") did not in any way denote our physical geoid for the
Hamlet's Mill
62
archaics. It applies to the band of the zodiac, two dozen degrees
right and left of the ecliptic, to the tracks of the "true inhabitants"
of this world, namely, the planets. It comprises their various oscilla-
tions and curlicues from their courses, and also the "dragon," well
known from very early times, which causes eclipses by swallowing
the sun and moon.
On the zodiacal band, there are four essential points which domi-
nate the four seasons of the year. They are, in fact, in church
liturgy the quatuor tempora marked with special abstinences. They
correspond to the two solstices and the two equinoxes. The solstice
is the "turning back" of the sun at the lowest point of winter and at
the highest point of summer. The two equinoxes, vernal and
autumnal, are those that cut the year in half, with an equal balance
of night and day, for they are the two intersections of the equator
with the ecliptic. Those four points together made up the four
pillars, or corners, of what was called the "quadrangular earth."
This is an essential feature that needs more attention. We have
said above that "earth," in the most general sense, meant the ideal
plane laid through the ecliptic; meanwhile we are prepared to im-
prove the definition: "earth" is the ideal plane going through the
four points of the year, the equinoxes and the solstices. Since the
four constellations rising heliacally at the two equinoxes and the
two solstices determine and define an "earth," it is termed quad-
rangular (and by no means "believed" to be quadrangular by
"primitive" Chinese, and so on). And since constellations rule the
four corners of the quadrangular earth only temporarily, such an
"earth" can rightly be said to perish, and a new earth to rise from
the waters, with four new constellations rising at the four points of
the year. Virgil says: "I am redit et Virgo . . ." (already the Virgin
is returning). (It is important to remember the vernal equinox as the
fiducial point; it is from this fact that a new earth is termed to rise
from the waters. In reality, only the new vernal equinoctial con-
stellation climbs from the sea onto the dry land above the equator3—
the inverse happens diametrically opposite. A constellation that
3 In a similar sense, Petronius' Trimalchio says about the month of May: "totus
coelus taurulus fiat" ("the whole sky turns into a little bull").
63 • A Guide for the Perplexed
ceases to mark the autumnal equinox, gliding below the equator, is
drowned.) This "formula" will make it easier to understand the
myth of Deucalion, in which the devastating waves of the flood
were ordered back by Triton's blowing the conch: the conch had
been invented by Aigokeros, i.e., Capricornus, who ruled the win-
ter solstice in the world-age when Aries "carried" the sun.
At Time Zero, the two equinoctial "hinges" of the world had
been Gemini and Sagittarius, spanning between them the arch of
the Milky Way: both bicorporeal signs4—and so were Pisces, and
Virgo with her ear of wheat, at the two other corners—to mark
the idea that the way (the Milky Way itself) was open between
earth and heaven, the way up and the way down where men and
gods could meet in that Golden Age. As will be shown later, the
exceptional virtue of the Golden Age was precisely that the cross-
roads of ecliptic and equator coincided with the crossroads of
ecliptic and Galaxy, namely in Gemini and Sagittarius, both con-
stellations "standing" firmly at two of the four corners of the
quadrangular earth.
At the "top," in the center high above the "dry" plane of the
equator, was the Pole star. At the opposite top, or rather in the
depth of the waters below, unobserved from our latitudes, was the
southern pole, thought to be Canopus, by far the brightest star of
these regions, more remarkable than the Southern Cross.
This brief sketch of archaic theory indicates—to repeat—that
geography in our sense was never meant, but a cosmography of the
kind needed even now by navigators. Ptolemy, the great geogra-
pher of antiquity, had been thinking of nothing else. His Geog-
raphy is a set of coordinates drawn from the skies, and transferred
onto an uncouth outline map of our globe, with a catalogue of
earthly distances added on by sailors and travelers to pinpoint, or
confirm, the positions of countries around the Mediterranean world.
It was an uncouth outline map, for it covered only a few countries
known around the Mediterranean region. Nothing was shown be-
yond the latitude 16 deg. south of the equator and 63° north, cor-
4 These constellations were, originally, called "bicorporeal" for reasons very
different from those given by Ptolemy's Tetrabiblos 1.11
Hamlet's Mill
64
responding to Iceland. Nothing west beyond the Canary Islands or
east of the easternmost city of China, an arc of longitude fixed for
simplicity at 180 deg., twelve equinoctial hours from end to end, the
breadth over the whole latitudes being nine equinoctial hours. A
large part of the space is blank and the limits are assigned, as they
should be, astronomically. This is what the ancients knew after a
thousand years of exploration, and they handed it down to the
Renaissance. They called it the oikoumene, the inhabited earth.
One may well understand how the archaics gave this name for
purely astronomical reasons to the zodiacal band, about as wide in
degrees but embracing the whole globe. The world, the cosmos,
■was above, revolving majestically in twenty-four hours, and it lent
itself to the passionate exploration of cosmographers through the
starlit night. Astrology was the inevitable outcome of astronomy
through those ages. The early Greeks derived their mathematics
from astronomy. In those centuries, their insatiable curiosity de-
veloped a knowledge of our earth and the events on it which drove
them to create the beginnings of our science. But soon after Aris-
totle, the Stoics reverted to the oriental pattern and reinstalled
astrology. Three centuries of pre-Socratic thought had equipped
them with an interest in physics, but with it they had nowhere to
go. They still had no experimental science as we mean it. What
they needed was an interpretation of influences, to go with the
all-in-all that the cosmos has to be. Stoic physics was a seductive
presentment of a field theory, but it was a counterfeit. Nothing
was to come of it because the true implications of the archaic
cosmos, no less than those of the Platonic, were incompatible with
anything that our physics can think of. In Stoic physics there is no
simple location, no analytical space.
It should be understood once and for all that the gulf between
the archaic world and ours was as wide as science itself. Prodigies
of exactitude and computation could not bridge it. Only the astro-
nomical map could. Whitehead has summed it up succinctly: "Our
science has been founded on simple location and misplaced con-
creteness." Modern physics has turned the original words into
It
65 A Guide for the Perplexed
queries. For Newton, it had the force of evidence: "No person
endowed with a capacity of rational understanding will believe that
a thing acts where it is not." Newton himself put the first query,
by stating the theory of gravitation—mathematically irresistible,
physically unexplainable. He could only accept it: "I do not under-
stand it, and I am going to feign no suppositions." The answer was
to come only with Einstein. It amounted to pure mathematical
rationalization, which did away with simple location, and with
concreteness altogether. The edifice of Descartes lay in ruins.
Nonetheless, the mind of civilized man clung to both principles
invincibly, as being equal to common sense. It was a model case of
habit having become second nature. The birth of experimental
physics was a decisive factor in the change.
No such common sense obtained once upon a time, when time
was the only reality, and space had still to be discovered—or in-
vented—by Parmenides after 500 b.c. (See G. de Santillana, "Pro-
logue to Parmenides," in Reflections on Men and Ideas [1968], pp.
82-119.)
The task then was to recover from the remote past an utterly
lost science, linked to an equally lost culture—one in which an-
thropologists\have seen only illiterate "primitive man." It was as if
the legendary "Cathedrale Engloutie" emerged from the depth of
prehistory with its bells still ringing.
The problem was also clear: this lost science, immensely sophis-
ticated, had no "system," no systematic key that could be a basis
for teaching. It existed before systems could be thought of. It was,
to repeat, a spontaneously generated "Art of the Fugue." That is
why it took us so many years to work it out.
The archaics' vision of the universe appears to have left out all
ideas of the earth suspended, or floating, in space. Whether or not
this was really so cannot be decided yet: there are peculiar rumors
to be heard about innumerable "Brahma-Eggs," that is, spheres like
our own, in India. The Maori of New Zealand claimed, as the
Pythagoreans had done, that every star had mountains and plains,
and was inhabited like the earth. Varahamihira (5th century a.d.)
Hamlet's Mill • 66
even stated that the earth was suspended between magnets.5 For
the time being, one must continue to assume that the earth was
simply the center of the world, and a sphere, and that there was no
trace of Galilean relativism which is so natural to us, posing so
many problems of motion. The Greeks still had the old idea, but
they asked themselves questions about it. What moved was the sky,
but questions about the sky posed abstruse problems. The greatest
one was, of course, the slow motion of the tilt of the sky, described
above, which went through a Great Year of 26,000 years.
The Greek astronomers had enough instrumentation and data to
detect the motion, which is immensely slow, and they saw that it
applied to the whole of the sky. Hipparchus in 127 b.c. called it
the Precession of the Equinoxes. There is good reason to assume
that he actually rediscovered this, that it had been known some
thousand years previously, and that on it the Archaic Age based its
long-range computation of time. Modern archaeological scholars
have been singularly obtuse about the idea because they have cul-
tivated a pristine ignorance of astronomical thought, some of them
actually ignorant of the Precession itself. The split between the two
cultures begins right here. But apart from this, although the schol-
ars unanimously cling to the accepted conventions about the tempo
of historical evolution, they widely disagree when it comes to
judging the evidence in detail. The verdicts concerning the famil-
iarity of ancient Near Eastern astronomers with the Precession
depend, indeed, on arbitrary factors: namely, on the different
' scholarly opinions about the difficulty of the task. Ernst Dittrich,
for instance, remarked that one should not expect much astronomi-
cal knowledge from Mesopotamians around 2000 b.c. "Probably
they knew only superficially the geometry of the motions of sun
and moon. Thus, if we examine the simple, easily observable mo-
tions by means of which one could work out chronological deter-
minants with very little mathematical knowledge, we find only the
5 Pancasiddhantika, chapter JXII (Thibaut trans., p. 69): "The round ball of the
earth, composed of the five elements, abides in space in the midst of the starry
sphere, like a piece of iron suspended between magnets."
67 • A Guide for the Perplexed
Precession."6
There was also a learned Italian Church dignitary,
Domenico Testa, who snatched at this curious argument to prove
that the world had been created ex nihilo, as described in the first
book of Moses, an event that supposedly happened around 4000
B.C. If the Egyptians had had a background of many millennia to
reckon with, who, he asked, could have been unaware of the Pre-
cession? "The very sweepers of their observatories would have
known."7 Hence time could not have begun before 4000, Q.E.D.
The comparison of the views just quoted with those upheld by
the majority of modern scholars shows that one's own subjective
opinions about what is easy and what is difficult might not be the
most secure basis for a serious historiography of science. As Hans
Ludendorff once pointed out, it is an unsound approach to Maya
astronomy to start from preconceived convictions about what the
Maya could have known and what they could not possibly have
known: one should, instead, draw conclusions only from the data
as given in the inscriptions and codices.8 That this had to be stressed
explicitly reveals the steady decline of scientific ethics.
We today are aware of the Precession as the gentle tilting of our
globe, an irrelevant one at that. As the GI said, lost in the depth of
jungle misery, when his friends took refuge in their daydreams:
"When I close my eyes, I see only a mule's behind. Also when I
don't." This is, as it were, today's vision of reality. Today, the Pre-
cession is a well-established fact. The space-time continuum does
not effect it. It is by now only a boring complication. It has lost
relevance for our affairs, whereas once it was the only majestic
secular motion that our ancestors could keep in mind when they
looked for a great cycle which could affect humanity as a whole.
But then our ancestors were astronomers and astrologers. They
believed that the sliding of the sun along the equinoctial point af-
fected the frame of the cosmos and determined a succession of
6"Gibt es astronomische Fixpunkte in der altesten babylonischen Chronologie?"
OLZ 15 (1912), col. 104.
7 Il Zodiaco di Dendera lllustrato (1822), p. 17.
8"Zur astronomischen Deutung der Maya-Inschriften," SPAW (1936), p. 85.
Hamlet's Mill
68
world-ages under different zodiacal signs. They had found a large
peg on which to hang their thoughts about cosmic time, which
brought all things in fateful order. Today, that order has lapsed,
like the idea of the cosmos itself. There is only history, which has
been felicitously defined as "one damn thing after another."
And yet, were history really understood in this admittedly flat
sense of things happening one after another to the same stock of
people, we should be better off than we are now, when we almost
dare not admit the assumption from which this book starts, that our
ancestors of the high and far-off times were endowed with minds
wholly comparable to ours, and were capable of rational processes
—always given the means at hand. It is enough to say that this flies
in the face of a custom which has become already a second nature.
Our period may some day be called the Darwinian period, just as
we talk of the Newtonian period of two centuries ago. The simple
idea of evolution, which it is no longer thought necessary to ex-
amine, spreads like a tent over all those ages that lead from primitiv-
ism into civilization. Gradually, we are told, step by step, men
produced the arts and crafts, this and that, until they emerged into
the light of history.
Those soporific words "gradually" and "step by step," repeated
incessantly, are aimed at covering an ignorance which is both vast
and surprising. One should like to inquire: which steps? But then
one is lulled, overwhelmed and stupefied by the gradualness of it
all, which is at best a platitude, only good for pacifying the mind,
since no one is willing to imagine that civilization appeared in a
thunderclap.
One could find a key in a brilliant TV production on the Stone-
henge problem given a few years ago. With the resources of the
puissant techniques of ubiquity, various authorities were called to
the screen to discuss the possible meaning of the astronomical align-
ments and polygons discovered in the ancient Megalith since 1906,
when Sir Norman Lockyer, the famous astronomer, published the
results of his first investigation. Specialists, from prehistorians to
astronomers, expressed their doubts and wonderments down to the
last one, a distinguished archaeologist who had been working on
69 • A Guide for the Perplexed
the monument itself for many years. He had more fundamental
doubts. How could one not realize, he said, that the builders of
Stonehenge were barbarians, "howling barbarians" who were, to
say the least, utterly incapable of working out complex astronomi-
cal cycles and over many years at that? The uncertain coincidences
must be due to chance. And then, with perverse irony, the mid-
winter sun of the solstice appeared on the screen rising exactly be-
hind the Heel Stone, as predicted. The "mere" coincidences had
been in fact ruled out, since Gerald Hawkins, a young astronomer
unconcerned with historical problems, had run the positions
through a computer and discovered more alignments than had been
dreamed of. Here was the whole paradox. Howling barbarians
who painted their faces blue must have known more astronomy
than their customs and table manners could have warranted. The
lazy word "evolution" had blinded us to the real complexities of
the past.
That key term "gradualness" should be understood to apply to a
vastly different time scale than that considered by the history of
mankind. Human history taken as a whole in that frame, even ra-
dation itself, is only an evolutionary episode. In that whole, Cro-
Magnon man is the last link. All of protohistory is a last-minute
flickering.
But while the biologists were wondering, something great had
come upon the scene, arriving from unexpected quarters. Sir James
George Frazer was a highly respected classical scholar who, while
editing the Description of Greece by Pausanias, was impressed with
the number of beliefs, practices, cults and superstitions spread over
the classical landscape of Greece in classical times. This led him to
search deeper into the half-forgotten strata of history, and out of
it came his Golden Bough. The historian had turned ethnologist,
and extended his investigations to the whole globe. Suddenly, an
immense amount of material became available about fertility cults
as the universal form of earliest religion, and about primitive magic
connected with it. This appeared to be the humus from which
civilization had grown—simple deities of the seasons, a dim multi-
tude of peasants copulating in the furrows and building up rituals
Hamlet's Mill
70
of fertility with human sacrifice. Added to this, in political circles,
there came the vision of war as both inherent in human nature and
ennobling—the law of natural selection applied to nations and
races. Thus, many materials and much history went to build the
temple of evolutionism. But as the theory moved on, its high-
minded aspects began to wane; psychoanalysis moved in as a tidal
wave. For if the struggle for life (and the religions of the life force)
can explain so much, the unconscious can explain anything. As we
know today only too well.
The universal and uniform concept of gradualness thus defeated
itself. Those key words (gradualness and evolution) come from the
earth sciences in the first place, where they had a precise meaning.
Crystallization and upthrust, erosion and geosynclinals are the re-
sult of forces acting constantly in accordance with physical laws.
They provided the backdrop for Darwin's great scenario. When it
comes to the evolution of life, the terms become less precise in
meaning, though still acceptable. Genetics and natural selection
stand for natural law, and events are determined by the rolling of
the dice over long ages. But we cannot say much about the why
and the how of this instead of that specific form, about where spe-
cies, types, cultures branched off. Animal evolution remains an
overall historical hypothesis supported by sufficient data—and by
the lack of any alternative. In detail, it raises an appalling number
of questions to which we have no answer. Our ignorance remains
vast, but it is not surprising.
And then we come to history, and the evolutionary idea reap-
pears, coming in as something natural, with all scale lost. The
accretion of plausible ideas goes on, its flow invisibly carried by
"natural law" since the time of Spencer. It all remains within an
unexamined kind of Naturphilosophie. For if we stopped to think,
we would agree that as far as human "fate" is concerned organic
evolution ceased before the time when history, or even prehistory,
began. We are on another time scale. This is no longer nature act-
ing on man, but man on nature. People like to think of a constancy
of laws which apply to us. But man is a law unto himself.
71 • A Guide for the Perplexed
When, riding on the surf of the general "evolutionism," Ernst
Haeckel and his faithful followers proposed to solve the "world
riddles" once and for all, Rudolf Virchow9 warned time and again
of an evil "monkey wind" blowing round; he reminded his col-
leagues of the index of excavated "prehistoric" skulls and pointed
to the unchanged quantity of brain owned by the species Homo
sapiens. But his contemporaries paid no heed to his admonitions;
least of all the humanists who applied, without blinking, the strictly
biological scheme of the evolution of organisms to the cultural
history of the single species Homo sapiens.
In later centuries historians may declare all of us insane, because
this incredible blunder was not detected at once and was not re-
futed with adequate determination. Mistaking cultural history for
a process of gradual evolution, we have deprived ourselves of every
reasonable insight into the nature of culture. It goes without saying
that the still more modern habit of replacing "culture" by "society"
has blocked the last narrow path to understanding history. Our
ignorance not only remained vast, but became pretentious as well.
A glimpse at some Pensees might show the abyss that yawns
between us and a serious thinker of those golden days before the
outbreak of "evolution." This is what Pascal asked: "What are our
natural principles but principles of custom? In children they are
those which they have received from the habits of their fathers, as
hunting in animals. A different custom will cause different natural
principles." And: "Custom is a second nature which destroys the
former. But what is nature? For is custom not natural? I am much
afraid that nature is itself only a first custom, as custom is a second
nature."10
This kind of question, aimed with precision at the true problem-
;iiie;il spots, would have been enough to make hash of social an-
ihropology two centuries ago, and also of anthropological sociol-
ogy. Although fully aware of the knot of frightening problems
"In several of his addresses to the "Versammlungen deutscher Naturforscher und
Arzte."
10Pensees, nos. 92, 93 (Trotter trans. [1941}, p. 36).
Hamlet's Mill • 72
arising from the results of the most modern neurophysiology—the
building up of microneurons in the brain after birth, etc.—we are
by no means entitled to feign any hypotheses beyond saying that
the master brain who will, sooner or later, fashion a new philo-
sophical anthropology deserving the title, one that will account for
all the new implications, will find himself up against these same few
questions of Pascal.
Some words have still to be said about the problem that is at the
very root of the many misunderstandings, that of translation. Most
of the texts were written—if they were ever originally written—
in remote and half-obliterated languages from the far past. The
task of translation has been taken over by a guild of dedicated,
highly specialized philologists who have had to reconstruct the dic-
tionaries and grammars of these languages. It would be bad grace
to dismiss their efforts, but one must take into account several layers
of error: (1) personal or systematic errors, arising from their pre-
conceptions and from well-implanted prejudices (psychological
and philosophical) of their age; (2) the very structure of our own
language, of the architecture of our own verbal system, of which
very few individuals are aware. There was once a splendid article
by Erwin Schroedinger, with the title "Are there quantum jumps?"
which laid bare many such misunderstandings inside the well-
worked area of modern physics.11 And all this ties up with another
major source of error that comes from the underestimation of the
thinkers of the far past. We instinctively dismiss the idea that five
to ten thousand years ago there may very well have been thinkers
of the order of Kepler, Gauss, or Einstein, working with the means
at hand.
In other words, we must take language seriously. Imprecise lan-
guage discloses the lack of precision of thought. We have learned to
take the language of Archimedes or Eudoxos seriously, simply be-
cause it can translate directly into modern forms of thought. This
should extend to forms of thought utterly different from ours in
appearance. Take that great endeavor on the hieroglyphic language,
11 British Journal for the Philosophy of Science j (1952), pp. 112ff.
73 'A Guide for the Perplexed
embodied in the imposing Egyptian dictionary of Erman-Grapow.
For our simple word "heaven" it shows thirty-seven terms whose
nuances are left to the translator and used according to his lights.
So the elaborate instructions in the Book of the Dead, referring to
the soul's celestial voyage, translate into "mystical" talk, and must
be treated as holy mumbo jumbo. But then, modern translators be-
lieve so firmly in their own invention, according to which the
underworld has to be looked for in the interior of our globe—in-
stead of in the sky—that even 370 specific astronomical terms
would not cause them to stumble.
One small example may indicate the way in which texts are "im-
proved." In the inscriptions of Dendera, published by Dumichen,
the goddess Hathor is called "lady of every joy." For once, Dumi-
chen adds: "Literally . . . 'the lady of every heart circuit.' "12
This is not to say that the Egyptians had discovered the circulation
of the blood. But the determinative sign for "heart" often figures
as the plumb bob at the end of a plumb line coming from a well-
known astronomical or surveying device, the merkhet. Evidently,
"heart" is something very specific, as it were the "center of grav-
ity."13 And this may lead in quite another direction. The Arabs
preserved a name for Canopus—besides calling the star Kalb at-tai-
man ("heart of the south"):14 Suhail el-wezn, "Canopus Pondero-
sus," the heavy-weighing Canopus, a name promptly declared
meaningless by the experts, but which could well have belonged to
:m archaic system in which Canopus was the weight at the end of
the plumb line, as befitted its important position as a heavy star at
the South Pole of the "waters below." Here is a chain of inferences
which might or might not be valid, but it is allowable to test it,
and no inference at all would come from the "lady of every
joy." The line seems to state that Hathor (= Hat Hor, "House of
Horus") "rules" the revolution of a specific celestial body—
whether or not Canopus is alluded to—or, if we can trust the trans-
12Hon-t, rer het-neb; see J. Duemichen, "Die Bauurkunde der Tempelanlagen
von Edfu," Aeg.Z. p (1871), p. 28.
13See Aeg.Wb. 2, pp.55f. for the sign of the heart (ib) as expressing generally
"the middle, the center."
14 S. Mowinekcl, Die Sternnamen im Alien Testament (1928), p. 12.
Hamlet's Mill
74
lation "every," the revolution of all celestial bodies. As concerns the
identity of the ruling lady, the greater possibility speaks for Sirius,
but Venus cannot be excluded; in Mexico, too, Venus is called
"heart of the earth." The reader is invited to imagine for himself
what many thousands of such pseudo-primitive or poetic interpre-
tations must lead to: a disfigured interpretation of Egyptian in-
tellectual life.
The problem of astrology—The greatest gap between archaic
thinking and modern thinking is in the use of astrology. By this is
not meant the common or judicial astrology which has become
once again a fad and a fashion among the ignorant public, an escape
from official science, and for the vulgar another kind of black art
of vast prestige but with principles equally uncomprehended. It is
necessary to go back to archaic times, to a universe totally unsus-
pecting of our science and of the experimental method on which it
is founded, unaware of the awful art of separation which distin-
guishes the verifiable from the unverifiable. This was a time, rich
in another knowledge which was later lost, that searched for other
principles. It gave the lingua franca of the past. Its knowledge was
of cosmic correspondences, which found their proof and seal of
truth in a specific determinism, nay overdeterminism, subject to
forces completely without locality. The fascination and rigor of
Number made it mandatory that the correspondences be exact in
many forms (Kepler in this sense is the last Archaic). The multi-
plicity of relations seen or intuited brought the idea to a focus in
which the universe appeared determined not on one but on many
levels at once. This was the signature of "panmathematizing idea-
tion." This idea may well have led up to a pre-established harmony
on an infinite number of levels. Leibniz has shown us how far
it could go, given modern tools: the universe conceived all at once,
complete with its individual destinies for all time, out of an "efful-
guration" of the divine mind. Some prehistoric or protohistoric Py-
thagorean Leibniz, whose existence is far from inconceivable, may
■well have cherished this impossible dream, going to the limit more
innocently than our own historic sage. Starting from the power of
75 • A Guide for the Perplexed
Number, a whole logic is thinkable in this view. Fata regunt orbem,
certa stant omnia lege.
The only thinker of Antiquity who could be proof against this
temptation was Aristotle, for he thought that forms were only
potential in the beginning, and came into actualization only in the
course of their lifetime, thus undergoing their fate as individuals.
But that is because Aristotle refused mathematics from the start.
He had the grounds for opposing universal synchronicity (the word
and the idea were invented by C. G. Jung, replacing space with
time, which goes to show that the archaic scheme has more lives
than a cat).
Yet, here again, Dante comes to the fore as a witness; for, by art
of Gramarye, as the simple used to say, he spans the whole itinerary,
of shall we say the cheminement de la pensee, between two world
epochs. An Aristotelian to the core, steeped in the discipline of
Thomism, hence by inheritance anti-mathematical, his spirit in its
sweep understands the stars, in the sense of their Pythagorean im-
plications. In his ascent to the realm of heaven, he encounters his
friend and onetime companion of his wanton and romantic youth,
Charles Martel (Paradiso, viii.34-37), who tells him what it means
to be of the elect: "We circle in one orbit, at one pace, with one
thirst, along with the heavenly Princes whom thou didst once ad-
dress from the world"—"You Who by Understanding Move the
Third Heaven." This is one of his early poems, a celebrated one
at that, and it relates to the heavenly intelligences in a spirit of
unrestrained Platonic worship. The progress of his song through
the three realms will show him more and more wrapped in Platonic
harmonies, much as he had dreamed of in his youth, and it will
actually confirm his belief in astrology as a divine grant which keeps
nature in order. Thus, the requirements of both doctrines have been
laved: the arrangement of nature by genus and species (Aristotle)
and the free development of one's own self (Aquinas) in a kind of
Plotinian compromise overshadowed by the "Harmony of the
Spheres." Such was Dante's own inimitable "art of Gramarye."
Chapter V
The Unfolding in India
They reckon ill who leave me
out.
When Me they fly, I am the
wings;
I am the doubter and the doubt
I am the hymn the Brahmin sings.
Emerson, Brahma
The parallel between the Tale of Kai Khusrau and the final
plot of the vast Hindu epic, the Mahabharata, has received attention
for over a century. It was noticed by the great Orientalist James
Darmesteter. The translators of Firdausi are not unaware of it, and
they analyze the last phase of events as follows:
The legend of Kai Khusrau's melancholy, his expedition into the
mountains, and his attainment to heaven without having tasted death
has its parallel in the Mahabharata, where Yudhishthira, the eldest of
the five Pandavas, becoming weary of the world, resolves to retire
from the sovereignty and acquire merit by pilgrimage. On hearing of
his intentions his four brothers—Bhima, Arjuna, and the twins Na-
kula and Sahadeva—resolve to follow his example and accompany
him. Yudhishthira appoints successors to his various kingdoms. The
citizens and the inhabitants of the provinces, hearing the king's
words, became filled with anxiety and disapproved of them. "This
should never be done"—said they unto the king. The monarch, well
versed with the changes brought about by time, did not listen to
their counsels. Possessed of righteous soul, he persuaded the people
to sanction his views . . . Then Dharma's son, Yudhishthira, the King
of Pandavas, casting off his ornaments, wore barks of trees . . . The
five brothers, with Draupadi forming the sixth [she was the joint
wife of the brothers], and a dog forming the seventh, set out on their
journey. The citizens and the ladies of the royal household followed
77 • The Unfolding in India
them for some distance . . . The denizens of the city then returned
[exactly as Kai Khusrau's subjects had done]. The seven pilgrims
meanwhile had set out upon their journey. They first wandered east-
ward, then southward, and then westward. Lastly they faced north-
ward and crossed the Himalaya. Then they beheld before them a
vast desert of sand and beyond it Mount Meru. One by one the pil-
grims sank exhausted and expired, first Draupadi, then the twins, then
Arjuna, then Bhima; but Yudhishthira, who never even looked back
at his fallen comrades, still pressed on and, followed by the faithful
dog who turns out to be Dharma (the Law), in disguise, entered
Heaven in his mortal body, not having tasted death.
Among minor common traits, Warner stresses particularly these:
Both journey into the mountains with a devoted band, the number
of them is the same in both cases, and both are accompanied by a
divine being, for the part of the dog in the Indian legend is indicated
in the Iranian as being taken by Surush, the angel of Urmuzd. In
both, the leaders pass deathless into Heaven, and in both their mor-
tal comrades perish. One legend therefore must be derived from the
other, or else, and this seems to be the better opinion, they must be
referred to a common origin of great antiquity.1
Of great antiquity these legends must be, indeed; otherwise there
would not be a very similar end ascribed to Enoch and to Quetzal-
couatl. In fact, just as Kai Khusrau's paladins did not listen to the
Shah's advice not to remain with him until his ascension—the crowd
had been left behind, anyhow—so Enoch
urged his retinue to turn back: "Go ye home, lest death overtake you,
if you follow me farther." Most of them—800,000 there were—
heeded his words and went back, but a number remained with him
for six days. . . On the sixth day of the journey, he said to those still
accompanying him, "Go ye home, for on the morrow I shall ascend
to heaven and whoever will then be near me, he will die." Neverthe-
less, some of his companions remained with him, saying: "Whither-
soever thou goest, we will go. By the living God, death alone shall
part us." On the seventh day Enoch was carried into the heavens in
a fiery chariot drawn by fiery chargers. The day thereafter, the kings
who had turned back in good time sent messengers to inquire into the
fate of the men who had refused to separate themselves from Enoch,
for they had noted the number of them. They found snow and great
hailstones upon the spot whence Enoch had risen, and, when they
searched beneath, they discovered the bodies of all who had remained
1 Firdausi, Shahnama (Warner trans.), vol. 4, pp. 136
Hamlet's Mill • 78
behind with Enoch. He alone was not among them; he was on high
in heaven.2
Quetzalcouatl's paladins, "the slaves, the dwarves, the hunch
backed . . . they died there from the cold . . ., upon all of them fell
the snow," in the mountain pass between Popocatepetl and Iztacte-
petl.3 Quetzalcouatl, lamenting, and utterly lonely, had some more
stations to pass, before he took off on his serpent raft, announcing
he would come back, someday, "to judge the living and the dead"
(appendix #3).
Were it only the dry fact of Yudhishthira's ascension, and the
end of his companions high up in the mountains, we might have
avoided the maze of the Mahabharata altogether. But, labyrinthine
as this epic of twelve volumes truly is—and the same goes for the
Puranas—Indian myth offers keys to secret chambers to be had
nowhere else. The Mahabharata tells of the war of the Pandavas
and the Kauravas, that is the Pandu brothers and the Kuru brothers,
who correspond to the Iranians and Turanians, to the sons of Ka-
leva and the people of Untamo, etc. Thus far the general situation
is not foreign to us. But the epic states unmistakably that (this tre-
mendous war was fought during the interval between the Dvapara
and the Kali Yuga.4
This "dawn" between two world-ages can be specified further.
The real soul and force on the side of the Pandavas is Krishna—in
the words of Arjuna: "He, who was our strength, our might, our
heroism, our prowess, our prosperity, our brightness, has left us, and
departed."5 Now Krishna ("the Black") is the most outstanding
avatar of Vishnu. And it is only when Krishna has been shot in the
heel (or the sole of his foot), the only vulnerable spot of his body,
by the hunter Jara (= old age) that the Pandavas, too, resolve to
depart—just as Kai Khusrau did after the death of Kai Ka'us. There
was Kai Khusrau's statement: "And now I deem it better to de-
2 L. Ginzberg, Legends of the Jews (1954), vol. 1, pp. 129ff.
3E. Seler, Einige Kapitel aus dem Geschichtswerk des Fray B. de Sahagun
(1927), p. 290.
4Mbh. 1.2 (Roy trans., vol. 1, p. 18). See H. Jacobi's Mahabharata (1903), p. 2.
3 Vishnu Purana 1.38 (trans. H. H. Wilson [1840; 3d cd. 1961], p. 484).
79 • The Unfolding in India
part . . . Because this Kaian crown and throne will pass." And this
happens at the following crucial point:
When that portion of Vishnu (that had been born by Vasudeva and
Devaki) returned to heaven, then the Kali age commenced. As long
as the earth was touched by his sacred feet, the Kali age could not
affect it. As soon as the incarnation of the eternal Vishnu had de-
parted, the son of Dharma, Yudhishthira, with his brethren, abdicated
the sovereignty . . . The day that Krishna shall have departed from
the earth will be the first of the Kali age ... it will continue for
360,000 years of mortals.6
And as Krishna is reunited with Vishnu, as Arjuna returns into
Indra,7 and Balarama into the Shesha-Serpent, so it will happen to
the other heroes. Thus, when Yudhishthira is finally rejoined with
his whole Pandu-Family in heaven, the poet Sauti explains,
"That the various heroes, after exhausting their Karma, become re-
united with that deity of which they were avatars."8
Yudhishthira is reunited with Dharma, disguised as a faithful dog.9
Seen from this vantage point, the Finnish epic appears as a last dim
and apparently meaningless reflection. Kullervo goes with the black
dog Musti, the only living soul left from his home, into the forest
where he throws himself upon his sword.
Now what about Krishna, most beloved deity of the Hinduistic
Pantheon? Some of his innumerable deeds and victorious adventures
before his "departure" will look familiar.
6 Vishnu Purana 4.24 (Wilson trans., p. 390). Cf. 5.38, pp. 481f.: "and on the same
day that Krishna departed from the earth the powerful dark-bodied Kali age
descended. The ocean rose, and submerged the whole of Dvaraka," i.e., the town
which Krishna himself had built, as told in Vishnu Purana 5.23, p. 449.
7 See Vishnu Purana 5.12 (Wilson trans., p. 422), where Indra tells Krishna, "A
portion of me has been born as Arjuna."
8 Mbh. 18.5 (Swargarohanika Parva) (Roy trans., vol. 12, pp. 287-90). See also
Jacobi, p. 191.
• Arrived at the last stage of deterioration, we find Dharma, the Dog, in a fairy
tale from Albania: The youngest daughter of a king—her two sisters resemble
Regan and Goneril—offers to go to war in her father's place, asking for three suits
only, and for the paternal blessing. "Then the king procured three male suits, and
gave her his blessing, and this blessing changed into a little dog and went with the
princess." (J. G. von Hahn: Griechische und Albanische Marchen [1918], vol. 2,
p.146.).
Hamlet's Mill
80
81 • The Unfolding in India
Young Krishna is the persecuted nephew of a cruel uncle, Kansa
(or Kamsa), both being, as Keith10 styles it, "protagonists in a ritual
contest." This is not modestly understating it, but grossly mislead-
ing. Kansa is an Asura (appendix #4), and Krishna is a Deva, and
that means, again, that the affair concerns the great divine "Parties"
(Iranians-Turanians, and the like). The uncle, warned beforehand
through prophecies about the danger coming from the eighth son
of Devaki and Vasudeva, kills six children of this couple, but the
seventh (Balarama) and eighth (Krishna) are saved and live with
herdsmen. There young Krishna performs some of the deeds of the
"Strong Boy."
If Kullervo, three days old, destroyed his cradle, we might ex-
pect something spectacular from Krishna, and we are not disap-
pointed:
On one occasion, whilst Madhusudana was asleep underneath the
wagon, he cried for the breast, and kicking up his feet he overturned
the vehicle, and all the pots and pans were upset and broken. The
cowherds and their wives, hearing the noise, came exclaiming: "Ah!
ah!" and they found the child sleeping on his back. "Who could have
upset the wagon?" said the cowherds. "This child," replied some
boys, who witnessed the circumstance; "we saw him," said they,
"crying, and kicking the wagon with his feet, and so it was over-
turned: no one else had any thing to do with it." The cowherds were
exceedingly astonished at this account.11
One day the child repeatedly disobeyed his mother and she
became angry.
Fastening a cord round his waist, she tied him to the wooden mortar
Ulukhala, and being in a great passion, she said to him, "Now, you
naughty boy, get away from hence if you can." She then went to her
domestic affairs. As soon as she had departed, the lotus-eyed Krishna,
endeavouring to extricate himself, pulled the mortar after him to the
space between the two ariuna trees that grew near together. Having
dragged the mortar between these trees, it became wedged awry
there, and as Krishna pulled it through, it pulled down the trunks of
the trees. Hearing the crackling noise, the people of Vraja came to
see what was the matter, and there they beheld the two large trees,
10 A. B. Keith, Indian Mythology (1917), p. 126. For the deeds of Krishna, see
pp. 174ff.
11 Vishnu Purana 5.6 (Wilson trans., p. 406f.).
with shattered stems and broken branches, prostrate on the ground,
with the child fixed between them, with a rope round his belly,
laughing, and showing his little white teeth, just budded . The
elders of the cowherds . . . looked upon these circumstances with
alarm, considering them of evil omen. "We cannot remain in this
place," said they, "let us go to some other part of the forest."
Thus, they go to Vrindavana, exactly where the child had
wished. The Harivamsha explains the move to Vrindavana in this
way:
Krishna converts the hairs of his body into hundreds of wolves, who
so harass and alarm the inhabitants of Vraja—the said cowherds—,
that they determine to abandon their homes.12
In the Indian myth, for once, the episode of Krishna's hairs turn-
ing into hundreds of wolves seems a mere trifle, compared with
Kullervo's wolves which "he sang to cattle, and he changed the
bears to oxen," the more so, as Krishna's only "harass and alarm"
the cowherds. These wild beasts, however, indispensable to the
"Urkind," whether Kullervo or Dionysos—see above, p. 30—are
present in Krishna's story, and this is remarkable enough.
Kansa,13 hearing of the deeds of Krishna and Rama, determines to
have the boys brought to his capital Mathura and there to procure
their death, if he cannot slay them before. Needless to say, all is in
vain: Krishna kills Kansa and all his soldiers, and places Kansa's
father on the throne.
Krishna does not pretend to be a fool, the smiling one. He merely
insists again and again on being a simple mortal when everybody
wishes to adore him as the highest god, which he is. Nor is he
known particularly as an "avenger." He was delegated from higher
quarters to free the earth—"overburdened" as it was with Asura—
as he had done time and again in his former avatars. Krishna belongs
here, however, because Indian tradition has preserved the con-
sciousness of the cosmic frame, and it is this alone that gives mean-
12 Vishnu Purana 5.6 (Wilson trans., pp. 406f.).
"That "uncle"—really "the great Asura Kalanemi who was killed by the power-
ful Vislini .. . revived in Kansa, the son of Ugrasena" (Vishnu Purana 5.1 [Wilson
trans., p.396).
Hamlet's Mill
82
ing to the incidence of war and the notion of crime and punishment
as they appear in myth.
It is useful to keep philosophy and mythology carefully sepa-
rated, and yet the many gods and heroes who avenge their fathers
—beginning with "Horus-the-avenger-of-his-father" and "Ninurta
who has avenged his father"—have their function destined to them,
as has the long line of wicked uncles. These figures pay reparation
and atonement to each other for their mutual injustice in the order
of time, as Anaximander said. Anaximander was a philosopher.
Despite its fantastic language the Indian epic has an affinity with his
thought. Vishnu returns regularly in his capacity of "avenger,"
collecting the "reparations" of the bad uncle "according to the
order of time." In the Mahabharata he does so under the name of
Krishna, but he will come again in the shape of another avatar to
clean the earth of the Asura who overburden it. The Asura, too,
grow into "overbearing characters" strictly according to the order
of time. Under the name of Kalki the Vishnu figure is expected to
introduce a new Krita Yuga (Golden Age), when our present Kali
Yuga has come to its miserable end.
It is this regular returning of avatars of Vishnu which helps
clarify matters. Because it is Vishnu's function to return as avenger
at fixed intervals of time, there is no need in the epic to emphasize
the revenge taken by Krishna on Uncle Kansa. But in the West,
where the continuity of cosmic processes as told by myth has been
forgotten—along with the knowledge that gods are stars (or comets)—the very
same revenge is given great importance because it is an unrepeated
event accomplished by one figure, whether hero or god, and this
hero or god is, moreover, understood to be the creation of some
imaginative poet. The introduction of Indian tradition makes it
possible to rediscover the context in which such characters as
Saxo's Amlethus, such typically unlucky fellows as Kullervo, have
significance. Once it is fully realized that "the day Krishna shall
have departed from the earth will be the first of the Kali Yuga,"
the proper perspective is established. Our hero stands precisely on
the threshold between a closed age and a new Time Zero. In fact,
he closes the old one.
83 • The Unfolding in India
The most inconspicuous details become significant when ob-
served from this point of view. For instance Saxo, without giving
it much thought, divided the biography of Amlethus in two parts
(incidentally involving the hero in bigamy), in the same way as
Firdausi told us nine-tenths of Kai Khusrau's adventures in the
book on Kai Ka'us. This is actually the more puzzling of the two
as Firdausi states: "For from today new feasts and customs date
Because tonight is born Shah Kai Khusrau." Firdausi, who was well
versed in astrology, insisted on the Shah's birthday because, in the
astrological sense, birth is the decisive moment. But here, and in
related cases where chronology is at issue, it is the moment of
death, of leaving the stage, that counts. Krishna's departure gives
the scheme away. Al-Biruni, in his chapter on "The Festivals of
the Months of the Persians," describing the festival Nauroz ("New
Day") in the first month of spring, writes:
On the 6th day of Farwardin, the day Khurdadh, is the Great Nau-
roz, for the Persians a feast of great importance. On this day—they
say—God finished the creation, for it is the last of the six days . . .
On this day God created Saturn, therefore its most lucky hours are
those of Saturn. On the same day—they say—the Sors Zarathustrae
came to hold communion with God, and Kaikhusrau ascended into
the air. On the same day the happy lots are distributed among the
people of the earth. Therefore the Persians call it "the day of hope."14
The so-called Kaianian Dynasty—the "Heroes" according to
Al-Biruni's Chronology15—succeeding the first Pishdadian Dynasty
("the Just"), is supposed to have started with Kai Kubad, his son
Kai Ka'us, and the latter's grandson Kai Khusrau, and to have
ended with Sikander, Alexander the Great, with whose death a new
era actually began. But it is obvious that something new begins
with Kai Khusrau's assumption into heaven. Thus, the Warners
state that with our Shah "the old epic cycle of the poem comes to
an end, and up to this point the Kaianian may be regarded as the
complement of the Pishdadian dynasty."16
14 Al-Biruni, The Chronology of Ancient Nations (trans. C. E. Sachau [1879],
p.201).
l5p. 112.
16Firdausi, Shahnmna (Warner trans.), vol. 2, pp. 8f.
Hamlet's Mill • 84
In his introduction to the Firdausi translation, however, the
Warners claim that the poem is divided into two periods, one
mythic, the other historic: 17
This distinction is based not so much on the nature of the subject-
matter as on the names of the chief characters. At a certain point in
the poem the names cease to be mythic and become historic. The
mythic period extends from the beginning of the narrative down to
the reigns of the last two Shahs of the Kaianian dynasty . . . The
Shahs in question are Dara, son of Darab, better known as Darius
Codomanus, and Sikander (Alexander)."18
Firdausi makes it clear that the mythic period ends only with the
death of Alexander, the two last Shahs being Darius Codomanus
and Alexander who overcame him. After him begins the "historic"
period of the poem. In other words, "history" begins only when the
Iranian empire vanishes from the scene, to be replaced by the suc-
cessors of Alexander. To remove from history the great and solidly
historical feats of Darius I, Xerxes, Cambyses, etc., is paradoxical
for a poem which is meant to celebrate the Iranian empire. Pre-
sumably Firdausi meant that so long as the Zoroastrian religion
reigned, time was holy and thus belonged to myth rather than
ordinary history. This is confirmed by a strange statement of the
Warners: "Rightly or wrongly, Zoroastrian tradition couples Alex-
ander with Zahhak and Afrasiyab as one of the three arch-enemies
of the faith."19
The great myths of the Avestan religion have overcome chronol-
ogy and reshaped it to their purpose. The true kings of Persia have
disappeared notwithstanding their glory, and are replaced by myth-
ical rulers and mythical struggles. Kai Khusrau rehearses a "Jam-
shyd" role in his beginnings, and with his ascent to heaven—the
date of "which marks New Year from now on—the Holy Empire
17 The time structure is a very complicated one, and we cannot manage with a
subdivision of two "periods" at all, the less so, as the reigns of the Shahs overlap
with the rather miraculous lifetimes of the "heroes" or Paladins (Rustam, Zal, etc.).
The same goes for the "primordial" emperors of China and their "vassals." But
God protect us from meddling with lists of alleged "kings" from whichever area,
but particularly from the Iranian tables!
18 Firdausi, vol. 1, pp. 49f.
19 Firdausi, vol. 1, p. 59.
85 • The Unfolding in India
really comes to a close. The struggle has been between gods and
demons throughout)
We have been following the story of powers coming to an end,
embodied first in the Iranian then in the Indian "kings," a story
which is differently emphasized by two different legends. Each
legend has a disturbing similarity to the other, and each removes
the narration from any known classic pattern, forcing the events
to a catastrophic conclusion which is clearly commanded by Time
itself, and by a very different chain of causes than that indicated
by the actual sequence of events in the texts.
To avoid misunderstanding it should be emphasized that it is not
possible yet to know precisely who is who, or to make positive
identifications such as saying that Brjam is Yudhishthira or Krishna.
But the hints provided by Iranians and Indians may lead to a better
understanding of Kullervo ("Kaleva is reborn in him"), and may
indicate that the feat of the doggish fool Brutus in driving out the
Kings was significant on a higher level than the political. This is
not to deny that the Kings were expelled, but rather to point to
a special set of firmly coined "figures of speech" derived from
"large" changes or shifts (such as the onset of Kali Yuga) that
could be, and were, applied to minor historical events.
Chapter VI
Amlodhi's Quern
The stone which the builders refused
is become the head stone of the corner.
Psalm cxviii.2 2; Luke xx.17
Whosoever shall fall upon that stone shall be broken,
but on whomsoever it shall fall, it will grind him to powder.
Luke xx. 18
With suggestive insights from other continents, it is time to
take a fresh look at Shakespeare's Gentle Prince, a cultivated,
searching intellectual, the glass of fashion and the mold of form
in the Danish Court, who was known once upon a time as a per-
sonage of no ordinary power, of universal position, and, in the
North, as the owner of a formidable mill.
Well trained by the Church, Saxo could write excellent and
ornate Latin, a rare achievement in his time. Though inspired by
his patriotism to write the great chronicles of his own country, he
was in Denmark an isolated if respectable fish in a small provincial
pond. He remained oriented to the cultural pole of his times, which
was Iceland. From there he had to draw most of his materials even
if he helped to Danicize them, as we see in the story of Hamlet
where all the features point toward a local dynastic story. But what
he drew from Iceland were pieces of already "historical" lore. He
could not draw, as did Snorri Sturluson, on the resources of a high
position at the very center of Iceland's rich bilingual culture, and
on the experience of a wide-ranging and adventurous life. He could
never have formed, like Snorri, the great project of reorganizing
87 • Amlodhi's Quern
the corpus of pagan and skaldic tradition inside an already Christian
frame. Saxo seems to have known Icelandic fairly well, but not
enough to understand the precious and convoluted language of
ancient poetry. He was unsure of his bearings and simply arranged
his story as best he could even though the name of Hamlet's father,
Orvendel (see appendix #2), should have been sufficient to warn
him of its derivation from high myth. It is Snorri who provides a
piece of decisive information: and it appears, as earlier noted, in
chapter 16 of his Skaldskaparmal ("Poetical Diction"), a collection
of kenninear, or turns of speech from ancient bards. It is couched
in a language that even modern scholars can translate only tenta-
tively. Appendix #5 contains a discussion of the many versions.
The one quoted again here is that of Gollancz (p. xi), which ap-
pears to be the most carefully translated:
T'is said, sang Snaebjorn, that far out, off yonder ness, the Nine
Maids of the Island Mill stir amain the host-cruel skerry-quern—they
who in ages past ground Hamlet's meal. The good chieftain furrows
the hull's lair with his ship's beaked prow. Here the sea is called
Amlodhi's Mill.
The Mill is thus not only very great and ancient, but it must also
be central to the original Hamlet story. It reappears in the Skalds-
kaparmal, where Snorri explains why a kenning for gold is "Fro-
dhi's meal."1 Frodhi appears in the chronicles, but his name is really
an alias of Freyr, one of the great Vanir or Titans of Norse myth.
But Snorri, who likes to give things a historical ring as befits his
Christian upbringing, fixed his Frodhi to "the same time when Em-
peror Augustus established peace in the whole world, and when
Christ was born." Under King Frodhi the general state of things
was similar to that of the Golden Age, and it was called "Frodhi's
peace." Saxo follows suit and attributes unsuspectingly a duration
of thirty years to this peace.2
1 Skaldskap. 42, according to Brodeur (1929), pp. 163-69, and Neckel and
Niedner (Thule 20 [1942]), pp. 195f. The other translators of Snorri's Edda
cannot agree on the manner of dividing the work into chapters, if they do not
desist from doing so at all, as R. B. Anderson (1880), pp. 206-13, parts of whose
translation we quote here. (Simrock [n.d.], pp. 89-93, makes it chapter 63.)
2 P. Herrmann, Die Heldensagen des Saxo Grammaticus (1922), pp. 376ff.
Hamlet's Mill
88
89 • Amlodhi's Quern
Now Frodhi happened to be the owner of a huge mill, or quern,
that no human strength could budge. Its name was Grotte, "the
crusher." We are not told how he got it, it just happened, as in a
fairy tale. He traveled around looking for someone who could work
it, and in Sweden he recruited two giant maidens, Fenja and Menja,
who were able to work the Grotte. It was a magic mill, and Frodhi
told them to grind out gold, peace and happiness. So they did. But
Frodhi in his greed drove them night and day. He allowed them
rest only for so long as it took to recite a certain verse. One night,
when everybody else was sleeping, the giantess Menja in her anger
stopped "work, and sang a dire song.
This obscure prophetic imprecation, as Muellenhoff has shown,
is the oldest extant document of skaldic literature, antedating
Snorri's tale by far. It contains the biography of the grim sisters:
Frode! you were not / Wary enough,—
You friend of men,— / When maids you bought!
At their strength you looked, / And at their fair faces,
But you asked no questions / About their descent.
Hard was Hrungner / And his father;
Yet was Thjasse / Stronger than they,
And Ide and Orner / Our friends, and
The mountain-giants' brothers, / Who fostered us two.
Not would Grotte have come / From the mountains gray,
Nor this hard stone / Out from the earth;
The maids of the mountain-giants / Would not thus be grinding
If we two knew / Nothing of the mill.
Such were our deeds / In former days,
That we heroes brave / Were thought to be.
With spears sharp / Heroes we pierced,
So the gore did run / And our swords grew red.
Now we are come / To the house of the king,
No one us pities. / Bond-women are we.
Dirt eats our feet / Our limbs are cold,
The peace-giver we turn. / Hard it is at Frode's.
Now hold shall the hands / The lances hard,
The weapons bloody,— / Wake now, Frode! Wake now, Frode!
If you would listen / To our songs,—
To sayings old.
Fire I see burn / East of the burg,—
The war news are awake. / That is called warning.
A host hither / Hastily approaches
To burn the king's / Lofty dwelling.
No longer you will sit / On the throne of Hleidra
And rule o'er red / Rings and the mill.
Now must we grind / With all our might,
No warmth will we get / From the blood of the slain.
Now my father's daughter / Bravely turns the mill.
The death of many / Men she sees.
Now broke the large / Braces 'neath the mill,—
The iron-bound braces. / Let us yet grind!
Let us yet grind! / Yrsa's son
Shall on Frode revenge / Halfdan's death.
He shall Yrsa's / Offspring be named,
And yet Yrsa's brother. / Both of us know it.
However obscure the prophecy, it brought its own fulfillment.
The maidens ground out for Frodhi's "a sudden host," and that
very day Mysingr, the Sea-King, landed and killed Frodhi. Mysingr
("son of the Mouse"—see appendix #6) loaded Grotte on his ship,
and with him he also took the giantesses. He ordered them to grind
again. But this time they ground out salt.
"And at midnight they asked whether Mysingr were not weary
of salt. He bade them grind longer. They had ground but a little
while, when down sank the ship,"
"the huge props flew off the bin,
the iron rivets burst,
the shaft tree shivered,
Hamlet's Mill • 90
the bin shot down,
the massy mill-stone rent in twain"3
"And from that time there has been a whirlpool in the sea where
the water falls through the hole in the mill-stone. It was then that
the sea became salt."
Here ends Snorri's tale (appendix #7). Three fundamental and
far-reaching themes have been set: the broken mill, the whirlpool,
the salt. As for the curse of the miller women, it stands out alone
like a megalith abandoned in the landscape. But surprisingly it can
also be found, already looking strange, in the world of Homer, two
thousand years before.4
It is the last night, in the Odyssey (20.103-19, Rouse trans.),
which precedes the decisive confrontation. Odysseus has landed in
Ithaca and is hiding under Athena's magic spell which protects him
from recognition. Just as in Snorri, everybody sleeps. Odysseus
prays to Zeus to send him an encouraging sign before the great
ordeal.
Straightaway he thundered from shining Olympus, from on high
from the place of the clouds; and goodly Odysseus was glad. More-
over, a woman, a grinder at the mill, uttered a voice of omen from
within the house hard by, where stood the mills of the shepherd of
the people. At these handmills twelve women in all plied their task,
making meal of barley and of wheat, the marrow of men. Now all the
others were asleep, for they had ground out their task of grain, but
one alone rested not yet, being the weakest of all. She now stayed her
quern and spake a word, a sign to her Lord [epos phato sema anakti].
"Father Zeus, who rulest over gods and man, loudly hast thou thun-
dered from the starry sky, yet nowhere is there a cloud to be seen:
this is surely a portent thou art showing to some mortal. Fulfil now, I
pray thee, even to miserable me, the word that I shall speak. May the
wooers, on this day, for the last and latest time make their sweet
feasting in the halls of Odysseus! They that have loosened my knees
■with cruel toil to grind their barley meal, may they now sup their
last!"
"The weakest of all," yet a giant figure in her own right. In the
tight and shapely structure of the narrative, the episode is fitted
3 These five verses are taken from Gollancz (p. xiii), the three previous and
the two last lines from Brodeur (pp. 162f.); otherwise, we followed the Anderson
translation.
4It was J. G. von Hahn (Sagwissenschaftliche Studien [ 1876], pp. 401f.) who
first pointed to the similarity of the episodes in Snorri's Edda and in the Odyssey.

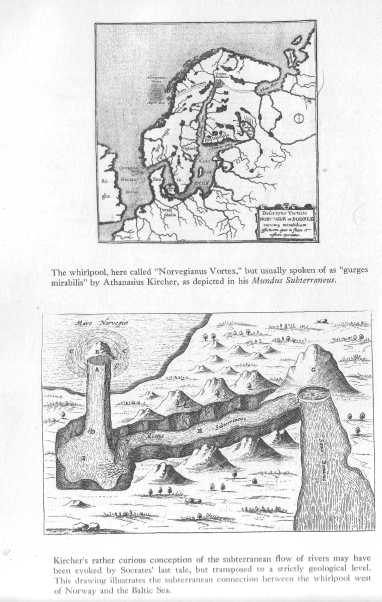
91 . Amlodhi's Quern
with art, yet it stands out like a cyclopean stone embedded in a
house. There are many such things in Homer.
Going back to Grotte, the name has an interesting story. It is
still used today in Norwegian for the "axle-block," the round
block of wood which fills the hole in the millstone, and in which
the end of the mill axle is fixed. In the Faroer as well as in the
Shetland dialect, it stands for "the nave in the millstone." The
original Sanskrit nabhi covers both "nave" and "navel," and this
point should be kept in mind. In the story, it is obviously the nave
that counts, for it created a hole when the mill tree sprang out of
it, and the whirlpool formed in the hole. But "navel of the sea" was
an ancient name for great whirlpools. Gollancz, with sound instinct,
saw the connection right away:
Indeed, one cannot help thinking of a possible reference to the mar-
vellous Maelstroem, the greatest of all whirlpools, one of the wonders
of the world; Umbilicus marls according to the old geographers,
"gurges mirabilis omnium totius orbis terr arum celeberrimus et maxi-
mus" as Fr. Athanasius Kircher describes it in his fascinating folio
"Mundus Subterraneus." According to Kircher, it was supposed that
every whirlpool formed around a central rock: a great cavern opened
beneath; down this cavern the water rushed; the whirling was pro-
duced as in a basin emptying through a central hole. Kircher gives a
curious picture of this theory, with special reference to the Mael-
stroem.5
Clearly, the Mill is not a "chose transitory," as lawyers say in
their jargon. It must belong to the permanent equipment of the
ancient universe. It recurs all the time, even if its connotations are
rarely pleasant. From another corner of memory, there come the
lines of Burns' "John Barleycorn":
They wasted o'er a scorching flame
The marrow of his bones
But a miller used him worst of all
For he crushed him between two stones.
The mock tragedy of the yearly rural feast is part of the immense
lore on fertility rites that Frazer has unfolded, with the ritual
lamentations over the death of Tammuz, Adonis, the "Grain-
Osiris" of Egypt; and no one would deny that the Tammuz festival
5 I. (Gollancz, Hamlet in Iceland (1898), p. xiv.
Hamlet's Mill
92
was a seasonal ritual celebrating the death and rebirth of vegetation.
It has entered the commonplaces of our knowledge. But was this
the original meaning? An irresistible preconception leads to the
thought that when peasant rites are found tied to vegetation, there
is the most elementary and primitive level of myth from which all
others derive. It carries, too, its own moral tidings: "if the grain die
not . . . ," which led on to higher religious thought.
In truly archaic cults, however, such as that of the Ssabians of
Harran, reflected also in Ibn Wa'shijja's "Book of Nabataean Agri-
culture," the death and grinding up of Tammuz is celebrated and
lamented by the images of all the planetary gods gathered in the
temple of the Sun suspended "between earth and heaven," in the
same way as they once cried and lamented over the passing of
Jamshyd (or Jambushad as they then called him). This is a strange
and unusual note, very un-agrarian, which deserves more careful
study.
But this leads back to the Norse myth of the Mill, and in fact
to Snorri himself, who in his "Fooling of Gylfi" commented on a
verse from the Vafthrudnismal which has been much discussed
since. In this ancient poem, the end of Ymer is recounted. Ymer is
the "initial" world giant from whose scattered body the world was
made. Snorri states that Ymer's blood caused a flood which
drowned all giants except Bergelmer, who, with his wife, "betook
himself upon his ludr and remained there, and from there the race
of giants are descended." The word ludr, as Snaebjorn said, stands
for Mill. But in Vafthrudnismal (ch. 35), Odin asks the wise giant
Vafthrudner of the oldest event he can think of, and gets this
answer: "Countless ages ere the earth was shapen, Bergelmer was
born. The first thing I remember—is when he a var ludr um lagidr"
(appendix #8). Rydberg renders the words as "laid on a mill," and
understands them as "laid under a millstone." Accordingly, he ex-
plains Snaebjorn's lidmeldr, which the great mill grinds, as "limb
grist."6 As will appear later, there is a different interpretation to
propose.
6 V. Rydbcrg, Teutonic Mythology (1907), p. 575.
93 • Amlodhi's Quern
The problem, however, keeps turning up. In the Lokasenna
(43ff.), Freyr, the original master of Grotte, is brought directly
into action. The occasion is a banquet to which Aegir invited the
gods. Loke uninvited made his appearance there to mix harm into
the ale of the gods and to embitter their pleasure. But when Loke
taunts Freyr, Byggver, the faithful retainer, becomes angry on his
master's behalf:
- "Had I the ancestry
of Ingunar Freyr
and so honoured a seat
know I would grind you
finer than marrow, you evil crow,
and crush you limb by limb.''
To which Loke replies:
"What little boy is that
whom I see wag his tail
and eat like a parasite?
Near Freyr's ears
always you are
and clatter 'neath the mill-stone."
There are several more clues which hint that this mill upon which
Bergelmer was "heaved" was a very distinct if unattractive mytho-
logical feature, and they cannot be dealt with here. But if it should
be remarked that Bergelmer was not in a state to produce offspring
for the giants, if he really was laid under the millstone, there is
also an example from Mexico, the "jewel-bone" or "sacrificial
bone" which Xolotl or Quetzalcouatl procures from the "under-
world," bringing it to Tamoanchan (the so-called "House of de-
scending"). There, the goddess Qua couatl or Quilaztli grinds the
precious bone on the grindstone, and the ground substance is put
into the jewel bowl (chalchiuhapaztli). Several gods maltreat
themselves, making blood flow from their penises on the "meal."
Out of this mixture mankind is fashioned.
Hamlet's Mill
94
These stories may not be in exquisite taste, but at least they are
grotesque and contorted enough to rid us of reliance on the natural
or intuitive understanding of artless tales sung by rustics dancing
on the green. Real cosmological similes are anything but intuitive.
One question remains from this discussion. Who was Snaebjorn,
that dim figure, a few of whose lines have revealed so much? The
scholars have gone searching, and have unearthed a veritable trea-
sure in the ancient "Book of Iceland Settlements." It links the poet
with the first discovery of America. In that book, writes Gollancz:
There is a vivid picture of a tenth-century Arctic adventurer, Snae-
bjorn by name, who went on a perilous expedition to find the un-
known land, "Gunnbjorn's Reef," after having wrought vengeance,
as became a chivalrous gentleman of the period, on the murderer of a
fair kinswoman. It is generally accepted, and there can be little doubt,
that this Snaebjorn is identical with the poet Snaebjorn.
His family history is not without interest. His great-grandfather,
Eywind the Easterling, so called because he had come to the Hebrides
from Sweden, married the daughter of Cearbhall, Lord of Ossory,
who ruled as King of Dublin from 882 to 888, "one of the principal
sovereigns of Europe at the time when Iceland was peopled by the
noblemen and others who fled from the tyranny of Harold Harfagr."
Cearbhall was descended from Connla, the grandson of Crimhthann
Cosgach, the victorious King of Ireland, who is said to have flourished
about a century before the Christian era. Lann or Flann, the half-
sister of Cearbhall, was married to Malachy I., King of Ireland, whose
daughter Cearbhall had married. Flann was the mother of King
Sionna and of the Lady Gormflaith, whom a cruel fate pursued; a
king's daughter, the wife of three kings, [she was] forced at last to
beg for bread from door to door. About the date of Snaebjorn's
Arctic expedition (circa 980), his cousin, Ari Marson, is said to have
landed on "White Man's band," or "Great Iceland,"—that part of
the coast of North America which extends from Chesapeake Bay,
including North and South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida,—and
became famous as one of the earliest discoverers of the New World.7
Thus Snaebjorn, as a member of an Irish royal family, typifies
the mutual influence of Celtic and Scandinavian culture, between
a.d. 800 and 1000, that influence which has been traced into the
Eddic songs by Vigfusson in his Corpus Poeticum Boreale. The
7 Gollancz, pp. xviif.
95 • Amlodhi's Quern
Hamlet story itself typifies that exchange. For an earlier and simpler
form of it may have been brought to Iceland from Ireland, whither
the Vikings had originally taken the story of the great Orvendel's
son.
This places Hamlet within the circle not only of Norse tradition,
but of that prodigious treasury of archaic myth which is Celtic
Ireland, from which many lines have been traced to the Near
East. The universality of the Hamlet figure becomes more under-
standable.
Chapter VII
The Many-Colored Cover
There is a mill which grinds by
itself, swings of itself, and scat-
ters the dust a hundred versts
away. And there is a golden pole
with a golden cage on top which
is also the Nail of the North.
And there is a very wise tomcat
which climbs up and down this
pole. When he climbs down, he
sings songs; and when he climbs
up, he tells tales.
Tale of the Ostyaks of the lrtysh
The Kalevala is vaguely known by the general public as the
national epic of Finland. It is a tale of wild fancy, enticing absurdity
and wonderfully primitive traits, actually magical and cosmological
throughout. It is all the more important in that the Ugro-Finnic
tradition has different roots from Indo-European ones.
Until the 19th century the epic existed only in fragments en-
trusted to oral transmission among peasants. From 1820 to 1849,
Dr. Elias Lonnrot undertook to collect them in writing, wander-
ing from place to place in the most remote districts, living with the
peasantry, and putting together what he heard into some kind of
tentative sequence. Some of the most valuable songs ■were discov-
ered in the regions of Archangel and Olonetz in the Far North,
which now belong again to Russia. The 1849 final edition of Lonn-
rot comprises 22,793 verses in fifty runes or songs. A large amount
of new material has been discovered since.
The poem has taken its name from Kaleva, a mysterious ancestral
personage who appears nowhere in the tale. The heroes arc his
97 • The Many-Colored Cover
three sons: Vainamoinen,1 "old and truthful," the master of magic
song; Ilmarinen, the primeval smith, the inventor of iron, who can
forge more things than are found on land or sea; and the "beloved,"
or "lively," Lemminkainen, a sort of Arctic Don Juan. Kullervo,
the Hamlet-like one whose story was told earlier, fair-haired Kul-
lervo "with the bluest of blue stockings," is another "son of Kaleva,"
but his adventures seem to unfold separately. They tie up only at
one point with Ilmarinen, and seem to belong to a different frame
of time, to another world-age.
It is time now to deal with the main line of events. The epic opens
with a very poetical theory of the origin of the World. The virgin
daughter of the air, Ilmatar, descends to the surface of the waters,
where she remains floating for seven hundred years until Ukko, the
Finnish Zeus, sends his bird to her. The bird makes its nest on
the knees of Ilmatar and lays in it seven eggs, out of which the
visible world comes. But this world remains empty and sterile until
Vainamoinen is born of the virgin and the waters. Old since birth,
he plays the role, as it were, of "midwife" to nature by causing
her to create animals and trees by his magic song. An inferior
magician from Lapland, Youkahainen, challenges him in Song and is
sung step by step into the ground, until he rescues himself by
promising Vainamoinen his sister, the lovely Aino. But the girl
will not have Vainamoinen, he looks too old. She wanders off in
despair and finally comes to a lake. She swims to a rock, seeking
death; "when she stood upon the summit, on the stone of many
colors, in the waves it sank beneath her." Vainamoinen tries to
fish for her, she swims into his net as a salmon, mocks him for not
recognizing her, and then escapes forever. Vainamoinen decides
to look for another bride, and embarks upon his quest. His goal is
the country of Pohjola, the "North country," a misty land "cruel
to heroes," strong in magic, vaguely identified with Lapland. Events
unfold as in a dream, with surrealistic irrelevance. The artlessness,
the wayward charm and the bright nonsense suggest Jack and the
Beanstalk, but behind them appear the -fossil elements of a tale
as old as the world—at least the world of man's consciousness—
Hamlet's Mill
98
whose meaning and thread were lost long ago. The pristine archaic
themes remain standing like monumental ruins.
The main sequence is built around the forging and the conquest
of a great mill, called the Sampo (rune 10 deals with the forging,
runes 39-42 with the stealing of the Sampo).
Comparetti's studies have shown that the Sampo adventure is a
distinct unit (like Odysseus' voyage to the underworld), "a mythic
formation which has remained without any action that can be nar-
rated" and which was then fitted more or less coherently into the
rest of the tradition.2 Folk legend has lost its meaning, and treats the
Sampo as some vague magic dispenser of bounty, a kind of Cornu-
copia, but the original story is quite definite.
Vainamoinen, "sage and truthful," conjurer of highest standing,
is cast upon the shore of Pohjola much as Odysseus lands on Skyra
after his shipwreck. He is received hospitably by Louhi, the Mis-
tress (also called the Whore) of Pohjola, who asks him to build for
her the Sampo, without explanation. He tells her that only Ilmari-
nen, the primeval smith, can do it, so she sends Vainamoinen home
on a ship to fetch him. Ilmarinen, who addresses his "brother" and
boon companion rather flippantly as a liar and a vain chatterer, is
not interested in the prospect, so Vainamoinen, ancient of days and
wise among the wise, has recourse to an unworthy trick. He lures
the smith with a story of a tall pine, which, he says, is growing
Near where Osmo's field is bordered.
On the crown the moon is shining,
In the boughs the Bear is resting.
Ilmarinen does not believe him; they both go there, to the edge of
Osmo's field,
Then the smith his steps arrested,
In amazement at the pine-tree,
With the Great Bear in the branches,
And the moon upon its summit.
Ilmarinen promptly climbs up the tree to grasp the stars.
2 D.C. Comparetti, The Traditional Poetry of the Finns (1898).
99 • The Many-Colored Cover
Then the aged Vainamoinen,
Lifted up his voice in singing:
"Awake, oh Wind, oh Whirlwind
Rage with great rage, oh heavens,
Within thy boat, wind, place him
Within thy ship, oh east wind
With all thy swiftness sweep him
To Pohjola the gloomy."s
Then the smith, e'en Ilmarinen
Journeyed forth, and hurried onwards,
On the tempest forth he floated,
On the pathway of the breezes,
Over moon, and under sunray,
On the shoulders of the Great Bear
Till he reached the halls of Pohja,
Baths of Sariola the gloomy.
In this utterly unintended manner, Ilmarinen lands in Pohjola, and
not even the dogs are barking, which astonishes Louhi most of all.
She showed herself hospitable,
Gave the hero drink in plenty,
And she feasted him profusely,
then spoke to him thus:
"O thou smith, 0 Ilmarinen,
Thou the great primeval craftsman,
If you can but forge a Sampo,
With its many-coloured cover,
From the tips of swan's white wing-plumes,
From the milk of barren heifer,
From a little grain of barley
From the wool of sheep in summer,4
Will you then accept this maiden
As reward, my charming daughter?"
3 The Magic Spell, published in the Variants and translated by Comparetti, was
sung by Ontrei in 1855.
See the epigraph to the Introduction, p. 1.
Hamlet's Mill • 100
Ilmarinen agrees to the proposal, and looks around three days for a
proper spot on which to erect his smithy, "in the outer fields of
Pohja." The next three days his servants keep working the bellows.
On the first day of their labour
He himself, smith Ilmarinen,
Stooped him down, intently gazing,
To the bottom of the furnace,
If perchance amid the fire
Something brilliant had developed.
From the flames there rose a crossbow,
Golden bow from out the furnace;
'Twas a gold bow tipped with silver,
And the shaft shone bright with copper.
And the bow was fair to gaze on,
But of evil disposition
And a head each day demanded,
And on feast-days two demanded,
He himself, smith Ilmarinen,
Was not much delighted with it,
So he broke the bow to pieces,
Cast it back into the furnace.
The next day, Ilmarinen looks in anew,
And a boat rose from the furnace,
From the heat rose up a red boat,
And the prow was golden-coloured,
And the rowlocks were of copper.
And the boat was fair to gaze on,
But of evil disposition;
It would go to needless combat,
And would fight when cause was lacking.
Ilmarinen casts the boat back into the fire, and on the following day
he gazes anew at the bottom of the furnace,
101 • The Many-Colored Cover
And a heifer then rose upward;
With her horns all golden-shining,
With the Bear-stars on her forehead;
On her head appeared the Sun-disc.
And the cow was fair to gaze on,
But of evil disposition;
Always sleeping in the forest,
On the ground her milk she wasted.
Therefore did smith Ilmarinen
Take no slightest pleasure in her,
And he cut the cow to fragments,
Cast her back into the furnace.
The fourth day:
And a plough rose from the furnace,
With the ploughshare golden-shining,
Golden share, and frame of copper,
And the handles tipped with silver.
And the plough was fair to gaze on,
But of evil disposition,
Ploughing up the village cornfields,
Ploughing up the open meadows,
Therefore did smith Ilmarinen
Take no slightest pleasure in it.
And he broke the plough to pieces,
Cast it back into the furnace,
Called the winds to work the bellows
To the utmost of their power.
Then the winds arose in fury,
Blew the east wind, blew the west wind,
And the south wind yet more strongly,
And the north wind howled and blustered.
Thus they blew one day, a second,
And upon the third day likewise.
Fire was flashing from the windows,
Hamlet's Mill • 102
From the doors the sparks were flying
And the dust arose to heaven,
With the clouds the smoke was mingled.
Then again smith Ilmarinen,
On the evening of the third day,
Stooped him down, and gazed intently
To the bottom of the furnace,
And he saw the Sampo forming,
With its many-coloured cover.
Thereupon smith Ilmarinen,
He the great primeval craftsman,
Welded it and hammered at it,
Heaped his rapid blows upon it,
Formed with cunning art the Sampo.
And on one side was a corn-mill,
On another side a salt-mill,
And upon the third a coin-mill.
Now was grinding the new Sampo,
And revolved the pictured cover,
Chestfuls did it grind till evening,
First for food it ground a chestful,
And another ground for barter,
And a third it ground for storage.
Now rejoiced the Crone of Pohja,
And conveyed the bulky Sampo,
To the rocky hills of Pohja,
And within the Mount of Copper,
And behind nine locks secured it.
There it struck its roots around it,
Fathoms nine in depth that measured,
One in Mother Earth deep-rooted,
In the strand the next was planted,
In the nearest mount the third one.
103 • The Many-Colored Cover
Ilmarinen does not gain his reward, not yet. He returns without
a bride. For a long while we hear nothing at all about the Sampo.
Other things happen: adventures, death, and resuscitation of Lem-
niinkainen, then Vainamoinen's adventures in the belly of the ogre.
This last story deserves telling. Vainamoinen set about building a
boat, but when it came to putting in the prow and the stern, he
found he needed three words in his rune that he did not know,
however much he sought for them. In vain he looked on the heads
of the swallows, on the necks of the swans, on the backs of the
geese, under the tongues of the reindeer.5 He found a number of
words, but not those he needed. Then he thought of seeking them
in the realm of Death, Tuonela, but in vain. He escaped back to the
world of the living only thanks to potent magic. He was still miss-
ing his three runes. He was then told by a shepherd to search in the
mouth of Antero Vipunen, the giant ogre. The road, he was told,
went over swords and sharpened axes.
Ilmarinen made shoes, shirt and gloves of iron for him, but
warned him that he would find the great Vipunen dead. Neverthe-
less, the hero went. The giant lay underground, and trees grew
over his head. Vainamoinen found his way to the giant's mouth,
and planted his iron staff in it. The giant awoke and suddenly
opened his huge mouth. Vainamoinen slipped into it and was swal-
lowed. As soon as he reached the enormous stomach, he thought
of getting out. He built himself a raft and floated on it up and down
inside the giant. The giant felt tickled and told him in many and no
uncertain words where he might go, but he did not yield any runes.
Then Vainamoinen built a smithy and began to hammer his iron on
an anvil, torturing the entrails of Vipunen, who howled out magic
songs to curse him away. But Vainamoinen said, thank you, he was
very comfortable and would not go unless he got the secret words.
Then Vipunen at last unlocked the treasure of his powerful runes.
1 In the Eddie lay of Sigrdrifa, the valkyria enumerates the places where can be
found hugruna, i.e., the runes that give wisdom and knowledge, among which are
the following: the shield of the sun, the ear and hoof of his horses, the wheel of
Rognir's chariot, Sleipnir's teeth and Bragi's' tongue, the beak of the eagle, the
clutch of the bear, the paw of the wolf, the nail of the Norns, the head of the
bridge, etc. (Sigrdr. vs. 13-17).
Hamlet's Mill
104
Many days and nights he sang, and the sun and the moon and the
waves of the sea and the waterfalls stood still to hear him. Vaina-
moinen treasured them all and finally agreed to come out. Vipunen
opened his great jaws, and the hero issued forth to go and build his
boat at last.
The story then switches abruptly to introduce Kullervo, his ad-
ventures, incest and suicide. When Kullervo incidentally kills the
wife that Ilmarinen had bought so dearly in Pohjola, the tale re-
turns again to Ilmarinen's plight. He forges for himself "Pandora,"
a woman of gold. Finding no pleasure with her, he returns to
Pohjola and asks for the second daughter of Louhi. He is refused.
Ilmarinen then captures the girl, but she is so spiteful and unfaith-
ful that he changes her into a gull. Then he visits Vainamoinen,
who asks for news from Pohjola. Everything is fine there, says
Ilmarinen, thanks to the Sampo. They decide, therefore, to get hold
of the Sampo, even against Louhi's will. The two of them go by
boat, although Ilmarinen is much more in favor of the land route,
and Lemminkainen joins them. The boat gets stuck on the shoulder
of a huge pike. Vainamoinen kills the fish and constructs out of his
jawbones (appendix #10) the Kantele, a harp which nobody can
play properly except Vainamoinen himself. There follows a com-
pletely Orphic chapter about Vainamoinen's Kantele music, the
whole world falling under its spell. Finally, they arrive at Pohjola,
and Louhi, as was to be expected, will not part with the Sampo, nor
will she share it with the heroes. Vainamoinen then plays the Kan-
tele until all the people of Pohjola are plunged in sleep. Then the
brothers go about stealing the Sampo, which turns out to be a diffi-
cult task.
Then the aged Vainamoinen
Gently set himself to singing
At the copper mountain's entrance,
There beside the stony fortress,
And the castle doors were shaken,
And the iron hinges trembled.
105 • The Many-Colored Cover
Thereupon smith Ilmarinen,
Aided by the other heroes,
Overspread the locks with butter,
And with bacon rubbed the hinges,
That the doors should make no jarring,
And the hinges make no creaking.
Then the locks he turned with fingers,
And the bars and bolts he lifted,
And he broke the locks to pieces,
And the mighty doors were opened.
Then the mighty Vainamoinen
Spoke aloud the words that follow:
"O thou lively son of Lempi,
Of my friends the most illustrious,
Come thou here to take the Sampo,
And to seize the pictured cover.''
Then the lively Lemminkainen,
He the handsome Kaukomieli,
Always eager, though unbidden,
Ready, though men did not praise him,
Came to carry off the Sampo,
And to seize the pictured cover . . .
Lemminkainen pushed against it,
Turned himself, and pushed against it,
On the ground his knees down-pressing,
But he could not move the Sampo,
Could not stir the pictured cover,
For the roots were rooted firmly,
In the depths nine fathoms under.
There was then a bull in Pohja,
Which had grown to size enormous,
And his sides were sleek and fattened,
And his sinews from the strongest;
Hamlet's Mill
Horns he had in length a fathom,
One half more his muzzle's thickness,
So they led him from the meadow,
On the border of the ploughed field,
Up they ploughed the roots of Sampo
Those which fixed the pictured cover,
Then began to move the Sampo,
And to sway the pictured cover.
Then the aged Vainamoinen,
Secondly, smith llmarinen,
Third, the lively Lemminkainen,
Carried forth the mighty Sampo,
Forth from Pohjola's stone mountain,
From within the hill of copper,
To the boat away they bore it,
And within the ship they stowed it.
In the boat they stowed the Sampo,
In the hold the pictured cover,
Pushed the boat into the water,
In the waves its sides descended.
Asked the smith, said llmarinen,
And he spoke the words which follow:
u Whither shall we bear the Sampo,
Whither now we shall convey it,
Take it from this evil country,
From the wretched land of Pohja?"
Vainamoinen, old and steadfast,
Answered in the words which follow:
"Thither will we bear the Sampo,
And will take the pictured cover,
To the misty island's headland,
At the end of shady island.
There in safety can we keep it,
106
107 • The Many-Colored Cover
There it can remain for ever,
There's a little spot remaining,
Yet a little plot left over,
Where they eat not and they fight not,
Whither swordsmen never wander.
The Sampo, then, is brought on board the ship—just as Mysingr
the pirate brought Grotte on board his boat—and the heroes row
away as fast as possible. Lemminkainen wants music—you can row
far better with it, he claims. Vainamoinen demurs, so Lempi's son
sings quite by himself, with a voice loud but hardly musical, indeed,
for
On a stump a crane was sitting,
On a mound from swamp arising,
And his toe-bones he was counting,
And his feet he was uplifting,
And was terrified extremely
At the song of Lemminkainen.
Left the crane his strange employment,
With his harsh voice screamed in terror,
Over Pohjola in terror,
And upon his coming thither,
When he reached the swamp of Pohja,
Screaming still, and screaming harshly,
Screaming at his very loudest,
Waked in Pohjola the people,
And aroused the evil nation.
Thus, pursuit begins; impediment after magic impediment is thrown
across their path by Louhi, wretched hostess of Pohjola, but Vaina-
moinen overcomes them. He causes her warship to be wrecked
upon a cliff which he has conjured forth, but on that occasion his
beloved Kantele, the harp, sinks to the bottom of the sea. Finally,
Louhi changes herself into a huge eagle which fills all the space
between waves and clouds, and she snatches the Sampo away.
Hamlet's Mill • 108
From the boat she dragged the Sampo,
Down she pulled the pictured cover,
From the red boat's hold she pulled it,
'Mid the blue lake's waters cast it,
And the Sampo broke to pieces,
And was smashed the picture cover.
Fragments of the colored cover are floating on the surface of the
sea. Vainamoinen collects many of them, but Louhi gets only one
small piece; hence Lapland is poor, Suomi (Finland) well off and
fertile. Vainamoinen sows the fragments of Sampo, and trees came
out of it:
From these seeds the plant is sprouting
Lasting welfare is commencing,
Here is ploughing, here is sowing,
Here is every kind of increase.
Thence there co?nes the lovely sunlight,
O'er the mighty plains of Suomi,
And the lovely land of Suomi.
Vainamoinen constructs a new Kantele, of birchwood this time,
and with the hairs of a young maiden as strings—but the strings
come last. Before that he asks,
"Now the frame I have constructed,
From the trunk for lasting pleasure,
Whence shall now the screws be fashioned,
Whence shall come the pegs to suit me?
'Twas an oak with equal branches,
And on every branch an acorn,
In the acorns golden kernels,
On each kernel sat a cuckoo.
When the cuckoos all were calling,
In the call five tones were sounding
Gold from out their mouths was flowing,
Silver too they scattered round them,
109 • The Many-Colored Cover
On a hill the gold was flowing,
On the ground there flowed the silver,
And from this he made the harp-screws,
And the pegs from that provided."
Once more, Vainamoinen begins to play on his irresistible instru-
ment, but this time Louhi manages to capture sun and moon. She
was able to do so because
. . . the moon came from his dwelling,
Standing on a crooked birch-tree,
And the sun came from his castle,
Sitting on a flr-tree's summit,
To the kantele to listen,
Filled with wonder and rejoicing.
The grasping Louhi hides sun and moon in an iron mountain.
Ilmarinen forges a substitute sun and moon, but they will not shine
properly. Eventually, Louhi sets free the luminaries, since she has
become afraid of the heroes; repeatedly she complains that her
strength has left her with the Sampo.
But time is running out, too, on the ancient Vainamoinen. All that
is left for him to do is kindle a new fire, and he does. Beginning
far back, he had sung all there was to sing.
Day by day he sang unwearied,
Night by night discoursed unceasing,
Sang the songs of by-gone ages,
Hidden words of ancient wisdom,
Songs which all the children sing not,
All beyond men's comprehension,
In these ages of misfortune,
When the race is near its ending.
Now a Miraculous Child was born, heralding a new era. Vaina-
moinen knew that there was not room for both of them in the
world. If the child lived, he must go. He said good-bye to his
country,
Hamlet's Mill
110
111
The Many-Colored Cover
And began his songs of magic,
For the last time sang them loudly,
Sang himself a boat of copper,
With a copper deck provided.
In the stern himself he seated,
Sailing o'er the sparkling billows,
Still he sang as he was sailing:
"May the time pass quickly o'er us,
One day passes, comes another,
And again shall I be needed,
Men will look for me and miss me,
To construct another Sampo,
And another harp to make me,
Make another moon for gleaming,
And another sun for shining.
When the sun and moon are absent,
In the air no joy remaineth."
Then the aged Vainamoinen
Went upon his journey singing,
Sailing in his boat of copper,
In his vessel made of copper,
Sailed away to loftier regions,
To the land beneath the heavens.
Actually, there are more runes which tell of Vainamoinen's de-
parture, as we learn from Haavio. He plunges
to the depths of the sea;
to the lowest sea
to the lowest bowels of the earth
to the lowest regions of the heavens
to the doors of the great mouth of death.
Or, he sailed
into the throat of the maelstroem
into the mouth of the maelstroem,
into the gullet of the maelstroem,
into the maw of the monster of the sea.
This is the Vortex that swallows all waters, the one that comes
of the destruction of Grotte, which must be dealt with later. Its
Norse name is Hvergelmer; its most ancient name is Eridu. But
that name belongs to another story and world.
It is difficult for moderns to grasp the quality of that ancient
recitation, the laulo, of only a few notes going on interminably
with freely improvised verbal "cadenzas," yet with a core of for-
mulas rigidly preserved in the canonic form. It is not actually folk
poetry in the accepted sense even though its "copyists," its "print-
ers" and its "publishers" are only peasants with an iron memory.6
An old laulaja who recited the origin of the world told Lonnrot:
"You and I know that this is the real Truth about how the world
began." He said this after centuries of Christendom, never doubt-
ing, for the essence of the rune was an incantation, sung or mur-
mured (cf. the German raunen), which brings things back to their
actual beginning, to the "deep origins." To heal a wound from a
sword, the laulaja had to sing the rune of the "origin of iron," and
one wrong word would have ruined its power. In this way frag-
ments of ageless antiquity remained embedded in living folk poetry.
Those whom the Greeks called the "nameless ones," typhlos aner,
who had preserved the epic rhapsodies, reach out to meet us almost
in our days, in those humble villages of the Far North, their names
of our own time: Arhippa Perttunen, Simana of Mekrijarvi, Okoi
of Audista, Ontrei, the Pack Peddler.
Out of the whole bewildering story, one thing is established
beyond controversy, that the Sampo is nothing but heaven itself.
The fixed adjective kirjokansi, "many-coloured," did apply to the
cover of the heavenly vault in Finnish folk poetry, as Comparetti
and others showed long ago. As for the name Sampo, it resisted the
efforts of linguists, until it was found that the word was derived
from the Sanskrit skambha, pillar, pole.7 Because it "grinds,"
Sampo is obviously a mill. But the mill tree is also the world axis,
so the inquiry returns to the Norse mill, and to the complex of
meanings involved in the difficult word ludr (with radical r) which
6M. Haavio, Vainamoinen, Eternal Sage (1952), p. 40 (quoting Setala).
7See Chapter VIII.
Hamlet's Mill
112
stands for the timbers of the mill and reappears as "loor," a
wind instrument. This involves time both ways: the setting and the
scansion of time. This does not present embarrassing ambiguity, but
a richer meaning, which must have appeared heaven-sent to early
thinkers.
The Sampo is—or was—the dispenser of all good things and this
is delightfully underscored by the many variants which insist that
because most of it fell into the sea, the sea is richer than the land.
Men were bound to compare the teeming life of Arctic waters with
the barren land in the Far North. But the Sampo did undergo a
catastrophe as it was being moved, and that clinches the parallel
with Grotte. The astronomical idea underlying these strange repre-
sentations has been described in the Intermezzo, and will be taken
up again in chapter IX.
Chapter VIII
Shamans and Smiths
■/
Of this base metal may be filed a
key
That will unlock the door they
howl without.
Omar Khayyam
In addition to the Sampo, there are many myths embedded in
the Kalevala's narrative sequence whose analysis would yield sur-
prises. There was the contest of Vainamoinen with Youkahainen
(see p. 97), a malevolent Lapp magician who seems to be his con-
stant opponent. Youkahainen tries to overcome the ancient sage by
asking cosmogonic riddles, but Vainamoinen "sings" the Lapp step
by step into the bog up to his throat, and sings his magic formulae
"backwards" to free him only when the Lapp has promised him
Aino, his only sister. There was also the tale of Vainamoinen
searching in the dead giant's belly for three lost runes. These, unless
they are treated as "just so stories," look very much like "erratic
boulders" deposited in Finland by the glacial movement of time.
For once, it is possible to trace the archaic formation back to
Egypt.1 A young Egyptian called Setna (or Seton Chamwese)
wanted to steal the magic book of Thoth from the corpse of Nefer-ka
Ptah, one of the great Egyptian gods, who was often portrayed as a
mummy. Ptah, however, was awake and asked him: "Are you able
to take this book away with the help of a knowing scribe, or do you
want to overcome me at checkerboards? Will you play 'Fifty-
Two'?" Setna agreed, and the board with its "dogs" (pieces) being
1 G. Roeder, Altaegyptische Erzahlungen und Marchen (1927), p. 149; A. Wiede-
mann, Herodots Zweites Buch(1890), p, 455.
Hamlet's Mill
114
brought up, Nefer-ka Ptah won a game, spoke a formula, laid the
checkerboard upon Setna's head and made him sink into the ground
up to his hips. On the third time, he made him sink up to his ears;
then Setna cried aloud for his brother, who saved him.
There is also a Finnish folktale which repeats the well-known
Babylonian story of Etana and the Eagle.2 Here, instead of the
King, it is the "Son of the Widow" (no reason is given for this
epithet, which appears to belong to Perceval in the first line, but
we find it again in later Masonic tradition)3 who is taken up into
the air by a griffin and sees the earth growing smaller and smaller
under him. When the earth appears "no bigger than a pea" (analo-
gous similes are to be found also in Etana), the griffin plunges
straightaway to the bottom of the sea, where the hero finds a cer-
tain object for which he had looked everywhere, and finally he is
restored to land. This looks like the full story of what in the Baby-
lonian cuneiform is interrupted halfway through because the tablet
is broken off: it might be the first version of the legend of Alex-
ander exploring the Three Realms.
The anomalous position of Kullervo in the Kalevala remains a
puzzle. Where Lonnrot put him in the sequence, he remains a
displaced person, seeming to come, as was noted, from another
age. There are many such incongruities. On the basis of the
variants discovered, it has been boldly suggested that he was sup-
posed to appear only after the departure of Vainamoinen—in fact,
that he himself is the nameless Miraculous Child who compelled
Vainamoinen to quit the scene, and that would be why the two
never met. The people now understand the Child to be Christ him-
self, but that is the normal transforming influence of the Church.
The Child in Virgil's Fourth Eclogue was also later thought to be
Christ, and Virgil earned a reputation as a magician on the strength
2 See M. Haavio, Der Etanamythos in Finnland (1955), pp. 8-12; also S. Langdon,
The Legend of Etana and the Eagle (1932), pp. 46-50.
3 Such words have long lives. At the height of Pickett's Charge at Gettysburg,
the first man over the wall was Gen. Armistead, who fell into the breach mortally
wounded. To those who picked him up, the general kept repeating: "I am a Son
of the Widow"—obviously the password of a secret military brotherhood that his
captors did not understand, nor the historian either.
115 * Shamans and Smiths
of his supposed prophecy. Actually, the mother says of Vaina-
moinen's and her illegitimate little son (50.199f): "He shall be a
mighty conqueror, strong as even Vainamoinen." This struck the
English editor of the Kalevala, the more so as the baby is also called
"the two-week-old Kaleva." For Kullervo is both in Finnish and in
Estonian tradition the son of Kaleva—"Kalevanpoika" or "Kale-
vipoeg"—much more explicitly than the other heroes, who are
' 'sons", only generically. It would fit into the mythical picture, for
reasons which will soon be evident, to have a time-bound tragic
avatar of Vainamoinen, following upon the timeless sage.
But then, who is Kaleva? He is a mysterious entity that shines
by his absence, and yet is the eponymous presence through the
whole poem. The connotation of "giant" is attached to him: in some
of the Finnish versions of the Old Testament, the gigantic Rephaim
and Enakim are called "children of Kaleva." But there are many
reasons for understanding the word as smith.4 Kaleva might be a
smith even more primeval than Ilmarinen. There is a strange line
in the spell describing the origin of iron: "Poor Iron, man Kaleva,
at that time thou wast neither great nor small." In any case, the
current notion that Kaleva is a "personification" of Finland, a sort
of Britannia with her trident, can be dismissed as unserious. Those
were no times for rhetorical figures. Kaleva remains for the present
a significant void. But Setala notes that the Russian by lini, the
close neighbors of the Estonian runes, sing the feats of Koly-
vanovic, the son of Kolyvan, and say next to nothing of Kolyvan
himself.
The Russian texts give the full name as Samson Kolyvanovic,
just as in Finland it is Kullervo Kalevanpoika. Here perhaps by
chance a name turns up which runs like a barely visible thread
through the whole tradition. We have Samson in the Kalevala right
in the first rune; his name is Sampsa Pellervoinen, who "sows the
trees" and also helps Vainamoinen to cut them down.5 His name,
4 E. N. Setala, "Kullervo-Hamlet," FUF 7 (1907), p. 249. See also K. Krohn,
Kalevalastudien 1. Einleitung (1924), pp. 93-101.
5 Krohn suggests deriving Sampsa from Sampo. Comparetti would like it the
Other way around. Neither is convinced or convincing, but they both show that
the name of Samson is a rarity which has to be accounted for.
Hamlet's Mill
116
117
Shamans and Smiths
"the man of the field" or the "earth-begotten," shows him to be
a rural deity, which might translate into the Greek Triptolemus, or
the Etruscan Aruns Velthymnus. One can no longer tell what his
role was in the original order of the poem. It is enough that he is
there. The lore of the Mill begins to extend beyond reach. It will be
no surprise, then, to find Lykophron, the master mythologist, speak-
ing of Zeus the Miller (435). With it, paradoxically, goes again
the name of Mylinos, "Miller," given to the leader of the Battle of
the Giants against the Gods. The struggle was seen obviously as one
for the control of the Mill of Heaven.
It is, then, maybe not by chance that the name of Samson appears
in the Far North. For Samson himself, Samson Agonistes, should
have a place of honor among the giant Heroes of the Mill. He is in
fact the first one in our literature. We are told (Judges xvi.21) how
he ground away, "eyeless in Gaza, at the mill, with slaves," until
his cruel captors unbound him to "make sport" for them in their
temple, and with his last strength he took hold of the middle pillars
and brought the temple crushing down on the heads of the Philis-
tines. Like Menja, he had taken his revenge.
But Samson leads beyond the confines of this topic into a world-
wide context. He brings more abstruse concepts into play. He had
better be reserved for the next chapter.
Now, at the end of the strange story of the Sampo, one is en-
titled to ask: does all this make much sense by itself? Is it relevant
at all beyond literary history? Comparetti, the great old scholar
who in the last century tackled the difficult study of Finnish poetry,
set himself a neat and classic philological question. Would it help
us to understand the birth of the Homeric poems? Yes, he says. Yet
he admits that the Homeric question remains open. In other words,
the famous "commission of Orphic and Pythagorean experts set up
by Pisistratus to collect the scattered rhapsodies" can hardly have
produced by itself any more than Lonnrot could, such works as
the Iliad and the Odyssey. Hence in conclusion there must still have
been a Homer. Which goes to show that the conventional idea of
epic genius ends up in mystery even for the comparative philologist.
But Comparetti is prompt to point out that those experts were no
scholars in today's sense, belonging as they did to a period when
myth, poetry and intellectual creation were all one.
It might have been better perhaps to take the question from the
other end. Supposing that Lonnrot had been himself some kind of
"Orphic and Pythagorean" in the old sense, might he not have pro-
duced a better reconstruction than the—surely intelligent—stitch-
ing together to which he had to limit himself? Was he not hampered
by his ignorance of the archaic background? Firdausi did actually
know the astrological doctrines through which his scattered sources
made coherent sense, and this is undoubtedly what allowed him to
weld his Shahnama into a real whole. Lonnrot was not, but the
"short songs" of Finnish peasant tradition were too far removed
from the original thought for anyone to recapture it. His successors
who unearthed a bewildering number of variants to every single
rune have left the confusion intact. Instead of forcing the bulky
piece into an arbitrary whole, the Finnish Folklore Fellows (F. F.
for short) have taken up comparative mythology, the only means
by which order can be established eventually.
As concerns Homer and the presupposed Homeric rhapsodies,
this is dangerous territory. Not so much because Homer belongs in
fee simple to the redoubtable guild of Homeric scholars—Compa-
retti as a respectable member of the guild could afford deviations—
but essentially because it is not fitting to try to reduce to a "scheme"
what remains a prodigious and subtle work of art, the limpidity and
immediacy of which should not be spoiled. It is unfortunately a
common prejudice that to work out high theoretical allusions con-
tained in the text reduces the text to an irrelevant conundrum,
whereas, for instance, the Catalogue of Ships studied literally re-
veals hidden beauties to the reader. It is enough to suggest here that
Homer found pre-existent materials at hand, squared blocks and
well-cut ashlars, which he transformed into poetry. One of those
prefabricated pieces, the Curse of the Miller Woman, is located
in chapter VI, and there is more such evidence to come. Homer's
Craft lay really in reshaping and humanizing these materials so well
that they became inconspicuous. In the case of the Greek tragedies
more is known, thanks to Apollodorus. His "Library" of myths,
Hamlet's Mill
118
119
Shamans and Smiths
supplemented by Frazer's wonderful notes, shows that the "Li-
brary" provided the "book" for every tragedy, those that we have
and those that are lost, those written and those never written. Yet it
took an Aeschylus or a Sophocles to transform the meaning, to
make out of it a work of art.
Much closer to hand, and better known, are the sources of the
Divine Comedy—history, philosophy and myth, measures and inter-
vals—which provide a virtually complete structure without gaps.
Yet because of this, Dante is all the more a true creator. Clearly, it
is the very idea of "poet," poietes, which has to be redefined in
moving closer to traditional sources. Veteres docti poetae as Ovid
said, himself not the least of them. "Learned" is the key word, not
in theoretical tropes and allegories, but in the living substances of
mythical doctrine.
But here again common usage is misleading. Today, a learned
man is usually one who understands what it is all about. Dante was
certainly one. But was it so in remote ages? There is reason to doubt
it. An esoteric doctrine, as defined by Aristotle, is one which is
learned long before being understood. Much of the education of
Chinese scholars was until very recently along those lines. Under-
standing remained something apart. It might never come at all, and
at best would come when the learning was complete. There were
other ways.
One can give an extreme case from Rome. Athenaeus6 says that
there was a much-applauded mime, Memphis by name, who in a
brief dance was said to convey faultlessly the whole essence of the
Pythagorean doctrine. It is not said that he understood it: he may
have had an inkling, and the rest was his extraordinarily sharpened
sense of expression. He had, so to speak, a morphological under-
standing that he could only express in action. His public understood
surely no more than he: but they would be strict and unforgiving
judges. Dictum sapienti sat, the wise would say. But here even the
one word was missing. His spectators would shout deliriously none-
theless, in their own demotic language: "I dig you, Jack." And for
6 Deipnosophistai 1.2od. Sec also Lucian's De Saltatione p.70.
the slightest lapse from the exact form, they were ready with eggs
and overripe tomatoes. Here is a case of true communication which
does not need understanding. It takes place only through the form,
morphe. In mystery rites there were things which "could not be
said" (arrheta) but could only be acted out.
Such happenings must be kept in mind when trying to determine
how well the poet understood the material handed on to him. Cre-
ative misunderstanding may have been of the essence of his "free-
dom": but strict respect was there nonetheless. The rune of the
"origin of iron" (the ninth of the Kalevala) was incomprehensible
to the laulaja, yet he knew he had to recite this "deep origin" to
control the lethal powers of cold iron. Magic and mantic implica-
tions were present always in the grim business of the smith, as they
were in the high business of the poet. Understanding lay beyond
them.
Every era, of course, has freely invented its own ballads, ro-
mances, songs and fables to entertain it. That is another matter.
This concerns the poet, poietes, as he was understood in early times.
There was an original complex of meaning which comprised the
words poet, vates, prophet, seer. Every knowledge and law, Vico
wrote with a flash of genius two centuries ago, must once upon a
time have been "serious poetry," poesia seriosa. It is in this sense
that Aristotle in a sophisticated age still refers respectfully to "the
grave testimony of [early] poets."
Now that documents of the earliest ages of writing are available,
one is struck with a wholly unexpected feature. Those first prede-
cessors of ours, instead of indulging their whims with childlike
freedom, behave like worried and doubting commentators: they
always try an exegesis of a dimly understood tradition. They move
among technical terms whose meaning is half lost to them, they deal
with words which appear on this earliest horizon already "tottering
with age" as J. H. Breasted says, words soon to vanish from our
ken. Long before poetry can begin, there were generations of
strange scholiasts.
The experts have noted the uncertainty prevailing in the succes-
sors of old texts, the attempts in them to establish correct names
Hamlet's Mill
120
and their significance from obsolete formulas and ideograms.
S. Schott, dealing with early star lists of Egypt,7 points to the per-
plexity of later generations concerning the names of constellations,
even those of the "greatest gods of the Decans, Orion and Sothis,
who in Ancient Egyptian are called by the names of old hiero-
glyphs, without anybody knowing, in historical times, what these
hieroglyphs had meant, once upon a time. During the whole long
history of these names we meet attempts at interpretation." This
last sentence goes for every ancient text, not only for the names
contained therein: there is no end of commentaries on the Pyramid
Texts, the Coffin Texts and the Book of the Dead,8 on the Rigveda,
the I Ching, just as in the Old Testament.9 W. von Soden regrets
that we depend on the documents of the "Renaissance of Sumerian
culture" (around 2100 b.c.) instead of having the real, old material
at our disposal.10 The mere fact that Sumerian was the language of
the educated Babylonian and Assyrian, the existence of the many
Sumerian-Akkadian "dictionaries" and the numerous translations
of the Gilgamesh epic betray the activity of several academies re-
sponsible for the officially recognized text editions. One can almost
see the scholars puzzling and frowning over the texts. And in
Mexico it was the same. In Chimalpahin's Memorial Breve we find
notes such as "In the year '5-house' certain old men explained some
pictographs to the effect that king Hueymac of Tollan [the mythi-
cal Golden Age city] had died."11 This took place before the com-
ing of the Spaniards. The Greek "Renaissance," no less than those
of the previous millennia in the Near East, was the result of such
an antiquarian effort. Hesiod still bears the mark of it.
These few notions should be present in any ideas about "trans-
mission." The word need in no way imply "understanding" on
7 W. Gundel, Dekane und Dekansternbilder (1936), p. 5.
8 See, for example, G. Roeder, Urkunden zur Religion des Alten Aegypten
(1915), pp. 185f., 199f., 224.
9 J. Dowson (A Classical Dictionary of Hindu Mythology, p. 60) bluntly calls
the Brahmanas "a Hindu Talmud."
10 "Licht und Finsternis in der sumerischen und babylonisch-assyrischen Reli-
gion," Studium Generate 13 (1960), p. 647.
11 Chimalpahin, Memorial Breve, trans. W. Lehmann and G. Kutscher (1958),
p. 10.
121
Shamans and Smiths
the part of those who transmit, and this is true from early ages
down to contemporary minstrels. As has been pointed out, it is easy
to slip into ordinary literary history if the origins are not seriously
investigated. Does the tale of the Sampo have a wider interest than
this? A few handsome cosmic motifs scattered through the tale of
magic might still have reached Finland through the "corridors of
Time" from other cultures without any meaning attached. In short,
it might all be "folk poetry" in the usual sense.
The editors of the Kalevala themselves insistently described the
background as "shamanistic," by which they simply understood
some kind of primitive "religion." It corresponded in their minds
to primeval, instinctive magic, to be found in all five continents,
associated with the tribal "medicine man." Then came Frazer to
introduce the cleavage between "magic" and "religion" as distinct
forms, to complicate matters further. Shamanism remained until
recently a catchword of an uncertain sort—a portmanteau term for
specialists, a vague notion for the public, of the kind that gives one
the pleasant impression of understanding what it is all about—like
that other too-famous term, mana. One of the present authors is
willing to admit ruefully that he once stressed the link of Pytha-
goras and Epimenides with Thracian shamans, with no more
thought than to show that there was much in them of the ageless
medicine man.12 This was several years ago, and it seemed to cor-
respond to the state of the art. It is no longer so. To have uncovered
the inadmissibility of the general usage of the term is the merit of
Laszlo Vajda's short but dense and logical study on the subject.13
Vajda has shown that no historical verdict based on such generali-
ties is valid. It is inadmissible to reduce shamanism to memories of
Eskimo angekoks or to a "technique of induced ecstasy," or to
derive such phenomena from the Asiatic North where, undeniably,
this particular kind of queerness is fostered.
"Shaman" is a Tungusian word. Shamanism has its epicenter in
Ural-Altaic Asia, but it is a very complex phenomenon of culture
12 G. de Santillana, The Origins of Scientific Thought (1961), p. 54.
13 "Zur Phaseologischen Stellung des Schamanismus," in Ural-Altaische Jahr-
bulcher 3`(1959), pp.456-85.
Hamlet's Mill
122
123
Shamans and Smiths
which can be explained neither by psychologists nor by sociologists,
but only by way of historical ethnology. To put it in a few words,
a shaman is elected by spirits, meaning that he cannot choose his
profession. Epileptics and mentally unhinged persons are obvious
privileged candidates. Once elected, the future shaman goes to
"school." Older shamans teach him his trade, and only after the
concluding ceremony of his education is he accepted. This is, so
to speak, the visible part of his education. The real shamanistic ini-
tiation of the soul happens in the world of spirits—while his body
lies unconscious in his tent for days—who dismember the candidate
in the most thorough and drastic manner and sew him together
afterwards with iron wire, or reforge him, so that he becomes a
new being capable of feats which go beyond the human. The duties
of a shaman are to heal diseases which are caused by hostile spirits
who have entered the body of the patient, or which occur because
the soul has left the body and cannot find the way back. Often
the shaman is responsible for guiding the souls of the deceased to
the abode of the dead, as he also escorts the souls of sacrificed ani-
mals to the sky. His help is needed, too, when the hunting season
is bad; he must find out where the game is. In order to find out all
the things which he is expected to know, the shaman has to ascend
to the highest sky to get the information from his god—or go into
the underworld. On his way he has to fight hostile spirits, and/or
rival shamans, and tremendous duels are fought. Both combatants
have with them their helping spirits in animal form, and much
shape-shifting takes place. In fact, these fantastic duels form the
bulk of shamanistic stories. The last echoes are the so-called "magic-
flights" in fairy tales. The shaman's soul ascends to the sky when he
is in a state of ecstasy; in order to get into this state, he needs his
drum which serves him as a "horse," the drumstick as a "whip."14
Now, the "frame" within which the shaman proper acts, that is, the
14 The shamans also use as a "main artery" a stream flowing through all levels of
the sky, and they identify it with the Yenissei—a conception which will become
clearer at a later point of this inquiry. (U. Holmberg, Finno-Ugric and Siberian
Mythology [1964], pp. 307f).
world conception of Ural-Altaic shamanism, has been successfully
traced back to India (under its Hinduistic and Buddhistic aspects,
including Tibetan Lamaism and Bon-po) as well as to Iran. When
reading Radloff's many volumes, one runs into insufficiently dis-
guised Bodhisatvas at every corner (Manjirae = Manjusri; Mait-
erae, or Maidere = Maitreya, etc.), but the best organized material
has been provided by Uno Holmberg (Uno Harva) ,15 who has been
quoted here and will be quoted frequently.
This world conception, however, with its three "domains," with
seven or nine skies, one above the other, and with corresponding
"underworlds," with the "world-pillar" running through the cen-
ter of the whole system, crowned by the "north Nail," or "World
Nail" (Polaris), goes farther back than Indian and Iranian culture,
namely to the most ancient Near East, whence India and Iran de-
rived their idea of a "cosmos"—a cosmos being in itself by no
means an obvious assumption. The shaman climbing the "stairs" or
notches of his post or tree, pretending that his soul ascends at the
same time to the highest sky, does the very same thing as the Meso-
potamian priest did when mounting to the top of his seven-storied
pyramid, the ziggurat, representing the planetary spheres.16
15 See the bibliography.
16 Nine skies, instead of seven, within the sphere of fixed stars, result from the
habit of including among the planets the (invisible) "head" and "tail" of the
"Dragon," which is to say the lunar nodes, conjunctions or oppositions in the
vicinity of which cause the eclipses of Sun and Moon; the revolution of these
"draconitic points" is c. 18.5 years. This notion, upheld in medieval Islamic astrol-
ogy, is Indian, but apparently not of Indian origin, as will come out eventually.
Reuter, Germanische Himmelskunde (1934), pp. 291ff., thinks that the Teutonic
idea of nine planets including the draconitic points goes back to the common "Ur-
zeit" of Indo-Europeans, and refers to Luise Troje, Die 13 und 12 im Traktat Pelliot
(1925), pp. 7f., 25, 149f. Even if the "Dragon" should go back to this time, we do
not take the Indo-Europeans, whether united or not, for the inventors of this idea.
As concerns Islamic and Indian tradition, see the most thorough and thoughtful
inquiries by Willy Hartner, "The Pseudoplanetary Nodes of the Moon's Orbit in
Hindu and Islamic Iconographies," in Ars lslamica 5 (1938), Pt. 1; Le Probleme de
la planete Kaid (1955); "Zur Astrologischen Symbolik des 'Wade Cup'," in Fest-
schrift Kuchnel (1959), pp. 234-43. Whether we shall find the time to deal in
the appropriate form with the tripartite Universe in this essay remains doubtful.
This much can be safely stated: it goes back to "The Ways of Anu, Enlil, and
Ea" in Babylonian astronomy.
Hamlet's Mill
124
From the majestic temple at Borobudur in Java to the graceful
stupas which dot the Indian landscape, stretches a schematized re-
minder of the seven heavens, the seven notches, the seven levels.
Says Uno Holmberg: "This pattern of seven levels can hardly be
imagined as the invention of Turko-Tatar populations. To the in-
vestigator, the origin of the Gods ruling those various levels is no
mystery, for they point clearly to the planetary gods of Babylon,
which already in their far-away point of origin, ruled over seven
superposed starry circles."17 This was also the considered conclusion,
years ago, of Paul Mus. To have taken the conception of several
skies and underworlds as natural, ergo primitive, was a grievous
blunder which distorted the historical outlook of the last two cen-
turies. It stems from the fact that philologists and Orientalists have
lost all contact with astronomical imagination, or even the funda-
mentals of astronomy. When they find something which savors
undeniably of astronomical lore, they find a way to label it under
"prelogical thought" or the like.
But even apart from the celestial "ladder," and the sky-travel of
the shaman's soul, a close look at shamanistic items always discloses
very ancient patterns. For instance, the drum, the most powerful
device of the shaman, representing the Universe in a specific way,
is the unmistakable grandchild of the bronze lilissu drum of the
Mesopotamian Kalu-priest (responsible for music, and serving the
god Enki/Ea).18 The cover of the lilissu drum must come from a
black bull, "which represents Taurus in heaven," says Thureau-
Dangin.19 Going further, W. F. Albright and P. E. Dumont20
17 Der Baum des Lebens (1922), p. 123.
18 See B. Meissner, Babylonien und Assyrien (1925), vol. 2, p. 66.
19Rituels accadiens (1921), p. 2. See also E. Ebeling, Tod und Leben nach den
Vorstellungen der Babylonier (1931), for a cuneiform text in which the hide is
explicitly said to be Anu (p. 29), and C. Bezold, Babylonisch-Assyrisches Glossar
(1926), p. 210 s.v. "sugugalu, 'the hide of the great bull,' an emblem of Anu." We
might point, once more, to the figure of speech used by Petronius' Trimalchio,
who, talking of the month of May, states: "Totus coelus taurulus fiat" ("the whole
heaven turns into a little bull").
20 "A Parallel between Indian and Babylonian Sacrificial Ritual," JAOS 54 (1934),
pp. 107-28.
• Shamans and Smiths
compared the sacrifice of the Mesopotamian bull, the hide of which
was to cover the lilissu drum, with the Indian Ashvamedha, a huge
horse sacrifice which only the most successful king (always a
Kshatrya) could afford. They found that the Indian horse must
have the Krittika, the Pleiades, on his forehead, and this too, accord-
ing to Albright, is what the Akkadian text prescribes concerning
the bull. This should be enough to indicate the level of phenomena
brought into play.
The striking of the drum covered with that specific bull hide was
meant as a contact with heaven at its most significant point, and in
the Age of Taurus (c. 4000-2000 b.c.) this was also explicitly said
to represent Anu, now casually identified as "God of Heaven." But
Anu was a far more exact entity. In cuneiform script, Anu is writ-
ten with one wedge, which stands for the number 1 and also for 60
in the sexagesimal system (the Pythagoreans would have said, he
stands for the One and the Decad). All this does not mean some
symbolic or mystical, least of all magical quality or quantity, but
the fundamental time measure of celestial events (that is, motions) .21
Striking the drum was to involve (this time, yes, magically) the
essential Time and Place in heaven.
It is not clear whether or not the Siberian shamans were still
aware of this past. The amount of highly relevant star lore collected
by Holmberg, and the innumerable figures of definitely astronomi-
cal character found on shamanistic drums could very well allow
for much more insight than the ethnologists assume, but this is
irrelevant at this point. What is plain and relevant is that the Si-
berian shamans did not invent the zodiac, and all that goes with it.
There is no need for a detailed inspection of Chinese mythical
drums, merely a few lines from an "Ocean of Stories":
In the Eastern Sea, there is to be found an animal which looks like an
ox. Its appearance is green, and it has no horns. It has one foot only.
When it moves into the water or out of it, it causes wind or rain. Its
21 Compare the sexagesimal round of days in customary notation of the oracle
bones of Shang China, 15th century B.C., about which Needham states that it is
"probably an example of Babylonian influence on China" (Science and Civilisation
in China [1962], vol. 4, Pt. 1, p. 181).
Hamlet's Mill • 126
127
Shamans and Smiths
shining is similar to that of the sun and the moon. The noise it makes
is like the thunder. Its name is K'uei. The great Huang-ti, having
captured it, made a drum out of its skin.22
This looks prima facie like the description of an ancient case of
delirium tremens, but the context makes it sober enough. This is a
kind of Unnatural Natural History which has small regard for living
species, but deals with events from another realm. The One-Legged
Being, in particular, can be followed through many appearances
beginning with the Hunrakan of the Mayas, whose very name
means "one-leg." From it comes our "hurricane," so there is no
wonder that he disposes of wind, rain, thunder and lightning in
lavish amounts. But he is not for all that a mere weather god, since
he is one aspect of Tezcatlipoca himself, and the true original One-
Leg that looks down from the starry sky—but his name is not
appropriate yet.
And so back by unexpected ways to mythical drums and their
conceivable use. A lot more might be found by exploring that
incredible storehouse of archaic thought miraculously preserved
among the Mande peoples of West Sudan.23 In the large and com-
plicated creation myth of the Mande, there are two drums. The
first was brought down from heaven by the bardic ancestor, shortly
after the Ark (with the eight twin-ancestors) had landed on the
primeval field. This drum was made from Faro's skull and was
used for producing rain. (The experts style Faro usually "le Moni-
22 M. Granet, Danses et Legendes de la Chine ancienne (1959), p. 509. Such
imagery is by no means unique. E.g., the Taittiriya Sanhita says: "The pressing
stone [of the Soma-press] is the penis of the sacrificial horse, Soma is his seed;
when he opens his mouth, he causes lightning, when he shivers, it thunders, when
he urinates, it rains" (7.5.25.2 = Shatapatha Brahmana 10.6.4.1 =Brihad Aranyaka
Upanishad 1.1; see R. Pischel and K. F. Geldner, Vedische Studien, vol. 1, p. 86).
It will come out later why it is important to supplement these strange utterances
with the statement of the Shatapatha Brahmana: "In the water having its origin
is the horse," which sounds ever so inconspicuous until E. Sieg (Die Sagen-
stoffe des Rigveda, p. 98) obliges the non-Sanskritist by giving the Sanskrit words
in transcription, i.e., "apsuyumi va asvah"; apsu is something more specific than
just water; it is, in fact, the very same topos as the Babylonian apsu (Sumerian:
abzu).
23 In East Africa, the drum occupied the place that the Tabernacle had in the
Old Testament, as Harald von Sicard has shown in Ngoma Lungundu: Eine afri-
kanische Bundeslade (1952).
teur," thus avoiding mislabeling him as culture hero, savior or god.)
The first sanctuary was built, and the "First Word" revealed (30
words there were) to mankind through the mouth of one of the
twin-ancestors, who "talked the whole night, ceasing only when
he saw the sun and Sirius rising at the same time." When the "Second
Word" was to be revealed (consisting of 50 words this time), and
again connected with the heliacal rising of Sirius, the ancestor "de-
cided to sacrifice in the sanctuary on the hill the first twins of mixed
sex. He asked the bard to make an arm-drum with the skin of the
twins.24 The tree, from which he carved the drum, grew on the hill
and symbolized Faro's only leg."25
Here again are important one-legged characters, of whom there
are a bewildering number with various functions all over the world.
It is not necessary to enter that jungle, except to note that the tem-
porary mock-king of Siam, who was set up for yearly expiatory
ceremonies, also had to stand on one leg upon a golden dais during
all the coronation ceremonies, and he had the fine-sounding title of
"Lord of the Celestial Armies."26 The Chinese K'uei is then no iso-
lated character. The Chinese myth is more explicit than the others
and becomes more understandable because the Chinese were ex-
tremely sky-conscious. Their sinful monsters are thrown into pits
or banished to strange mountain regions for the sin of having upset
the calendar.
As for K'uei himself, engagingly introduced as a green oxlike crea-
ture of the Eastern Sea, he will grow more bewildering as his nature
unfolds. Marcel Granet writes that the Emperor Shun made K'uei
"master of music"—actually ordered no less a power than the
Sun (Chong-li) to fetch him from the bush and bring him to
court, because K'uei alone had the talent to bring into harmony
24 It is an hourglass-shaped drum, with two skins, said "to recall the two geo-
graphic areas, Kaba and Akka, and the narrow central part of the drum is the
river itself [Niger] and hence Faro's journey."
25 Germaine Dieterlen, "The Mande Creation Story," Africa 27 (1957), pp. 124-
38; cf. JSA 25 (1955), pp. 39-76. See also Marcel Griaule, "Symbolisme des tam-
bours soudanais," Melanges historiques offerts a M. Masson 1 (1955), pp. 79-86;
Griaule and Dieterlen, Signes Graphiques Soudanais (1951), p. 19.
20 W. Deonna, Un divertissetment de table "a cloche-pied'" (1959), p. 33. See
J. Frazier, The Dying God (Pt. Ill of The Golden Bough), pp.149f
Hamlet's Mill
128
the six pipes and the seven modes, and Shun, who wanted to bring
peace to the empire, stood by the opinion that "music is the essence
of heaven and earth."27 K'uei also could cause the "hundred animals"
to dance by touching the musical stone, and he helped Yu the
Great, that indefatigable earth-mover among the Five First Em-
perors, to accomplish his labor of regulating the "rivers." And it
turns out that he was not only Master of the Dance, but Master of
the Forge as well. He must have been a remarkable companion for
Yu the Great, whose dancing pattern (the Step of Yu) "per-
formed" the Big Dipper.28
Enough of drums, and of their shamanic use. They have at least
ceased to seem like tribal tom-toms. They are connected with time,
rhythm and motion in heaven.
Moving now to another great theme, in fact a very great one, it
is possible to trace back the significance of the blacksmith in Asiatic
shamanism, particularly the celestial blacksmith who is the legiti-
mate heir to the divine "archi-tekton" of the cosmos. Several repre-
sentatives of this type, whom we call Deus Faber, still have both
functions, being architects and smiths at the same time, e.g., the
Greek Hephaistos, who builds the starry houses for the gods and
forges masterworks, and the Koshar-wa-Hasis of Ras Shamra, who
builds Baal's palace and forges masterworks also.
The Yakuts claim: "Smith and Shaman come from the same
nest," and they add: "the Smith is the older brother of the Sha-
man,"29 which might be valid also for Vainamoinen, coupled with
Ilmarinen, who is said to have "hammered together the roof of the
sky." It is the primeval Smith who made the Sampo, as we know,
and forged sky and luminaries in Estonia. It is no idle fancy that
the representative of the celestial smith, the King, is himself fre-
quently titled "Smith." Jenghiz Khan had the title "Smith"30 and
27Granet, Danses et Legendes, pp. 311, 505-508.
28 We are indebted for this last piece of information to Professor N. Sivin.
29 P. W. Schinldt, Die asiatischen Hirtenvolker (1954), pp. 346f. Concerning the
terrestrial blacksmith: the many iron pieces which belong to the costume of a
shaman can be forged only by a blacksmith of the 9th generation, i.e., eight of his
direct ancestors must have been in the profession. A smith who dared forge a
shamanistic outfit without having those ancestors would be torn by bird spirits.
30 A. Alfoldi, "Smith As a Title of Dignity" (in Hungarian), in Magyar Nyelv
28 (1952), pp. 205-20.
129
Shamans and Smiths
the standard of the Persian Empire was the stylized leather apron
of the Smith Kavag (appendix #11). The Chinese mythical em-
perors Huang-ti and Yin are such unmistakable smiths that Marcel
Granet drew historic-sociological conclusions all the way, forget-
ting the while that Huang-ti, the Yellow Emperor, is acknowl-
edged to be Saturn. And just as the Persian Shahs held their royal
jubilee festival after having reigned thirty years, which is the Satur-
nian revolution, so the Egyptian Pharaoh also celebrated his jubilee
after thirty years, true to the "inventor" of this festival, Ptah, who
is the Egyptian Saturn, and also Deus Faber. It was necessary to
enter this subject in depth abruptly and lay stress on these few
selected data, because otherwise the charming and harmless-looking
Finnish runes would not be seen for what they are, the badly dam-
aged fragments of a once whole and "multicolored cover." It does
no harm to stamp Vainamoinen a "shaman" as long as one remains
aware of the background of shamanism. In fact, there is again a
vision in depth from seeing that Vainamoinen has discarded the
drum which remains the one instrument of his Lapp cousins; he has
created the harp, and this means that he must be seen as the Orpheus
of the North.
Last survivals are not easily recognized. It needs experience, and
it cannot be expected that an unsuspecting reader of "folk poetry"
would spot well-known divine characters when they come his way
clad in Longfellow's meter. For instance, in reading Kalevala
9.107ff., it is not easy to discover the mighty Iranian God of Time,
Zurvan akarana, who is portrayed as standing upon the world egg,
Carrying in his hands the tools of the architect:
Then was born smith Ilmarinen
Thus was born and thus was nurtured
Born upon a hill of charcoal,
Reared upon a plain of charcoal,
In his hands a copper hammer,
And his little pincers likewise.
Ilmari was born at night time,
And at day he built his smithy.
Since Christendom was very successful in destroying old traditions,
Altaic and Siberian survivals are often found in far better shape
Hamlet's Mill
130
than Finnish runes, but even the Lapps still speak of " Waralden ol-
may, 'World Man' . . . and this is the same as Saturnus."31 Nor are
Jupiter and Mars absent, the former being called Hora Galles
(Thorkarl), the latter Bieka Galles, the "Wind Man."32 Voguls,
Yakuts and Mongols tell of God's seven sons, or seven gods (or
nine), among whom are a "Scribe Man,"33 and a "Man observing the
World." The latter has been compared straightaway with Kullervo
by Karl Kerenyi,34 who claims his name to be the literal translation
of Avalokiteshvara, the very great Bodhisatva, known in China as
Kuan-yin, literally "deserving (musical) modes." One wonders
whether this "World-observer" does not go back much farther:
to Gilgamesh. We have to keep in mind that the Babylonians called
their texts after their opening words; e.g., the Creation Epic they
called Enuma elish, i.e., "When above"; accordingly, what we call
the Epic of Gilgamesh was with them Sha naqba imuru, "Who saw
everything." Such are the bewildering changes rung by time on
great and familiar themes. And there is more. Actually, when still
young, this Vogulian "World-observing Man"—Avalokiteshvara
himself, this great and worshiped deity of Buddhist countries—
was, like Kullervo, a much-plagued orphan, first in the house of
his uncle, then in the house of "the Russian" and in that "of the
Samoyed." After years of misery—quite specific "measured" mis-
ery35—he kills all his tormentors. The revenge he takes is for
31 This information comes from Johan Radulf (1723), quoted by K. Krohn,
"Priapkultus," FUF 6 (1906), p. 168, who identifies Waralden olmay with Freyr.
G. Dumezil, La Saga de Hadingus (1950), identifies him with Njordr.
32 K. Krohn, "Windgott und Windzauber," FUF 7 (1907), pp. 1731"., where the
god is once called Ilmaris.
33 The Ostyaks talk even of a golden Book of Destiny, and Holmberg points out
that the Ostyaks who have no writing are not likely to have hit upon such notions
by themselves. (Holmberg, Der Baum des Lebens, p. 97). Cf. the entire chapter,
"The Seven Gods of Fate" (pp. 113-33 of the same work) and Holmberg's Finno-
Ugric and Siberian Mythology, p. 415.
34 "Zum Urkind-Mythologem," in Paideuma 2 (1940), pp. 245ff. See now C. G.
Jung and K. Kerenyi, Essays on a Science of Mythology (1949), pp. 30-39.
35 E.g., in the house of "the Russian," he is kept in the door hinge (in the English
translation this and other details are blurred to insignificance), and dishwater is
emptied upon him. To be damned to play door hinge is one of the hellish punish-
ments in Egypt, because the hinge is supposed to turn in the victim's eye. As con-
cerns the heart-warming custom of abusing One's celestial fellow travelers as sink
131 * Shamans and Smiths
himself. His father, who had lowered down the beloved son from
the sky in a cradle, remained aloft.
These hints will suffice for the time being. It does not matter
whether or not pieces, or even the whole, of cosmological tradition
came late to the Ural-Altaic populations, that is, whether Mani-
cheism had a part in their propagation. The Manicheans took over
the whole parcel of old traditions, changing only the signs, as hap-
pens with every Gnostic system. Gnostics never have been of the
inventive sort. Their very title, derived from their key word, gives
the scheme away, gnosis tes hodou = knowledge of the way. The
"Way" which had to be learned by heart is that which leads out-
wards-upwards through the planetary spheres, past the threatening
"watchtowers" of the zodiac to the desired timeless Light be-
yond the sphere of fixed stars, above the Pole star: beyond and
above everything, where the unknown god (agnostos theos) resides
eternally.36
This "Way" is not exactly the same for everybody, and the larg-
est highroads are not everlasting, but the principle remains un-
Or toilet: we find this in the Eddie Lokasenna (34), where Loke says of Njordr
that he was used as chamber pot by Hymir's daughters; with the Polynesian case
of Tawhaki, whose father Hema is abused in the very same manner, we deal in the
chapter on Samson (see p. 175); this model of a "Horus-avenger-of-his-father"
fulfills not only his filial duty, he does it by means of Amlethus' own "Net-trick."
The Samoyed binds the pitiable "World-observing Man" to his sledge with an
iron wire of thirty fathoms length. We do not know yet what this means precisely.
We know that victorious characters use the vanquished as this or that vehicle,
saddle horse, etc.—Marduk uses Tiamat as "ship," as does Osiris with Seth; Ninur-
ta's "Elamitic chariot, carrying the corpse of Enmesharra" is drawn by "horses
Who are the death-demon of Zu" (Ebeling, Tod und Leben, p. 33); Tachma Rupa
rides on Ahriman for thirty years around the two ends of the earth (Yasht 19.29;
Yasht 19, the Zamyad Yasht, is the one dedicated to Hvarna)—but these code
formulae have not yet been broken.
36Absurd as it sounds, the many Gnostic sects who hated nothing more than
philosophers and mathematicians have never denied or doubted the validity of
their "evil" teachings. Sick with disgust, they learned the routes of ascension
through (or across) those abominable spheres ruled by number, created by the
evil powers. Surely, their "Father of Greatness" would not have created such a
thing as a cosmos. Tradition does use the most peculiar vehicles for its motion
through historical time. Or should one say, tradition did use? Face to face with
the outbreaking revolution of "simple souls" against whichever rational thought,
there is small reason for hope that our contemporary gnostics will hand down any
tradition at all.
Hamlet's Mill
132
changed. The shaman travels through the skies in the very same
manner as the Pharaoh did, well equipped as he was with his Pyra-
mid Text or his Coffin Text, which represented his indispensable
timetable and contained the ordained addresses of every celestial
individual whom he was expected to meet.37 The Pharaoh relied
upon his particular text as the less distinguished dead relied upon
his copy of chapters from the Book of the Dead, and he was pre-
pared (as was the shaman) to change shape into the Sata serpent,
a centipede, or the semblance of whatever celestial "station" must
be passed, and to recite the fitting formulae to overcome hostile
beings.38
To sum it up—whether Shamanism is an old or a relatively young
offshoot of ancient civilization is irrelevant. It is not primitive at all,
but it belongs, as all our civilizations do, to the vast company of
ungrateful heirs of some almost unbelievable Near Eastern ancestor
who first dared to understand the world as created according to
number, measure and weight.
If the Finnish runes and Altaic legends sound harmless enough,
so do the popular traditions of most of the European countries, in-
cluding Greece: the kind of mythology known through Bulfinch.
But here at least there are additional less popular traditions which
have preserved more of the severe spirit and style of old. So the
(13th) Orphic Hymn to Kronos addresses the god as "Father of
37 The ephemerides on the inner side of the coffin lids of the Middle Kingdom,
and the astronomical ceilings in tombs of the New Kingdom, as well as the
"Ramesside Star Clocks," made navigation still easier for the royal soul.
38 Many of the heavenly creatures do all the damage they possibly can; they try,
for instance, to rob the dead of his text without which he would be helpless, and
generally their conduct, as described in the literature of the Hereafter, is weird.
Thus, in chapter 32 of the Book of the Dead, the crocodile of the West is accused
of eating certain stars; the properly equipped soul, however, knows how to play up
to the celestial monsters, and the traveler addresses the Northern crocodile with
the words: "Get thee back, for the goddess Serqet is in my interior and I have not
yet brought her forth." The goddess Serqet is the constellation Scorpius. As con-
cerns the Sata serpent, "whose years are infinite . . . who dwells at the farthest
ends of the earth . . . who renews his youth everyday" (Book of the Dead, ch. 87),
he makes himself suspect of representing the sphere of Saturn, whereas the centi-
pede is not likely to fit any "body" besides Moon or Mercury; that it is no con-
stellation is certain.
133
Shamans and Smiths
the blessed gods as well as of man, you of changeful counsel, . . .
strong Titan who devours all and begets it anew [lit. "you who
consume all and increase it contrariwise yourself"], you who hold
the indestructible bond according to the apeirona (unlimited) order
of Aion, Kronos father of all, wily-minded Kronos, offspring of
Gaia and starry Ouranos . . . venerable Prometheus." Such sayings
suddenly thrust information out of the usual patterns and show the
true professional minds of ancient mythology working out their
theorems. The only conventional attribute is "Son of Ouranos and
Gaia." Kronos is termed a Titan, because the word "God" belongs
properly to the Olympian generation, whereas Saturn's empire is
not of "this world," any more than that of the Indian Asura and
the king of the golden Krita Yuga, Varuna; and the formula is
found still in the medieval "Kaiser-Sage." At the end of Thidrek's
(Theodoric's) reign when there are only corpses left, a dwarf ap-
pears and asks the king to follow him; "your empire is no more in
this world."39 More puzzling, Kronos "is" that other Titan, Prome-
theus, that other adversary of the "gods," the Lighter of Fire. He
"is" many more characters, too, but it will take some time to clear
this up. We are at the heart of an "implex."
"Who holdest the unbreakable bond . . ." Assyrian Ninurta, too,
holds "the bond of heaven and earth." We shall also hear of a magi-
cal invocation (see p. 147) that addresses Kronos as "founder of the
world we live in." These words are, however, insufficient and
ambiguous. Not only are translations imprecise generally, but in
our times of accelerated decay of language even the best-intentioned
reader is likely to overlook such words as "bond" or "to found."
if instead he were to read "inch scale" and "to survey"—a divine
foundation is every time a "temenos"—he would promptly react
in a different manner. Kronos-Saturn has been and remains the one
who owns the "inch scale," who gives the measures, continuously,
because he is "the originator of times," as Macrobius says, although
39W. Grimm, Die Deutsche Heldensage (1957), p. 338: "Du solt mit mir gan.dyn
reich ist nit me in dieser welt." The corresponding most popular folktale shows
Theodoric of Verona ravished by a demon horse and cast headlong into the crater
of Etna.
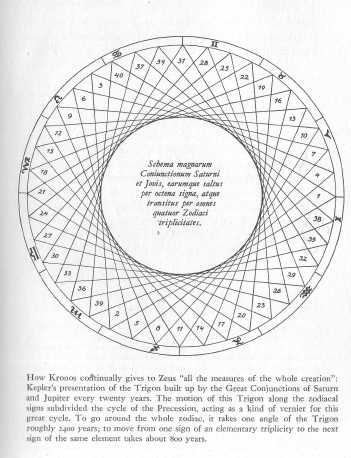
Hamlet's Mill • 134
the poor man mistakes him for the sun for this very reason.40 But
"Helios the Titan" is not Apollo, quite explicitly.
Apart from this, apart also from Plutarch's report, according to
which Kronos, sleeping in that golden cave in Ogygia, dreams what
Zeus is planning,41 there is an Orphic fragment of greater weight,
preserved in Proclus' commentary on Plato's Cratylus.42 The Orphic
text being one of the delicate sort, we quote some sentences only:
The greatest Kronos is giving from above the principles of intelligi-
bility to the Demiurge [Zeus], and he presides over the whole "crea-
tion" [demiourgia]. That is why Zeus calls him "Demon" according
to Orpheus, saying: "Set in motion our genus, excellent Demon!"
And Kronos seems to have with him the highest causes of junctions
and separations ... he has become the cause of the continuation of
begetting and propagation and the head of the whole genus of Titans
from which originates the division of beings [diairesis ton onton].
The passage ends thus: "Also Nyx prophesies to him [i.e., occa-
sionally] but the father does so continuously [prosechos], and
he gives him all the measures of the whole creation."43
In Proclus' style, the same phenomena which look simply flat and
childish, mere "etymologizing," when handled by others, sound
extremely difficult—which they actually are. So let us shortly com-
pare how Macrobius deals with the responsibility of Kronos for the
"division of beings" (Sat. 7.8.6-7). After having mentioned the cur-
rent identification of Kronos (Saturn) and Chronos (Time), so
often contested by philologists, Macrobius states:
They say, that Saturn cut off the private parts of his father Caelus
[Ouranos], threw them into the sea, and out of them Venus was born
who, after the foam [aphros] from which she was formed, accepted
the name of Aphrodite. From this they conclude that, when there
was chaos, no time existed, insofar as time is a fixed measure derived
from the revolution of the sky. Time begins there; and of this is be-
40 Sat.1.22.8: Saturnus ipse, qui auctor est temporum.
41 De facie in orbe lunae 941: "Hosa gar ho Zeus prodianoeitai, taut' oneiropolein
ton Kronon."
42 Fr. 155, Kern, p. 194.
43 Kai panta ta metra tes holes demiourgias endidosin. We might even say:
Kronos "grants" him all the measures.
135 . Shamans and Smiths
lieved to have been born Kronos who is Chronos, as was said before
[see appendix #12].44
The fact is that the "separation of the parents of the world,"
accomplished by means of the emasculation of Ouranos, stands for
the establishing of the obliquity of the ecliptic: the beginning of
measurable time. (The very same "event" was understood by Mil-
ton as the expulsion from Paradise [appendix #13].) And Saturn
has been "appointed" to be the one who established it because he is
the outermost planet, nearest to the sphere of fixed stars.45 "This
planet was taken for the one who communicated motion to the
Universe and who was, so to speak, its king"; this is what Schlegel
reports of China L'Uranographie Chinoise, pp. 628ff.).
Saturn does give the measures: this is the essential point. How are
we to reconcile it with Saturn the First King, the ruler of the
Golden Age who is now asleep at the outer confines of the world?
The conflict is only apparent, as will be seen. For now it is essential
to recognize that, whether one has to do with the Mesopotamian
Saturn, Enki/Ea, or with Ptah of Egypt, he is the "Lord of
Measures"—spell it me in Sumerian, parshu in Akkadian, maat in
Egyptian. And the same goes for His Majesty, the Yellow Emperor
of China—yellow, because the element earth belongs to Saturn—
"Huang-ti established everywhere the order for the sun, the moon
and the stars."46 The melody remains the same. It might help to
44 Ex quo intellegi volunt, cum chaos esset, tempora non fuisse, siquidem tempus
est certa dimensio quae ex caeli conversione colligitur. Tempus coepit inde; ab
ipso natus putatur Kronos qui, ut diximus, Chronos est.
45 It is not hidden from us that the indestructible laws of philology do not allow
for the identification of Kronos and Chronos, although in Greece to do so "was
customary at all times" (M. Pohlenz, in RE 11, col. 1986). We have, indeed, no acute
reason to insist upon this generalizing identification—the "name" of a planet is a
function of time and constellation—yet it seems advisable to emphasize, on the
one hand, that technical terminology has its own laws and is not subject to the
jurisdiction of linguists, and to point, on the other hand, to one of the Sanskrit
names of Saturn, i.e., "Kala," meaning "time" and "death," and "blue-black" (A.
Scherer, Gestirnnamen bei den indogermanischen Volkern [1953], pp. 84f)—a
Color which suits the planet perfectly, all over the world—and to point, moreover,
to a passage from the Persian Minokheird (West trans, in R. Eisler, Weltenmantel
and Himmelszelt [1910], p. 410): "The creator, Auharmazd (Jupiter) produced
his creation . . . with the blessing of Unlimited Time (Zurvan akarana)."
46M. Granet, Chinese Civilization (1961), p. 12.
Hamlet's Mill
136
understand the general idea, but particularly the lucubration of
Proclus, to have a look at the figure drawn by Kepler, which
represents the moving triangle fabricated by "Great Conjunctions,"
that is, those of Saturn and Jupiter. One of these points needs
roughly 2,400 years to move through the whole zodiac. The next
chapter will show why this is of high importance: here it suffices to
point to one possible manner in which measures are given "con-
tinuously."
Saturn, giver of the measures of the cosmos, remains the "Star
of Law and Justice" in Babylon,47 also the "Star of Nemesis" in
Egypt,48 the Ruler of Necessity and Retribution, in brief, the Em-
peror.49 In China, Saturn has the title "Genie du pivot," as the god
who presides over the Center, the same title which is given to the
Pole star.50 This is puzzling at first, and so is the laconic state-
ment coming from Mexico: "In the year 2-Reed Tezcatlipoca
changed into Mixcouatl, because Mixcouatl has his seat at the North
pole and, being now Mixcouatl, he drilled fire with the fire sticks
for the first time." It is not in the line of modern astronomy to
establish any link connecting the planets with Polaris, or with any
star, indeed, out of reach of the members of the zodiacal system.
Yet such figures of speech were an essential part of the technical
idiom of archaic astrology, and those experts in ancient cultures
who could not understand such idioms have remained completely
helpless in the face of the theory. What has Saturn, the far-out
planet, to do with the pole? Yet, if he cannot be recognized as the
"genie of the pivot," how is it possible to support Amlodhi's claim
to be the legitimate owner of the Mill?
47P. Jensen, Die Kosmologie der Babylonier (1890), p. 115; Meissner, Babylonien
und Assyrien (1925), vol. 2, pp. 145, 410; P. F. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum
(1950), 230.
48 Achilles Tatius, see A. Bouche-Leclerq, L'Astrologie Grecque (1899), p. 94;
W. Gundel, Neue Astrologische Texte des Hermes Trismegistos (1936), pp. 260,
316.
49 "The title basileus is stereotyped with Kronos" (M. Mayer, in Roscher s.v.
Kronos, col. 1458; see also Cornford in J. E. Harrison's Themis, p. 254). For
China, see G. Schlegel, L'Uranographie Chinoise (1875), pp. 361, 63off. Even the
Tahitian text "Birth of the Heavenly Bodies" knows it: "Saturn was king" (T.
Henry, Ancient Tahiti [1928], pp. 359ff.).
50 Schlegel, L'Uranographie Chinoise, pp. 525, 628ff.
Chapter IX
Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
Tops of different sorts, and jointed dolls,
and fair golden
apples from the clear-voiced Hesperides . . .
Orpheus the Thracian
Though I am not by nature rash or splenetic
Yet there is in me something dangerous
Which let thy wisdom fear . . .
Hamlet, Act V
A reasonable case has been made for the extreme antiquity
and continuity of certain traditions concerning the heavens. Even if
Amlodhi's Quern, the Grotte and the Sampo as individual myths
cannot be traced back beyond the Middle Ages, they are derived
in different ways from that great and durable patrimony of astro-
nomical tradition, the Middle East.
Now it is time to locate the origin of the image of the Mill, and
further, what its alleged breakup and the coming into being of the
Whirlpool can possibly mean.
The starting place is Greece. Cleomedes (c. a.d. 150), speaking
of the northern latitudes, states (1.7): "The heavens there turn
around in the way a millstone does." Al-Farghani in the East takes
up the same idea, and his colleagues will supply the details. They
call the star Kochab, beta Ursae Minoris, "mill peg," and the stars
of the Little Bear, surrounding the North Pole, and Fas al-rahha
(the hole of the mill peg) "because they represent, as it were, a hole
(the axle ring) in which the mill axle turns, since the axle of the
equator (the polar axis) is to be found in this region, fairly close
Hamlet's Mill
138

to the star Al-jadi (he-goat, Polaris: alpha Ursae Minoris)." These
are the words of the Arab cosmographer al-Kazvini. Ideler com-
ments:1
Kotb, the common name of the Pole, means really the axle of the
movable upper millstone which goes through the lower fixed one,
what is called the "mill-iron." On this ambiguity is founded the anal-
ogy mentioned by Kazvini. The sphere of heaven was imagined as a
turning millstone, and the North Pole as the axle bearing in which the
mill-iron turns ... Fas is explained by Giggeo ... as rima, scissura etc.
. . . The Fas al-rahha of our text, which stands also in the Dresden
globe beside the North Pole of the Equator, should therefore repre-
sent the axle bearing.
Farther to the east, in India, the Bhagavata Purana tells us how
the virtuous prince Dhruva was appointed as Pole star.2 The par-
ticular "virtue" of the prince, which alarmed even the gods, is
worth mentioning: he stood on one leg for more than a month,
motionless. This is what was announced to him: "The stars, and
their figures, and also the planets shall turn around you." Accord-
ingly, Dhruva ascends to the highest pole, "to the exalted seat of
Vishnu, round which the starry spheres forever wander, like the
upright axle of the corn mill circled without end by the labouring
oxen."
The simile of the oxen driven around is not alien to the West. It
has remained in our languages thanks to the Latin Septemtriones,
the seven threshing oxen of Ursa Major: "that we are used to call-
ing the Seven Oxen," according to Cicero's translation of Aratus.
On a more familiar level there is a remark by Trimalchio in Pe-
tronius (Satyricon 39): "Thus the orb of heaven turns around like
a millstone, and ever does something bad." It was not a foreign idea
1 Ludwig Ideler: Untersuchung uber den Ursprung und die Bedeutung der Stern-
namen (1809), pp. 4, 17.
2F. Normann, Mythen der Sterne (1925), p. 208. See now The Srimad-Bhaga-
vatam of Krishna-Dwaipayana Vyasa 5.3 (trans. J. N. Sanyal, vol. 2, pp. 248f.):
"Just as oxen, fastened to a post fixed in the center of a threshing floor, leaving
their own station, go round at shorter, middle or longer distances, similarly fixed
on the inside and outside of the circle of time, stars and planets exist, supporting
themselves on Dhruva; and propelled by the wind, they range in every direction
till the end of a Kalpa."
139 • Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
to the ancients that the mills of the gods grind slowly, and that the
result is usually pain.
Thus the image travels far and wide by many channels, reaches
the North by way of Celtic-Scandinavian transmission and appears
in Snaebjorn's account of his voyage of discovery in the Arctic.
There should be added to those enigmatic lines of his what is known
now of the background in Scandinavian lore. The nine grim god-
desses who "once ground Amlodhi's meal," working now that
"host-cruel skerry quern" beyond the edge of the world, are in
their turn only the agents of a shadowy controlling power called
Mundilfoeri, literally "the mover of the handle" (appendix #15).
The word mundil, says Rydberg, "is never used in the old Norse
literature about any other object than the sweep or handle with
which the movable millstone is turned,"3 and he is backed by
Vigfusson's dictionary which says that "mundil" in "Mundilfoeri"
clearly refers to "the veering round or revolution of the heavens."
The case is then established. But there is an ambiguity here
which discloses further depths in the idea. " 'Moendull' comes from
Sanskrit 'Manthati,' " says Rydberg, "it means to swing, twist, bore
(from the root manth-, whence later Latin mentula), which occurs
in several passages in the Rigveda. Its direct application always
refers to the production of fire by friction."4
So it is, indeed. But Rydberg, after establishing the etymology,
has not followed up the meaning. The locomotive engineers and
airplane pilots of today who coined the term "joy stick" might have
guessed. For the Sanskrit Pra-mantha is the male fire stick, or churn
stick, which serves to make fire. And Pramantha has turned into
the Greeks' Prometheus, a personage to whom it will be necessary
3V. Rydberg, Teutonic Mythology (1907), pp. 581ff. Webster's New Interna-
tional Dictionary, 2d ed., lists "mundle": A stick for stirring. Obsolete except for
dialectical use. (We are indebted for this reference to Mrs. Jean Whitnack.)
4 To term it "friction" is a nice way to shut out dangerous terms: actually, the
Sanskrit radical math, manth means drilling in the strict sense, i.e., it involves al-
ternate motion (see H. Grassmann, Worterbuch zum Rig-Veda [1955], pp. 976L)
as we have it in the famous Amritamanthana, the Churning of the Milky Ocean,
and this very quality of India's churn and fire drill has had far-reaching influence
on cosmological conceptions.
Hamlet's Mill
140
to come back frequently. What seems to be deep confusion is in
reality only two differing aspects of the same complex idea. The
lighting of fire at the pole is part of that idea. But the reader is not
the first to be perplexed by an imagery which allows for the pres-
ence of planets at the pole, even if it were only for the purpose of
kindling the "fire" which was to last for a new age of the world,
that world-age which the particular "Pramantha" was destined to
rule. The handle, "moendull," and the fire drill are complemen-
tary: both have had great developments which superimpose on each
other and on a multitude of myths. The obstacles which imagina-
tion has to overcome are the associations which are connected spon-
taneously with "fire," that is, the real burning fire in chimney or
hearth, and the kind of "fire" associated with the mentioned "joy
stick." Both are irrelevant as far as cosmological terminology is
concerned, but they lent the linguistic vehicle which was used to
carry the ideas of astronomy and alchemy.
It should be stated right flow that "fire" is actually a great circle
reaching from the North Vole of the celestial sphere to its South
Pole, whence such strange utterances as Rigveda 5.13.6: "Agni!
How the felly5 the spokes, thus you surround the gods." (Agni is
the so-called "fire-god," or the personified fire.) The Atharva Veda
says, moreover, that the fire sticks belong to the skambha6 the
world's axis, the very skambha from which the Sampo has been
derived (see above, p. 111).
The identity of the Mill, in its many versions, with heaven is
thus universally understood and accepted. But hitherto nobody
seems to have wondered about the second part of the story, which
also occurs in the many versions. How and why does it always
happen that this Mill, the peg of which is Polaris, had to be wrecked
or unhinged? Once the archaic mind had grasped the forever-
enduring rotation, what caused it to think that the axle jumps out
of the hole? What memory of catastrophic events has created this
5 The rim of the wheel in which the spokes fit.
6 10.8.20. Cf. RV 10.24.4 and 10.184.3 with Geldner's remark that in this stanza of
the Atharva Veda the fire sticks are treated as a great secret and attributed to
skambha.
141 • Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
story of destruction? Why should Vainamoinen (and he is not the
only one) state explicitly that another Mill has to be constructed
(see p. 110) ? Why had Dhruva to be appointed to play Pole star—
and for a given cycle?7 For the story refers in no way to the crea-
tion of the world. One might even ask, as the alternative solution
to Rydberg's challenging "limb-grist," whether Bergelmer was not
heaved in the same manner "upon the millstone," that is, appointed
to play Pole stair (see above, p. 92).
The simple answer lies in the facts of the case. The Pole star
does get out of place, and every few thousand years another star
has to be chosen which best approximates that position. It is well
known that the Great Pyramid, so carefully sighted, is not oriented
at our Pole Star but at alpha Draconis, which occupied the position
at the pole 5,000 years ago. But, as has been mentioned above (In-
termezzo, p. 66), it is the more difficult for moderns to imagine
that in those far-off ages men could keep track of such impercep-
tible shifting, as many of them are not aware of the mere facts. As
Dr. Alexander Pogo, the Palomar astronomer, has written in frus-
tration: "I give up quoting further examples of the obstinate belief
of our Egyptologists in the immobility of the heavenly pole."8
Yet there is quite a collection of myths to show that once upon
a time it was realized that the sphere of fixed stars is not meant to
circle around the same peg forever and ever. Several myths tell how
Polaris is shot down, or removed in some other way. That is re-
served for an appendix (#15).
Most of these myths, however, come under a misleading name.
They have been understood to deal with the end of the world. But
there are extremely few "eschatological" myths entitled to this
label. For example, the Twilight of the Gods is understood as the
world's end, yet there is unambiguous testimony to the contrary
from the Voluspa and other chapters of the Edda. What actually
comes to an and is a world, in the sense of a world-age. The catas-
7 The Vishnu Purana 1.12 (cf. 2.8, p. 187 of the Wilson translation) betrays the
Indian predilection for huge and unrealistic numbers and periods: Dhruva is meant
to last one kalpa-—4,320,000 years.
8"Zuin Problem der Identification der nordlichen Sternbilder der alten Aegyp-
ter," isis 16 (1931), p. 105.
Hamlet's Mill
142
trophe cleans out the past, which is replaced by "a new heaven
and a new earth," and ruled by a "new" Pole star. The biblical
flood was also the end of a world, and Noah's adventure is re-
hearsed in many traditions and many forms all over the planet. The
Greeks knew of three successive destructions.
Coherence will be re-established in this welter of traditions if it
is realized that what is referred to is that grandest of heavenly
phenomena, the Precession of the Equinoxes. The phenomenon has
been dealt with in the Intermezzo already, but it is essential enough
to be taken up more than once. Being so slow, and in a man's age so
imperceptible, it has been taken for granted9 that no one could have
detected the Precession prior to Hipparchus' alleged discovery
of the phenomenon, in 127 b.c. Hipparchus discovered and proved
that the Precession turns around the pole of the ecliptic.10 It is said
that it must have taken an almost modern instrumentation to detect
the motion over the brief space of a century, and this is certainly
correct. Nobody claims, however, that the discovery was deduced
from observations during one century. And the shift of 1 degree in
72 years, piling up over centuries, will produce appreciable shifts
in certain crucial positions, if the observers have enough intentness
of mind and know how to keep records. The technique of observa-
tion was relatively simple. It was based on the heliacal rising of
stars, which remained a fundamental feature in Babylonian astron-
omy. The telescope of early times, as Sir Norman Lockyer has said,
was the line of the horizon. If you came to realize that a certain star,
which was wont to rise just before the equinoctial sun, was no
longer visible on that day, it was clear that the gears of heaven
had shifted. If that star was the last one of a given zodiac figure, it
meant that the equinox was moving into a new figure. Nor is there
any doubt—as was already said—that far antiquity was already
aware of the shifting of the Pole star. But was it capable of con-
9 I.e., during the last hundred years, at least. In former times, when the Humani-
ties had not yet been "infected" by the biological scheme of evolution, the
scholars showed better confidence in the capacities of the creators of high civili-
zation.
10 Sec Ptolemy, Syntaxis 7.3 (Manitius trans., vol. 2, pp. 16f.). The magnitude
calculated by Hipparchus and accepted by Ptolemy was 1 degree in 100 years.
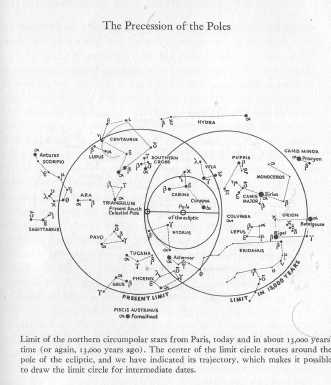
143 • Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
necting both motions? This is where modern specialists, operating
each from his own special angle of vision, have long hesitated.
What is the Precession? Very few have troubled to learn about
it, yet to any man of our time, who knows the earth to be spinning
around on her axis, the example of a spinning top with its inclined
axis slowly shifting around in a circle makes the knowledge intui-
tive. Anyone who has played with a gyroscope will know all about
the Precession. As soon as its axis is deflected from the vertical, the
gyroscope will start that slow and obstinate movement around the
compass which changes its direction while keeping its inclination
constant. The earth, a spinning top with an axis inclined with re-
spect to the sun's pull, behaves like a giant gyroscope, which per-
forms a full revolution in 25.920 years.
Antiquity was not likely to grasp this, since dynamics came into
this world only with Galileo. Hipparchus and Ptolemy could not
understand the mechanism. They could only describe the motion.
We must try to see through their eyes, and think only in terms of
kinematics. Over a period of a thousand years ancient observers
could discern in the secular shifting of the Great Gyroscope (it is
here in fact that the word "secular" now used in mechanics origi-
nates) a motion through about ten degrees. Once attuned to the
secular motion, they were able to detect, in the daily whirring of
heaven around the pole, in its yearly turning in the round of the
seasons, in the excruciatingly slow motion of the pole over the
years, a point which seemed intrinsically more stable than the pole
itself. It was the pole of the ecliptic,11 often referred to as the Open
Hole in Heaven because in that region there is no star to mark it.
The symmetries of the machine took shape in their minds. And
truly it was the time machine, as Plato understands it, the "moving
image of eternity." The "mighty marching and the golden burn-
ing," cycle upon cycle, even down to shifts barely perceptible over
the centuries, were the Generations of Time itself, the cyclical sym-
11 See A. Bouche-Leclerq, L'Astrologie Grecque (1899), p. 122: "On sait que le
pole par excellence etait pour les Chaldeans 1e pole de l'ecliptique, lequel est dans
la constellation du Dragon." Cf. also A. Kircher, Oedipus Aegyptiacus (1653), vol.
2. p2., p. 205: "Ponebant Aegyptii non Aequarorem, sed Zodiacum basis loco; ita
in centrum hemispherii utriusque non polum Mundi, sed polum Zodiaci referret."
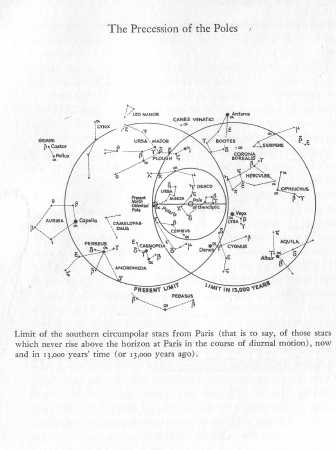
Hamlet's Mill
144
bol of everlastingness: for, as Aristotle says, what is eternal is circu-
lar, and what is circular is eternal.
Yet this uniformly working time machine could be marked
with important stations. The gyroscopic tilt causes a continual
shifting of our celestial equator, which cuts the inclined circle of
the ecliptic along a regular succession of points, moving uniformly
from east to west. Now the points where the two circles cross are
the equinoctial points. Hence the sun, moving on the ecliptic
through the year, meets the equator on a point which shifts steadily
with the years along the ring of zodiacal signs. This is what is meant
by the Precession of the Equinoxes. They "precede" because they
go against the order of the signs as the sun establishes this in its
yearly march. The vernal equinox—we called it the "fiducial point"
previously—which was traditionally the opening of spring and the
beginning of the year, will take place in one sign after another. This
gives great meaning to the change of signs in which the equinoctial
sun happens to rise.
Some additional words of guidance may be called for here, where
"signs" are mentioned—those "in" which the sun rises. For roughly
two thousand years official terminology has used only zodiacal
"signs," each of which occupies 30 degrees of the 360 degrees of the
whole circle. These signs have the names of the zodiacal constella-
tions, but constellations and signs are not congruent, the equinoctial
sign (= 1 deg. — 30 deg.) being called Aries regardless of the constellation
that actually rises before the equinoctial sun. In our time, the constel-
lation rising heliacally on March 21 is Pisces, but the "sign" preserves
the name Aries, and will continue to do so when in the future
Aquarius rules the vernal equinox. So much for sign versus constel-
lation.12 As concerns the second ambiguous expression, namely, the
12 Here, we leave out of consideration the much discussed question of exactly
when signs of equal length were first introduced; allegedly it was very late (see be-
low, p. 431, n. 1). The actual constellations differ widely in length—the huge Scor-
pion, e.g., covers many more degrees than 30, whereas the Ram is of modest dimen-
sions. One would think that this lack of uniformity would have so hampered the
ancient astronomers in making their calculations that they would have worked out
a more convenient frame of coordinates in sheer self-defense.
145 • Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
sun's rising "in" a constellation (or a sign)—this means that the sun
rises together with this constellation, making it invisible. There are
several reasons for assuming that a constellation (and a planet which
happened to be there), "in" which the equinoctial sun rose, was
termed to be "sacrificed," "bound to the sacrificial post," and the
like; and this might explain eventually why Christ, who opened the
world-age in which Pisces rose heliacally in the spring, was under-
stood as the sacrificed lamb. When Pisces is the last constellation
visible in the east before sunrise, the sun rises together, i.e., "in," the
constellation following next, the Ram.
Since the beginning of history, the vernal equinox has moved
through Taurus, Aries, and Pisces. This is all that historic experi-
ence has shown mankind: a section of about one-quarter of the
whole main circle of the machine. That it would come back full
circle was at best an inference. It might also, for all men knew,
have been part of an oscillation, back and forth, and in fact there
were two schools of thought about it, and the oscillation theory
seems to have exercised a greater attraction upon the mythographers
of old.
For us, the Copernican system has stripped the Precession of its
awesomeness, making it a purely earthly affair, the wobbles of an
average planet's individual course. But if, as it appeared once, it
was the mysteriously ordained behavior of the heavenly sphere, or
the cosmos as a whole, then who could escape astrological emotion?
For the Precession took on an overpowering significance. It became
the vast impenetrable pattern of fate itself, with one world-age suc-
ceeding another, as the invisible pointer of the equinox slid along
the signs, each age bringing with it the rise and downfall of astral
configurations and rulerships, with their earthly consequences.
Tales had to be told for the people about how successions of ruler-
ships arose from an origin, and about the actual creation of the
world, but for those in the know the origin was only a point in
the precessional circle, like the 0 = 24 of our dials. Our clocks today
show two pointers only; but the tale-tellers of those bygone days,
facing the immense and slow-moving machine of eternity, had to
Hamlet's Mill
146
keep track of seven planetary pointers besides the daily revolution
of the fixed sphere and of its secular motion in the opposite direc-
tion. All these motions meant parts of time and fate.
That things are not as they used to be, that the world is obvi-
ously going from bad to worse, seems to have been an established
idea through the ages. The unhinging of the Mill is caused by the
shifting of the world axis. Motion is the medium by which the
wrecking is brought about. The Mill is "transported," be it Grotte
or Sampo. The Grotte Song says explicitly that the giantesses first
ground forth enemy action whereby the Mill was carried away and
then, shortly afterwards, ground salt and wrecked the machine. It
was the end of "Frodhi's peace"—the Golden Age. Even in Snaeb-
jorn's famous lines, the grim goddesses "out at the edge of the world"
are those "who ground Amlodhi's meal in ages past." They can
hardly be doing it now, because the wrecked millstone is at the bot-
tom of the sea, with its hole become the funnel of the whirlpool. So
that Mill has been transferred to the waters, and it is now the sea
itself which has become "Amlodhi's churn." The heavenly Mill has
been readjusted, it goes on working in a new age. It churned once
gold, then salt, and today sand and stones. But one cannot expect the
rough Norse mythography to follow it in these legends, which are
centered upon storm and wreck, the end of that first age.
Even Hesiod is far from clear about the early struggles and cata-
clysms; it is enough that in his Works and Days he marks a succes-
sion of five ages. A more coherent picture can only be built out of
the convergence of several traditions, and this shall be the task of
further chapters. But right now, there is at least one age designated
as the first, when the Mill ground out peace and plenty. It is the
Golden Age, in Latin tradition, Saturnia regna, the reign of Saturn;
in Greek, Kronos. In this dim perplexing figure there is an extraordi-
nary concordance throughout world myths. In India it was Yama;
in the Old Persian Avesta it was Yima Xsaeta,13 a name which became
in New Persian Jamshyd; in Latin Saeturnus, then Saturnus. Saturn
13See H. Collitz, "Konig Yima und Saturn," Festschrift Pavry (1933), pp. 86-108.
See also A. Scherer, Gestirnnamen bei den indogermanischen Volkern (1953),
p. 87.
147 • Amlodhi the Titan and His Spinning Top
or Kronos in many names had been known as the Ruler of the
Golden Age, of that time when men knew not war and bloody
sacrifices not the inequality of classes—Lord of Justice and Mea-
sures, as Enki since Sumerian days, the Yellow Emperor and legis-
lator in China.
If one wants to find the traces of his sunken Mill in classical
mythology, they are not lacking.14 The oldest is to be found where
one would not expect it, in the Great Magical Papyrus of Paris,
which is dated about the first half of the fourth century a.d.15 In
its recipes is the "much demanded Oracle of Kronos, the so-called
Little Mill":
Take two measures of sea salt and grind it with a handmill, repeating
all the while the prayer that I give you, until the God appears. If you
hear while praying the heavy tread of a man and the clanking of
irons, this is the god that comes with his chains, carrying a sickle. Do
not be afraid, for you are covered by the protection that I give you.
Be wrapped in white linen such as the priests of Isis wear [here fol-
low a number of magic rites]. The prayer to be said while grinding
is as follows: I call upon thee, great and holy One, founder of the
whole world we live in, who sufferest wrong at, the hands of thy own
son, thee whom Helios bound with iron chains, so that All should not
come to confusion. Man-Woman, father of thunder and lightning,
thou who rulest also those below the earth. [There follow more rites
of protection, then the formula of dismissal]: Go, Lord of the World,
First Father, return to your own place, so that the All remain well
guarded. Be merciful, O Lord.16
14 Although the Telchines are entitled to be investigated thoroughly, we can only
mention them here: this strange family of "submarine magic spirits" and "demons
of the depth of the sea"—they are followers of Poseidon in Rhodes—have invented
the mill ; i.e., their leader did so—Mylas, "the miller." Knowing beforehand, it was
said, of the predestined flood which was to destroy Rhodes, these former inhabi-
tants left for Lycia, Cyprus and Crete, the more so, as they also knew that Helios
was going to take over the island after the flood. On the other hand, these envious
creatures—they have the "evil eye," too—are accused of having ruined the whole
vegetation of Rhodes by sprinkling it with Styx-water. As will come out later
(see "Of Time and the Rivers," p. 200), the waters of Styx are not so easily
to be had; that the Telchines, the "mill gods" (theoi mylantioi) had access to Styx
proves beyond doubt that these earliest defoliators had turned, indeed, into citizens
of the deep sea. See Griechische Mythologie, Preller-Robert (1964), vol. 1, pp.
650ff.; M. Mayer, Giganten und Titanen in der antiken Sage und Kunst (1887),
pp. 45, 98, 101; H. Usener, Gotternamen (1948), pp. 198f.
15 K. Preisendanz, Papyri Graecae Magicae (1928), vol. 1, p. 64.
10 4.308ff., Preisendanz, vol. 1, p. 173.
Hamlet's Mill
148
Sorcerers and conjurors are the most conservative people on
earth. Theirs is not to reason why; they call upon the Power in
terms they no longer understand, but they have to give an exact list
of the archaic attributes of the fallen god, and even grind out sea
salt from the Little Mill, the model of the whirlpool that marked his
downfall. What had once been science has become with them pure
technology, bent on preservation. A. Barb once coined a simile—
he had revealed religion in mind, however, not science; dealing with
the relation between magic practices and religion, he pointed to
Matt. xxiv.28, Luke xvii.37: "Wheresoever the carcase is, there will
the eagles be gathered together," and "Too many critical scholars
have been ready to assume that the carcase is therefore a creation
of the eagles. But eagles do not create; they disfigure, destroy and
dispense what life has left, and we must not mistake the colourful
display of decay for the blossoms and fruit of life."17 Poignant as
this image is, namely, in establishing the proper consecutio tem-
porum, it leaves out of consideration the preserving function of
magic and superstition: where would the historian of culture be
left without those "eagles"?
For all the titles and attributes here listed, there is justification in
archaic myth. Right here, only one point is of importance. The
Lord of the Mill is declared to be Saturn/Kronos, he whom his
son Zeus dethroned by throwing him off his chariot, and banished
in "chains" to a blissful island, where he dwells in sleep, for being
immortal he cannot die, but is thought to live a life-in-death,
wrapped in funerary linen, until his time, say some, shall come to
awaken again, and he will be reborn to us as a child.
17 "St. Zacharias," Journal of the Warburg and Courtauld Institutes 11 (1948),
p. 95. It has not escaped his attention, by the way, that it should be vultures.
Chapter X
The Twilight of the Gods
There was once, then, a Golden Age. Why, how, did it come
to an end? This has been a deep concern of mankind over time,
refracted in a hundred myths, explained in so many ways which
always expressed sorrow, nostalgia, despondency. Why did man
lose the Garden of Eden? The answer has always been, because of
some original sin. But the idea that man alone was able to commit
sin, that Adam and Eve are the guilty ones, is not very old. The
authors of the Old Testament had developed a certain conceit.
Christianity then had to come to rescue and restore cosmic propor-
tions, by insisting that God alone could offer himself in atonement.
In archaic times, this had seemed to be self-evident. The gods
alone could run or wreck the universe. It is there that we should
search for the origin of evil. For evil remains a mystery. It is not
in nature. The faultless and all-powerful machine of the heavens
should have yielded only harmony and perfection, the reign of
justice and innocence, rivers flowing with milk and honey. It did,
but that time did not last. Why did history begin to happen? His-
tory is always terrible. Philosophers from Plato to Hegel have
offered their own lofty answer: pure Being was confronted of a
necessity with Non-Being, and the result was Becoming, which is
an uninsurable business. This was substantially the original answer
of archaic times, but because of the lack of abstractions, it had to be
derived in terms of heavenly motions.
Aristotle, the Master of Those Who Know, has cleared up this
matter in a most important, yet little noted passage of Book Lambda
Hamlet's Mill
150
of Metaphysics (1074b) where he talks about Kronos, Zeus, Aphro-
dite, etc.:
Our forefathers in the most remote ages [archaioi kai panpalaioi]
have handed down to their posterity a tradition, in the form
[schema] of a myth, that these bodies are gods and that the divine
encloses the whole of nature. The rest of the tradition has been added
later in mythical form . . . ; they say that these gods are in the form
of men or like some of the other animals . . . But if one were to
separate the first point from these additions and take it alone—that
they thought the first substances to be gods, one must regard this as
an inspired utterance, and reflect that, while probably each art and
each science has often been developed as far as possible and has again
perished, these opinions, with others, have been preserved until the
present like relics [leipsana] of the ancient treasure.
Aristotle, being a true Greek, cannot conceive of progress in our
sense. Time proceeds for him in cycles of flowering and decay.
But this absence of modern preconceptions had left his mind open
to an ancient certainty. This certainty is what shines through the
mist of ages and through a language dimly understood. It was atten-
tion to the events of heaven which shaped men's minds before re-
corded history; but since there was as yet no writing, these thoughts
have receded, as astrophysicists would say, over the "event hori-
zon." They can survive only through fragments of tale and myth
because these made up the only technical language of those times.
Yet an enormous intellectual achievement is presupposed in this
organization of heaven, in naming the constellations and in tracing
the paths of the planets. Lofty and intricate theories grew to ac-
count for the motions of the cosmos. One would wonder about this
obsessive concern with the stars and their motion, were it not the
case that those early thinkers thought they had located the gods
which rule the universe and with it also the destiny of the soul
down here and after death.
In modern language, they had found the essential invariants
where Being is. In paying respect to those forefathers, Aristotle
shows himself clearly aware that his philosophical quest started with
them.
One should pay attention to the cosmological information con-
tained in ancient myth, information of chaos, struggle and violence.
151 • The Twilight of the Gods
They are not mere projections of a troubled consciousness: They
are attempts to portray the forces which seem to have taken part
in the shaping of the cosmos. Monsters, Titans, giants locked in
battle with the gods and trying to scale Olympus are functions and
components of the order that is finally established.
A distinction is immediately clear. The fixed stars are the essence
of Being, their assembly stands for the hidden counsels and the
unspoken laws that rule the Whole. The planets, seen as gods,
represent the Forces and the Will: all the forces there are, each of
them seen as one aspect of heavenly power, each of them one
aspect of the ruthless necessity and precision expressed by heaven.
One might also say that while the fixed stars represent the kingly
power, silent and unmoving, the planets are the executive power.
Are they in total harmony? This is the dream that the contem-
plative mind has expressed again and again, that Kepler tried to fix
by writing down the notes of his "Harmony of the Spheres," and
that was consecrated in the "turning over" of the sky. This is the
faith expressed by ancient thinkers in a Great Year, in which all the
motions brought back all the planets to the same original configura-
tion. But the computations created doubt very early and with it
anxiety. Only rarely is there an explicit technical statement of those
views. Here is one from the Egyptian Book of the Dead, Osiris
speaking:
"Hail, Thoth! What is it that hath happened to the divine children of
Nut! They have done battle, they have upheld strife, they have made
slaughter, they have caused trouble: in truth, in all their doing the
mighty have worked against the weak. Grant, BO might of Thoth, that
that which the God Atum hath decreed (may be accomplished)! And
thou regardest not evil nor art thou provoked to anger when they
bring their years to confusion and throng in and push to disturb their
months; for in all that they have done unto thee, they have worked
iniquity in secret."1
Thoth is the god of science and wisdom; as for Atum, he precedes,
SO to speak, the divine hierarchy. Described only in metaphysical
terms, he is the mysterious entity from which the All sprang: his
1 Chapter 179, 1-8, W. Budge trans. The italics are ours.
Hamlet's Mill • 152
name might be Beginning-and-End. He is thus the Presence and the
secret Counsel whom one feels tempted to equate with the starry
sky itself. His decree must be of immutable perfection. But here it
appears that there are forces which have worked iniquity in secret.
They appear everywhere, these forces, and regularly they are de-
nounced as "overbearing," or "iniquitous," or both. But these
"forces" are not iniquitous right from the beginning: they turn out
to be, they become overbearing in the course of time. Time alone
turns the Titans, who once ruled the Golden Age, into "workers of
iniquity" (compare appendix #12). The idea of measure stated or
implied will show the basic crime of these "sinners": it is the over-
reaching, overstepping of the ordained degree, and this is meant
literally.2 Says the Mahabharata about the Indian Titans, the Asura:
"assuredly were the Asura originally just, good and charitable, knew
the Dharma and sacrificed, and were possessed of many other vir-
tues . . . But afterwards as they multiplied in number, they became
proud, vain, quarrelsome . . . they made confusion in everything.
Thereupon in the course of time . . ." they were doomed.3
Thus severe consequences must be expected when Gen. vi.i com-
mences with the formula, "when men began to multiply on the
face of the earth . . ." And sure enough, ten verses later, Gen. vi.11,
the time for grave decisions has come: "And God said to Noah,
'I have determined to make an end of all flesh!' " More outspoken
is the 18th chapter of the Book of Enoch, where an Angel acts as
Enoch's guide through the celestial landscape. In showing him the
quarters destined for iniquitous personalities, the Angel tells Enoch:
"These stars which roll around over the fire are those who, at rising
time, overstepped the orders of God: they did not rise at their ap-
2 It is only the careless manner in which we usually deal with precise terms that
blocks the understanding: e.g., Greek moira, also written moros, is translated as
"fate," "destiny," sometimes as "doom"; moira is one degree of the 360 deg. of the
circle; when we keep this in mind we understand better such lines as Od. 1.
34-35, where Aegisthus is accused twice of having done deeds "hyper moron,"
beyond degree. How could one overstep one's destiny? How could one be over-
measured against fate? This would invalidate the very concept of "destiny."
3 V. Fausboll, Indian Mythology according to the Mahabharata (1902), pp. 40f.
153 • The "Twilight of the Gods"
pointed time. And He was wroth with them, and He bound them
for 10,000 years until the time when their sin shall be fulfilled."4
Yet one must beware of simplifications. The wording, "assuredly
were the Asura originally just, good and charitable," goes for the
Titans, too, the forces of the first age of the world. But seen
through the "eyeglasses" of the preceding state of things, Titans,
Asura and their like had committed atrocities first. And so did
Saturn, the "originator of times," and in the drastic measure he
took to accomplish the "separation of the parents of the world,"
which stands for the falling apart of the axes of equator and
ecliptic. Before this separation time did not exist. These "united
parents"—heartlessly called "chaos" by Macrobius—resented the
breaking up of the original eternity by the forces which worked
iniquity in secret.5 These forces as they appear in the Enuma elish,
the so-called Babylonian Creation Epic, are the children of Apsu
and Tiamat and they crowded in between their parents. "They
disturbed Tiamat as they surged back and forth; yea, they troubled
the mood of Tiamat. Apsu could not lessen their clamor . . . Un-
savory were their ways, they were overbearing."6
Not having "multiplied" yet, this first generation of the world
established the Golden Age under the rule of Him of many names
—Enki, Yima, Freyr and many more. "But these sons whom he
begot himself, great Heaven [megas Ouranos] used to call Titans
[Strainers] in reproach, for he said that they strained and did pre-
sumptuously a fearful deed, and that vengeance for it would come
afterwards," as Hesiod has it (Theogony 207-10).7 And so it
would, after their "multiplication," when they overstrained the
4 E. Kautzsch, ed., Die Apokryphen und Pseudoepigraphen des Alien Testaments
(1900)Vol. 2, pp. 249f.
5 There is no complete unanimity among mythographers, though; in Hesiod's
Theogony, Gaia "rejoiced greatly in spirit" (173) when Kronos promised to do
away with Father Ouranos according to Gaia's very own plan and advice.
6EE Tabl. 1 .22-28 (E. Speiser trans.), ANET, p. 61.
7 This translation by H. G. Evelyn-White (LCL) pays no regard to a "pun," a
rather essential one, indeed. Hesiod makes use, side by side in these few lines, of
both radicals from which "Titan" was supposed to have been derived: titaino, "to
strain," and tisis, "vengeance."
Hamlet's Mill
measure. And it was bound to happen again when future genera-
tions would construct "forbidden ways to the sky,"8 or build a
tower which happened to be too high. The one secure measure, the
"golden rope" of the solar year,9 is stretched beyond repair. The
equinoctial sun had been gradually pushed out of its Golden Age
"sign," it had started on the way to new conditions, new configura-
tions. This is the frightful event, the inexpiable crime that was
ascribed to the Children of Heaven. They had nudged the sun out
of place, and now it was on the move, the universe was out of kilter
and nothing, nothing—days, months or years, the rising or setting of
stars—was going to fall into its rightful place any more. The equi-
noctial point had nudged and nuzzled its way forward, in the very
same way as a car with automatic gearshift will nuzzle its way for-
ward unless we put it in neutral—and there was no way of putting
the equinox in neutral. The infernal pushing and squeezing of the
Children of Heaven had separated the parents, and now the time
machine had been set rolling forever, bringing forth at every new
age "a new heaven and a new earth," in the words of Scripture. As
Hesiod says, the world had entered now the second stage, that of
the giants, who were to wage a decisive battle with the restraining
forces before their downfall.
The vision of a whole world-age with its downfall is given by
the Edda. It comes in the very first poem, the Song of the Sibyl, the
Voluspa, in which the prophetess Vala embraces past and future in
adequately strange and obscure language. At the beginning of the
Age of the Aesir, the gods gather in council, and give names to
sun and moon, days and nights and seasons. They order the years
and assign to the stars their places. On Idavollr (the "whirl-field";
ida = eddy), they establish their seat "in the Golden Age" and play
checkers with golden pieces, and all is happiness until "the three
awful maidens" come (this is another mystery).10 But once before,
8 Claudianus 26.69-71, speaking of the Aloads, who piled Ossa upon Olympus.
9 See e.g., RV 5.85.5: "This great feat of the famous Asurian Varuna I shall pro-
claim who, standing in the air, using the Sun as an inch scale, measured the earth."
10 The three maidens from Jotunheimr are not the Norns, this much can be safely
said, but should be Gulveig the "thrice born," whom the Aesir killed "thrice, and
still she is living" (Voluspa 8): one more "iniquity" asking for vengeance.
155 • The Twilight of the Gods
it is hinted, there has been a "world war" between Aesir and Vanir,
which was terminated by a sharing of power. In a vision in which
past and future blend in a flash, Vala sees the outcome and an-
nounces it to the "high and low children of Heimdal," that is, to
all men. She asks them to open their eyes, to understand what the
gods had to know: the breaking of the peace, the murder of Thjassi,
Odin himself abetting the crime and nailing Thjassi's eyes to
heaven. With this a curtain is lifted briefly over a phase of the
past. For Thjassi belongs to the powers that preceded the Aesir.
In Greek terms, the Titans came before the gods. The main Vana
or Titanic powers (in Rydberg's thoughtful reconstruction) are
the three brothers, Thjassi/Volund, Orvandil/Eigil, and Slagfin:
the Maker, the Archer, and the Musician. This finally locates Or-
vandil the Archer, the father of Amlethus. He is one of the three
"sons of Ivalde," just as their counterparts in the Finnish epic are
the "sons of Kaleva."11 And Ivalde, like Kaleva, is barely mentioned,
never described, at least not under the name Ivalde: there is a
glimpse at him under his other name, Wate. Like Kaleva, he is a
meaningful void. But all this is of the past. The Sibyl's vision is
projected toward the onrushing end. True, Loke has been chained
in Hell since he brought about the death of Balder, the great Fenrir
wolf is still fettered with chains, once cunningly devised by Loke
himself, and they are made up of such unsubstantial things as the
footfall of a cat, the roots of a rock, the breath of a fish, the spittle
of a bird.12
Now the powers of the Abyss are beginning to rise, the world is
coming apart. At this point Heimdal comes to the fore. He is the
Warner of Asgard, the guardian of the Bridge between heaven and
earth, the "Whitest of the Aesir," but his role, his freedom of
action, is severely limited. He has many gifts—he can hear grass
grow, he can see a hundred miles away—but these powers seem to
11 Strange to say, the three brothers, Volund, Eigil and Slagfin, are called "synir
Finnakonungs," i.e., "sons of a Finnish king" (J. Grimm, TM, p. 380).
12 Again, strange to say, this very kind of "un-substance"— including the milk of
Mother Eagle, and the tears of the fledglings—had to be provided for by Tibetan
Bogda Gesser Khan, who also snared the sun.
154
Hamlet's Mill
156
remain ineffectual. He owns the Gjallarhorn, the great battle horn
of the gods; he is the only one able to sound it, but he will blow it
only once, when he summons the gods and heroes of Asgard to
their last fight.
Nordic speculation down to Richard Wagner has dwelt with
gloomy satisfaction on Ragnarok,13 the Twilight of the Gods, which
will destroy the world. There is the prediction in the Song of
the Sibyl, and also in Snorri's Gylfaginning: when the great dog
Garni barks in front of the Gnipa cave, when the Fenrir wolf
breaks his fetters and comes from "the mouth of the river,"14 his
jaws stretching from heaven to earth, and is joined by the Midgard
Serpent, then Heimdal will blow the Gjallarhorn, the sound of
which reaches through all the worlds: the battle is on. But it is
written that the forces of order will go down fighting to atone for
the initial wrong done by the gods. The world will be lost, good
and bad together. Naglfar, the ship of the dead, built with the
nail parings of the living, will sail through the dark waters and
bring the enemy to the fray. Then, adds Snorri:
The heavens are suddenly rent in twain, and out ride in shining squad-
rons Muspel's sons, and Surt with his flaming sword, at the head of
the fylkings.15
13 For the etymology of ragnarok, see Cleasby-Vigfusson, An Icelandic-English
Dictionary, in which regin (whence ragna) is defined as "the gods as the makers
and rulers of the universe"; rok as "reason, ground, origin" or "a wonder, sign,
marvel"; and ragna rok as "the history of the gods and the world, but especially
with reference to the last act, the last judgment." The word rdkr, a possible alter-
nate to rok, is defined as "the twilight . . . seldom of the morning twilight," and
"the mythological phrase, ragna rokr, the twilight of gods, which occurs in the
prose Edda (by Snorri), and has since been received into modern works, is no
doubt merely a corruption from rok, a word quite different from rokr."
Taking into consideration that the whole war between the Pandavas and the
Kauravas, as told in the Mahabharata, takes place in the "twilight" between
Dvapara and Kali Yuga, there is no cogent reason to dismiss Snorri's ragna rokr
as a "corruption." But then, the experts also condemned Snorri's comparison be-
tween Ragnarok and the Fall of Troy: the logical outcome of their conviction that
"poetry" is some kind of creatio ex nihilo, whence the one question never raised
is whether the poets might not be dealing with hard scientific facts.
14Lokasenna 41; see also V. Rydberg, Teutonic Mythology (1907), p. 563.
15 Gylf. 51.
157 • The Twilight of the Gods
All-engulfing flames come out with Surt "the Black," Who kills
Freyr, the Lord of the Mill. Snorri makes Surt "Lord of Gimle"
and likewise the king of eternal bliss "at the southern end of the
sky."16 He must be some timeless force which brings destructive
fire to the world; but of this later.
Hitherto all has been luridly and catastrophically and murkily
confused as it should be. But the character of Heimdal raises a
number of sharp questions. He has appeared upon the scene as "the
son of nine mothers"; to be the son of several mothers is a rare dis-
tinction even in mythology, and one which Heimdal shares only
with Agni in the Rigveda,17 and with Agni's son Skanda in the
Mahabharata. Skanda (literally "the jumping one" or "the hopping
one") is the planet Mars, also called Kartikeya, inasmuch as he was
borne by the Krittika, the Pleiades. The Mahabharata18 insists on
six as the number of the Pleiades as well as of the mothers of Skanda
and gives a very broad and wild description of the birth and the
installation of Kartikeya "by the assembled gods ... as their gen-
eralissimo," which is shattering, somehow, driving home how little
one understands as yet.19
The nine mothers of Heimdal bring to mind inevitably the nine
goddesses who turn the mill. The suspicion is not unfounded. Two
of these "mothers," Gjalp and Greip, seem to appear with changed
16 Gylf. 17;,cf. R. B. Anderson, The Younger Edda (1880), p. 249. That Surt is
Lord of Gimle is a particularly important statement; it will not be found in the
current translations of Snorri, but only in the Uppsala Codex: "there are many
good abodes and many bad; best it is to be in Gimle with Surt" (Rydberg, p. 651).
17 RV 10.45.2 points to nine births, or mothers; 1.141.2 tells of the seven mothers
of Agni's second birth. Most frequently, however, Agni has three "mothers," cor-
responding to his three birthplaces: in the sky, on the earth, in the waters.
18Mbh. 9.44-46 (Roy trans, vol. 7, pp. 130-43). It should be emphasized, aloud
and strongly, that in Babylonian astronomy Mars is the only planetary representa-
tive of the Pleiades. See P. F. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum (1950), p. 279:
"In der Planetenvertretung kommt fur die Plejaden nur Mars in Frage."
19The least which can be said, assuredly: Mars was "installed" during a more or
less close conjunction of all planets; in Mbh. 945 (p. 133) it is stressed that the
powerful gods assembled "all poured water upon Skanda, even as the gods had
poured water on the head of Varuna, the lord of waters, for investing him with
dominion." And this "investiture" took place at the beginning of the Krita Yuga,
the Golden Age.
Hamlet's Mill
158
names or generations as Fenja and Menja.20 Rydberg claims Heim-
dal to be the son of Mundilfoeri. The story is then astronomical.
Where does it lead? Thanks to the clues provided by Jacob Grimm,
Rydberg and O. S. Reuter, and thanks to many hints hidden in the
Rigveda, Atharva Veda and at other unexpected places, one can
offer a probable conclusion: Heimdal stands for the world axis,
the skambha. His head is the "measurer" (mjotudr) of the same
measures that the Sibyl claims to understand: "Nine worlds I know,
nine spaces of the measure-tree which is beyond (fyr) the earth."
"Measure-tree" is the translation of mjowidr,21 which so-called
poetic versions usually render as "world tree." The word fyr ap-
pears here again; it connotes priority; in this verse 2 of Voluspa it
is translated as "below" in most of the cases. The question "who
measures what?" would require an extensive analysis; here, with
no need for so many details, it is important only to learn that Heim-
dal is honored by a second name, Hallinskidi (appendix #16).
This name is said to mean a bent, bowed or slanted stake or post.
To be bent or inclined befits the world axis and all that belongs
to it, with the one exception of the observer who stands exactly at
the terrestrial North Pole. Why not call it "oblique" or slanting
right away?22 Whether bent or oblique, Grimm rightly says that it
20 For the names of these mothers, see Hyndluljod 38; for Gjalp and Greip,
daughters of the giant Geirroed, see Snorri's Skaldskaparmal 2, and Thorsdrapa,
broadly discussed by Rydberg (pp. 932-52), who established Greip as the mother
of the "Sons of Ivalde." R. Much claims the identity of Geirroed with Surt ("Der
germanische Himmelsgott," in Ablandlungen zur germemische Philologie [1898],
p. 221). The turning up of a plurality of mothers in the ancient North, and in India
(see also J. Pokorny, "Ein neun-monatiges Jahr im Keltischen," OLZ 21 [1918],
pp. 130-33) might induce the experts eventually to reopen the trial of those per-
fectly nonsensical seven or nine, even fourteen, "motherwombs" which haunt the
Babylonian account of the creation of man. (Cf. E. Ebeling, Tod und Leben
[1931], pp. 172-77; E. A. Speiser (trans.), "Akkadian Myths and Epics," ANET,
pp. 99f.; W. von Soden, Or. 26, pp. 309ff.)
21 O. S. Reuter, Germanische Himmelskunde (1934), pp. 236, 319. As concerns
mjotudr (measurer) and its connection with Sanskrit matar and with meter, men-
sar, etc., see Grimm, TM, pp. 22, 1290. Reuter (p. 236) quotes Lex. Poet. Boreale
408, where mjotudr = fate.
22 We have more of this mythological species of oblique posts or trees—e.g., the
Rigvedic "sacrificial post"—and even Bears are not afraid to inhabit the one or the
other. See F. G. Speck and J. Moses, The Celestial Bear Comes Down to Earth:
The Bear Sacrifice Ceremony of the Munsee-Mohican in Canada (1945).
159 • The Twilight of the Gods
is "worthy of remark that Hallinskidi and Heimdal are quoted
among the names for the Ram.23 Heimdal is the "watcher" of the
much-trodden bridge of the gods which finally breaks down at
Ragnarok; his "head" measures the crossroads of ecliptic and
equator at the vernal equinox in Aries,24 a constellation which is
called "head" also by Cleomedes,25 and countless astromedical illus-
trations show the Ram ruling the head (Pisces the feet). Accord-
ingly, one might say that the Sibyl addresses herself to "the high
and low children of Aries."
Recalling Rigvedic Agni, son of seven to nine mothers like Heim-
dal, and remembering what has been said of "fire," that it means
a great circle connecting the celestial poles, the scheme becomes
more understandable. Heimdal stands for the equinoctial colure
which "accompanies" the slowly turning, wholly abstract and invis-
ible axis along the surface of the sphere. It will emerge presently
that "axis" always means the whole "frame" of a world-age, given
by the equinoctial and solstitial colures.26 More understandable also
becomes another epithet of Heimdal, namely, Vindler, of which
Rydberg states (p. 595): "The name is a subform of vindill and
comes from vinda, to twist or turn, wind, to turn anything around
rapidly. As the epithet 'the turner' is given to that god who
brought friction-fire (bore-fire) to man, and who is himself the
personification of this fire, then it must be synonymous with 'the
borer.' "
23 TM, p. 234. Rydberg (p. 593) spells it: "In the old Norse poetry Vedr (wether,
ram) Heimdal and the Heimdal epithet hallinskidi, are synonymous."
24 A. Ohlmarks, Heimdalls Horn und Odins Auge (1937), p. 144, makes the god
a he-goat. That would not be bad, either, if he is right, since Capella, alpha
Aurigae, "capricious" all over, whether male or female, has the name "asar bar-
dagi = Fight of the Aesir" (Reuter, p. 279). Of Auriga-Erichthonios we shall hear
more in the future.
25 Instead of "head" (kephalos), Nonnos calls Aries mesomphalos, "midnavel,"
of Olympus.
26 It should be remarked that Snorri's identification (Glyf.13) of the bridge
Bifroest with the rainbow made scholars rush to rescue a definitely regular phenom-
enon from the hazardous existence which is allotted to a rainbow; they voted for
the Milky Way instead. With this we are not likely to agree. See A. Ohlmarks,
"Stellt die mythische Bifroest den Regenbogen oder die Milchstrasse dar?" Medd.
Lunds Astron. Observ. (1941), scr. II, no. 110, and Router, p. 284, quoting addi-
tional literature.
Hamlet's Mill
160
The Sibyl's prophecy does not end with the catastrophes, but it
moves from the tragic to the lydic mode, to sing of the dawning of
the new age:
Now do I see
the Earth anew
Rise all green
from the waves again . . .
Then fields unsowed
bear ripened fruit
All ills grow better.
Even if that generation of gods has perished, the younger ones re-
main: Balder and Hoder, also the two sons of Thor, and Vidar the
son of Odin. The House of the Wise Vanir is not affected as a
whole, even if Freyr fell in battle. As the Vanir belong to a past age,
this crisis apparently does not concern them. There is in fact a cer-
tain perversely nightmarish or neurotic unreality about the tragedy
as a whole. The Wolf's fetters were made of nothing but he was
able to snap them only when the time came, when Odin and the
Sun had to be devoured. The next instant, young Vidar kills the
monster simply by thrusting his shoe down his throat (he has one
shoe only, just like Jason). It is guilt and the ensuing chaos, more
than actual forces, which dragged down the Establishment once
the appointed time came, as decreed by fate and sounded on the
Gjallarhorn.
What happens after (or happened, or will happen sometime, for
this myth is written in the future tense), is told in the Voluspa, but
it is also amplified in Snorri's Gylfaginning (53), a tale of a strange
encounter of King Gylfi with the Aesir themselves, disguised as
men, who do not reveal their identity but are willing to answer
questions: "What happens when the whole world has burned up,
the gods are dead, and all of mankind is gone? You have said earlier,
that each human being would go on living in this or that world."
So it is, goes the answer, there are several worlds for the good and
the bad. Then Gylfi asks : "Shall any gods be alive, and shall there
be something of earth and heaven?" And the answer is:
161 • The Twilight of the Gods
"The earth rises up from the sea again, and is green and beautiful and
things grow without sowing. Vidar and Vali are alive, for neither the
sea nor the flames of Surt have hurt them and they dwell on the
Eddyfield, where once stood Asgard. There come also the sons of
Thor, Modi and Magni, and bring along his hammer. There come
also Balder and Hoder from the other world. All sit down and con-
verse together. They rehearse their runes and talk of events of old
days. Then they find in the grass the golden tablets that the Aesir once
played with. Two children of men will also be found safe from the
great flames of Surt. Their names, Lif and Lifthrasir, and they feed
on the morning dew and from this human pair will come a great
population which will fill the earth. And strange to say, the sun, be-
fore being devoured by Fenrir, will have borne a daughter, no less
beautiful and going the same ways as her mother."
Then, all at once, concludes Snorri's tale wryly, a thunderous
cracking was heard from all sides, and when the King looked again,
he found himself on the open plain and the great hall had vanished.
The times and tenses are deliberately scrambled, but the state-
ments, even if elliptical, are pregnant with ancient meaning. The
rediscovery of the pieces of the game lying around in the grass,
already told in the Voluspa, becomes clearer if one thinks of the
Rigveda, where the gods themselves are said to go around like
ay as, that is, casts of dice.27 It becomes more understandable still
when one considers that the name of the Indian world-ages (Yuga)
has been taken from the idiom of dicing.28 But both data could be
dismissed as unrevealing were it forgotten that in several kinds of
"proto-chess"—to use an expression of J. Needham—board garner
and dicing were combined: the number of eyes thrown by the dice
determined the figure which was to be moved.29 That this very rule
was also valid for tafl, the board game mentioned in the Voluspa,
has been shown by A. G. van Hamel.30 Thus, the dice forced the
hands of the chess player—a game called "planetary battles" by the
Indians, and in 16th-century Europe still termed "Celestial War, or
27 RV 10.116.9; in 10.34.8, the dice are called vrata, i.e., an organized "gang"
under a king; the king is Rudra.
28 Krita, Treta, Dvapara, Kali, this last one being the worst cast (which the
Greeks termed "dog"). See H. Luders, Das Wurfelspiel im Alten lndien (1907),
pp. 41,63f.
W. H. Luders, p. 69; see also S. Culin, Chess and Playing Cards (1898), p. 857.
30 "The Game of the Gods," Arkiv fur Nor disk Filologi 50 (1934), p, 230.

Hamlet's Mill • 162
Astrologer's Game,"31 whereas the Chinese chessboard shows the
Milky Way dividing the two camps. Which goes to show that the
Icelanders knew what they were talking about.
Finally, there is one remarkable and disturbing coincidence from
the same direction. It is known that in the final battle of the gods,
the massed legions on the side of "order" are the dead warriors, the
"Einherier" who once fell in combat on earth and who have been
transferred by the Valkyries to reside with Odin in Valhalla—a
theme much rehearsed in heroic poetry. On the last day, they issue
forth to battle in martial array. Says the Grimnismal (23): "Five
hundred gates and forty more—are in the mighty building of Wal-
halla—eight hundred 'Einherier' come out of each one gate—on
the time they go out on defence against the Wolf."
That makes 432,000 in all, a number of significance from of old.
This number must have had a very ancient meaning, for it is also
the number of syllables in the Rigveda. But it goes back to the basic
figure 10,800, the number of stanzas in the Rigveda (40 syllables
to a stanza) which, together with 108, occurs insistently in Indian
tradition. 10,800 is also the number which has been given by Hera-
clitus for the duration of the Aion, according to Censorinus (De die
natali 18), whereas Berossos made the Babylonian Great Year to
last 432,000 years. Again, 10,800 is the number of bricks of the
Indian fire-altar (Agnicayana).32
"To quibble away such a coincidence," remarks Schroder, "or
to ascribe it to chance, is in my opinion to drive skepticism beyond
its limits."33 Shall one add Angkor to the list? It has five gates, and
to each of them leads a road, bridging over that water ditch which
surrounds the whole place. Each of these roads is bordered by a row
of huge stone figures, 108 per avenue, 54 on each side, altogether
540 statues of Deva and Asura, and each row carries a huge Naga
31 A. Bernhardi, "Vier Konige," BA 19 (1936), pp. 171f. See J. Needham, Science
and Civilization in China, vol. 4, Pt. I: Physics (1962), p. 325, about a book on
chess published in 1571 under the title Uranomachia seu Astrologorum Ludus.
32 See J. Filliozat, "L'Inde et les echanges scientifiques dans l'antiquite," Cahiers
d'histoire mondiale 1 (1953), pp. 358f.
33 F. R. Schroder, Altgermcmische Kulturprobleme (1929), pp. 80f.

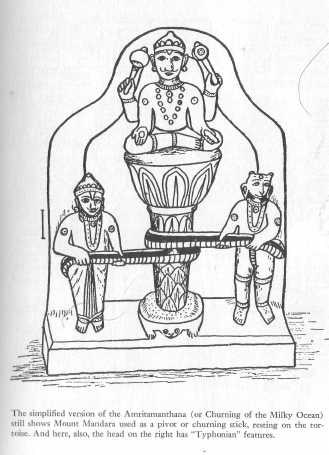
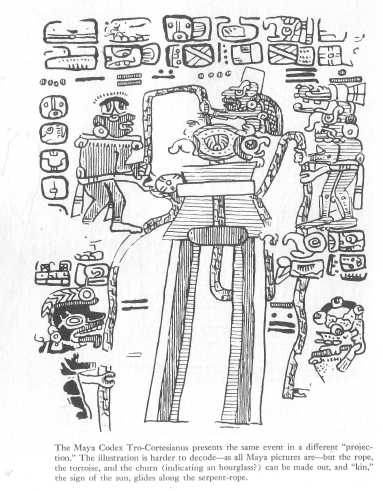
163 • The Twilight of the Gods
serpent with nine heads. Only, they do not "carry" that serpent,
they are shown to "pull" it, which indicates that these 540 statues
are churning the Milky Ocean, represented (poorly, indeed) by the
water ditch,34 using Mount Mandara as a churning staff, and Vasuki,
the prince of the Nagas, as their drilling rope. (Just to prevent mis-
understanding: Vasuki had been asked before, and had agreeably
consented, and so had Vishnu's tortoise avatar, who was going to
serve as the fixed base for that "incomparably mighty churn," and
even the Milky Ocean itself had made it clear that it was willing to
be churned.) The whole of Angkor thus turns out to be a colossal
model set up for "alternative motion" with true Hindu fantasy and
incongruousness to counter the idea of a continuous one-way
Precession from west to east.
Now there is a last paragraph in the Gylfaginning, which is usu-
ally considered an afterword, and its authorship is in doubt, for it is
supposed that Snorri's Edda was completed by Olaf Hvitaskald
(d. 1259), Snorri's nephew. In any case, this addition is somewhat
out of the previous context, but it reinforces it:
The Aesir now sat down to talk, and held their counsel, and remem-
bered all the tales that were told to Gylfi. They gave the very same
names that had been named before to the men and places that were
there. This they did for the reason that, when a long time had elapsed,
men should not doubt that those to whom the same names were
given, were all identical. There was one who is called Thor, and he
is Asa-Thor, the old. He is Oeku-Thor (Chariot-Thor) and to him
are ascribed the great deeds by Hektor in Troy.
As for the rebirth of the world, another "Twilight" comes to
mind. It is in the Kumulipo, a Polynesian cosmogonic myth from
Hawaii. "Although we have the source of all things from chaos, it
is a chaos which is simply the wreck and ruin of an earlier world."35
Now turns the swinging of time over on the burnt-out world
Back goes the great turning of things upwards again
As yet sunless the time of shrouded light;
34 R. von Heine-Geldern, "Weltbild und Bauform in Siidostasien," in Wiener
Beitrage zur Kunst- und Kulturgeschicte 4 (1930), pp. 41f.
35 R. B. Dixon, Oceanic Mythology (1910), p. 15.
Hamlet's Mill
164
Unsteady, as in dim moon-shimmer,
From out Makalii's night-dark veil of cloud
Thrills, shadow-like, the prefiguration of the world to be?6
So sang an Oceanian Empedocles long ago. The poem was drawn
from very old royal tradition, just as Virgil had drawn his from
the story of the Gens Julia, for the true original line of Hawaiian
kings was supposed to come from Kane, the Demiurge God of the
Pacific.
36 A. Bastian, Die Heilige Sage der Polynesier (1881), pp. 69-121. Along with
Roland B. Dixon, who translated the last three lines above, we have relied on the
German of Bastian, who was an outstanding authority on Polynesian culture and
language. Modern experts have their own way. M. Beckwith (Hawaiian Mythology
[1940], p. 58) translates these lines thus: "At the time when the earth became hot/
At the time when the heavens turned about/At the time when the earth was
darkened/To cause the moon to shine/The time of the rise of the Pleiades."
As concerns Makalii (Maori: Matariki; Micronesian and Melanesian dialects
spell it Makarika, and the like), it is the name for the Pleiades, although more often
we come across the phrase "the net of Makalii" (the correct form: Huihui-o-
Matariki, i.e., the cluster of M.). The "person" Makalii, to whom this net belongs,
as well as a second one (see p. 175) which we have reason to take for the Hyades,
remains in the dark. See E. Tregear, The Maori-Polynesian Comparative Dic-
tionary (1891) s.v. Matariki; N. B. Emerson, Unwritten Literature of Hawaii
(1909), p. 17; M. W. Makemson, The Morning Star Rises: An Account of Poly-
nesian Astronomy (1941), nos. 327, 380; Beckwith, p. 368; K. P. Emory, Tuamo-
tuan Religious Structures and Ceremonies (1947), p. 61. For the Hyades and
Pleiades as "celestial hunting nets" of the Chinese sphere, see G. Schlegel, L'Urano-
graphie Chinoise (1875; repr. 1967), pp. 365-70.
Chapter XI
Samson Under Many Skies
Why was my breeding ordered and prescribed
As of a person separate to God,
Designed for great exploits, if I must die
Betrayed, captived, and both my eyes put out. . .
O dark dark dark, amid the blaze of noon,
Irrevocably dark, total eclipse
Without all hope of day!
O first-created beam, and thou great Word,
"Let there be light, and light was over all"
Why am I thus bereaved thy prime decree?
Samson Agonistes
he story of Samson stands out in the Bible as a grand tissue
of absurdities. Sunday school pupils must long have been puzzled
about his weapon for killing Philistines: But there is much more to
puzzle about (Judges xv):
15. And he found a new jawbone of an ass, and put forth his hand
and took it, and slew a thousand men therewith.
16. And Samson said, with the jawbone of an ass, heaps upon heaps,
with the jaw of an ass have I slain a thousand men.
17. And it came to pass, when he had made an end of speaking, that
he cast away the jawbone out of his hand, and called that place
Ramathle'hi.
18. And he was sore athirst, and called on the Lord, and said, Thou
hast given this great deliverance into the hand of thy servant: and
now shall I die for thirst, and fall into the hand of the uncircumcised?
19. But God clave an hollow/place that was in the jaw, and there
Came water thereout; and when he had drunk, his spirit came again,
and he revived: wherefore he called the name thereof En-hak'ko-re,
which is in Le'hi unto this day.
20. And he judged Israel in the days of the Philistines twenty years.
If
Hamlet's Mill
166
■/
The passage has been bowdlerized in the Revised Version to
make it more plausible, but verse 18 is an unshakable reminder that
this was not an ordinary bone, or even "the place" of it as suggested
recently. For that jaw is in heaven. It was the name given by the
Babylonians to the Hyades, which were placed in Taurus as the
"Jaw of the Bull." If we remember the classic tag "the rainy
Hyades" it is because Hyades meant "watery." In the Babylonian
creation epic, which antedates Samson, Marduk uses the Hyades as
a boomeranglike weapon to destroy the brood of heavenly mon-
sters. The whole story takes place among the gods. It is known,
too, that Indra's powerful weapon, Vajra, the Thunderbolt made
of the bones of horse-headed Dadhyank, was not of this earth (see
appendix #19).
The story is so universal that it must be seen as spanning the
globe. In South America, where bulls were still unknown, the
Arawaks, the Tupi, the Quechua of Ecuador spoke of the "jaw of
the tapir," which was connected with the great god, Hunrakan, the
hurricane, who certainly knows how to slay his thousands. In our
sky, the name of the celestial Samson is Orion, the mighty hunter,
alias Nimrod. He remains such even in China as "War Lord Tsan,"
the huntmaster of the autumn hunt, but the Hyades are changed
there into a net for catching birds. In Cambodia, Orion himself
became a trap for tigers; in Borneo, tigers not being available, pigs
have to substitute; and in Polynesia, deprived of every kind of big
game, Orion is found in the shape of a huge snare for birds. It is this
snare that Maui, creator-hero and trickster, used to catch the Sun-
bird; but having captured it, he proceeded to beat it up, and with
what?—the jawbone of Muri Ranga Whenua, his own respected
grandmother.
If one brings Samson—the biblical Shimshon—back to earth, he
becomes a preposterous character, or rather, no character at all,
except for his manic violence and his sudden passions. It comes as
a shock, after reading that chaotic and whimsical life, to find: "And
he judged Israel twenty years." For if anyone was bereft of judg-
ment, it was this berserker. As Frazer remarks, one doubts whether
he particularly adorned the bench. Yet there is a mysterious im-
167 • Samson Under Many Skies
portance to his person. On him was piled a hoard of classic fairy
tales, like "the man whose soul was placed elsewhere" (the ex-
ternal soul), and the insistent motif of fatal betrayal by women, the
motif of Herakles and Llew Llaw Gyffes. More than that, he is
an incongruous montage of nonhuman functions which could no
longer be put together intelligibly, and were crowded together
with cinematographic haste. Even his feats as a young Herakles, tear-
ing a lion apart, change over in a flash to the generation of bees
from a carcass, recalling the time-honored bougonia of the fourth
book of Virgil's Georgies.
Of the many nonsense feats there are some which take particular
relief from the context. Samson was displeased (Judges xiv-xv)
because the wife of his heart, a Philistine, had given away to the
children of her people the meaning of his riddle on the lion: "Out
of the eater came forth meat, and out of the strong came forth
sweetness," so that he was held to pay forfeit for his last bet.
xiv. 19. And the Spirit of the Lord came upon him, and he went down
to Ashkelon, and slew thirty men of them, and took their spoil, and
gave change of garments unto them which expounded the riddle.
And his anger was kindled, and he went up to his father's house.
20. But Samson's wife was given to his companion, whom he had used
as his friend.
xv. 1. But it came to pass within a while after, in the time of wheat
harvest, that Samson visited his wife with a kid; and he said, I will go
in to my wife into the chamber. But her father would not suffer him
to go in.
2. And her father said, I verily thought that you hadst utterly hated
her; therefore I gave her to your companion. Is not her younger sister
fairer than she? Take her, I pray thee, instead of her to your com-
panion.
3. And Samson said concerning them, Now shall I be more blameless
than the Philistines, though I do them a displeasure.
4. And Samson went and caught three hundred foxes, and took fire-
brands, and turned tail to tail, and put a firebrand in the midst be-
tween two tails.
5. And when he had set the brands on fire, he let them go into the
standing corn of the Philistines, and burnt up both the shocks, and
also the standing corn, with the vineyards and olives.
6. Then the Philistines said, Who hath done this? And they an-
swered, Samson, the son in law of the Timnite, because he had taken
Hamlet's Mill
168
his wife, and given her to his companion. And the Philistines came up,
and burnt her and her father with fire.
7. And Samson said unto them, Though ye have done this, yet will I
be avenged of you, and after that I will cease.
8. And he smote them hip and thigh with a great slaughter: and he
went down and dwelt in the top of the rock Etam.
Leaving the great Shimshon there sitting in the top of the rock,
a brief interlude before he goes out again on his own wayward,
rash and splenetic way to provoke his enemies, one is moved to
reflection.
To catch and corral three hundred foxes, and tie them in pairs
by the tail, just to work off a spite, seems more the daydream of
a juvenile delinquent or a Paul Bunyan or a "Starke Hans" than the
feat of a warrior. It is as if Scripture had remembered that he had
to stand out as a great hunter, but had misplaced the occasion of
his hunts. After all, lions are not to be found behind every hedge-
row, and foxes might do, if only to annoy. But we know from Ovid
(Fasti 4, 631ff.) that in April, at the feast of Ceres, foxes with burn-
ing fur were chased through the Circus. This might be the real
context. The modern "fertility rite" explanations are so futile that
it might be more to the point to be reminded of the three hundred
elite "dogs" that Gideon recruited for his band, and which still
stand unexplained. One should also consider a more important occa-
sion to which attention has been drawn by Felix Liebrecht: the
"Sada-Festival," during which animals were kindled and chased,
burning, through the whole Iranian countryside. This, however,
would lead back to Firdausi's Book of Kings, and beyond that to
the whole problem of Kynosoura, that cannot be tackled at this
point because it calls for an examination of all that was implied by
the starting of celestial fires.
But the main theme of the story will appear more clearly if it is
transposed in an utterly different narrative convention, the adven-
tures of Susanowo the Japanese god. They are found in the Japanese
Scriptures, in this case the Nihongi, compiled about the 8th century
a.d. but going back to unknown times. They are the full equivalent
of what the Bible was in our recent past, and even more, for "this
169 • Samson Under Many Skies
body of legend, folklore to us but credible history to the people of
the archipelago, is tangled in the roots of everything Japanese."
The quotation is from Post Wheeler, who prepared the latest edi-
tion of the Japanese mythical corpus. To quote him further: "In
no other land do we find a people's sacred legend so interknit with
the individual's daily thoughts and life. Its episodes peer at us from
every nook and byway. The primeval myth of the slaughter of the
Eight-Forked-Serpent by the deity Brave-Swift-Impetuous-Male,
brother of Bright-Shiner the Sun-Goddess, is pictured on Japan's
paper currency. I have seen it produced au grand serieux at Tokyo's
Imperial Theatre, in the same week as one of Ibsen's tragedies and a
Viennese light opera."1
Most of Hebrew mythology wears the hempen homespun of
peasants and patriarchs from Palestine. Japanese myth bears the
mark of an already refined perverse feudal world, back of which
there is the baroque elegance and fantasy of late Chinese culture.
With this premise, here is the story of the Japanese Samson, Susa-
nowo, whose name means Brave-Swift-Impetuous-Male. No better
set of attributes for Mars; he is also officially a god, since his sister
Amaterasu, the sun-goddess, is still today the worshiped ancestor
of the Imperial dynasty; the courtly precedences are neatly estab-
lished. The hero need no longer masquerade as a boor from the
tribe of Dan who raged in Ashkelon and destroyed himself in Gaza.
Now Susanowo was banished from the sky for having thrown
the hind part of his backward-flayed piebald stallion in the weaving
hall of his sister Amaterasu. These sudden discourteous gestures
seem to be part of the code: Enkidu had thus thrown the hind
quarter of the Bull from Heaven in the face of Ishtar, but here
there is the additional code feature (it is code) of the backward-
flayed animal. Susanowo's gesture caused the Sun-lady to withdraw
in anger into a cave: the world was plunged into darkness. The
80,000 gods assembled in the Milky Way to take counsel, and at last
came upon a device to coax the Sun out of the cave and end the
great blackout. It was a low-comedy trick, part of the stock-in-
1 P. Wheeler, The Sacred Scriptures of the Japanese (1952), pp. vf.
Hamlet's Mill
170
trade that is used to coax Ra in Egypt, Demeter in Greece (the
so-called Demeter Agelastos or Unlaughing Demeter) and Skadi
in the North—obviously another code device.2
Now light was restored to the world, but on earth the hero-god
moving out of the darkness had nowhere to lay his head; he wan-
dered around and succeeded in killing the "Eight-Forked-Serpent,"
thus saving a damsel.
Afterwards he arranged "The Drawing of the Lands," and the
sowing of more land, giving the islands the shape which they
have now. Finally, Brave-Swift-Impetuous-Male, having traveled
about the limits of the sky and the earth, even to the Sky-Upright-
Limiting-Wall, dwelt on Mount Bear-Moor and finally went to the
Lower World, also called the Nether-Distant-Land.
To this his place came a Jason, namely the Kami (Divine Prince)
Great-Land-Master, looking for some helpful device against his
brothers, "the 80 Kami" who had succeeded in killing him several
times (Sky-Producer revived him). Before reaching the house, he
married Susanowo's daughter, Princess-Forward, and this Medea
was to support him faithfully, so that he survived the different
"stations" which Susanowo had prepared for him3 as proper guest
rooms: the fire, the snake-house, the centipede-and-wasp-house
(Dostoyevsky's Svidrigailov must have been a great seer):
Then Brave-Swift-Impetuous-Male, having shot a humming arrow
into the midst of a great grass-moor, sent him to fetch it, and when
he had entered the moor, set fire to it on all sides. But when Great-
Land-Master found no place of exit, there came a mouse which said,
"The inside is hollowly hollow; the outside is narrowly narrow." Even
as it spoke thus, he trod on the spot, and falling into the hollow, hid
himself until the fire had burned over, when the mouse brought him
the humming arrow in its mouth, and the arrow's feathers were
brought in like manner by its young ones.
2 The obscene dance of old Baubo, also called Iambe in Eleusis, parallels the
equally unsavory comic act of Loke in the Edda. The point in all cases is that the
deities must be made to laugh (cf. also appendix #36).
3 For a comparison of the sequence of troublesome caves, holes, or "houses" that
heroes of the Old World as well as of the New World have to pass through, see L.
Frobenius, Das Zeitalter des Sonnengottes (1904), pp. 371f.
171
Samson Under Many Skies
Now his wife, Princess-Forward, weeping, made preparation for the
funeral, and her father, deeming Great-Land-Master dead, went out
and took stand on the moor, but he found his guest standing there,
who brought the arrow and gave it to him. Then the great Kami
Susanowo took him into the palace and into a great-spaced room,
where he made Great-Land-Master pick the lice from his head,
among which were many centipedes. His wife, however, gave him
aphananth berries and red earth, and he chewed up the berries and
spat them out with the red earth which he held in his mouth, so that
the great Kami, believing him to be chewing and spitting out the
centipedes, began to feel a liking for him in his heart and fell asleep.
Then Great-Land-Master bound Brave-Swift-Impetuous-Male's hair
fast to the palace rafters, and blocking up the door with a five-hun-
dred-man-lift rock, took his wife Princess-Forward on his back,
possessed himself of the Kami's great life-preserving sword, his bow-
and-arrows, and his Sky-speaking lute, and fled. But the Sky-speaking
lute smote against a tree so that the earth resounded, and the great
Kami [Susanowo] started from sleep at the sound and pulled down
the palace.
While he was freeing his hair from the rafters, however, Great-
Land-Master fled a long way; so pursuing after him to the Level-
Pass-of-the-Land-of-Night, and gazing on him from afar, Brave-
Swift-Impetuous-Male called out to him, saying, "With the great,
life-preserving sword and the bow-and-arrow which you carry, pur-
sue your low-born brethren till they crouch on the hill-slopes and are
swept into the river currents! And do you, fellow! make good your
name of Great-Land-Master, and your name of Spirit-of-the-Living-
Land, and making my daughter Princess-Forward your chief wife,
make strong the pillars of your palace at the foot of Mount Inquiry
in the lowest rock bottom, and rear its crossbeams to the Plain-of-the-
High-Sky, and dwell there!"
Then, bearing the great sword and book, Great-Land-Master pur-
sued and scattered the eighty Kami, saying, "They shall not be
permitted within the circle of the blue fence of mountains." He
pursued them till they crouched on every hill-slope, he pursued them
till they were swept into every river, and then he began to rule the
Land. (Therefore the place where he overtook them was called Come-
Overtake.)4
Later on, the "Genesis" part of the Nihongi will be shown to
meet the requirements of archaic theory very exactly. Even inci-
dents that seem like minor embellishments, the little mouse in her
4 Wheeler, pp. 44f.
Hamlet's Mill
172
burrow, are really recurrent elements in the ancient fugue. Because
it is necessary to deal with one theme at a time, much of the tale
of Susanowo appears wildly arbitrary although no more so than
that of Samson. Also the narrative is confusingly interwoven with
other classic plots, recognizably those of Theseus and the Argo-
nauts. And yet there Susanowo is, a maker of darkness at noon,
Samson strength-in-hair, who "went away with the pin of the
beam, and with the web," walking off with rafters and rocks and
gates and posts, pulling down a palace (his own, for a change),
smiting and scattering low-born workers of iniquity "not to be
permitted again within the circle of the blue fence." But the
Nihongi shows the ampler scheme in which the old order is
smashed and the new foundation of an order is undertaken: "make
strong the pillars of your palace at the foot of Mount Inquiry in
the lowest rock-bottom, and rear its crossbeams to the Plain-of-
the-High Sky, and dwell there."
The god has not only judged and apportioned, he has also estab-
lished and sowed for the future in his capacity as the new king
of the Underworld; he has gone to sleep in his Ogygia, and ap-
pointed his successor as ruler of the new age. Further, the Great-
Land-Master had to procure something in the Nether-Distant-Land
(in Japan the dead go down there by land with countless wind-
ings, whereas the whirlpool in the ocean is good only for trans-
porting there the "sinful dirt"). He had been sent there to get
"counsel" from Susanowo (who identified him at the first glance
as: "This is the Kami Ugly-Male-of-the-Reed-Plains"), he eventu-
ally got it, and added to it the precious life-preserving sword which
Susanowo had found in the tail of the Eight-Forked Dragon, and
the "bow-and-arrows," and his Orphic Sky-speaking lute, not to
forget Princess-Forward. A complicated affair. But the Great-
Land-Master undeniably plays a Jupiter role against Susanowo's
Mars, the more so, as his beloved Princess-Forward turns out to be
extremely jealous.
Now, after this Far Eastern interlude, Samson's own tragedy can
be seen in better focus (Judges xvi):
173 • Samson Under Many Skies
19. And [Delilah] made him sleep upon her knees; and she called
for a man, and she caused him to shave off the seven locks of his head;
and she began to afflict him, and his strength went from him.
20. And she said, The Philistines be upon thee, Samson. And he
awoke out of his sleep, and said, I will go out as at other times before,
and shake myself. And he wist not that the Lord was departed from .
him.
21. But the Philistines took him, and put out his eyes, and brought
him down to Gaza, and bound him with fetters of brass; and he did
grind in the prison house. [ Appendix #17]
22. Howbeit the hair of his head began to grow again after he was
shaven.
23. Then the lords of the Philistines gathered them together for to
offer a great sacrifice unto Dagon their god, and to rejoice: for they
said, Our god hath delivered Samson our enemy into our hand.
24. And when the people saw him, they praised their god: for they
said, Our god hath delivered into our hands our enemy, and the
destroyer of our country, which slew many of us.
25. And it came to pass, when their hearts were merry, that they
said, Call for Samson, that he may make us sport. And they called for
Samson out of the prison house; and he made them sport; and they
set him between the pillars.
26. And Samson said unto the lad that held him by the hand, Suffer
me that I may feel the pillars whereupon the house standeth, that I
may lean upon them.
27. Now the house was full of men and women; and all the lords of
the Philistines were there; and there were upon the roof about three
thousand men and women, that beheld while Samson made sport.
28. And Samson called unto the Lord, and said, O Lord God, remem-
ber me, pray thee, and strengthen me, I pray thee, only this once, O
God, that I may be at once avenged of the Philistines for my two
eyes.
29. And Samson took hold of the two middle pillars upon which
the house stood, and on which it was borne up, of the one with his
right hand, and of the other with his left.
30. And Samson said, Let me die with the Philistines. And he bowed
himself with all his might; and the house fell upon the lords, and
upon all the people that were therein. So the dead which he slew at
his death were more than they which he slew in his life.
Such is the great story, and it has gone through innumerable
variations.
The general design of the tragedy is obviously faulty, more even
than most Bible narratives which are superbly indifferent to such
Hamlet's Mill
174
considerations. If Samson had been bred as "a person separate to
God," by the care of the Lord "who sought an occasion against the
Philistines," he does not compare with chiefs like Joshua and
Gideon. He remains, mythically speaking, a misguided missile. Most
great feats of the mythistorical past would not have rated the atten-
tion of news media, but Samson's achievements make so little sense,
even on the micro-scale of Palestine power politics, that Milton
finds it hard to justify the ways of God to man. Certain "central"
events like the fall of royal houses, whether in Greece or Babylon
or Denmark, are capable of a truer and deeper reverberation. That
is why great motifs like "darkness at noon" and "pulling down the
edifice" combine into a larger theme, obviously cosmic, which is
here obscured. The Nihongi is truer to this larger style.
In the arabesque of interlaced motifs, one can mark those where
the theme of "pulling down the structure" is in evidence. The
powerful Maori hero Whakatau, bent on vengeance,
laid hold of the end of the rope which had passed round the posts of
the house, and, rushing out, pulled it with all his strength, and
straightaway the house fell down, crushing all within it, so that the
whole tribe perished, and Whakatau set it on fire.5
This is familiar. At least one such event comes down dimly from
history. It happened to the earliest meetinghouse of the Pytha-
gorean sect, and it is set down as a sober account of the outcome
of a political conflict, but the legend of Pythagoras was so artfully
constructed in early times out of prefabricated materials that doubt
is allowable. The essence of true myth is to masquerade behind
seemingly objective and everyday details borrowed from known
circumstances. However that may be, in many other stories the
destruction of the building is linked with a net. Saxo's Amlethus
does not pull down pillars; he reappears at the banquet set by the
king for his own supposed funeral, like Great-Land-Master himself.
He throws the knotted carpet net prepared by his mother over the
drunken crowd and burns down the hall. In Japan the parallel does
not go farther than that but it has its own relevance nevertheless.
It suggests the fall of the House of Atreus. The net thrown by
5 See Sir George Grey, Polynesian Mythology (1956; 1st ed. 1855), pp. 97f.
175 • Samson Under Many Skies
Clytemnestra over the king struggling in "his bath cannot have come
in by chance. But this is an uncertain lead as yet.
The Sacred Book of the ancient Maya Quiche, the famous Popol
Vuh (the Book of Counsel) tells of Zipacna, son of Vucub-Caquix
(=Seven Arara). He sees 400 youths dragging a huge log that they
want as a ridgepole for their house. Zipacna alone carries the tree
without effort to the spot where a hole has been dug for the post
to support the ridgepole. The youths, jealous and afraid, try to kill
Zipacna by crushing him in the hole, but he escapes and brings
down the house on their heads. They are removed to the sky, in a
"group," and the Pleiades are called after them (appendix #18).
Then there is a true avenger-of-his-father, the Tuamotuan Ta-
haki, who, after long travels, arrives in the dark at the house of
the goblin band who tortured his father. He conjures upon them
"the intense cold of Havaiki" (the other world) which puts them
to sleep.
Then Tahaki gathered up the net given to him by Kuhi, and carried
it to the door of the long house. He set fire to the house. When the
goblin myriads shouted out together "Where is the door?" Tahaki
called out: "Here it is." They thought it was one of their own band
who had called out, and so they rushed headlong into the net, and
Tahaki burned them up in the fire.6
What the net could be is known from the story of Kaulu. This
adventurous hero, wanting to destroy a she-cannibal, first flew up
to Makalii the great god, and asked for his nets, the Pleiades and the
Hyades, into which he entangled the evil one before he burned
down her house.7 It is clear who was the owner of the nets up there.
The Pleiades are in the right hand of Orion on the Farnese Globe,8
and they used to be called the "lagobolion" (hare net). The Hyades
were for big game.9
At the end of this far-ranging exploration, it is fair now to ask,
who could Samson have been? Clearly a god, and a planetary
6 J. F. Stimson, The Legends of Maui and Tahaki (1934), pp. 51, 66.
7 A. Fornander, Hawaiian Antiquities (1916-1920), vol. 4, pp. 350f.; vol. 5, p. 368.
8 R. Eisler, Orpheus the Fisher (1921), pp. 25f.
9. G. Schlegel, L'Urano graphic Chinoise (1967), pp. 351-58, 365-70.
Hamlet's Mill
176
Power, for such were the gods of old. As Brave-Swift-Impetuous-
Male, as the Nazirite Strong One, he has all the countersigns that
belong to Mars, and to none other. Clearly, while trying to draw
the concluding episode of the investigation of Amlethus-Kronos,
King of the Cosmic Mill, something else has come into view, the
new and formidable personage of Mars—or Ares as the Greeks
called him. He will come back more than once. Yet there is no
question but that the name of Samson comes up quite spontane-
ously in connection with the Sampo, the original quern. It was
clearly and unequivocally within the Amlethus design. At this
point, the intrusion of this new planetary Power must be recog-
nized. Even Susanowo substitutes for Kronos in his very reign of
the Underworld. It would have been desirable to present the
Powers separately, and each in his own shape, as will be done
farther on. But the many-threaded tale has its own rules, and this
exemplifies an important one. There are no Powers more diverse
than Saturn and Mars; yet this is not the only time they will appear
as a confusing and unexplained doublet of the two.
One of the motifs, destruction, is often associated with the Am-
lethus figure. The other belongs more specifically to Mars. There
is a peculiar blind aspect to Mars, insisted on in both Harranian
and Mexican myths. It is even echoed in Virgil: "caeco Marte."
But it does not stand only for blind fury. It must be sought in the
Nether World, which will come soon. Meanwhile, here is the first
presentation of the double figure of Mars and Kronos. In Mexico,
it stands out dreadfully in the grotesque forms of the Black and the
Red Tezcatlipoca. There is a certain phase in the Great Tale, obvi-
ously, in which the wrecking powers of Mars unleashed make up
a fatal compound with the avenging implacable design of Saturn.
Shakespeare has, with his preternatural insight, alluded to both
when he made Hamlet warn the raging Laertes before their final
encounter:
Though I am not by nature rash and splenetic
Yet there is in me something dangerous
Which let thy wisdom fear ...
177 • Samson Under Many Skies
But obviously there is more, and what emerges here lifts the veil
of a fundamental archaic design. The real actors on the stage of
the universe are very few, if their adventures are many. The most
"ancient treasure"—in Aristotle's word—that was left to us by our
predecessors of the High and Far-Off Times was the idea that the
gods are really stars, and that there are no others. The forces reside
in the starry heavens, and all the stories, characters and adventures
narrated by mythology concentrate on the active powers among
the stars, who are the planets. A prodigious assignment it may seem
for those few planets to account for all those stories and also to run
the affairs of the whole universe. What, abstractly, might be for
modern men the various motions of those pointers over the dial
became, in times without writing, where all was entrusted to images
and memory, the Great Game played over the aeons, a never-
ending tale of positions and relations, starting from an assigned
Time Zero, a complex web of encounters, drama, mating and
conflict.
Lucian of Samosata, that most delightful writer of antiquity, the
inventor of modern "science fiction," who knew how to be light
and ironic on serious subjects without frivolity, and was fully aware
of the "ancient treasure," remarked once that the ludicrous story
of Hephaistos the Lame surprising his wife Aphrodite in bed with
Mars, and pinning down the couple with a net to exhibit their
shame to the other gods, was not an idle fancy, but must have
referred to a conjunction of Mars and Venus, and it is fair to add,
a conjunction in the Pleiades.
This little comedy may serve to show the design, which turns out
to be constant: the constellations were seen as the setting, or the
dominating influences, or even only the garments at the appointed
time by the Powers in various disguises on their way through their
heavenly adventures.
No one could deny, in the case of the Amlethus-Samson epiph-
any, that this fierce power, or momentary combination of powers,
wears here the figure of Orion the blind giant, called also Nimrod
the Hunter, brandishing the Hyades, working the Mill of the
Hamlet's Mill
178
Stars, like Talos, the bronze giant of Crete. For the feature which
clinches the case has been named. Orion was blind, the only blind
figure of constellation myth. He was said to have regained his sight
eventually, as befits an eternal personage. But this is how legend
portrays him, wading through the rushing flood of the whirlpool
at his feet (where he will appear again), guided by the eyes of little
Tom Thumb sitting on his shoulder, whose name, Kedalion, sug-
gests a low-comedy occupation. But who are we to impose Mrs.
Grundy on the assembly of heaven?
Chapter XII
Socrates' Last Tale
Al suo aspetto tal dentro mi fei
Qual si fe' Glauco nel gustar dell'erba
Che il fe' consorto in mar degli altri dei.
Dante, Paradiso 1.67
What a man has to say in the last hours of his life deserves
attention. Most especially if that man be Socrates, awaiting execu-
tion in his jail and conversing with Pythagorean friends. He has
already left the world behind, has made his philosophical will and
is now quietly communing with his own truth. This is the close of
the Phaedo (107D-115A), and it is expressed in the form of a myth.
Strangely enough, innumerable commentators have not taken the
trouble to scrutinize it, and have been content to extract from it
some pious generalities about the rewards of the soul. Yet it is a
thoughtful and elaborate statement, attributed to an authority
whom Socrates (or Plato) prefers not to name. It is clothed in a
strange physical garb. It is worth accepting Plato's suggestion to
take it with due attention. Socrates is quietly moving into the other
world, he is a denizen of it already, and his words stand, as it were,
for a rite of passage:
"The story goes that when a man dies his guardian deity, to whose lot
it fell to watch over the man while he was alive, undertakes to con-
duct him to some place where those who gather must submit their
cases to judgment before journeying to the other world; and this they
do with the guide to whom the task has been assigned of taking them
there. When they have there met with their appropriate fates and
waited the appropriate time, another guide brings them back here
again, after many long cycles of time. The journey, then, is not as
Aeschylus' Telephys describes it: he says that a single track leads to
Hamlet's Mill
180
181
Socrates' Last Tale
the other world, but I don't think that it is 'single' or 'one' at all.
If it were, there would be no need of guides; no one would lose the
way, if there were only one road. As it is, there seem to be many
partings of the way and places where three roads meet. I say this,
judging by the sacrifices and rites that are performed here. The
orderly and wise soul follows on its way and is not ignorant of its
surroundings; but that which yearns for the body, as I said before,
after its long period of passionate excitement concerning the body
and the visible region, departs only after much struggling and suffer-
ing, taken by force, with great difficulty, by the appropriate deity.
When it arrives where the others are, the unpurified soul, guilty of
some act for which atonement has not been made, tainted with
wicked murder or the commission of some other crime which is akin
to this and work of a kindred soul, is shunned and avoided by every-
one, and no one will be its fellow-traveller or guide, but all by itself
it wanders, the victim of every kind of doubt and distraction, until
certain periods of time have elapsed, and when they are completed, it
is carried perforce to its appropriate habitation. But that soul which
has spent its life in a pure and temperate fashion finds companions
and divine guides, and each dwells in the place that is suited to it.
There are many wonderful places in the world, and the world itself
is not of such a kind or so small as is supposed by those who generally
discourse about it; of that a certain person has convinced me."
"How do you mean, Socrates?" asked Simmias. "I too have heard a
great deal about the world, but not the doctrine that has found favour
with you. I would much like to hear about it."
"Well, I don't think it requires the skill of a Glaucus1 to relate my
theory; but to prove that it is true would be a task, I think, too dif-
ficult for the skill of Glaucus. In the first place I would probably not
even be capable of proving it, and then again, even if I did know how
to, I don't think my lifetime would be long enough for me to give
the explanation. There is, however, no reason why I should not tell
you about the shape of the earth as I believe it to be, and its various
regions."
"That will certainly do," said Simmias.
"I am satisfied," he said, "in the first place that if it is spherical and
in the middle of the universe, it has no need of air or any other force
of that sort to make it impossible for it to fall; it is sufficient by itself
to maintain the symmetry of the universe and the equipoise of the
1 Whoever this (unidentified) Glaucus is, he has nothing to do with the Glaucus
of Anthedon mentioned in the epigraph, a fisherman who on eating a certain plant
was overtaken by a transmutation and threw himself into the sea where he became
a marine god.
■/
earth itself. A thing which is in equipoise and placed in the midst of
something symmetrical will not be able to incline more or less
towards any particular direction; being in equilibrium, it will remain
motionless. This is the first point," he said, "of which I am con-
vinced!"2
"And quite rightly so," said Simmias.
"And again, I am sure that it is very big," he said, "and that we who
live between the Phasis river and the pillars of Hercules inhabit only
a small part of it, living round the coast of the sea like ants or frogs
by a pond, while many others live elsewhere, in many similar regions.
All over the earth there are many hollows of all sorts of shape and
size, into which the water and mist and air have collected. The earth
itself is a pure thing lying in the midst of the pure heavens, in which
are the stars; and most of those who generally discourse about such
things call these heavens the 'ether.' They say that these things I have
mentioned are the precipitation of the 'ether' and flow continually
into the hollows of the earth. We do not realize that we are living in
the earth's hollows, and suppose that we are living up above on the
top of the earth — just as if someone living in the middle of the sea-
bed were to suppose that he was living on the top of the sea, and
then, noticing the sun and the stars through the water, were to
imagine that the sea was sky; through sluggishness and weakness he
might never have reached the top of the sea, nor by working his way
up and popping up out of the sea into this region have observed how
much purer and more beautiful it is than theirs; nor even heard about
it from anyone who had seen it. That is exactly what has happened
to us: we live in a hollow in the earth, but suppose that we are living
on top of it; and we call the air sky, as though this were the sky, and
the stars moved across it. But the truth of the matter is just the same
—through weakness and sluggishness we are not able to pass through
to the limit of the air. If anyone could climb to the air's surface, or
grow wings and fly up, then, as here the fishes of the sea pop their
heads up and see our world, so he would pop his head up and catch
sight of that upper region; and if his nature were such that he could
bear the sight, he would come to realize that that was the real sky and
the real light and the real earth. This earth of ours, and the stones,
and all the region here is corrupted and corroded, just as the things
in the sea are corroded by the brine; and in the sea nothing worth
mentioning grows, and practically nothing is perfect—there are just
caves and sand and indescribable mud and mire, wherever there is
2 Thus far, this is Anaximander and his Principle of Sufficient Reason. But we
cannot draw further conclusions: Socrates is, here, deep in his own myth already,
and far beyond Ionian physics which, in His opinion, ought not to be taken
seriously.
■/
Hamlet's Mill • 182
earth too, and there is nothing in any way comparable with the
beautiful things of our world; but those things in the upper world, in
their turn, would be seen far to surpass the things of our world. If it
is a good thing to tell a story then you should listen, Simmias, and
hear what the regions on the earth beneath the sky are really like."
"We should certainly very much like to hear this story, Socrates,"
said Simmias.
"In the first place, then, my friend, the true earth is said to appear to
anyone looking at it from above like those balls "which are made of
twelve pieces of leather, variegated, a patchwork of colours, of which
the colours that we know here—those that our painters use—are sam-
ples, as it were. There the whole earth is made of such colours, and
of colours much brighter and purer than these: part of it is purple,
of wondrous beauty, and part again golden, and all that part which is
white is whiter than the whiteness of chalk or snow; and it is made
up of all the other colours likewise, and of even more numerous and
more beautiful colours than those that we have seen. Indeed these
very hollows of the earth, full of water and of air, are said to present
a kind of colour as they glitter amid the variety of all the other
colours, so that the whole appears as one continuous variegated pic-
ture. And in this colourful world the same may be said of the things
that grow up—trees and flowers and all the fruits; and in the same
way again the smoothness and transparency and colours of the stars
are more beautiful than in our world. Our little stones, these highly
prized ones, sards and jaspers and emeralds and so on, are but frag-
ments of those there; there, they say, everything is like this, or even
more beautiful than these stones that we possess. The reason is that
the stones there are pure, and not corroded or corrupted, as ours are,
by rust and brine, as a result of all that has collected here, bringing
ugliness and diseases to stones and to soil, and to animals and to plants
besides. The earth itself, they say, is ornamented with all things, and
moreover with gold and silver and all things of that sort. They are
exposed to view on the surface, many in number and large, all over
the earth, so that the earth is a sight for the blessed to behold. There
are many living creatures upon it, including men; some live inland,
some live round about the borders of the air as we do on the coasts
of the sea, while others again live on islands encompassed by air near
the mainland. In a word, what the water and the sea are to us, for our
purposes, the air is to them; and what the air is to us, the 'ether' is to
them. Their climate is such that they are free from illnesses, and live
much longer than the inhabitants of our world, and surpass us in sight
and hearing and wisdom and so on, by as much as the pureness of
air surpasses that of water, and the pureness of 'ether' surpasses that
of air. Moreover they have groves and temples sacred to the gods, in
183
Socrates' Last Tale
which the gods really dwell, and utterances and prophesies and visions
of the gods; and other such means of intercourse are for them direct
and face to face. And they see the sun and moon and stars as they
really are, and their blessedness in other respects is no less than in
these.
"This is the nature of the earth as a whole, and of the regions round
about it, and in the earth, in the cavities all over its surface, are many
regions, some deeper and wider than that in which we live, others
deeper but with a narrower opening than ours, while others again are
shallower than this one and broader. All of these are connected with
each other by underground passages, some narrower, some wider—
bored through in many different places; and they have channels along
which much water flows, from one region to another, as into mixing-
bowls; and they have, too, enormous ever-flowing underground
rivers and enormous hot and cold springs, and a great deal of fire,
and huge rivers of fire, and many rivers also of wet mud, some clearer,
some denser, like the rivers of mud that flow before the lava in Sicily,
and the lava itself; and they fill the several regions into which, at any
given time, they happen to be flowing. They are all set in motion,
upwards and downwards, by a sort of pulsation within the earth.
The existence of this pulsation-is due to something like this: one of
the chasms of the earth is not only the biggest of them all, but is
bored right through the earth—the one that Homer meant, when he
said that it is 'very far off, where is the deepest abyss of all below
the earth.' Homer elsewhere—and many other poets besides—have
called this Tartarus. Now into this chasm all the rivers flow together,
and then they all flow back out again; and their natures ark deter-
mined by the sort of earth through which they flow. The reason why
all these streams flow out of here and flow in is this, that this fluid
has no bottom or resting place: it simply pulsates and surges upwards
and downwards, and the air and the wind round about it does the
same; they follow with it, whenever it rushes to the far side of the
earth, and again whenever it rushes back to this side, and as the breath
that men breathe is always exhaled and inhaled in succession, so the
wind pulsates in unison with the fluid, creating terrible, unimaginable
blasts as it enters and as it comes out. Whenever the water withdraws
to what we call the lower region, the streams flow into the regions
on the farther side of the earth and fill them, like irrigating canals;
and whenever it leaves those parts and rushes back here, it fills the
streams here afresh, and they when filled flow through their several
channels and through the earth, and as each set of streams arrives at
the particular regions to which its passages lead, it creates seas and
marshes and rivers and springs; and then, sinking back again down
into the earth, some encircling larger and more numerous regions,
others fewer and smaller, these streams issue back into Tartarus again
Hamlet's Mill
184
—some of them at a point much lower down than that from which
they were emitted, others only a little lower, but all flow in below
the place from which they poured forth. Some flow into the same
part of Tartarus from which they sprang, some into the part on the
opposite side; and others again go right round in a circle, coiling
themselves round the earth several times like snakes, before descend-
ing as low as possible and falling back again.
"It is possible to descend in either direction as far as the centre, but
not beyond, for the ground on either side begins to slope upwards in
the face of both sets of streams.
"There are many large streams of every sort, but among these many
there are four that I would mention in particular. The largest, the
one which flows all round in a circle furthest from the centre, is that
which is called Oceanus; over against this, and flowing in the opposite
direction, is Acheron, which flows through many desert places and
finally, as it flows under the earth, reaches the Acherusian lake, where
the souls of most of the dead arrive and spend certain appointed
periods before being sent back again to the generations of living
creatures. The third of these rivers issues forth between these two,
and near the place where it issues forth it falls into a vast region
burning with a great fire, and forms a marsh that is larger than our
sea, boiling with water and mud. Thence it makes its way, turbulent
and muddy, and as it coils its way round inside the earth it arrives,
among other places, at the borders of the Acherusian lake, but it does
not mix with the water of the lake; and having coiled round many
times beneath the earth, it flows back at a lower point in Tartarus.
This is the river they call Pyriphlegethon, and volcanoes belch forth
lava from it in various parts of the world. Over against this, again, the
fourth river flows out, into a region that is terrible and wild, all of a
steely blue-grey colour, called the Stygian region; and the marsh
which the river forms as it flows in is called the Styx. After issuing
into this marsh and receiving terrible powers in its waters, it sinks
down into the earth, and coiling itself round proceeds in the opposite
direction to that of Pyriphlegethon, and then meets it coming from
the opposite way at the Acherusian lake. The water of this river
likewise mixes with no other, but itself goes round in a circle and then
flows back into Tartarus opposite to Pyriphlegethon; and the name
of this river, according to the poets, is Cocytus.
"Such is the nature of the world; and when the dead reach the region
to which their divine guides severally take them, they first stand trial,
those who have lived nobly and piously, as well as those who have
not. And those who are found to have lived neither particularly well
nor particularly badly journey to Acheron, and embarking on such
vessels as are provided for them arrive in them at the lake. There they
185
Socrates' Last Tale
dwell and are purified; paying due penalties, they are absolved from
any sins that they have committed, and receive rewards for their
good deeds, each according to his merits. Those who are judged in-
curable because of the enormity of their crimes, having committed
many heinous acts of sacrilege or many treacherous and abominable
murders or crimes of that magnitude, are hurled by their fitting des-
tiny into Tartarus, whence they never more emerge. Those who are
judged to be guilty of crimes that are curable but nevertheless great
—those, for example, who having done some act of violence to father
or mother in anger live the rest of their lives repenting of their
wickedness, or who have killed someone in other circumstances of a
similar nature—must fall into Tartarus; but when they have fallen in
and stayed there a year, the wave casts them forth—the murderers
along Cocytus, those who have struck their fathers or mothers along
Pyriphlegethon; and when they are being carried past the Acheru-
sian lake, they shout and cry out to those whom they have murdered
or outraged, and calling upon them beg and implore them to let them
come out into the lake, and to receive them; and if they can prevail
upon them, they come out and cease from their woes, but if not, they
are carried again into Tartarus, and from there once more into the
rivers, and they do not stop suffering this until they can prevail upon
those whom they have wronged, for such is the sentence that the
judges have pronounced upon them. Lastly, those who are found to
have lived exceptionally good lives are released from these regions
within the earth and allowed to depart from them as from a prison,
and they reach the pure dwelling place up above and live on the sur-
face of the earth; and of these, those who have sufficiently purified
themselves by means of philosophy dwell free from the body for all
time to come, and arrive at habitations even fairer than these, habita-
tions that it is not easy to describe; and there is not time to make the
attempt now. But for these reasons, Simmias, which we have dis-
cussed, we should do all in our power to achieve some measure of
virtue and of wisdom during our lives, for great is the reward, and
great the hope.
"No man of sense should affirm decisively that all this is exactly as I
have described it. But that the nature of our souls and of their habita-
tions is either as I have described or very similar, since the soul is
shown to be immortal—that, I think, is a very proper belief to hold,
and such as a man should risk: for the risk is well worth while. And
one should repeat these things over and over again to oneself, like a
charm, which is precisely the reason why I have spent so long in
expounding the story now.
"For these reasons, then, a man should have no fears about his soul, if
throughout his life he has rejected bodily pleasures and bodily adorn-
ments, as being alien to it and doing more harm than good, and has
Hamlet's Mill
186
concentrated on the pleasures of learning, and having adorned his soul
with adornments that are not alien to it, but appropriate—temperance
and justice and courage and freedom and truth—continues to wait,
thus prepared, for the time to come for him to journey to the other
world. As for you, Simmias and Cebes and all you others, you will
make your several journeys later, at an appointed time; but in my
case, as a character in a tragedy might put it, Destiny is already sum-
moning me; and it is almost time for me to go to the bath. I think it
is better to have a bath before drinking the poison, and not to give
the women the trouble of washing a corpse."3
The end has an invincible beauty, calm and serene, already shim-
mering with immortality, and yet preserving that light skeptical
irony which makes "a man of sense" in this world. It puts the seal
of confidence on what might otherwise be really an incantation
that one repeats to himself in his last moments.
Readers who are insensitive to this magic will be tempted to dis-
miss the story as so much poetic nonsense. If Socrates, or rather
Plato, is really talking of a system of rivers within the earth, then
he obviously does not understand the first thing about hydraulics,
and he has only let his fancy run wild. But looking again at the
setting, one begins to wonder if he is referring at all to the earth as
we understand it. He mentions a certain place where we live, and
it looks like a marsh in a hollow or maybe like the bottom of a lake,
full of rocks, and caverns, and sand, "and an endless slough of
mud." The "true earth," which is like a ball of twelve colored
pieces, is above us, and one may think instinctively that Plato refers
to the upper limits of the stratosphere, but of course he has never
heard of that. He is dealing with "another" world above us, and
although there are some fantasies of lovely landscapes and animals
and gems, it is in the "aether" as the Greeks understood it. It is
above us, and centered like "our" place, whatever that is, on the
center of the universe. There, the celestial bodies have become clear
to the mind, and the gods are visible and present already. If they
have "temples and houses in which they really dwell," these look
very much like the houses of the zodiac. Although some features
are scrambled for keeping up an impression of the wondrous, one
3 R. S. Bluck trans. (1955), pp. 128-39.
187
Socrates' Last Tale
suspects that this is heaven pure and simple. Then comes the un-
equivocal geometric countersign.
That world is a dodecahedron. This is what the sphere of twelve
pieces stands for: there is the same simile in the Timaeus (55c),
and then it is said further that the Demiurge had the twelve faces
decorated with figures (diazographon) which certainly stand for
the signs of the zodiac. A. E. Taylor insisted rather prosily that
one cannot suppose the zodiacal band uniformly distributed on a
spherical surface, and suggested that Plato (and Plutarch after him)
had a dodecagon in mind and they did not know what they were
talking about. This is an unsafe way of dealing with Plato, and
Professor Taylor's suffisance soon led him to grief. Yet Plutarch
had warned him: the dodecahedron "seems to resemble both the
Zodiac and the year."
Is their opinion true who think that he ascribed a dodecahedron to
the globe, when he says that God made use of its bases and the ob-
tuseness of its angles, avoiding all rectitude, it is flexible, and by
circumtension, like globes made of twelve skins, it becomes circular
and comprehensive. For it has twenty solid angles, each of which is
contained by three obtuse planes, and each of these contains one and
the fifth part of a right angle. Now it is made up of twelve equilateral
and equangular quinquangles (or pentagons), each of which consists
of thirty of the first scalene triangles. Therefore it seems to resemble
both the Zodiac and the year, it being divided into the same number
of parts as these.4
In other words, it is stereometrically the number 12, also the num-
ber 30, the number 360 ("the elements which are produced when
each pentagon is divided into 5 isosceles triangles and each of the
hitter into 6 scalene triangles")—the golden section itself. This is
what it means to think like a Pythagorean.
Plato did not worry about future professional critics very much.
He only provided a delectable image, and left them to puzzle it
out. But what stands firm is the terminology. After the Demiurge
had used the first four perfect bodies for the elements, says the
Timaeus, he had the dodecahedron left over, and he used it for the
4Quaestiones Platonicae 5.1, 1003c (R. Brown trans.), in Plutarch's Morals, cd.
W. W. Goodwin (1870), vol. 5, p. 433.
Hamlet's Mill
188
frame of the whole. There is no need to go into the reasons,
geometrical and numerological, which fitted the "sphere of twelve
pentagons," as it was called, for the role. What counts here: it was
the whole, the cosmos, that was meant. Plato had stood by the origi-
nal Pythagorean tradition, which called cosmos the order of the
sun, moon and planets with what it comprised. As a free-roving
soul, you can look at it "from above." (Archimedes in the Sand-
reckoner still uses the term cosmos loosely in that sense, at least by
way of a concession to old usage.)
To conclude: the "true earth" was nothing but the Pythagorean
cosmos, and the rivers that flowed from its surface to the center
and back can hardly be imagined as strictly terrestrial: although
with that curious archaic intrication of earth and heaven which
has become familiar and which makes great rivers flow from heaven
to earth, it is not surprising to find oneself dealing with "real" fiery
currents like Pyriphlegethon connected with volcanic fire. But
where is Styx? Hardly down here, with its landscape of blue. And
the immense storm-swept abyss of Tartaros is not a cavern under
the ground, it belongs somewhere in "outer" space.
This is all the world of the dead, from the surface down and
throughout. It localizes as poorly as the nether world of the Repub-
lic. The winding rivers which carry the dead and which go back
on their tracks are suggestive more of astronomy than of hydrau-
lics. The "seesaw" swinging of the earth (n.b.: it has to be the
"true earth") might well be the swinging of the ecliptic and the
sky with the seasons. There is no need now to go into the con-
fusing earthy or infernal details of the description except to note
that Numenius of Apamea, an important exegete of Plato, comes
out flatly with the contention that the other world rivers and Tar-
taros itself are the "region of planets." But Proclus, an even more
important and learned exegete, comes out flatly against Numenius.5
Enough is known, indeed more than enough of the welter of orien-
tal traditions on the Rivers of Heaven with their bewildering mix-
ture of astronomical and biological imagery, which culminated in
Anaximander's idea of the "Boundless Flow," the Apeiron, to see
5 Sec F. Buffiere, Les Mythes d'Homere et la Pensee Grecque (1956), p. 444.
189
Socrates' Last Tale
whence early Greece got its lore. It can be left alone here. But
Socrates is citing an Orphic version, whence his restraint in naming
his authorities, and its strange entities, such as Okeanos and Chro-
nos, deserve attention. What is meant here is not Kronos, Saturn,
but really Chronos, Time. As concerns Okeanos, even Jane Harri-
son, who could hardly be accused of a tendency to search for the
gods somewhere else than on the surface or in the interior of the
earth, had to admit: "Okeanos is much more than Ocean and of
other birth."6 In her eyes he is "a daimon of the upper air." An im-
portant concession which may lead a long way.
We bypass for the moment the imposing work of Eisler, Welten-
mantel und Himmelszelt (1910), an inexhaustible lode but one
which provides more information than guidance. Onians' Origins of
European Thought offers a more recent appraisal.7 He compares
Okeanos to Achelous, the primal river of water that "was con-
ceived as a serpent with human head and horns." He goes on:
The procreation element in any body was the psyche, which ap-
peared in the form of a serpent. Okeanos was, as may now be seen,
the primeval psyche and this would be conceived as a serpent in rela-
tion to procreative liquid . . . Thus we may see, for Homer, who
refers allusively to the conception shared by his contemporaries, the
universe had the form of an egg girt about by "Okeanos, who is the
generation of All" . . . We can perhaps also better understand . . .
why in this Orphic version [Frgs. 54, 57, 58 Kern] the serpent was
called Chronos and why, when asked what Chronos was, Pythagoras
answered that it was the psyche of the universe. According to Phere-
kydes it was from the seed of Chronos that fire and air and water
were produced.
The great Orphic entity was Chronos Aion (the Iranian Zurvan
akarana), commonly understood as "Time Unbounded," and in
"Ai5n" Professor Onians sees "the procreative fluid with which the
psyche was identified, the spinal marrow believed to take serpent
form" and it may well be so, since these are timeless ideas which
still live today in ophidic cults and in the "kundalini" of Indian
Yoga. But Aion certainly meant "a period of time," and age, hence
6 J. E. Harrison, Themis (1960), pp. 456f.
7 P. B. Onians: The Origins of European Thought about the Body, the Mind,
the Soul, the World, Time, and Fate (2nd ed. 1953), pp. 249.
Hamlet's Mill
190
"world-age" and later "eternity," and there is no reason to think
that the biological meaning must have been prior and dominant. It
is known that for the Orphics Chronos was mated to Ananke,
Necessity, "which also, according to the Pythagoreans, surrounds
the universe. Time and Necessity circling the universe, this is a
fairly clear and fundamental conception; it is linked with heavenly
motions independently from biology, and it leads directly to Plato's
idea of time as "the moving image of eternity."
It would be helpful if historians of archaic thought would first
present straight data, without pressing and squeezing their material
into a shape that reflects their preconceived conclusion, that bio-
logical images must come first in "primitive" psychology, like all
that is concerned with generation.
If one wants psychology, one can go back to Socrates in a very
different phase of his life, where he is really talking psychology in
the Theaetetus (152E): "When Homer sings the wonder of 'Ocean
whence sprang the Gods and Mother Tethys,' does he not mean
that all things are the offspring of flux and motion?" The question
arises, would the ocean be an image of flux except for the tides? But
Socrates' Aegean had no tides. The image comes to him from
Hesiod's description of Okeanos (Theogony 790ff.): "With nine
swirling streams he winds about the earth and the sea's wide back,
and then falls into the main; but the tenth flows out from a rock, a
sore trouble to the Gods." That dreaded tenth is the river of Styx.
Jane Harrison was right. Okeanos is "of another birth" than our
Ocean.
The authority of Berger can reconstruct the image.8 The at-
tributes of Okeanos in the literature are "deep-flowing," "flowing-
back-on-itself," "untiring," "placidly flowing," "without billows."
These images, remarks Berger, suggest silence, regularity, depth,
stillness, rotation—what belongs really to the starry heaven. Later
the name was transferred to another more earthbound concept: the
actual sea which was supposed to surround the land on all sides.
But the explicit distinction, often repeated, from the "main" shows
that this was never the original idea. If Okeanos is a "silver-swirl-
8 E.H.. Berger, Mythische Kosmographie der Griechen (1904), pp, 1ff.
191
Socrates' Last Tale
ing" river with many branches which obviously never were on sea
or land, then the main is not the sea either, pontos or thalassa, it has
to be the Waters Above. The Okeanos of myth preserves these
imposing characters of remoteness and silence. He was the one who
could remain by himself when Zeus commanded attendance in
Olympus by all the gods. It was he who sent his daughters to
lament over the chained outcast Prometheus, and offered his power-
ful mediation on his behalf. He is the Father of Rivers; he dimly
appears in tradition, indeed, as the original god of heaven in the
past. He stands in an Orphic hymn9 as "beloved end of the earth,
ruler of the pole," and in that famous ancient lexicon, the Ety-
mologicum magnum, his name is seen to derive from "heaven."
9 83.7 (ed. Quandt, p. 55): terma philon gaies, arche polou.
Chapter XIII
Of Time and the Rivers
Di, quibus imperium est animarum, umbraeque silentes
Et Chaos et Phlegethon, loca tacentia late
Sit mihi fas audita loqui...
Virgil, Aeneid vi.264
Socrates' inimitable habit of discussing serious things while
telling an improbable story makes it very much worth while to take
a closer look at his strange system of rivers.
It appears again in Virgil, almost as a set piece. The Aeneid is
noble court poetry, and was not intended to say much about the fate
of souls; one cannot expect from it the grave explicit Pythagorean
indications of Cicero's Dream of Scipio. But while retaining con-
ventional imagery and the official literary grand style which befitted
a glorification of the Roman Empire, it repays attention to its hints,
for Virgil was not only a subtle but a very learned poet. Thus,
while Aeneas' ingress into Hades begins with a clangorous overture
of dark woods, specters, somber caves and awesome nocturnal rites,
which betoken a real descent into Erebus below the earth, he soon
finds himself in a much vaguer landscape. Ibant obscuri sola sub
nocte per umbram . . . "On they went dimly, beneath the lonely
night amid the gloom, through the empty halls of Dis and his
unsubstantial realm, even as under the grudging light of an incon-
stant moon lies a path in the forest."
The beauty of the lines disguises the fact that the voyage really
is not through subterranean caverns crowded with the countless
dead, but through great stretches of emptiness suggesting night
193 • Of Time and the Rivers
space, and once the party has crossed the rivers and passed the gates
of Elysium thanks to the magic of the Golden Bough, they are in a
serene land "whence, in the world above, the full flood of Eridanus
rolls amid the forest." Now Eridanus is and was in heaven—surely
not, in this context, on the Lombard plain. And here also "an
ampler aether clothes the meads with roseate light, and they know
their own sun, and stars of their own." There is no mention here
of the "pallid plains of asphodel" of Homeric convention. Those
hovering souls, "peoples and tribes unnumbered," are clearly on the
"true earth in heaven," for it is also stated that many of them await
the time of being born or reborn on earth in true Pythagorean
fashion. And there is more than an Orphic hint in the words of
father Anchises: "Fiery is the vigour and divine the source of those
life-seeds, so far as harmful bodies clog them not . . ." But when
they have lived, and died, "it must needs be that many a taint, long
linked in growth, should in wondrous use become deeply ingrained.
Therefore, they are schooled with penalties, for some the stain of
guilt is washed away under swirling floods or burned out in fire.
Each of us suffers his own spirit." Some remain in the beyond
and become pure soul; some, after a thousand years (this comes
from Plato) are washed in Lethe and then sent to life and new
trials.
This is exactly Socrates' belief. The words "above" and "below"
are carefully equivocal, here as there, to respect popular atavistic
beliefs or state religion, but this is Plato's other world.
When Dante took up Virgil's wisdom, his strong Christian pre-
conceptions compelled him to locate the world of ultimate punish-
ment "physically below." But his Purgatory is again above, under
the open sky, and there is no question but that most, if not quite all,
of Virgil's world is a Purgatory and definitely "up above" too.
Socrates' strange descriptions have remained alive.
But Virgil offers even more than this. In the Georgics (1.242f.) it
is said: "One pole is ever high above us, while the other, beneath
our feet, is seen of black Styx and the shades infernal" (sub pedibus
Styx atra videt Manesque profundi). What can it mean, except that
Hamlet's Mill
194
Styx flows in sight of the other pole? The circle which began with
Hesiod is now closed.1
Great poets seem to understand each other, and to use informa-
tion usually withheld from the public; Dante carries on where the
Aeneid left off. As the wanderers, Dante and the shade of Virgil as
his guide, make their way through the upper reaches of Hell (In-
ferno vii. 102) they come across a little river which bubbles out of
the rock. "Its water was dark more than grey-blue"; it is Styx, and as
they go along it they come to the black Stygian marsh, where are
immersed the souls of those who hated "life in the gentle light of the
sun" and spent it in gloom and spite. Then they have to confront
the walls of the fiery city of Dis, the ramparts of Inner Hell,
guarded by legions of devils, by the Furies with the dreadful Gor-
gon herself. It takes the intervention of a Heavenly Messenger to
spring the barred gates with the touch of his wand (a variant of
Aeneas' Golden Bough) to admit the wanderers into the City of
Perdition. As they proceed along the inner circle, there is a river
of boiling red water, which eventually will turn into a waterfall
plunging toward the bottom of the abyss (baratro = Tartaros). At
this point Virgil remarks (xiv.85): "Of all that I have shown you
since we came through the gate that is closed to none, there is
nothing you have seen as notable as this stream, whose vapors screen
us from the rain of fire." Those are weighty words after all that
they have gone through; then comes the explanation, a rather far-
fetched one: "In the midst of the sea," Virgil begins, "there lies a
ruined country which is called Crete, under whose king [i.e.,
Saturn] the world was without vice." There, at the heart of Mount
Ida where Zeus was born of Rhea, there is a vast cavern in which
sits a great statue. Dante is going back there to an ancient tradition
1 The symmetry of both polar zones is clearly in the poet's mind. "Five zones
comprise the heavens; whereof one is ever glowing with the flashing sun, ever
scorched by his flames. Round this, at the world's ends, two stretch darkling to
right and left, set fast in ice and black storms. Between them and the middle zone,
two by grace of the Gods have been vouchsafed to feeble mortals; and a path is
cut between the two [the ecliptic], wherein the slanting array of the Signs may
turn" (Georgics 1.233-38).
195 • Of Time and the Rivers
to be found in Pliny, that an earthquake broke open a cavern in
the mountain, where a huge statue was found, of which not much
was said, except that it was 46 cubits high; but Dante supplies the
description from a famous vision of Daniel, when the prophet was
asked by King Nebuchadnezzar to tell him what he had seen in a
frightening dream that he could not remember. Daniel asked God
to reveal to him the dream:
"Thou, O king, sawest, and beheld a great image. This great image,
whose size was immense, stood before thee; and the form thereof was
terrible. This image's head was of fine gold, his breast and his arms of
silver, his belly and his thighs of bronze. His legs of iron, his feet part
of iron, and part of clay.
Thou sawest till that a stone was cut out without hands which smote
the image upon his feet that were of iron and clay, and brake them
to pieces . . . and the stone that brake the image became a great
mountain and filled the whole earth."
At this point Dante takes leave of Daniel, and with that in-
souciance which marks him even when speaking of Holy Prophets,
whom he treats as his equals, he dismisses the royal shenanigans in
Babylon. His instinct tells him that the vision must really deal with
older and loftier subjects, with the cosmos itself. Hence he proceeds
to complete the vision on his own. The four metals stand for the
four ages of man, and each of them except the gold (symbol of the
Age of Innocence) is rent by a weeping crack from whence issue
the rivers which carry the sins of mankind to the Nether World.
They are Acheron, Styx and Phlegethon. We have noted that he de-
scribes the original flow of Styx as dark gray-blue, or steel-blue
(perso), just as written in Hesiod and Socrates that he had never
read. It may have come to him by way of Servius or Macrobius, no
matter; what is remarkable is the strictness with which he preserves
the dimly understood tradition of the lapis lazuli landscape of Styx,
which will be seen to extend all over the world. As far as Phlege-
thon goes, the course of the stream follows quite exactly what
Socrates had to say about Pyriphlegethon, the "flaming river." We
have seen in the Phaidon a low-placed fiery region traversed by a
stream of lava, which even sends off real fire to the surface of the
Hamlet's Mill
196
earth. Whereas some interpreters thought it flowed through the in-
terior of our earth, others transferred Pyriphlegethon, as well as the
other rivers, into the human soul,2 but there is little doubt that it
was originally, as Dieterich has claimed,3 a stream of fiery light in
heaven, as Eridanus was. In any case, the flaming torrent, as the
Aeneid calls it, goes down in spirals carefully traced in Dante's
topography, until it cascades down with the other rivers to the icy
lake of Cocytus, "where there is no more descent," for it is the cen-
ter, the Tartaros where Lucifer himself is frozen in the ice. (Dante
has been respectful of the Christian tradition which makes the uni-
verse, so to speak, diabolocentric.) But why does he say that the
fiery river is so particularly "notable"?
G. Rabuse4 has solved this puzzle in a careful analytical study of
Dante's three worlds. First, he has found by way of a little-known
manuscript of late antiquity, the so-called "Third Vatican Mythog-
rapher," that the circular territory occupied by the Red River in
Hell was meant "by certain writers" to be the exact counterpart of
the circle of Mars in the skies "because they make the heavens to
begin in the Nether World" (5.6.4) .5 So Numenius was not wrong
after all. The rivers are planetary. Dante subscribed to the doctrine
and worked it out with a wealth of parallel features. Mars to him was
important because, centrally placed in the planetary system, he held
the greatest force for good or evil in action. As the central note in
the scale, he can also become the harmonizing force. Both Hermetic
tradition and Dante himself are very explicit about it. Is he the
planetary Power that stands for Apollo? That requires future
investigation.
2Cf. Macrobius, Commentary on the Dream of Scipio 1.10.11 (Stahl trans., p.
128): "Similarly, they thought that Phlegethon was merely the fires of our wraths
and passions, that Acheron was the chagrin we experienced over having said or
done something, . . . that Cocytus was anything that moved us to lamentation or
tears, and that Styx was anything that plunged human minds into the abyss of
mutual hatred."
3 A. Dieterich, Nekyia (1893), p. 27.
4Der kosmische Aujbau der Jenseitsreiche Dantes (1958), pp. 58-66, 88-95.
5 See Scriptores Rerum Mythicarum Latini, ed. G. H. Bode (1968; 1st ed. 1934)
vol. 1, p. 176: Eundem Phlegethontem nonnulli, qui a caelo infernum incipere
autumant, Martis circulum dicunt sicut et Campos Elysios . . . circulum Jovis esse
contendunt.
197 • Of Time and the Rivers
In the sky of Mars in his Paradise Dante placed the sign of the
Cross ("I come to bring not peace but a sword"), a symbol of reck-
less valor and utter sacrifice, exemplified by his own ancestor the
Crusader with whom he passionately identified. In the circle of Mars
in Hell he placed, albeit reluctantly, most of the great characters he
really admired, from Farinata, Emperor Frederick II, his Chancellor
Pier della Vigna, to Brunetto, Capaneus and many proud con-
querors. In truth, even Ulysses belongs in it, clothed in the "ancient
flame," the symbol of his "ire" more than of his deceit. Virtues
appear down there with the sign minus; they stand as fiery refusal,
"blind greed and mad anger" which punish themselves: but their
possessors are nonetheless, on the whole, noble, as, in the Nihongi,
Brave-Swift-Impetuous-Male, the force of action par excellence.
The meek may inherit the earth, but of the Kingdom of Heaven it
has been written: violenti rapiunt Mud. Christ stands in Dante as
the Heliand, the conquering hero, the judge of the living and the
dead: rex tremendae majestatis.
However that may be, the equivalence of above and below, of
the rivers with the planets, remains established. By artifice Dante
brings in at this point the figure of the Colossus of Crete, built out
of archaic mythical material. By identifying the rivers with the
world-ages, he emphasizes the identity of the rivers with Time: not
here the Time that brings into being, but that of passing away—the
Time that takes along with it the "sinful dirt," the load of errors of
life as it is lived.
Men's minds in the 13th century were still very much alive to the
archaic structure. But over and above this, by way of the Circle
of Mars, an unexpected insight appears. Through the solemn Chris-
tian architecture of the poem, through the subtle logical organiza-
tion, beyond the "veil of strange verses" and the intention they
cloaked, there is a glimpse of what the author cared for more than
he would say, of the man Alighieri's own existential choice. Poets
cannot guard their own truth. Ulysses setting out toward the south-
west in a last desperate attempt foreordained to failure by the order
of things, trying to reach the "world denied to mortals," swallowed
by the whirlpool in sight of his goal, that is the symbol. It is re-
Hamlet's Mill
198
199 • Of Time and the Rivers
vealed not by the poet's conscious thinking, but by the power of the
lines themselves, so utterly remote, like light coming from a "quasi-
stellar object." To be sure, the Greek stayed lost in Hell for his
ruthless resourcefulness in life as much as for his impiety: he was
branded by Virgil as "dire and fierce"; the sentence was accepted.
But he was the one who had willed to the last, even against God,
to conquer experience and knowledge. His Luciferian loftiness re-
mains in our memory more than the supreme harmony of the choirs
of heaven.
To pursue this hazardous inquiry the first source is Homer, "the
teacher of Hellas." The voyage of Odysseus to Hades is the first
such expedition in Greek literature. It is undertaken by the weary
hero to consult the shade of Teiresias about his future. The advice
he eventually gets is startlingly outside the frame of his adventures
and of the Odyssey itself (10.508ff.). It will be necessary to come
back to this strange prophecy. But as far as the voyage itself goes,
Circe gives the hero these sailing instructions:
"Set your mast, hoist your sail, and sit tight: the North Wind will
take you along. When you have crossed over the ocean, you will see
a low shore, and the groves of Persephoneia, tall poplars and fruit-
wasting willows; there beach your ship beside deep-eddying Okeanos,
and go on yourself to the dank house of Hades.
There into Acheron, the river of pain, two streams flow, Pyriphlege-
thon blazing with fire, and Cocytos resounding with lamentation,
which is a branch of the hateful water of Styx: a rock is there, by
which the two roaring streams unite. Draw near to this, brave man,
and be careful to do what I bid you. Dig a pit about one cubit's length
along and across, and pour into it a drink-offering for all souls ..."
Many centuries later, a remarkable commentary on this passage
was made by Krates of Pergamon, a mathematician and mythog-
rapher of the Alexandrian period. It has been preserved by Strabo:6
Odysseus coming from Circe's island, sailing to Hades and coming
back, "must have used the part of the Ocean which goes from the
hibernal tropic [of Capricorn] to the South Pole, and Circe helped
6 1.1..7. Referring to Odyssey 11.639-12.2. See H. J. Mette, Sphairophoiia (1936),
pp- 75, 250.
with sending the North Wind." This is puzzling geography, but
astronomically it makes sense, and Krates seems to have had good
reasons of his own to make the South Pole the objective.
The next information comes from Hesiod in his Theogony (775-
814), and very obscure it is. After having heard of the "echoing
halls" of Hades and Persephone, he says:
"And there dwells the goddess loathed by the deathless gods, terrible
Styx, eldest daughter of backflowing Ocean. She lives apart from the
gods in her glorious house vaulted over with great rocks and propped
up to heaven all around with silver pillars. Rarely does the daughter
of Thaumas, swift-footed Iris, come to her with a message over the
sea's wide back.
"But when strife and quarrel arise among the deathless gods, and
when any one of them who live in the house of Olympus lies, then
Zeus sends Iris to bring in a golden jug the great oath of the gods
from far away, the famous cold water which trickles down from a
high and beetling rock.
"Far under the wide-pathed earth a branch of Oceanus flows through
the dark night out of the holy stream, and a tenth part of his water is
allotted to her. With nine silver-swirling streams he winds about the
earth and the sea's wide back, and then falls into the main; but the
tenth flows out from a rock, a sore trouble to the gods. For whoever
of the deathless gods that hold the peaks of snowy Olympus pours a
libation of her water and is forsworn, lies breathless until a full year
is completed, and never comes near to taste ambrosia and nectar, but
lies spiritless and voiceless on a strewn bed: and a heavy trance
[coma] covers him.
"But when he has spent a long year in his sickness, another penance
and a harder follows after the first. For nine years he is cut off from
the eternal gods and never joins their councils or their feasts, nine full
years. But in the tenth year he comes again to join the assemblies of
the deathless gods who live in the house of Olympus. Such an oath,
then, did the gods appoint the eternal and primeval water of Styx to
be: and it spouts through a rugged place.
"And there, all in their order, are the sources and limits of the dark
earth and misty Tartarus and the unfruitful sea [pontos] and starry
heaven, loathsome and dank, which even the gods abhor. And there
are shining gates and an immoveable threshold of bronze having un-
ending roots and it is grown of itself. And beyond, away from all
the gods, are the Titans, beyond gloomy Chaos."
Hamlet's Mill
200
This is Hesiod's version of the "Foundations of the Abyss." Its
very details make confusion worse confounded, as befits the sub-
ject. The difficult word ogygion, translated often with "primeval,"
seems to designate things vaguely beyond time and place; one might
say, the hidden treasure at the end of the rainbow. It was also the
name for the resting place of Kronos, where he awaited the time
of his return. But the paradoxical piling up of sources, limits,
"unending roots" of earth, sea, heaven, and Tartaros too, remove
any thought of a location at the earth's core, such as the cryptic
words were popularly felt to convey. This "deeper than the deep"
must have been "beyond the other side of the earth," and for
reasons of symmetry, opposite to our pole. The shining gates and
the immovable threshold of bronze are said elsewhere in the text
to be the gates of Night and Day. Two centuries later, Parrnenides,
taking up Hesiod's allegorical language, speaks again of those gates
of Night and Day.7 But his image becomes clearer, as befits his
invincibly geometrical imagination. The gates are "high up in the
aether," leading to the abode of the Goddess of Truth and Neces-
sity, and in his case too they must be at the Pole for explicit reasons
of symmetry. We once tentatively suggested the North Pole, but
many concurrent clues would indicate now the other one, the un-
known, the Utterly Inaccessible. Hesiod says that Styx is a branch
of Okeanos in heaven, "under the wide-pathed earth"; its dreaded
goddess lives in a house "propped up to heaven all around with sil-
ver pillars," the water drips from a high rock. It can be reached by
Iris coming with her rainbow "from snowy Olympus in the north."
This ogygion region, that the gods abhor, has to be both under
and beyond the earth; this should mean something like 'on the
other side of heaven." Homer never spoke of "above" and "below"
in the strict sense. He simply made Odysseus land on a flat shore
far away.
But what of the dreadful Styx which seems to be the core of the
mystery? A river of death, even to gods, who can at least expect to
come out of their coma at the appointed time. It is inimical to all
7 G. de Santillana, Prologue to Parmenides, U. of Cincinnati, Semple Lecture,
1964. Reprinted in Reflections on Man and Ideas (1968), p. 82.
201 • Of Time and the Rivers
matter: it cracks glass, metal, stone, any container. Only a horse's
hoof is proof against it, says the legend.8 It adds that to men that
water is inescapably lethal—except for one day of the year, which
no one knows, when it becomes a water of immortality. This leads
finally to the tragic ambiguity which gives drama to the tale of
Gilgamesh and Alexander.
It is clear by now that the rivers are understood to be Time—
the time of heaven. But images have their own logic. Where are the
sources? The Colossus of Crete is Dante's own invention. Before
him, there were many other accounts of the cracks from which
flow the world-ages. Kai Khusrau, the Iranian Amlethus, was per-
secuted by a murderous uncle, established a Golden Age and then
moved off in melancholy into the Great Beyond. The bad uncle,
Afrasiyab, in his desperate efforts to seize the holy legitimacy, the
"Glory" (Hvarna), had turned himself into a creature of the deep
waters and plunged into the mystic Lake Vurukasha, diving after
the "Glory." Three times he dove, but every time "this glory
escaped, this glory went away": and at every try, it escaped
through an outlet which led to a river to the Beyond. The name of
the first outlet was Hausravah, the original Avestan name of Kai
Khusrau. This should make the epoch and design tolerably plain.
An equally ancient story of three outlets comes from Hawaii.
It appears in Judge Fornander's invaluable Account compiled a
century ago, when the tradition was still alive. The "living waters"
belong to Kane, the world-creating Demiurge or craftsman god.
These waters are to be found in an invisible divine country, Pali-uli
(= blue mountain), where Kane, Ku, and Lono created the first
man, Kumu honua ("earth-rooted") or alternatively, the living
waters are on the "flying island of Kane" (the Greek Hephaistos
lived also on a floating island). Fornander describes the spring of
this "living water" as
beautifully transparent and clear. Its banks are splendid. It had three
outlets: one for Kane, one for Ku, one for Lono; and through these
outlets the fish entered the pond. If the fish of this pond were thrown
8 Pausanias #.18.4-6; cf. J. G. Frazer, Pausanias'-Description of Greece 4, pp. 248-
56; also O. Waser, Roscher 4, cols. 1574, 1576. Pausanias leaves it open whether
or not Alexander was killed by means of Stygian water, as was fabled.
Hamlet's Mill
202
on the ground or on the fire, they did not die; and if a man had been
killed and was after-wards sprinkled over with this water he did soon
come to life again.9
An extraordinary theme has been set, that of the "revived fish"
which will later show itself as central in Mid-Eastern myth, from
Gilgamesh to Glaukos to Alexander himself. And then there are
again the three outlets. These may help individualize the notion of
Kane's "spring of life," which might otherwise sound as common-
place to folklorists as the Fountain of Youth. But something really
startling can be found in good sound Pythagorean tradition. Plu-
tarch in his essay "Why oracles no longer give answer" tells us
(422e) that Petron, a Pythagorean of the early Italian school, a
contemporary and friend to the great doctor Alcmaeon (c. 550
b.c.) theorized that there must be many worlds—183 of them. More
about these 183 worlds was reported by Kleombrotos, one of the
persons taking part in the conversation about the obsolescence of
oracles, who had received his information from a mysterious "man"
who used to meet human beings only once every year near the
Persian Gulf, spending "the other days of his life in association with
roving nymphs and demigods" (421a). According to Kleombrotos,
he placed these worlds on an equilateral triangle, sixty to each side,
and one extra at each corner. No further reason is given, but
they were so ordered that one always touched another in a circle, like
those who dance in a ring. The plain within the triangle is ... the
foundation and common altar to all these worlds, which is called the
Plain of Truth, in which lie the designs, moulds, ideas, and invariable
examples of all things which were, or ever shall be; and about there is
Eternity, whence flowed Time, as from a river, into the worlds.
Moreover, that the souls of men, if they have lived well in this world,
do see these ideas once in ten thousand years; and that the most holy
mystical ceremonies which are performed here are not more than a
dream of this sacred vision.10
What is this? A mythical prefiguration of Plato's metaphysics?
And why this triangular "Plain of Truth," which turns out again
9 A. Fornander, An Account of the Polynesian Race, Its Origin and Migrations
(1878), vol. 1, pp. 72f. Cf. Fornander Collection of Hawaiian Antiquities and
Folk-Lore, Mem. BPB Mus. 6 (1920), pp. 77f.
10 Plutarch, De defectu oraculorum, ch. 22, 422BC.
203 • Of Time and the Rivers
to be a lake of Living Water? Pythagoreans did not care to explain.
Nor did Plutarch.11 But here is at least one original way of linking
Eternity with the flow of Time. When it came to geometric fan-
tasy, no one could outbid the Pythagoreans.
11 Proclus (comm. on Plato's Timaeus 138B, ed. Diehl, BT, vol. 1, p. 454) claimed
this to be a "barbarous opinion" (doxe barbarike). He shows no particular interest
in the triangular plain of truth, alias our "lake" with its outlets, but he has more to
say about the 180 "subordinate" and the 3 "leading" worlds (hegemonas) at the
angles, and how to interpret them. To which Festugiere, in his (highly welcome
and marvelous) translation of Proclus' commentary, remarks (vol. 2, p. 336, n. 1):
"On notera que Proclus donne a la fois moins et plus que Plutarque. A-t-il lu ces
elucubrations pythagoriciennes elles-memes?"
Chapter XIV
The Whirlpool
Tre volte il fe' girar con tutte l'acque
alia quarta voltar la poppa in suso
e la prora ire in giu, com'altrui piacque
Infin che'l mar fu sopra noi richiuso.
Dante, Inferno
Dante kept to the tradition of the whirlpool as a significant
end for great figures, even if here it comes ordained by Providence.
Ulysses has sailed in his "mad venture" beyond the limits of the
world, and once he has crossed the ocean he sees a mountain loom-
ing far away, "hazy with the distance, and so high I had never
seen any." It is the Mount of Purgatory, forbidden to mortals.
"We rejoiced, and soon it turned to tears, for from the new land
a whirl was born, which smote our ship from the side. Three times
it caused it to revolve with all the waters, on the fourth to lift its
stern on high, and the prow to go down, as Someone willed, until
the sea had closed over us." The "many thoughted" Ulysses is on
his way to immortality, even if it has to be Hell.
The engulfing whirlpool belongs to the stock-in-trade of ancient
fable. It appears in the Odyssey as Charybdis in the straits of Mes-
sina—and again, in other cultures, in the Indian Ocean and in the
Pacific. It is found there too, curiously enough, with the overhang-
ing fig tree to whose boughs the hero can cling as the ship goes
down, whether it be Satyavrata in India, or Kae in Tonga. Like
Sindbad's magnetic mountain, it goes on in mariners' yarns through
the centuries. But the persistence of detail rules out free invention.
Such stories have belonged to the cosmographical literature since
205 • The Whirlpool
antiquity. Medieval writers, and after them Athanasius Kircher,
located the gurges mirabilis, the wondrous eddy, somewhere off the
coast of Norway, or of Great Britain. It was the Maelstrom, plus
probably a memory of Pentland Firth.1 It was generally in the
direction north-northwest, just as Saturn's island, Ogygia, had been
vaguely placed "beyond" the British Isles by the Greeks.
On further search this juxtaposition seems to be the result of the
usual confusion between uranography and geography. There is
frequently a "gap" in the northwest ("Nine-Yin" for the Chinese)
of the heavens and inasmuch as the skeleton map of earth was de-
rived from that of the sky, the gap was pinned down here as the
Maelstrom, or Ogygia. Both notions are far from obvious, as are
the localizations, and it is even more remarkable that they should
be frequently joined.
For the Norse (see chapter VI) the whirlpool came into being
from the unhinging of the Grotte Mill: the Maelstrom comes of the
hole in the sunken millstone. This comes from Snorri. The older
verses by Snaebjorn which described Hamlet's Mill stated that the
nine maids of the island mill who in past ages ground Amlodhi's
meal now drive a "host-cruel skerry-quern." That this skerry-quern
means the whirlpool, and not simply the northern ocean, is backed
up through some more lines which Gollancz ascribes to Snaebjorn;
not that they were of crystal clarity, but again mill and whirlpool
are connected:
The island-mill pours out the blood of the flood goddess's sisters
[i.e., the waves of the sea], so that [it] bursts from the feller of the
land: whirlpool begins strong.2
No localization is indicated here, whereas the Finns point to
directions which are less vague than they sound. Their statement
that the Sampo has three roots—one in heaven, one in the earth, the
third in the water eddy—has a definite meaning, as will be shown.
1 See for Ireland, W. Stokes, "The Prose Tales in the Rennes Dindsenchas," RC
16 (1895), no. 145: "A great whirlpool there is between Ireland and Scotland on
the North. It is the meeting of many seas [from NSEW]—it resembles an open
caldron which casts the draught down [and] Up, and its roaring is heard like far-
off thunder..."
2 I. Gollancz, Hamlet in Iceland (1898), pp. xvii.
Hamlet's Mill
206
207 • The Whirlpool
■/
But then also, Vainamoinen driving with his copper boat into the
"maw of the Maelstrom" is said to sail to "the depths of the sea,"
to the "lowest bowels of the earth," to the "lowest regions of the
heavens." Earth and heaven—a significant contraposition. As con-
cerns the whereabouts of the whirlpool, one reads:
Before the gates of Pohjola,
Below the threshold of color-covered Pohjola,
There the pines roll with their roots,
The pines fall crown first into the gullet of the whirlpool.3
Then in Teutonic tradition, one finds in Adam of Bremen (nth
century):
Certain Frisian noblemen made a voyage past Norway up to the
farthest limits of the Arctic Ocean, got into a darkness which the
eyes can scarcely penetrate, were exposed to a maelstroem which
threatened to drag them down to Chaos, but finally came quite un-
expectedly out of darkness and cold to an island which, surrounded
as by a wall of high rocks, contains subterranean caverns, wherein
giants lie concealed. At the entrances of the underground dwellings
lay a great number of tubs and vessels of gold and other metals which
"to mortals seem rare and valuable." As much as the adventurers
could carry of these treasures they took with them and hastened to
their ships. But the giants, represented by great dogs, rushed after
them. One of the Frisians was overtaken and torn into pieces before
the eyes of the others. The others succeeded, thanks to our Lord and
Saint Willehad, in getting safely on board their ships.4
The Latin text (Rydberg, p. 422) uses the classical familiar name
of Euripus. The Euripus, which has already come up in the Phaedo,
was really a channel between Euboea and the mainland, in which
the conflict of tides reverses the current as much as seven times a
day, with ensuing dangerous eddies—actually a case of standing
waves rather than a true whirl.5
3 M. Haavio, Vainamoinen, Eternal Sage (1952), pp. 191-98.
4 V. Rydberg, Teutonic Mythology (1907), p. 320.
5 We meet the name again at a rather unexpected place, in the Roman circus or
hippodrome, as we know from J. Laurentius Lydus (De Mensibus 1.12.), who states
that the center of the circus was called Euripos; that in the middle of the stadium
was a pyramid, belonging to the Sun; that by the Sun's pyramid were three altars,
of Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, and below the pyramid, altars of Venus, Mercury and the
And here the unstable Euripus of the Ocean, which flows back to the
beginnings of its mysterious source, dragged with irresistible force
the unhappy sailors, thinking by now only of death, towards Chaos.
This is said to be the maw of the abyss, that unknown depth in which,
it is understood, the ebb and flow of the whole sea is absorbed and
then thrown up again, which is the cause of the tides.
This is reflection of what had been a popular idea of antiquity.
But here comes a version of the same story in North America.6 It
concerns the canoe adventure of two Cherokees at the mouth of
Suck Creek. One of them was seized by a fish, and never seen again.
The other was
taken round and round to the very lowest center of the whirlpool,
when another circle caught him and bore him outward. He told after-
wards that when he reached the narrowest circle of the maelstroem
the water seemed to open below and he could look down as through
the roof beam of a house, and there on the bottom of the river he had
seen a great company, who looked up and beckoned to him to join
them, but as they put up their hands to seize him the swift current
caught him and took him out of their reach.
It is almost as if the Cherokees have retained the better memory,
when they talk of foreign regions, inhabited by "a great company"
—which might equally well be the dead, or giants with their dogs—
there, where in "the narrowest circle of the maelstroem the water
seemed to open below." It will be interesting to see whether or not
this impression is justifiable,7
Snorri, who has preserved the Song of Grotte for us, does not
actually name the whirlpool in it, but there is only one at hand,
Moon, and that there were not more than seven circuits (kykloi) around the pyra-
mid, because the planets were only seven. (See also F. M. Cornford's chapter on the
origin of the Olympic games in J. Harrison's Themis (1962), p. 228; G. Higgins'
Anacalypsis (1927), vol. 2, pp. 377ff.) This brings to mind (although not called
Euripus, obviously, but "the god's place of skulls") the Central American Ball
Court which had a round hole in its center, termed by Tezozomoc "the enigmatic
significance of the ball court," and from this hole a lake spread out before Uitzilo-
pochtli was born. See W. Krickeberg, "Der mittelamerikanische Ballspielplatz und
seine religiose Symbolik," Paideuma 5 (1948), pp. 135ff., 155, 162.
6 J. Mooney, Myths of the Cherokee (1900), p. 340.
7 Sec illustrations (p. 60) showing Mount Meru in the shape of an hourglass.
Hamlet's Mill
208
namely the "Hvergelmer" in Hel's abode of the dead, from and to
which "all waters find their way.'8 Says Rydberg:
It appears that the mythology conceived Hvergelmer as a vast reser-
voir, the mother fountain of all the waters of the world. In the front
rank are mentioned a number of subterranean rivers which rise in
Hvergelmer, and seek their courses thence in various directions. But
the waters of earth and heaven also come from this immense fountain,
and after completing their circuits they return thither.
The myth about Hvergelmer and its subterranean connection with
the ocean gave our ancestors the explanation of ebb and flood tide.
High up in the northern channels the bottom of the ocean opened
itself in a hollow tunnel, which led down to the "kettle-roarer," "une
one roaring in his basin" (hverr=kettle; galm = Anglo-Saxon gealm =
a roaring). When the waters of the ocean poured through this tunnel
down into the Hades-well there was ebb-tide, when it returned water
from its superabundance then was flood-tide.
Between the death-kingdom and the ocean there was, therefore, one
connecting link, perhaps several. Most of the people who drowned
did not remain with Ran. Aegir's wife, Ran, received them hospita-
bly, according to the Icelandic sagas of the middle ages. She had a
hall in the bottom of the sea, where they were welcomed and offered
. . . seat and bed. Her realm was only an ante-chamber to the realms
of death.9
There are several features of the Phaedo here, but they will turn
up again in Gilgamesh. This is not to deny that Hvergelmer, and
other whirlpools, explain the tides, as indicated previously. (Perhaps
it will be possible to find out what tides "mean" on the celestial
level.) But it is clear that the Maelstrom as the cause of the tides does
not account for the surrounding features, not even for the few
mentioned by Rydberg—for instance, the wife of the Sea-god
Aegir who receives kindly the souls of drowned seafarers in her
antechamber at the bottom of the sea—nor the circumstance that the
Frisian adventurers, sucked into the Maelstrom, suddenly find them-
selves on a bright island filled with gold, where giants lie concealed
8 Grimnismal 26; cf. Snorri, Gylf. 15.
9 Rydberg, pp. 414, 421f. Cf. the notions about the nun Saint Gertrude, patron of
travelers, particularly on sea voyages, who acted also as patron saint of inns 'and
finally it was claimed that she was the hostess of a public house, where the souls
spent the first night after death" (M. Hako, Das Wiesel in der europaischen
Volksuberlieferung, FFC 167 [1956], p. [19).
209 • The Whirlpool
in the mountain caves. This island begins to look very much like
Ogygia I, where Kronos/Saturn sleeps in a golden mountain cave,
whereas the reception hall of Ran—her husband Aegir was famous
for his beer brewing, and his hall it was, where Loke offended all
his fellow gods as reported in the Lokasenna—would suggest rather
Ogygia II, the island of Calypso, sister of Prometheus, called
Omphalos Thalasses, the Navel of the Sea. Calypso was the daughter
of Atlas, "who knew the depths of the whole sea." She, Calypso, has
been authoritatively compared10 to the divine barmaid Siduri, who
dwells by the deep sea and will be found later on in the tale of
Gilgamesh.
Mythology, meaning proper poetic fable, has been of great as-
sistance but it can help no further. The golden island of Kronos,
the tree-girt island of Calypso, remain unlocatable, notwithstanding
the efforts of Homeric scholars. Through careful analysis of navi-
gational data, one of them (Berard) has placed Calypso in the
island of Perejil near Gibraltar, another (Bradfield) in Malta,
others even off Africa. Presumably it should not be too far from
Sicily, since Ulysses reaches it riding on the mast of his ship, right
after having escaped from Charybdis in the straits of Messina, in
the setting that Homer describes so plausibly. It appears throughout
time in many places.11 Some data in Homer look like exact geogra-
phy, as Circe's Island with its temple of Feronia, or the Land of the
Laistrygones, which should be the bay of Bonifacio. But most ele-
ments from past myth, like Charybdis or the Planktai, are illusion-
istic. They throw the whole geography into a cocked hat, as do
the Argonauts themselves.
Without trying to fathom Ogygia, or Ogygos, the adjective
"Ogygian"—which has been used as a label for the Waters of Styx
—has also assumed the connotation of "antediluvian." As for Hver-
gelmer, "roaring kettle," it is the "navel of the waters" but it is
certainly "way down," as is the strange "Bierstube" of Aegir. And
when it is found, as it soon will be, that Utnapishtim (the builder
10 See chapter XXII, "The Adventure and the Quest."
11 The last learned attempt to locate it—by H. H. and A. Wolf, Der Weg des
Odysseus (1968)—proves as illusionistic as the previous ones.
Hamlet's Mill
210
of the Ark, who can be reached only by the road leading through
the bar of the divine Siduri and hence also, one would say, through
the inn of beer-brewing Aegir) lives forever at the "confluence of
the rivers," this might have charmed Socrates with his idea of con-
fluences, but it will not make things much clearer.
Yet there are some footholds to climb back from the abyss. It is
known (chapter XII) that Socrates and the poets really referred to
heaven "seen from the other side."
It has been shown that the way through the "navel of the waters"
was taken by Vainamoinen, and we shall see (chapter XIX) that the
same goes for Kronos-Phaethon, and other powerful personalities
as well, who reached the Land of Sleep where time has ceased. One
can anticipate that the meaning will be ultimately astronomical.
Hence, backing out of fable, one can turn again for assistance to
the Royal Science.
That there is a whirlpool in the sky is well known; it is most prob-
ably the essential one, and it is precisely placed. It is a group of stars
so named (zalos) at the foot of Orion, close to Rigel (beta Orionis,
Rigel being the Arabic word for "foot"), the degree of which was
called "death," according to Hermes Trismegistos,12 whereas the
Maori claim outright that Rigel marked the way to Hades (Castor
indicating the primordial homeland). Antiochus the astrologer enu-
merates the whirl among the stars rising with Taurus. Franz Boll
takes sharp exception to the adequacy of his description, but he
concludes that the zalos must, indeed, be Eridanus "which flows
from the foot of Orion."13 Now Eridanus, the watery grave of
Phaethon—Athanasius Kircher's star map of the southern hemi-
sphere still shows Phaethon's mortal frame lying in the stream—
was seen as a starry river leading to the other world. The initial
frame stands, this time traced in the sky. And here comes a crucial
confirmation. That mysterious place, pi narati, literally the "mouth
of the rivers," meaning, however, the "confluence" of the rivers,
was traditionally identified by the Babylonians with Eridu. But the
12 Vocatur mors. W. Gundel, Neue Astrologische Texte des Hermes Trismegistos
(1936), pp. i96f., 216f.
13Sphaera (1903), pp. 57, 164-67.
211
The Whirlpool
archaeological site of Eridu is nowhere "near the confluence of
the Two Rivers of Mesopotamia. It is between the Tigris and
Euphrates, which flow separately into the Red Sea, and placed
rather high up. The proposed explanation, that it was the expand-
ing of alluvial land which removed Eridu from the joint "mouth"
of the rivers, did not contribute much to an understanding of the
mythical topos of pi Marat, and some perplexed philologist sup-
posed in despair that those same archaic people who had built up
such impressive waterworks had never known which way the
waters flow and had believed, instead, that the two rivers had their
source in the Persian Gulf.
This particular predicament was solved by W. F. Albright, who
exchanged "mouth" and "source";14 he left us stranded "high and
dry"—a very typical mythical situation, by the way—in the Arme-
nian mountains around the "source." And though he stressed,
rightly, that Eridu-pz Marat could not mean geography, he banished
it straightaway into the interior of the planet.
The "source" is as unrevealing as the "mouth" has been, and as
every geographical localization is condemned to be. Eridu, Sumerian
mulNUNki, is Canopus, alpha Carinae, the bright star near the South
Pole, as has been established irrefragably by B. L. van der Waerden,15
a distinguished contemporary historian of astronomy. That one or
another part of Argo was meant had been calculated previously.16
And that, finally, made sense of the imposing configuration of
myths around Canopus on the one hand, and of the preponderance
of the "confluence of the rivers" on the other hand. This unique
topos will be dealt with later.
One point still remains a problem. The way of the dead to the
other world had been thought to be the Milky Way, and that since
the oldest days of high civilization. This image was still alive with
the Pythagoreans. When and how did Eridanus come in? A reason-
able supposition is that this was connected with the observed shift-
14 "The Mouth of the Rivers," AJSL 55 (1919), pp. 161-95.
15 "The Thirty-six Stars," JNES 8 (1949), p. 14-. "The bright southern star Cano-
pus was Ea's town Eridu (NUNki dE-a)."
16 See P. F. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum (1950), 306.
Hamlet's Mill • 212
ing of the equinoctial colure17 due to the Precession. But the analysis
of this intricate problem of rivers will come in the chapter on the
Galaxy.
One thing meanwhile stands firm: the real, the original, way from
the whirlpool lies in heaven. With this finding, one may plunge
again into the bewildering jungle of "earthly" myths concerning
the Waters from the Deep.
17 The equinoctial colure is the great circle which passes through the celestial
poles and the equinoctial points: the solstitial colure runs through both the celes-
tial and ecliptic poles and through the solstitial points. Macrobius has it, strange
to say, that "they are not believed to extend to the South Pole," whence kolouros,
meaning "dock-tailed," "which are so called because they do not make complete
circles" (Comm. Somn. Scip. 1.15.14). The translator, W. H. Stahl (p. 151), refers,
among others, to Geminus 5.49-50. Geminus, however (5.49, Manitius, pp. 60-
61), does not claim such obvious nonsense; he states the following: "Kolouroi they
are called, because certain of their parts are not visible (dia to mere tina auton
atheoreta ginesthai). Whereas the other circles become visible in their whole ex-
tension with the revolution of the cosmos, certain parts of the Colures remain invi-
sible, 'docked' by the antarctical circle below the horizon."
Chapter XV
The Waters from the Deep
The glacier knocks in the cup-
board,
The desert sighs in the bed,
And the crack in the tea cup
opens
A lane to the land of the dead.
W. H. Auden, "As I Walked
Out One Evening"
here is a tradition from Borneo of a "whirlpool island" with
a tree that allows a man to climb up into heaven and bring back
useful seeds from the "land of the Pleiades."1 The Polynesians have
not made up their mind, apparently, concerning the exact localiza-
tion of their whirlpool which serves in most cases as entrance to the
abode of the dead; it is supposed to be found "at the end of the sky,"
and "at the edge of the Milky Way."2
On this side of the Atlantic the Cuna Indians also knew the basic
scheme,3 although they, too, failed to give the accepted localization:
"God's very own whirlpool" (tiolele piria) was right beneath the
Palluwalla tree, "Saltwater-Tree," and when the Sun-God, or the
Tapir, a slightly disguised Quetzalcouatl, chopped down the tree,
saltwater gushed forth to form the oceans of the world.
1 A. Maass, "Sternkunde und Sterndeuterei im Malaiischen Archipel" (1924), in
Tijdschrift lndische Taal-, Land-, en Volkenkunde 64, p. 388.
2 M. W. Makemson (The Morning Star Rises: An Account of Polynesian As-
tronomy [1941], no. 160) suggests Sagittarius. For Samoa, see A. Kraemer, Die
Samoa-lnseln (1902), vol. 1, p. 369. For Mangaia, see P. Buck, Mangaian Society
(1934), p. 198; and R. W. Williamson, Religious and Cosmic Beliefs of Central
Polynesia (1924), vol. 2, p. 251.
3 C. E. Keeler, Secrets of the Cuna Earthmother (i960), pp. 67ff., 78f.
Hamlet's Mill • 214
There are three elements here, which combine into a curious
tangle: (a) the whirlpool represents, or is, the connection of the
world of the living with the world of the dead; (b) a tree grows
close to it, frequently a life-giving or -saving tree; (c) the whirl
came into being because a tree was chopped down or uprooted, or
a mill's axle unhinged, and the like. This basic scheme works into
many variants and features in many parts of the world, and it pro-
vides a very real paradox or conundrum: it is as if the particular
waters hidden below tree, pillar, or mill's axle waited only for the
moment when someone should remove that plug—tree, pillar, or
mill's axle—to play tricks.
This is no newfangled notion. Alfred Jeremias remarks casually,
"The opening of the navel brings the deluge. When David wanted
to remove the navel stone in Jerusalem, a flood was going to start
[see below, p. 220]. In Hierapolis in Syria the altar of Xisuthros
[= Utnapishtim] was shown in the cave where the flood dried up."4
The pattern reveals itself in the Indonesian Rama epic.5 When
Rama is building the huge dike to Lanka (Ceylon) the helpful mon-
keys throw mountain after mountain into the sea, but all of them
vanish promptly. Enraged, Rama is going to shoot his magic arrow
into the unobliging sea, when there arises a lady from the waters
who warns him that right here was a hole in the ocean leading to
the underworld, and who informs him that the water in that hole
was called Water of Life.
Rama would seem to have won out with his threat since the dike
was built. But the same story comes back in Greece when Herakles
crosses the sea in order to steal the cattle of Geryon. Okeanos,
represented here as a god, works up the waters into a tumult which
are the waters of the original flood; Herakles threatens with his
drawn bow, and calm is re-established.
Neither whirlpool nor confluence are mentioned in these cases,
but they clearly extend to them. This gives great importance to the
Catlo'ltq story from the American Northwest that is paradigmatic
(see chapter XXII) of the maiden who shoots her arrow into the
4 HAOG, p. 156, n. 7 ("wo die Flut versiegte").
5 W. Stutterheim, Rama-Legenden und Rama-Reliefs in Indonesien (1925), p. 54.
215 • The Waters from the Deep
"navel of the waters which was a vast whirlpool," thus winning
fire. Some very fundamental idea must be lurking behind the story,
and a pretty old one, since it was said of Ishtar that it is "she who
stirs up the apsu before Ea."6
A strange pastime for the heavenly queen, but it seems to have
been a rather celestial sport. The eighth Yasht of the Avesta,7 dedi-
cated to Sirius-Tishtriya, says of this star: "We worship the splen-
did, brilliant Tishtriya, which soars rapidly to Lake Vurukasha,
like the arrow quick-as-lightning, which Urxsa the archer, the
best archer among the Aryans, shot from Mount Aryioxsutha to
Mount Huvanvant."8 And what does Sirius do to this sea? It causes
"Lake Vurukasha to surge up, to flood asunder, to spread out; at
all shores surges Lake Vurukasha, the whole center surges up" (Yt.
8.31; see also 5.4). Whereas Pliny9 wants to assure us that "the
whole sea is conscious of the rise of that star, as is most clearly seen
in the Dardanelles, for sea-weed and fishes float on the surface, and
everything is turned up from the bottom." He also remarks that at
6 "Descent of Ishtar to the Nether World," obv. 1. 27, ANET, p. 107; see also
W. F. Albright, "The Mouth of the Rivers," AJSL 55 (1919), p. 184.
7 Yasht 8.6 and 8.37 (H. Lommel, Die Yashts des Awesta [1927]).
8 See for the feat of this unpronounceable archer (Rkhsha) the report given by
Al-Biruni, who spells him simply Arish (The Chronology of Ancient Nations,
trans. E. Sachau [1879], p. 205). The background of the tale: Afrasiyab had prom-
ised to restore to Minocihr a part of Eranshar (which had been conquered by him)
as long and as broad as an arrow shot. Arish shot the arrow on the 13 th day of the
month Tir-Mah, after having announced: "I know that when I shoot with this bow
and arrow I shall fall to pieces and my life will be gone." Accordingly, when he
shot, he "fell asunder into pieces. By order of God the wind bore the arrow away
from the mountain of Ruyan and brought it to the utmost frontier of Khurasan be-
tween Farghana and Tabaristan; there it hit the trunk of a nut-tree that was so large
that there had never been a tree like it in the world. The distance between the place
where the arrow was shot and that where it fell was 1,000 Farsakh." (See also
S. H. Taqizadeh, Old Iranian Calendars [1938], p. 44.) Tir or Tira is the name for
Mercury (see T. Hyde, Veterum Fersarum et Parthorum Religionis historia [1760],
p. 24: "Tir, i.e., Sagitta . . ., quo etiam nomine appellatur Mercurius Planeta propter
velociorem motum"), but it is also, along with Tishtriya, the name for Sirius (see
A. Scherer, Gestirnnamen bet den indogermanischen Volkern [1953], pp. 113f.),
and the 13th day of every month is dedicated to Sirius-Tishtriya (see Lommel,
p. 5). We must leave it at that: Sirius-the-arrow has made more mythical "noise"
than any other star, and also its connection with the ominous number 13 appears
to be no Iranian monopoly.
9 9.58. Cf. Aristotle, Historia Animalium 8.15.599B-600.
Hamlet's Mill • 216
the rising of the Dog-Star the wine in the cellars begins to stir up
and that the still waters move (2.107)— and the Avesta offers as
explanation (Yt. 8.41) that it is Tishtriya, indeed, "by whom count
the waters, the still and the flowing ones, those in springs and in
rivers, those in channels and in ponds."10
This is, however, no Iranian invention: the ritual text of the
Babylonian New Year addresses Sirius as "mulKAK.SI.DI. who mea-
sures the depth of the Sea." mul is the prefix announcing the star,
KAK.SI.DI means "arrow," and it is this particular arrow which
is behind most of the bewildering tales of archery. The bow from
which it is sent on its way is a constellation, built from stars of
Argo and Canis Major, which is common to the spheres of Meso-
potamia, Egypt and China.11 And since the name Ishtar is shared by
both Venus and Sirius, one may guess who "stirs up the apsu
before Ea."
And here is what the "fire" accomplished, according to a Finnish
rune of origin,12 after it had been "cradled . . . over there on the
navel of the sky, on the peak of the famous mountain," when it
rushed straightaway through seven or nine skies and fell into the
sea: "The spark . . . rolled ... to the bottom of Lake Aloe, roaring
it rushed to the bottom of the sea, down into the narrow depres-
sion (?). This Lake Aloe then, thrice in the summernight, rose
foaming to the height of its firs, driven in fury beyond its banks.
Thereupon again Lake Aloe thrice in the summernight dried up its
waters to the bottom, its perch on the rocks, its pope [small fishes]
on the skerries."
A violent spark this seems to have been; yet—is it not also said
of the old Sage: "Vainamoinen in the mouth of the whirlpool boils
like fire in water"?13 Which goes to show that mythical "fire" means
more than meets the eye. Actually, the enigmatical events in "Lake
10 Trans. E. Herzfeld, Zoroaster and His World (1947), p. 587.
11 There is strong circumstantial evidence of this bow and arrow in Mexico also:
the bow of the Chichimeca, the Dog-people.
12 K. Krohn, Magische Ursprungsrunen der Finnen (1924), pp. 115ff. See also F.
Ohrt, The Spark in the Water (1926), pp. 3f.
13 M. Haavio, Vainamoinen, Eternal Sage (1952), p. 196.
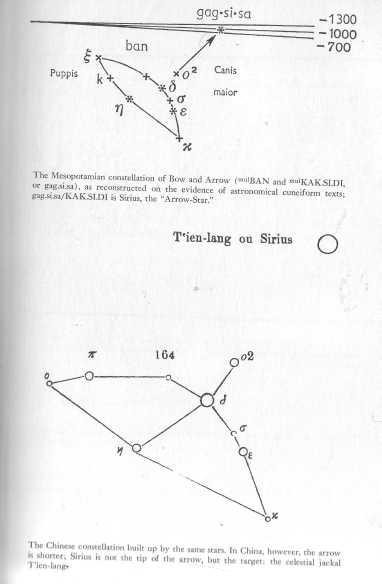


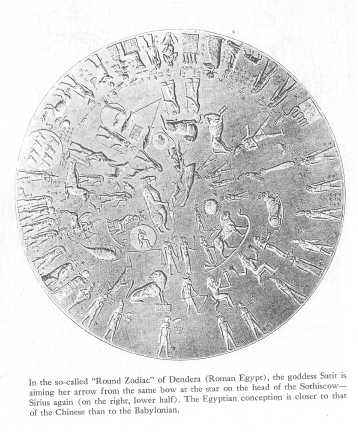
217 . The Waters from the Deep
Aloe" cannot be severed from those occurring in Lake Vurukasha
and the coming into being of the "three outlets," the first of which
had the name Hausravah/Kai Khusrau (see chapter XIII, "Of Time
and the Rivers," p. 201).
Before we move on to many motifs which will be shown as
related to the same "eddy-field" or whirl, it is appropriate to quote
in full a version of the fire and water story from the Indians of
Guyana. This not only provides charming variations, but presents
that rarest of deities, a creator power neither conceited nor touchy
nor jealous nor quarrelsome nor eager to slap down unfortunates
with "inborn sin," but a god aware that his powers are not really
unlimited. He behaves modestly, sensibly and thoughtfully and is
rewarded with heartfelt cooperation from his creatures, at least
from all except for the usual lone exception.
The Ackawois of British Guiana say that in the beginning of the
world the great spirit Makonaima [or Makunaima; he is a twin-hero;
the other is called Pia] created birds and beasts and set his son Sigu to
rule over them. Moreover, he caused to spring from the earth a great
and very wonderful tree, which bore a different kind of fruit on each
of its branches, while round its trunk bananas, plantains, cassava,
maize, and corn of all kinds grew in profusion; yams, too, clustered
round its roots; and in short all the plants now cultivated on earth
flourished in the greatest abundance on or about or under that mar-
vellous tree.
In order to diffuse the benefits of the tree all over the world, Sigu
resolved to cut it down and plant slips and seeds of it everywhere, and
this he did with the help of all the beasts and birds, all except the
brown monkey, who, being both lazy and mischievous, refused to
assist in the great work of transplantation. So to keep him out of
mischief Sigu set the animal to fetch water from the stream in a basket
of open-work, calculating that the task would occupy his misdirected
energies for some time to come.
In the meantime, proceeding with the labour of felling the miraculous
tree, he discovered that the stump was hollow and full of water in
which the fry of every sort of fresh-water fish was swimming about.
The benevolent Sigu determined to stock all the rivers and lakes on
earth with the fry on so liberal a scale that every sort of fish should
swarm in every water.

Hamlet's Mill • 218
But this generous intention was unexpectedly frustrated. For the
water in the cavity, being connected "with the great reservoir some-
where in the bowels of the earth, began to overflow; and to arrest the
rising flood Sigu covered the stump with a closely woven basket. This
had the desired effect. But unfortunately the brown monkey, tired of
his fruitless task, stealthily returned, and his curiosity being aroused
by the sight of the basket turned upside down, he imagined that it
must conceal something good to eat. So he cautiously lifted it and
peeped beneath, and out poured the flood, sweeping the monkey him-
self away and inundating the whole land. Gathering the rest of the
animals together Sigu led them to the highest points of the country,
where grew some tall coconut-palms. Up the tallest trees he caused
the birds and climbing animals to ascend; and as for the animals that
could not climb and were not amphibious, he shut them in a cave
with a very narrow entrance, and having sealed up the mouth of it
with wax he gave the animals inside a long thorn with which to pierce
the wax and so ascertain when the water had subsided. After taking
these measures for the preservation of the more helpless species, he
and the rest of the creatures climbed up the palm-tree and ensconced
themselves among the branches.
During the darkness and storm which followed, they all suffered in-
tensely from cold and hunger; the rest bore their sufferings with
stoical fortitude, but the red howling monkey uttered his anguish in
such horrible yells that his throat swelled and has remained distended
ever since; that, too, is the reason why to this day he has a sort of
bony drum in his throat.
Meanwhile Sigu from time to time let fall seeds of the palm into the
water to judge of its depth by the splash. As the water sank, the
interval between the dropping of the seed and the splash in the water
grew longer; and at last, instead of a splash the listening Sigu heard
the dull thud of the seeds striking the soft earth. Then he knew that
the flood had subsided, and he and the animals prepared to descend.
But the trumpeter-bird was in such a hurry to get down that he
flopped straight into an ant's nest, and the hungry insects fastened on
his legs and gnawed them to the bone. That is why the trumpeter-
bird has still such spindle shanks. The other creatures profited by this
awful example and came down the tree cautiously and safely.
Sigu now rubbed two pieces of wood together to make fire, but just
as he produced the first spark, he happened to look away, and the
bush-turkey, mistaking the spark for a fire-fly, gobbled it up and
flew off. The spark burned the greedy bird's gullet, and that is why
turkeys have red wattles on their throats to this day.
219 • The Waters from the Deep
The alligator was standing by at the time, doing no harm to anybody;
but as he was for some reason an unpopular character, all the other
animals accused him of having stolen and swallowed the spark. In
order to recover the spark from the jaws of the alligator Sigu tore out
the animal's tongue, and that is why alligators have no tongue to
speak of down to this very day.14
There are many more stories over the world of a plug whose
removal causes the flood: with the Agaria, an ironsmith tribe of
Central India, it is the breaking of a nail of iron which causes their
Golden Age town of Lohripur to be flooded.15 According to the
Mongolians, the Pole star is "a pillar from the firm standing of
which depends the correct revolving of the world, or a stone which
closes an opening: if the stone is pulled out, water pours out of the
opening to submerge the earth."16 In the Babylonian myth of
Utnapishtim, "Nergal [the God of the Underworld] tears out
the posts; forth comes Ninurta and causes the dikes to follow"
(GE 11.10.1f.). But the new thing to be faced is the appearance of
the Ark in the flood, Noah's or another's.
The first ark was built by Utnapishtim in the Sumerian myth;
one learns in different ways that it was a cube—a modest one, mea-
suring 60 x 60 x 60 fathoms, which represents the unit in the sexa-
gesimal system where 60 is written as 1. In another version, there
is no ark, just a cubic stone, upon which rests a pillar which reaches
from earth to heaven. The stone, cubic or not, is lying under a
cedar, or an oak, ready to let loose a flood, without obvious reasons.
Confusing as it is, this seems to provide the new theme. In Jewish
legends, it is told that "since the ark disappeared there was a stone
in its place . . . which was called foundation stone." It was called
foundation stone "because from it the world was founded [or
started]." And it is said to lie above the Waters that are below the
Holy of Holies.
14 W. H. Brett, The Indian Tribes of Guiana (1868), pp. 378-84; Sir Everard F.
im Thurn, Among the Indians of Guiana (1883), pp. 379-81 (quoted in J. G.
Frazer, Folklore in the Old Testament [1918], vol. 1, p. 265). The italics are ours.
15 V. Elwin, The Agaria (1942), pp. 96ff.
16 G. M. Potanin, quoted by W. Ludtke, "Die Verchrung Tschingis-Chans bei
den Ordos-Mongolen," ARW 25 (1927), p. 115.
Hamlet's Mill
220
This might look like a dream sequence, but it is buttressed by a
very substantial tradition, taken up by the Jews but to be found
also in Finno-Ugrian tradition.17 The Jewish story then goes on:
When David was digging the foundations of the Temple, a shard was
found at a depth of 1500 cubits. David was about to lift it when the
shard exclaimed: "Thou canst not do it." "Why not?" asked David.
"Because I rest upon the abyss." "Since when?" "Since the hour in
which the voice of God was heard to utter the words from Sinai, 'I
am the Lord, your God,' causing the world to quake and sink into the
Abyss. I lie here to cover up the Abyss."
Nevertheless David lifted the shard, and the waters of the Abyss
rose and threatened to flood the earth. Ahithophel was standing by
and he thought to himself: "Now David shall meet with his death and
I shall be king." Just then David said: "Whoever knows how to stem
the tide of waters and fails to do it, will one day throttle himself."
Thereupon Ahithophel had the name of God inscribed upon the
shard, and the shard thrown into the Abyss. The waters at once com-
menced to subside, but they sank to so great a depth that David
feared the earth might lose her moisture, and he began to sing the
fifteen "Songs of Ascents," to bring the waters up again.
The foundation stone here has become a shard and its name in
tradition is Eben Shetiyyah, which is derived from a verb of many
meanings:18 "to be settled, satisfied; to drink; to fix the warp, to lay
the foundations of," among which "to fix the warp" is the most
revealing, and a reminder of the continuing importance of "frames."
Within that "frame" there is a surging up and down of the waters
below (as in the Phaedo myth) which suggests catastrophes un-
recorded by history but indicated only by the highly colored termi-
nology of cosmologists. Had they only known of a Cardan suspen-
sion, the world might haye been conceived as more stable.
Hildegard Lewy's researches19 on Eben Shetiyyah brought up a
passage in the Annals of Assur-nasir-apli in which the new temple
17 L. Ginzberg, The Legends of the Jews (1954), vol. 4, p. 96; cf. also vol. 1, p. 12;
vol. 5, p. 14. We are indebted to Irvin N. Asher for the quotation, as well as for
the ones from Jastrow that follow. Cf. V. J. Mansikka, "Der blaue Stein," FUF
11 (1911),p. 2.
18 The verb is shatan; the meanings are given in Jastrow's dictionary.
19 "Origin and Significance of the Magen Dawid," Archiv Orientalni 18 (1950),
Pt- 3. PP- 344ff.
221
The Waters from the Deep
of Ninurta at Kalhu is described as founded at the depth of 120
layers of bricks down "to the level of the waters," or, down to the
water table. This comes back to the waters of the deep in their
natural setting. But what people saw in them is something else
again. If David and the Assyrian king dug down to subsoil water,
so did the builders of the Ka'aba in Mecca. In the interior of that
most holy of all shrines there is a well, across the opening of which
had been placed, in pre-Islamic times, the statue of the god Hubal.
Al-Biruni says that in the early Islamic period this was a real well,
where pilgrims could quench their thirst at least at the time of the
Arab pilgrimage. The statue of Hubal had been meant to stop the
waters from rising. According to the legends, the same belief had
once been current in Jerusalem. Hence the holy shard. But Mecca
tells more. Hildegard Lewy points out that, in pre-Islamic days, the
god Hubal was Saturn, and that the Holy Stone of the Ka'aba had
the same role, for it was a cube, and hence originally Saturn. Kep-
ler's polyhedron inscribed in the sphere of Saturn is only the last
witness of an age-old tradition.
The humble little shard was brought in by pious legend to try to
say that what counted was the power of the Holy Name. But the
real thing was the cube: either as Utnapishtim's ark or, in other
versions, as a stone upon which rests a pillar which reaches from
earth to heaven. Even Christ is compared to "a cube-shaped moun-
tain, upon which a tower is erected."20 Hocart writes that "the
Sinhalese frequently placed inside their topes a square stone repre-
senting Meru. If they placed in the center of a tope a stone repre-
senting the center of the world it must have been that they took the
tope to represent the world"21—which goes without saying. But it
is said otherwise that this stone, the foundation stone, lies under a
great tree, and that from under the stone "a wave rose up to the
sky."
This sounds like a late mixture, with no reasons given; the way
to unscramble the original motifs is to take them separately.
20 In the ninth simile of the "Pastor of Hermas," according to F. Kampers ( Vom
Werdegange der abendlandischen Kaisermystik [1924], p. 53).
21 Kingship, p. 179 (quoted by P. Mus, Barabudur 1935 , p. 108,11. 1).
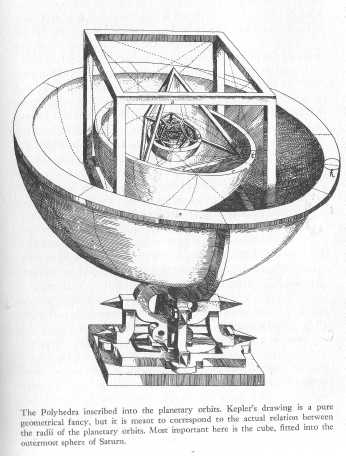
Hamlet's Mill • 222
But first, some stock-taking is in order at this point. There are a
number of figures to bring together. The brown monkey, father of
mischief in Sigu's idyllic creation, is familiar under many disguises.
He is the Serpent of Eden; the lone dissenter. He is Loke who
persuaded the mistletoe not to weep over Balder's death, thus
breaking the unanimity of creatures. Sigu himself, benevolent king
of the Golden Age, is an unmistakably Saturnian figure, who dwelt
among his creatures, and so is Iahwe, at least when he still "walked
with Adam in the garden." A ruler who "means well" is a Saturnian
character. No one but Saturn dwelt among men. Says an Orphic
fragment: "Orpheus reminds us that Saturn dwelt openly on earth
and among men."22 Dionysius of Halicarnassus (1.36.1) writes:
"Thus before the reign of Zeus, Kronos ruled on this very earth
to which Maximilian Mayer crisply annotates: "We find no men-
tion anywhere of such an earthly sojourn on the part of Zeus.
In a similar way, Sandman Holmberg states with respect to Ptah,
the Egyptian Saturn: "The idea of Ptah as an earthly king returns
again and again in Egyptian texts," and also points to "the remark-
able fact that Ptah is the only one of the Egyptian gods who is
represented with a straight royal beard, instead of with a bent
beard."24
The Saturnalia, from Rome to Mexico, commemorated just this
aspect of Saturn's rule, with their general amnesties, masters serving
slaves etc., even if Saturn was not always directly mentioned.
When this festival was due in China, so to speak "sub delta Gemi-
norum"—more correctly, delta and the Gemini stars 61 and 56 of
Flamsteed—"there was a banquet in which all hierarchic distinctions
were set aside ... The Sovereign invited his subjects through the
'Song of Stags.'"25
The cube was Saturn's figure, as Kepler showed in his Mysterium
Cosmographicum; this is the reason for the insistence on cubic
stones and cubic arks. Everywhere, the power who warns Noah
22 Orphicorum Fragmenta (1963), frg. 139, p. 186, from Lactantius.
23 M Mayer, in Roscher s.v. Kronos, pp. 1458f.
24 M. Sandman Holmberg, The God Ptah (1946), pp. 83, 85.
25 G. Schlegel, L'Uranographie Chinoise (1875), p. 424.
223 . The Waters from the Deep
and urges him to build his ark is Saturn, as Jehovah, as Enki, as
Tane, etc. Sigu's basket stopper was obviously an inadequate ver-
sion of the cube seen through the fantasy of basket-weaving na-
tives. This leads to the conclusion that Noah's ark originally had a
definite role in bringing the flood to an end. An interesting and
unexpected conclusion for Bible experts.
One of the great motifs of myth is the wondrous tree so often
described as reaching up to heaven. There are many of them—the
Ash Yggdrasil in the Edda, the world-darkening oak of the Kale-
vala, Pherecydes' world-oak draped with the starry mantle, and the
Tree of Life in Eden. That tree is often cut down, too. The other
motif is the foundation stone, which sometimes becomes a cubic ark.
These motifs must first be traced through. After reading the
beautiful story of Sigu's wonder tree, in whose stump are all the
kinds of fish to populate the world, it needs patience to cope with
the cubic stone which is found in the middle of the sea, under which
dwells a mystic character whose guises vary from a miraculous fish,
even a whale, to a "green fire," the "king of all fires," the "central
fire," to the Devil himself. The chief source for him are Russian26
and Finnish magic formulae, and these "superstitions" ("left-overs")
are Stone Age fragments of flinty hardness embedded in the softer
structure of historic overlay. Magic material withstands change,
just because of its resistance to the erosion of common sense. As far
as these magic formulae go, they became embedded in a Christian
context as the particular populations underwent conversion, but
they remain as witnesses for a very different understanding of the
cosmos. For example, Finnish runes on the origin of water state that
"all rivers come from the Jordan, into which all rivers flow," that
"water has its origin in the eddy of the holy river—it is the bathing
water of Jesus, the tears of God."27 On the other hand, Scandina-
vian formulae stress the point that Christ "stopped up the Jordan"
or "the Sea of Noah" (Mansikka, pp. 244f., 297, n. 1) which, in its
turn, fits into the Pastor of Hennas, where Christ is compared to a
"cube-shaped mountain" (see above, p. 221). From this it is not
28 V. J. Mansikka, Uber russische Zauberformeln (1909), pp. 184-87, 189, 192.
27 Krolm, Ursprungsrunen, pp. 106f.
Hamlet's Mill • 224
strange that the Cross becomes the "new tree," marking new cross-
roads. One need not go as far as Russia for that. In the famous
frescoes of Piero della Francesca in Arezzo there is "the discovery
of the True Cross." It begins with the death of Adam, lying at the
foot of the tree. The wood from the tree will later provide the
material for the Cross. Later still, St. Helena, mother of Constan-
tine, sees it in a dream and causes the wood to be dug up to become
the holiest of relics. Piero illustrated nothing that was not in good
medieval tradition. This is, one might say, sensitive ground.
Chapter XVI
The Stone and the Tree
In Xanadu did Kubla Khan
A stately pleasure dome decree
Where Alph, the sacred river, ran
Through caverns measureless to man
Down to a sunless sea.
Coleridge, Kubla Khan
. he ground, indeed, is not only sensitive but difficult and shift-
ing as well. If the whirlpool turns up in the theory of the Cross, it
is certainly without the consent of theologians. Yet the instances so
far given are not isolated ones. It is necessary to deal with material
which may appear suspicious to the trained historical reader, who is
bound to be wary of omne ignotum pro magnifico. One should,
therefore, preface this chapter with a small case history, which may
show the infrangible tenacity of certain kinds of transmitted ma-
terial, fragments of a sort official memory is prone to dismiss or
neglect.
In the Gospel of Mark 111.17, the "twins" James and John, the
sons of Zebedee, are given by Jesus the name of Boanerges, which
the Evangelist explains as meaning "Sons of Thunder."1 This was
long overlooked but eventually became the title of a work by a
distinguished scholar, too soon forgotten, Rendel Harris. Here the
Thunder Twins were shown to exist in cultures as different as
Greece, Scandinavia and Peru. They call to mind the roles of Magni
and Modi, not actually called twins, but successors of Thor, in
Ragnarok. But to quote from Harris:-
1 Kai epetheken autois onoma Boanerges, ho estin hyioi brontes.
Hamlet's Mill • 226
We have shown that it does not necessarily follow that when the
parenthood of the Thunder is recognised, it necessarily extends to
both of the twins. The Dioscuri may be called unitedly, Sons of Zeus;
but a closer investigation shows conclusively that there was a ten-
dency in the early Greek cults to regard one twin as of divine paren-
tage, and the other of human. Thus Castor is credited to Tyndareus,
Pollux to Zeus . .. The extra child made the trouble, and was credited
to an outside source. Only later will the difficulty of discrimination
lead to the recognition of both as Sky-boys or Thunder-boys. An
instance from a remote civilization will show that this is the right
view to take.
For example, Arriaga, in his "Extirpation of Idolatry in Peru" tells
us that "when two children are produced at one birth, which they
call Chuchos or Curi, and in el Cuzco Taqui Hua-hua, they hold it
for an impious and abominable occurrence, and they say, that one of
them is the child of the Lightning, and require a severe penance, as if
they had committed a great sin."
And it is interesting to note that when the Peruvians, of whom Ar-
riaga speaks, became Christians, they replaced the name of Son of
Thunder, given to one of the twins, by the name of Santiago, having
learnt from their Spanish (missionary) teachers that St. James (San-
tiago) and St. John had been called Sons of Thunder by our Lord, a
phrase which these Peruvian Indians seem to have understood, where
the great commentators of the Christian Church had missed the
meaning . . .
Another curious and somewhat similar transfer of the language of the
Marcan story in the folk-lore of a people, distant both in time and
place . . . will be found, even at the present day, amongst the Danes
. . . Besides the conventional flint axes and celts, which commonly
pass as thunder-missiles all over the world, the Danes regard the fossil
sea-urchin as a thunderstone, and give it a peculiar name. Such stones
are named in Sailing, sebedaei-stones or s'bedaei; in North Sailing
they are called sepadeje-stones. In Norbaek, in the district of Viborg,
the peasantry called them Zebedee stones! At Jebjerg, in the parish
of Cerum, district of Randers, they called them sebedei-stones . . .
The name that is given to these thunderstones is, therefore, very well
established, and it seems certain that it is derived from the reference
to the Sons of Zebedee in the Gospel as sons of thunder. The Danish
peasant, like the Peruvian savage, recognised at once what was meant
by Boanerges, and called his thunderstone after its patron saint.2
This might have given pause to later hyperscholars like Bult-
mann, before they proceeded to "de-mythologize" the Bible. One
never knows what one treads underfoot. Conversely, it shows that
2 R. Harris, Boanerges (1913), pp. 9ff.
227
The Stone and the Tree
some misunderstanding beyond the knowledge of the experts must
be accounted for before one deals with the whole information.
Thus, there is no intention to dismiss the abundant legends and
runes dealing with the wood of the Cross. Lack of time, however,
does not allow for a proper investigation,3 and permits only some
remarks on Finnish and Russian notions about the "Great Oak,"
which is the nearest "relative" of Sumerian trees. Says one of the
Finnish runes: "Long oak, broad oak. What is the wood of its
root? Gold is the wood of its root. The sky is the wood of the
oak's summit. An enclosure within the sky. A wether in the en-
closure. A granary on the horn of the wether."4 The next version
boldly puts "the granary upon the top of the cross." According to
a further version, in the crown of the oak is a cradle with a little
boy, who has an axe upon his shoulder. More stunning notions
occur in a Russian Apocryph where Satanael planted the tree in
the paradise intending to get out of it a weapon against Christ:
"The branches of the tree spread over the whole paradise, and
it also covered the Sun. Its summit touched the sky, and from its
roots sprang fountains of milk and honey."5
This latter idea in its turn fits the medieval tradition according
to which the rivers of Paradise gushed forth from under the Cross.
There will be other bewildering "trees" in the chapter on Gilga-
mesh, but there also no attempt will be made to exhaust the huge
and ambiguous evidence.
But with the caveats distilled from the Sons of Thunder, and
similar instances, it is possible to deal with more outlandish data.
First, there is in the Atharva Veda, a whole hymn dedicated to
what may be called the world pillar (a highly multivalent pillar),
called the skambha from which—see above, p. 111—the Finnish
Sampo is derived. At this point only one verse will serve, in which
the fiery monster of the deep is mentioned:6
3 For a rich collection of material see F. Kampers, Mittelalterliche Sagen vom
Paradiese und vom Holze des Kreuzes Christi (1897).
4 K. Krohn, Magische Ursprungsrunen der Finnen (1924), p. 192.
5 Krohn, p. 197.
6 To prevent relentless experts from pointing to "fundamental" investigations
which are, no doubt, unknown to us: the chapter on yaksa in Pischel and Geldner's
Vedische Studien is not unknown to us; there arc several momentous reasons why
we prefer to stick to the "obsolete" submarine "monster."
Hamlet's Mill • 228
AV zo.7.38. A great monster [yaksa] in the midst of the creation,
strode in penance on the back of the sea—in it are set whatever gods
there are, like the branches of a tree roundabout the trunk.
Or, to take a testimony from "late" astrological sources, these
statements given by the Liber Hermetis Trismegisti which became
so famous in the Middle Ages, to the degrees of Taurus (Gundel,
pp. 54f, 217ff.):
18-20 deg oritur Navis et desuper Draco mortuus, vocatur Terra
rises the Ship, and on it the dead Dragon, called Earth
21-23 deg oritur qui detinet navem, Deus disponens universwn mundum
rises he who keeps (or detains) the ship, the God that orders
the whole universe. [Disponere corresponds to Greek kos-
meo.]
Whatever it is that rules "below" seems, indeed, a truly omnipo-
tent entity: There are, after all, very few, if any, characters who
are simply said to "order the whole universe."
This remarkable "kosmokrator" will be dealt with; the fiery
creature deep down in the sea, however, has to be banished into
an appendix. That it is relevant to the whole scheme can be seen
from the fact that "Vainamoinen in the mouth of the whirlpool
boils like fire in the water"7 (appendix #19).
The words of Hermes-Three-Times-Great, cryptic as they sound,
are part of the highly organized technical language of astrologers;
we mean not those who cast people's fortunes for pay, but those
•who speculated on the traditional system of the world, and made
use of whatever there was of astronomy, geography, mythology,
holy texts of the laws of time and change, to build up an ambitious
system. Abu Ma'shar and Michael Scotus were later dismissed as
triflers, false prophets, and magicians, but Tycho and Kepler still
held them in high esteem: they represented whatever there was
of real science in the 13th century, and produced many dar-
ing thoughts. The ignotum may conceivably turn out to be
magnificum.
7 M. Haavio, Vainamoinen, Eternal Sage (1952), p. 196.
229 • The Stone and the Tree
The few disconnected sayings quoted may be called lacking in
sense and method. They will be shored up with more material. Actu-
ally, we had to sentence this chapter—once "swelling" enough to
burst every seam—to the most meager of diets until it shriveled to
its present state of emaciation and apparent lack of coherence. But
first, one should understand what the latent geometrical design can
imply, as it broke through, time and again, in the past chapters.
Chapter XVII
The Frame of the Cosmos
La mythologie, dans son origine,
est l'ouvrage de la science; la
science seule l'expliquera.
Charles Dupuis
I
In Greek myth, the basic frame of the world is described in the
famous Vision of Er in the 10th Book of the Republic. In it we find
Er the Armenian, who was resurrected from the funeral pyre just
before it was kindled, and who describes his travel through the
other world (10.615.ff.). He and the group of souls bound for re-
birth whom he accompanies travel through the other world. They
come to "a straight shaft of light, like a pillar, stretching from above
throughout heaven and earth—and there, at the middle of the light,
they saw stretching from heaven the extremities of its chains; for
this light binds the heavens, holding together all the revolving
firmament like the undergirths of a ship of war. And from the
extremities stretched the Spindle of Necessity, by means of which
all the circles revolve."
Cornford adds in a note: "It is disputed whether the bond hold-
ing the Universe together is simply the straight axial shaft or a
circular band of light, suggested by the Milky Way,1 girdling the
heaven of fixed stars."2 Eisler understood it as the zodiac, strange
to say.3 Since those "undergirths" of the trireme did not go around
the ship horizontally, but were meant to secure the mast (the
1 Cf. O. Gruppe, Griechische Mythologie und Religionsgeschichte (1906), p.
1036, n. 1: "probably the Milky Way."
2 Plato's Republic (Cornford trans.), p. 353.
3 Eisler, Weltenmantel und Himmmelszelt (1910), pp. 97ff.
231 • The Frame of the Cosmos
"tree" of the ship) which points upwards, we stand, on princi-
ple, for the Galaxy, which, however, had to be "replaced" by in-
visible colures in later times.4 But Er also talks of the adventures of
the souls between incarnations, and in this context we might rely
on the Milky Way. Surely the "model" is far from clear, even, on
Cornford's concession, obviously intentionally so. And indeed, a
few paragraphs later, there comes the complete planetarium with
its "whorls," the "Spindle of Necessity" held by the goddess, by
which sit the Fates as they unwind the threads of men's lives. The
souls can listen to the Song of Lachesis, if they are still in the
"meadow," but the chains and shaft or band are no longer in
the picture. Plato refuses to be a correct geometrician of the Other
World, just as he would not be sensible about the hydraulics of
it. But previously in the Phaedo, Socrates had been ironic about
the "truths" of science, and insisted that the truths of myth are of
another order, and rebellious to ordinary consistency. It is here as if
Plato had juxtaposed a number of revered mythical traditions (in-
cluding the planetary harmony) without pretending to fit them into
a proper order. And so his image of the "framework" of the cosmos
is left inconclusive. But somehow the axis and the band and the
chains stand together, and this, one concludes, was the original idea.
The rotation of the polar axis must not be disjointed from the
great circles which shift along with it in heaven. The framework
is thought of as all one with the axis. This leads back to a Pythago-
rean authority whom Plato was supposed to have followed (Timon
even viciously said: plagiarized) and whom Socrates often quotes
with unfeigned respect. It is Philolaos, surely a creative astronomer
of high rank, from whom there are only a few surviving fragments,
and the authenticity of these has been rashly challenged by many
modern philologists.5 In fragment 12 of Philolaos, there is a brief
definition of the cosmos, very much in the spirit of Plato's dode-
4 Cf. also the discussion in J. L. E. Dreyer, A History of Astronomy from
Thales to Kepler (1953), pp. 56ff. Concerning the "chains," which he translates
"ligatures," Dreyer states: "The ligatures (desmoi) of the heavens are the solstitial
and equinoctial colures intersecting in the poles, which points therefore may be
called their extremities (akra)."
5G. de Santillana and W. Pitts, "Philolaos in Limbo," ISIS 42 (1951), pp. 112-20;
also in Reflections on Men and Ideas (1968), p.p. 190-201.
Hamlet's Mill
232

cahedron quoted in chapter XII. "In the sphere there are five ele-
ments, those inside the sphere, fire, and water and earth and air,
and what is the hull of the sphere, the fifth."6 Notwithstanding
Philolaos' graceless Doric, the statement is perfectly clear. The
"hull," (olkas) was the common name for freighters, built for bulk
cargo, broad in the beam. It is really more adequate than Plato's
slim trireme; and it is closer in shape to what both men meant
apparently: the dodecahedron, the "hull," i.e., the sphere, the
actual containing frame. It is clear from Plato that the "fifth" is the
sphere that he calls ether which contains the four earthly elements
but is wholly removed from them. Aristotle was to change it to the
crystalline heavenly "matter" that he needed for his system, but
it remained for him a "fifth essence." There has thus been twice
repeated the original "hull," the frame that has been sought. What
happened, and was noted in chapter VII, was that the etymology
of Sampo was discovered to be in the Sanskrit skambha.
The abstract idea of a simple earth axis, so natural today, was
by no means so logical to the ancients, who always thought of the
whole machinery of heaven moving around the earth, stable at the
center. One line always implied many others in a structure. So,
apparently one must accept the idea of the world frame as an implex
(as used here and later this word involves the necessary attributes
that are associated with a concept: e.g., the center and circumfer-
ence of a circle, the parallels and meridians implied by a sphere),
of which Grotte and Sampo were the rude models with their pon-
derous moving parts.
Like the axle of the mill, the tree, the skambha, also represents
the world axis. This instinctively suggests a straight, upright post,
but the word axis is a simplification of the real concept, There is the
invisible axis, of course, which is crowned by the North Nail, but
this image needs to be enriched by two more dimensions. The term
world axis is an abbreviation of language comparable to the visual
abbreviation achieved by projecting the reaches of the sky onto a
flat star map. It is best not to think of the axis in straight analytical
terms, one line at a time, but to consider it, and the frame to which
6 Sec H. Diels, Die Fragments der Vorsokratiker (1951), vol. 1, pp.412f.
233 • The Frame of the Cosmos
it is connected, as one whole. This involves the use of multivalent
terms and the recognition of a convergent involution of unusual
meanings.
As radius automatically calls circle to mind, so axis must invoke
the two determining great circles on the surface of the sphere, the
equinoctial and solstitial colures. Pictured this way, the axis resem-
bles a complete armillary sphere. It stands for the system of coor-
dinates of the sphere and represents the frame of a world-age.
Actually the frame defines a world-age. Because the polar axis and
the colures form an indivisible whole, the entire frame is thrown
out of kilter if one part is moved. When that happens, a new Pole
star with appropriate colures of its own must replace the obsolete
apparatus.
Thus the Sanskrit skambha, the world pillar, ancestor of the
Finnish Sampo, is shown to be an integral element in the scheme
of things. The hymn io.7of the Atharva Veda is dedicated to the
skambha, and Whitney, its translator and commentator7 sounds
puzzled in his footnote to 10.7.2: "Skambha, lit. 'prop, support,
pillar,' strangely used in this hymn as frame of the universe or held
personified as its soul." Here are two verses of it:
12. In whom earth, atmosphere, in whom sky is set, where fire, moon,
sun, wind stand fixed, that Skambha tell . . .
35. The Skambha sustains both heaven-and-earth here; the skambha
sustains the wide atmosphere, the skambha sustains the six wide
directions; into the skambha entered this whole existence.
The good old Sampo sounds less pretentious, but it does have its
three "roots," "one in heaven, one in the earth, one in the water-
eddy."8 To make a drawing of a pillarlike tree (let alone a mill),
with its roots distributed in the manner indicated, would be quite a
task. Notably it takes the "enormous bull of Pohja"—obviously a
cosmic bull—to plow up these strange roots: the Finnish heroes by
themselves had not been able to uproot the Sampo.
In the case of Yggdrasil, the World Ash, Rydberg tried his hard-
est to localize the three roots, to imagine and to draw them. Since he
7 Harvard Oriental Series, vol. 8, p. 590.
8 K. Krohn, Kalevalastudien 4. Sampo (1927), p. 13.
Hamlet's Mill
234
looked with steadfast determination into the interior of our globe,
the result was not overly convincing. One of the roots is said to
belong to the Asa in heaven, and beneath it is the most sacred foun-
tain of Urd. The second is to be found in the quarters of the frost-
giants "where Ginnungagap formerly was," and where the well of
Mimir now is. The third root belongs to Niflheim, the realm of the
dead, and under this root is Hvergelmer, the Whirlpool (Gylf. 15) .9
This precludes any terrestrial diagram. It looks as though the
"axis," implicating the equinoctial and solstitial colures, runs
through the "three worlds" which are, to state it roughly and most
inaccurately, the following:
(a) the sky north of the Tropic of Cancer, i.e., the sky proper, do-
main of the gods
(b) the "inhabited world" of the zodiac between the Tropics, the
domain of the "living"
(c) the sky south from the Tropic of Capricorn, alias the Sweet-
Water Ocean, the realm of the dead.
The demarcation plane between solid earth and sea is represented
by the celestial equator; hence half of the zodiac is under "water,"
the southern ecliptic, bordered by the equinoctial points. There
are more refined subdivisions, to be sure, "zones" or "belts" or
"climates," dividing the sphere from north to south and, most im-
portant, the "sky" as well as the waters of the south have a share
in the "inhabited world" allotted to them.10 This "summary is an
almost frivolous simplification, but for the time being it may be
sufficient.
9 We are aware that either Grotte "should" have three roots, or that Yggdrasil
should be uprooted, and that the Finns do not tell how the maelstrom came into
being. All of which can be explained; we wish, however, to avoid dragging more
and more material into the case. Several ages of the world have passed away, and
they do not perish all in the same manner; e.g., the Finns know of the destruction
of Sampo and of the felling of the huge Oak.
10 To clear up the exact range of the three worlds, it would be necessary to
work out the whole history of the Babylonian "Ways of Anu, Enlil, and Ea" (cf.
pp. 431f.), and how these "Ways" were adapted, changed, and defined anew
by the many heirs of ancient oriental astronomy. And then we would not
yet be wise to the precise whereabouts of Air, Saltwater, and other ambiguous
items.
235 • The Frame of the Cosmos
Meanwhile, it is necessary to explain again what this "earth" is
that modern interpreters like to take for a pancake. The mythical
earth is, in fact, a plane, but this plane is not our "earth" at all,
neither our globe, nor a presupposed homocentrical earth. "Earth"
is the implied plane through the four points of the year, marked by
the equinoxes and solstices, in other words the ecliptic. And this is
why this earth is very frequently said to be quadrangular. The four
"corners," that is, the zodiacal constellations rising heliacally at both
the equinoxes and solstices, parts of the "frame" skambha, are the
points which determine an "earth." Every world-age has its own
"earth." It is for this very reason that "ends of the world" are said
to take place. A new "earth" arises, when another set of zodiacal
constellations brought in by the Precession determines the year
points.
Once the reader has made the adjustment needed to think of the
frame instead of the "pillar" he will understand easily many queer
scenes which would be strictly against nature—ideas about planets
performing feats at places which are out of their range, as both the
poles are. He will understand why a force planning to uproot (or
to chop down) a tree, or to unhinge a mill, or merely pull out a
plug, or a pin, does not have to go "up"—or "down"—all the way
to the pole to do it. The force causes the same effect when it pulls
out the nearest available part of the "frame" within the inhabited
world.
Here are some examples of the manipulation of the frame, begin-
ning with a most insignificant survival. Actually this is a useful
approach, because the less meaningful the example, the more aston-
ishing is the fact of its surviving. Turkmen tribes of southern
Turkestan tell about a copper pillar marking the "navel of the
earth," and they state that "only the nine-year-old hero Kara Par
is able to lift and to extract" it.11 As goes without saying, nobody
comments on the strange idea that someone should be eager to
"extract the navel of the earth." When Young Arthur does it with
Excalibur, the events have already been fitted into a more familiar
frame and they provoke no questions.
11Radloff, quoted by W. E. Roscher, Der Omphalosgedanke (1918), pp. if.
Hamlet's Mill
236
In its grandiose style, the Mahabharata presents a similar prodigy
as follows:
It was Vishvamitra who in anger created a second world and numer-
ous stars beginning with Sravana . . . He can burn the three worlds
by his splendour, can, by stamping (his foot), cause the Earth to
quake. He can sever the great Meru from the Earth and hurl it to any
distance. He can go round the 10 points of the Earth in a moment.12
Vishvamitra is one of the seven stars of the Big Dipper, this at
least has been found out. But each planet is represented by a star of
the Wain, and vice versa, so this case does not look particularly
helpful.13
A cosmic event of the first order can be easily overlooked when
it hides modestly in a fairy tale. The following, taken from the
Indian "Ocean of Stories," tells of Shiva: "When he drove his tri-
dent into the heart of Andhaka, the king of the Asuras, though he
was only one, the dart which that monarch had infixed into the
heart of the three worlds was, strange to say, extracted."14
A plot can also shrink to unrecognizable insignificance when it
12 Mbh. 1.71, Roy trans., vol. 1, p. 171.
13 The notion of "numerous [newly appointed] stars beginning with Sravana"
should enlighten us. Sravana, "the Lame," is, in the generally accepted order, the
twenty-first lunar mansion, alpha beta gamma Aquilae, also called by the name
Ashvatta, which stands for a sacred fig tree but which means literally "below which
the horses stand" (Scherer, Gestirnnamen, p. 158), and which invites a comparison
with Old Norse Yggdrasil, meaning'"the tree below which Odin's horse grazes"
(Reuter, Germanische Himmelskunde, p. 236). Actually, the solstitial colure ran
through alpha beta gamma Aquilae around 300 B.C., and long after the time when
it used to pass through one or the other of the stars of the Big Dipper; the
equinoctial colure, however, comes down very near eta Ursae Majoris. Consider-
ing that eta maintains the most cordial relations with Mars in occidental astrology,
Vishvamitra might be eta, and might represent Mars, and that would go well
with the violent character of this Rishi. But even if we accept this for a working
hypothesis, there remains the riddle of the "second world," i.e., "second" with
respect to which "first" world? Although we have a hunch, we are not going to
try to solve it here and now. Two pieces of information should be mentioned,
however: (1) Mbh. 14.44 (Roy trans., vol. 12, p. 83) states: "The constellations
[— lunar mansions, nakshatras] have Sravana for their first"; (2) Sengupta (in
Burgess' trans, of Surya Siddhanta, p. xxxiv) claims that "the time of the present
redaction of the Mahabharata" was called "Sravanadi kala, i.e., the time when the
winter solstitial colure passed through the nakshatra Sravana."
14 N. M. Penzer, The Ocean of Story (1924), vol. 7, p. 3.
237 • The Frame of the Cosmos
comes disguised as history, but this next story at least has been
pinned down to the proper historical character, and even has been
checked by a serious military historian like Arrianus, who tells us
the following:
Alexander, then, reached Gordium, and was seized with an ardent
desire to ascend to the acropolis, where was the palace of Gordius and
his son Midas, and to look at Gordius' wagon and the knot of the
chariot's yoke. There was a widespread tradition about this chariot
around the countryside; Gordius, they said, was a poor man of the
Phrygians of old, who tilled a scanty parcel of earth and had but two
yoke of oxen: with one he ploughed, with the other he drove his
wagon. Once, as he was ploughing, an eagle settled on the yoke and
stayed, perched there, till it was time to loose the oxen; Gordius was
astonished at the portent, and went off to consult the Telmissian
prophets, who were skilled in the interpretation of prodigies, inherit-
ing—women and children too—the prophetic gift. Approaching a
Telmissian village, he met a girl drawing water and told her the story
of the eagle: she, being also of the prophetic line, bade him return to
the spot and sacrifice to Zeus the King. So then Gordius begged her
to come along with him and assist in the sacrifice; and at the spot duly
sacrificed as she directed, married the girl, and had a son called Midas.
Midas was already a grown man, handsome and noble, when the
Phrygians were in trouble with civil war; they received an oracle
that a chariot would bring them a king and he would stop the war.
True enough, while they were discussing this, there arrived Midas,
with his parents, and drove, chariot and all, into the assembly. The
Phrygians, interpreting the oracle, decided that he was the man
whom the gods had told them would come in a chariot; they there-
upon made him king, and he put an end to the civil war. The chariot
of his father he set up in the acropolis as a thank-offering to Zeus the
king for sending the eagle.
Over and above this there was a story about the wagon, that anyone
who should untie the knot of the yoke should be lord of Asia. This
knot was of cornel bark, and you could see neither beginning nor
end of it. Alexander, unable to find how to untie the knot, and not
brooking to leave it tied, lest this might cause some disturbance in
the vulgar, smote it with his sword, cut the knot, and exclaimed, "I
have loosed it!"—so at least say some, but Aristobulus puts it that
he took out the pole pin, a dowel driven right through the pole, hold-
ing the knot together, and so removed the yoke from the pole. I do
not attempt to be precise how Alexander actually dealt with this
knot. Anyway, he and his suite left the wagon with the impression
Hamlet's Mill
238
that the oracle about the loosed knot had been duly fulfilled. It is
certain that there were that night thunderings and lightnings, which
indicated this; so Alexander in thanksgiving offered sacrifice next day
to whatever gods had sent the signs and certified the undoing of the
knot.15
Without going now into the relevant comparative material it
should be stressed that in those cases where "kings" are sitting in a
wagon (Greek hamaxa), i.e., a four-wheeled truck, it is most of the
time Charles' Wain.
Alexander was a true myth builder, or rather, a true myth-
attracting magnet. He had a gift for attracting to his fabulous per-
sonality the manifold tradition that, once, had been coined for
Gilgamesh.
But the time is not yet ripe either for Alexander or for Gilga-
mesh, nor for further statements about deities or heroes who could
pull out pins, plugs and pillars. The next concern is with the deci-
sive features of the mythical landscape and their possible localiza-
tion, or their fixation in time. It is essential to know where and
when the first whirlpool came into being once Grotte, Amlodhi's
Mill, had been destroyed. This is, however, a misleading expression
because our terminology is still much too imprecise. It would be
better to say the first exit from, or entrance to, the whirlpool. It
appears advisable to recapitulate the bits of information that have
been gathered on the whirlpool as a whole:
The maelstrom, result of a broken mill, a chopped-down tree,
and the like, "goes through the whole globe," according to the
Finns. So does Tartaros, according to Socrates. To repeat it in
Guthrie's words: "The earth in this myth of Socrates is spherical,
and Tartaros, the bottomless pit, is represented in this mythical
geography by a chasm which pierces the sphere right through from
side to side."16
It is source and mouth of all waters.
It is the way, or one among others, to the realm of the dead.
Medieval geographers call it "Umbilicus Maris," Navel of the
Sea, or "Euripus."
15 Anabasis of Alexander 2.3.1-8 (Robson trans., LCL).
16 Orpheus and Greek Religion (1952), p. 168.
239 • The Frame of the Cosmos
Antiochus the astrologer calls Eridanus proper, or some abstract
topos not far from Sirius, "zalos," i.e., whirlpool.
M. W. Makemson looks for the Polynesian whirlpool, said to be
"at the end of the sky," "at the edge of the Galaxy," in Sagittarius.
A Dyak hero, climbing a tree in "Whirlpool-Island," lands him-
self in the Pleiades.
But generally, one looks for "it" in the more or less northwest-
north-northwest direction, a direction where, equally vaguely,
Kronos-Saturn is supposed to sleep in his golden cave notwithstand-
ing the blunt statements (by Homer) that Kronos was hurled down
into deepest Tartaros.
And from those "infernal" quarters, particularly from the (Ogy-
gian) Stygian landscape, "one"—who else but the souls?—sees the
celestial South Pole, invisible to us.
The reader might agree that this summary shows clearly the
insufficiency of the general terminology accepted by the majority.
The verbal confusion provokes sympathy for Numenius (see above,
p. 188), and the Third Vatican Mythographer who took the rivers
for planets, their planetary orbs respectively. We think that the
whirlpool stands for the "ecliptical world" marked by the whirling
planets, embracing everything which circles obliquely with respect
to the polar axis and the equator—oblique by 23.5 degrees, more
or less, each planet having its own obliquity with respect to the
others and to the sun's path, that is, the ecliptic proper. It has been
mentioned earlier (p. 206, n. 5) that in the axis of the Roman circus
was a Euripus, and altars of the three outer planets (Saturn, Jupiter,
Mars), and the three inner planets (Venus, Mercury, Moon) on
both sides of the pyramid of the sun, and that there were not more
than seven circuits because the "planets are seven only."
The ecliptic as a whirl is only one aspect of the famous "implex."
It must be kept in mind that being the seat of all planetary powers,
it represented, so to speak, the "Establishment" itself. There is no
better symbol of the thinking of those planet-struck Mesopotamian
civilizations than the arrogant plan of the royal cities themselves,
as it has been patiently reconstructed by generations of Orientalists
and archaeologists. Nineveh proclaimed itself as the seat of stable
Hamlet's Mill
240
order and power by its seven-times crenellated circle of walls, col-
ored with the seven planetary colors, and so thick that chariots
could run along the top. The planetary symbolism spread to India,
as was seen in chapter VIII, and culminated in that prodigious
cosmological diagram that is the temple of Barabudur in Java.17 It is
still evident in the innumerable stupas which dot the Indian country-
side, whose superimposed crowns stand for the planetary heavens.
And here we have the Establishment seen as a Way Up and Be-
yond, as Numenius would have seen immediately, the succession
of spheres of transition for the soul, a quiet promise of transcen-
dence which marks the Gnostic and Hinduistic scheme. The skele-
ton map will always lack one or the other dimension. The Whirl is
then a way up or a way down? Heraclitus would say both ways
are one and the same. You cannot put into a scheme everything at
once.
This general conception of the whirlpool as the "ecliptical
world" does not, of course, help to understand any single detail.
Starting from the idea of the whirlpool as a way to the other world,
one must look at the situation through the eyes of a soul meaning
to go there. It has to move from the interior outwards, to "ascend"
from the geocentric earth through the planetary spheres "up" to the
fixed sphere, that is, right through the whole whirlpool, the eclip-
tical world. But in order to leave the ecliptical frame, there must
be a station for changing trains at the equator. One would expect
this station to be at the crossroads of ecliptical and equatorial coor-
dinates at the equinoxes. But evidently, this was not the arrange-
ment. A far older route was followed. It is true that it sometimes
looks as though the transfer point were at the equinoxes. The astro-
logical tradition that followed Teukros,18 for example, provided
a rich offering of celestial locations for Hades, the Acherusian lake,
Charon the ferryman, etc., all of them under the chapter Libra.
But this is a trap and one can only hope that many hapless souls
have not been deceived. For these astrological texts mean the sign
17 P. Mus, Barabudur (1935).
18F. Boll, Sphaera (1903), pp. 19, 28, 47, 246-51. Antiochus does not mention any
of these star groups.
241 • The Frame of the Cosmos
Libra, not the constellation. All "change stations" are found in-
variably in two regions: one in the South between Scorpius and
Sagittarius, the other in the North between Gemini and Taurus;
and this is valid through time and space, from Babylon to Nica-
ragua.19 Why was it ever done in the first place? Because of the
Galaxy, which has its crossroads with the ecliptic between Sagit-
tarius and Scorpius in the South, and between Gemini and Taurus
in the North.
19 The notion is not even foreign to the cheering adventures of Sun, the Chinese
Monkey (Wou Tch'eng Ngen, French trans, by Louis Avenol [1957]). One day,
two "harponneurs des morts" get hold of him, claiming that he has arrived at the
term of his destiny, and is ripe for the underworld. He escapes, of course. The
translator remarks (vol. i, p. iii) that it is the constellation Nan Teou, the Southern
Dipper, that decides everybody's death, and the orders are executed by these
"harponneurs des morts." The Southern Dipper consists of the stars mu lambda
phi sigma tau zeta Sagittarii (cf. G. Schlegel, L'Uranographie Chinoise [1875], pp.
172ff.; L. de Saussure, Les Origines de L'Astronomie Chinoise [1930], pp. 452f).
Chapter XVIII
The Galaxy
Voie Lactee, soeur lumineuse
des blanches rivieres de Canaan,
et des corps blancs de nos amoureuses,
nageurs morts suivrons nous d'ahan
ton cours vers d'autres nebuleuses.
Apollinaire,
La Chanson du Mal-Aime
Men's spirits were thought to dwell in the Milky Way be-
tween incarnations. This conception has been handed down as an
Orphic and Pythagorean tradition1 fitting into the frame of the
migration of the soul. Macrobius, who has provided the broadest
report on the matter, has it that souls ascend by way of Capricorn,
and then, in order to be reborn, descend again through the "Gate
of Cancer."2 Macrobius talks of signs; the constellations rising at
the solstices in his time (and still in ours) were Gemini and Sagit-
tarius: the "Gate of Cancer" means Gemini. In fact, he states ex-
plicitly (1.12.5) that this "Gate" is "where the Zodiac and the
Milky Way intersect." Far away, the Mangaians of old (Austral
Islands, Polynesia), who kept the precessional clock running in-
stead of switching over to "signs," claim that only at the evening
of the solstitial days can spirits enter heaven, the inhabitants of the
1See F. Boll, Aus der Offenbarung Johannes (1914), pp. 32, 72 (the first ac-
cepted authority has been Herakleides of Pontos); W. Gundel, RE s.v. Galaxias;
A. Bouche-Leclerq, L'Astrologie Grecque (1899), pp. 22f.; F. Cumont, After Life
in Roman Paganism (1959), pp. 94. 104, 152f.
2 Commentary on the Dream of Scipio 1.12.1-8.
243 • The Galaxy
northern parts of the island at one solstice, the dwellers in the
south at the other.3 This information, giving precisely fixed dates,
is more valuable than general statements to the effect that the Poly-
nesians regarded the Milky Way as "the road of souls as they pass
to the spirit world."4 In Polynesian myth, too, souls are not per-
mitted to stay unless they have reached a stage of unstained perfec-
tion, which is not likely to occur frequently. Polynesian souls have
to return into bodies again, sooner or later.5
Two instances of relevant American Indian notions are worth
mentioning without discussion. The important thing is that the
tradition is there, more or less intact. Among the Sumo in Hon-
duras- and Nicaragua their "Mother Scorpion ... is regarded as
dwelling at the end of the Milky Way, where she receives the souls
of the dead, and from her, represented as a mother with many
breasts, at which children take suck, come the souls of the new-
born."6 Whereas the Pawnee and Cherokee say:7 "The souls of
the dead are received by a star at the northern end of the Milky
Way, where it bifurcates, and he directs the warriors upon the dim
and difficult arm, women and those who die of old age upon the
brighter and easier path. The souls then journey southwards. At the
end of the celestial pathway they are received by the Spirit Star,
and there they make their home." One can quietly add "for a
while," or change it to "there they make their camping place."
Hagar takes the "Spirit Star" to be Antares (alpha Scorpii).
Whether or not it is precisely alpha, because the star marks the
southern "end" of the Galaxy, the southern crossroads with the
3 W. W. Gill, Myths and Songs from the South Pacific (1876), pp. 156ff., 185ft.
4 E. Best, The Astronomical Knowledge of the Maori (1955), p. 45.
5 Since so many earlier and recent "reporters at large" fail to inform us of tradi-
tions concerning reincarnation, we may mention that according to the Marquesans
"all the souls of the dead, after having lived in one or the other place (i.e., Paradise
or Hades) for a very long time, returned to animate other bodies" (R. W. Wil-
liamson, Religious and Cosmic Beliefs of Central Polynesia [1924], vol. 1, p. 208),
which recalls the wording of the case as we know it from book X of Plato's
Republic.
6 H. B. Alexander, Latin American Mythology (1916), p. 185.
7S. Hagar, "Cherokee Star-Lore," in Festschrift Boas (1906), p. 363; H. B. Alex-
ander, North American Mythology, p. 117.
Hamlet's Mill • 244
ecliptic, it is at any rate a star of Sagittarius or Scorpius.8 That fits
"Mother Scorpion" of Nicaragua and the "Old goddess with the
scorpion tail" of the Maya as it also fits the Scorpion-goddess Sel-
ket-Serqet of ancient Egypt and the Ishara tam.tim of the Baby-
lonians. Ishara of the sea, goddess of the constellation Scorpius, was
also called "Lady of the Rivers" (compare appendix # 30).
Considering the fact that the crossroads of ecliptic and Galaxy
are crisis-resistant, that is, not concerned with the Precession, the
reader may want to know why the Mangaians thought they could
go to heaven only on the two solstitial days. Because, in order to
"change trains" comfortably, the constellations that serve as "gates"
to the Milky Way must "stand" upon the "earth," meaning that
they must rise heliacally either at the equinoxes or at the solstices.
The Galaxy is a very broad highway, but even so there must have
been some bitter millennia when neither gate was directly available
any longer, the one hanging in midair, the other having turned into
a submarine entrance.
Sagittarius and Gemini still mark the solstices in the closing years
of the Age of Pisces. Next comes Aquarius. The ancients, no doubt,
would have considered the troubles of these our times, the over-
population, the "working iniquity in secret," as an inevitable pre-
lude to a new tilting, a new world-age.
But the coming of Pisces was long looked forward to, heralded
as a blessed age. It was introduced by the thrice-repeated Great
Conjunction of Saturn and Jupiter in Pisces in the year 6 B.C., the
star of Bethlehem. Virgil announced the return of the Golden Age
under the rule of Saturn, in his famous Fourth Eclogue: "Now the
Virgin returns, the reign of Saturn returns, now a new generation
descends from heaven on high. Only do thou, pure Lucina, smile on
the birth of the child, under whom the iron brood shall first cease,
and a golden race spring up throughout the world!" Although pro-
8 This is no slip of the tongue; the zodiacal Sagittarius of Mesopotamian bound-
ary stones had, indeed, the tail of a Scorpion: but we just must not be drowned in
the abyss of details of comparative constellation lore, and least of all in those con-
nected with Sagittarius, two-faced as he is, half royal, half dog.
245 • The Galaxy
moted to the rank of a "Christian honoris causa" on account of this
poem, Virgil was no "prophet," nor was he the only one who ex-
pected the return of Kronos-Saturn.9 "l am redit et Virgo, redeunt
Saturnia regna." What does it mean? Where has Virgo been, sup-
posedly, so that one expected the constellation "back"?
Aratus, in his renowned astronomical poem (95-136), told how
Themis-Virgo, who had lived among humans peacefully, retired at
the end of the Golden Age to the "hills," no longer mingling with
the silver crowd that had started to populate the earth, and that she
took up her heavenly abode near Bootes, when the Bronze Age
began.10 And there is Virgil announcing Virgo's return. This makes
it easy to guess time and "place" of the Golden Age. One need only
turn back the clock for one quarter "hour" of the Precession (about
6,000 years from Virgil), to find Virgo standing firmly at the sum-
mer solstitial corner of the abstract plane "earth." "Returning," that
is moving on, Virgo would indicate the autumnal equinox at the
time when Pisces took over the celestial government of the vernal
equinox, at the new crossroads.
Once the Precession had been discovered, the Milky Way took
on a new and decisive significance. For it was not only the most
spectacular band of heaven, it was also a reference point from
which the Precession could be imagined to have taken its start. This
would have been when the vernal equinoctial sun left its position
in Gemini in the Milky Way. When it was realized the sun had
been there once, the idea occurred that the Milky Way might mark
the abandoned track of the sun—a burnt-out area, as it were, a
scar in heaven. Decisive notions have to be styled more carefully,
however: so let us say that the Milky Way was a reference "point"
from which the Precession could be termed to have taken its start,
and that the idea which occurred was not that the Milky Way
9 See, for example, A. A. Barb, "St. Zacharias the Prophet and Martyr," Journal
Of the Warburg and Courtauld Institutes 11 (1948), pp. 54f., and "Der Heilige und
die Schlangen," MAGW 82 (1953), p. 20.
10 Cf. Al-Biruni, dealing with the Indian ages of the world, and quoting the
above passages from Aratus with a scholion (Alberuni's India, trans. E. C. Sachau
1964 , vol. 1, pp. 383-85).
Hamlet's Mill
246
might mark the abandoned track of the sun, but that the Milky
Way was an image of an abandoned track, a formula that offered
rich possibilities for "telling" complicated celestial changes.
With this image and some additional galactic lore, it is now
possible to concentrate on the formula by which the Milky Way
became the way of the spirits of the dead, a road abandoned by the
living. The abandoned path is probably the original form of the
notions insistently built around a projected Time Zero. If the Pre-
cession was seen as the great clock of the Universe, the sun, as it
shifted at the equinox, remained the measure of all measures, the
"golden cord," as Socrates says in Plato's Theaetetus (153c). In
fact, apart from the harmonic intervals, the sun was the only ab-
solute measure provided by nature. The sun must be understood to
be conducting the planetary fugues at any given moment as Plato
also showed in the Timaeus. Thus, when the sun at his counting
station moved on toward the Milky Way, the planets, too, were
termed to hunt and run this way.
This does not make very sound geometrical sense, but it shows
how an image can dominate men's minds and take on a life of its
own. Yet the technical character of these images should not be
forgotten, and it is to prevent this that the verbs "to term" and "to
spell out" are used so often instead of the customary expression "to
believe."
To the American Plains Indians, the Milky Way was the dusty
track along which the Buffalo and the Horse once ran a race across
the sky.11 For the Fiote of the African Loango Coast the race was
run by Sun and Moon.12 The East African Turu took it for the
"cattle track" of the brother of the creator,13 which is very close to
the Greek legend of Herakles moving the herd of Geryon.14 The
convergence of so many animal tracks along this heavenly way is,
once again, not a pointless conjunction of fancies. The Arawak of
Guyana call the Galaxy "the Tapir's way." This is confirmed in a
11 J. Mooney, Myths of the Cherokee, 19th ARBAE 1897-98 (1900), p. 443.
12 E. Pechuel-Loesche, Volkskunde von Loango (1907), p. 135.
13 S. Lagercrantz, "The Milky Way in Africa," Ethnos (1952), p. 68.
14 See W. Gundel, RE s.v. Galaxias.
247 • The Galaxy
tale of the Chiriguano and some groups of the Tupi-Guarani of
South America. According to Lehman-Nitsche, these people speak
of the Galaxy as "the way of the true father of the Tapir," a Tapir-
deity which is itself invisible.15 Now, if this hidden deity turns out
to be Quetzalcouatl himself, ruler of the Golden Age town Tollan,
no other than "Tixli cumatz," the tapir-serpent dwelling in the
"middle of the sea's belly," as the Maya tribes of Yucatan describe
him,16 the allusions begin to focus. Finally, the actual scheme is
found in that Cuna tradition described earlier: the Tapir chopped
down the "Saltwater Tree," at the roots of which is God's whirl-
pool, and when the tree fell, saltwater gushed out to form the
oceans of the world.
Should the Tapir still seem to lack the appropriate dignity, some
Asiatic testimonies should be added. The Persian Bundahishn calls
the Galaxy the "Path of Kay-us," after the grandfather and co-
regent of Kai Khusrau, the Iranian Hamlet.17 Among the Altaic
populations the Yakuts call the Milky Way the "tracks of God,"
and they say that, while creating the world, God wandered over the
sky; more general in use seems to have been the term "Ski-tracks of
God's son," whereas the Voguls spelled it out "Ski-tracks of the
forest-man." And here the human tracks fade out, although the
snowshoes remain. For the Tungus the Galaxy is "Snowshoe-tracks
of the Bear." But whether the figure is the son of God, the forest-
man, or the Bear, he hunted a stag along the Milky Way, tore it up
and scattered its limbs in the sky right and left of the white path, and
so Orion and Ursa Major were separated.18 The "Foot of the Stag"
reminded Holmberg immediately of the "Bull's Thigh" of ancient
Egypt—Ursa Major. With his penetrating insight he might easily
have gone on to recognize, in that potent thigh, the isolated "one-
leg" of Texcatlipoca, Ursa Major again, in Mexico—the day-sign
15 O. Zerries, "Sternbilder als Ausdruck jagerischer Geiteshaltung in Sudamer-
ika," Paideuma 5 (1951), pp. 220f.
16 E. Seler, Gesammelte Abhandlungen (1961), vol. 4, p. 56.
17 Bdh. V B 22, B. T. Anklcsaria, Zand-Akasih. Iranian or Greater Bundahishn
(1956), pp. 69, 71.
18 U. Holmberg, Die religiosen Vorstellungen der altaischen Volker (1938), pp,
201f..
Hamlet's Mill
248
"Crocodile" (Cipactli) had bitten it off—the great Hunrakan
(= 1 leg) of the Maya Quiche.19
There is an insistent association here, right below the surface,
which is still revealed by the old Dutch name for the Galaxy,
"Brunelstraat." Brunei, Bruns, Bruin (the Brown) is the familiar
name of the bear in the romance of Reynard the Fox, and is as
ancient as anything that can be traced.20 It is a strange lot of charac-
ters that were made responsible for the Milky Way: gods and
animals leaving the path that had been used at "creation" time.21 But
where did they go, the ones mentioned, and the many whom we
have left out of consideration? It depends, so to speak, from where
they took off. This is often hard to determine, but the subject of
"tumbling down" will be dealt with next.
As for Virgo, who had left the "earth" at the end of the Golden
Age, her whereabouts in the Silver Age could have been described
19 Going farther south, he would have found there again the lining up of Ursa
and Orion and the violent tearing up of celestial figures. Says W. E. Roth ("An
Inquiry into the Animism and Folk-lore of the Guiana Indians," 30th ARBAE
1908-09 [1915], p. 262; cf. Zerries, pp. 22of.) of the Indians of Guiana: "All the
legends relating to the constellations Taurus and Orion have something in common
in the detail of an amputated arm or leg." And that goes for parts of Indonesia too.
But then, Ursa Major is the thigh of a Bull, and the zodiacal Taurus is so badly
amputated, there is barely a half of him left. More peculiar still, in later Egyptian
times it occurs, if rarely, that Ursa is made a ram's thigh (see G. A. Wainwright,
"A Pair of Constellations," in Studies Presented to F. L. Griffith [1932], p. 373);
and on the round zodiac of Dendera (Roman period) we find a ram sitting on that
celestial leg, representing Ursa, and it even looks back, as befits the traditional
zodiacal Aries. We must leave it at that.
20 The notion of the Milky Way as "Brunelstraat" seems to be present in ancient
India: the Atharva Veda 18.2.31 mentions a certain path or road called rikshaka.
Riksha is the bear in both senses, i.e., the animal and Ursa Major (see H. Grass-
mann, Worterbuch zum Rig-Veda [1915] s.v. Riksha). Whitney (in his translation
of AV, p. 840) suggested rikshaka as a road "infested by bears (?)." A. Weber,
however, proposed to identify rikshaka with the Milky Way ("Miszellen aus dem
indogermanischen Familienleben," in Festgruss Roth [1893], p. 138). Since the
whole hymn AV 18.2 contains "Funeral Verses," and deals with the voyage of the
soul, that context too would be fitting. (That the souls have to first cross a river
"rich with horses" is another matter.)
21 The shortest abbreviation: the Inca called Gemini "creation time" (Hagar, in
14th International Amerikanisten-Kongress [1904], p. 599f.). But the very same
notion is alluded to, when Castor and Pollux (alpha beta Geminorum) are made
responsible for the first fire sticks, by the Aztecs (Sahagun) and, strange to say,
by the Tasmanians. (See below, chapter XXIII, "Gilgamesh and Prometheus.")
249 • The Galaxy
as being "in mid-air." Many iniquitous characters were banished to
this topos; either they were thrown down, or they were sent up
—Lilith dwelt there for a while, and King David,22 also Adonis,23
even the Tower of Babel itself, and first of all the Wild Hunter
(appendix #20). This assembly of figures "in mid-air" helps to
give meaning to an otherwise pointless tale, a veritable fossil
found in Westphalian folklore: "The Giants called to Hackelberg
[= Odin as the Wild Hunter] for help. He raised a storm and
removed a mill into the Milky Way, which after this is called the
Mill Way."24 There are other fossils, too, the wildest perhaps being
that of the Cherokee who called the Galaxy "Where the dog ran."
A very unusual dog it must have been, being in the habit of stealing
meal from a corn mill owned by "people in the South" and running
with it to the North; the dog dropped meal as he ran and that is
the Milky Way.25 It is difficult here to recognize Isis scattering ears
of wheat in her flight from Typhon.26 And yet, the preference of
the very many mythical dogs, foxes, coyotes—and even of the
"way-opening" Fenek in West Sudan—for meal and all sorts of
grain—more correctly "the eight kinds of grain"—a trait which is
hardly learned by eavesdropping on Mother Nature, could have
warned the experts to beware of these doggish characters. They are
not to be taken at their pseudo-zoological face value.
Thus, everybody and everything has left the course, Wild
Hunter, dog and mill—at least its upper half, since through the
hole in the lower millstone the whirlpool is seething up and down.
22See J. A. Eisenmenger, Entdecktes Judenthem (1711), vol. 1, p. 165; vol. 2,
pp. 417ff.
23 "Es ton eera," see F. K. Movers, Die Phonizier (1967), vol. 1, p. 205.
24 J. Grimm, TM, pp. 1587f.
25 Mooney, pp. 253, 443.
26 See R. H. Allen, Star Names (1963), p. 481; W. T. Olcott, Star Lore of All
Ages (1911),p. 393.
Chapter XIX
The Fall of Phaethon
Quel del sol, che suiando, fu combusto
Per l'orazion della terra devota
Quando fu Giove arcanamente giusto
Dante, Purg. xxix.118
he great and official myth concerning the Galaxy is Phae-
thon's transgression and the searing of the sky in his mad course.
Manilius tells it in his astrological poem:1
. . . thiswas once the Path
Where Phoebus drove; and that in length of Years
The heated track took Fire and burnt the Stars.
The Colour changed, the Ashes strewed the Way,
And still preserve the marks of the Decay:
Besides, Fame tells, by Age Fame reverend grown,
That Phoebus gave his Chariot to his Son,
And whilst the Youngster from the Path declines
Admiring the strange Beauty of the Signs,
Proud of his Charge, He drove the fiery horse,
And would outdo his Father in his Course.
The North grew warm, and the unusual Fire
Dissolved its Snow, and made the Bears retire;
Nor was the Earth secure, each Contrey mourn'd
The Common Fate, and in its City's burn'd.
Then from the scatter'd Chariot Lightning came,
1 1.730-49. Anonymous translation (T.C.) London, 1697; reprinted 1953 by Na-
tional Astrological Library, Washington, D.C., p. 44.
251 • The Fall of Phaethon
And the whole Skies were one continued Flame.
The World took Fire, and in new kindled Stars
The bright remembrance of its Fate it bears.
The myth of Phaethon has been told broadly and with magnifi-
cent fantasy by Ovid (Met. 1.747-2.400) and by Nonnos (Dio-
nysiaka Book 38). Gibbon in his old age, commemorating his own
adolescence, speaks of his rapt discovery of the beauty of Latin
poetry as he read Ovid's description of the tragic venture of
Phaethon. The story goes on that Helios, taking his oath by the
waters of Styx, promised to fulfill any wish of his rash young son
Pha-ethon, who was visiting him for the first time. The boy had only
one desire, to drive the Sun's chariot once, and the most desperate
requests of his father could not move him to change his mind.
Although knowing well that nothing could prevent the fatal ending
of this adventure, Helios did his best to teach Phaethon all the dan-
gers lurking at every step of the way—a welcome occasion for
both poets to elaborate the paternal admonitions into some kind of
"introduction to astronomy." As the father feared, Phaethon was
incapable of managing the horses and came off the proper path;
Ovid has it that the boy dropped the reins at the sight of Scorpius.
Unbelievable confusion results; no constellation remains in its place,
and the Earth is terribly scorched. In despair "she" cries aloud to
Jupiter to make him act immediately: "Look how your heavens
blaze from pole to pole—if fire consumes them the very universe
will fall to dust. In pain, in worry, Atlas almost fails to balance the
world's hot axis on his shoulders."2 And Nonnos states (38.350ff.):
"There was tumult in the sky shaking the joints of the immovable
universe; the very axle bent which runs through the middle of the
revolving heavens. Libyan Atlas could hardly support the self-
rolling firmament of stars, as he rested on his knees with bowed
back under this greater burden."
Zeus has to intervene and hurls his thunderbolt at the boy. Phae-
thon falls into the river Eridanus where, according to Apollonios
2 Met. 2.294-97: circumspice utrumquc:/ funiat utcrque polus quos si vitiaverit
ignis/atria vestra ruent Atlas en ipse laborat/ vixque suis umeris candentem sustinct
axem.
Hamlet's Mill
252
Rhodios, the stench of his half-burned corpse made the Argonauts
sick for several days when they came upon it in their travels
(4.619-23).
The Phaethon story has often been understood to commemorate
some great flashing event in the skies, whether comet or meteor.
Everyone rushes by instinct—more accurately, habit—for a so-
called natural explanation. But on examination, the case turns out
not to be so easy. The narrating of the cataclysm may be fanciful
and impressionistic, as if the poets enjoyed an emotional release
from the regularity of celestial orbs, but their account also makes
technical sense, as anyone would suspect who has read Stegemann's3
solid inquiry into Nonnos as the heir to Dorotheos of Sidon's tight-
knit astrology. As for Ovid, his standing as a scholar is by now
unchallenged and, in fact, he hints at rigid cosmological formulae
with surprising authority. In his description of the "hidden moun-
tains" emerging from the waves, when the seas shrank into sand
(2.26off.)—they rise as "new islands." How much better does this
image of "mountain peaks" and "islands" illustrate the stars of a
constellation rising, one after the other (at vernal equinox), than,
for instance, the Icelandic wording of the emerging of "a new
earth"!
In any case, an independent confirmation emerges in Plato's
version of the crisis, as he gives it in Timaeus 22CE. The Egyptian
priest talking with Solon states that the legend of Phaethon "has the
air of a fable; but the truth behind it is a deviation [parallaxis] of
the bodies that revolve in heaven round the earth, and a destruction,
occurring at long intervals, of things on earth by a great conflagra-
tion." This is a clear statement, and one in accordance with Ovid
and with Nonnos, as it should be, since it has to do with a Pytha-
gorean tradition: Aristotle tells us so.4
3 Astrologie und Universalgeschichte (1930).
4Meteorologica 1.8.345A: "The so-called Pythagoreans give two explanations.
Some say that the Milky Way is the path taken by one of the stars at the time
of the legendary fall of Phaethon; others say that it is the circle in which the sun
once moved. And the region is supposed to have been scorched or affected in
some other such way as a result of the passage of these bodies." See also H. Diels,
Doxographi, pp. 364f. = Aetius iii.i. (In former times when classical authors were
not yet eagerly prefixed with as many "pseudos" as possible, this was Plutarch,
De placitis 3.1.)
253 • The Fall of Phaethon
The Pythagoreans were neither idle storytellers, nor were they
even mildly interested in unusual sensational "catastrophes" caused
by meteors, and the like. Actually, the Egyptian priest said to Solon,
concerning the legend of Phaethon, "the story current also in your
part of the world." Where, then, is the story in Egypt? Since the
Egyptian cosmological language was more technical, in the old
sense, than that of the Greeks, it will take some time to find out
the exact parallel. Anyhow, in Egypt the down-hurled Phaethon
would have been termed "the lost eye," or rather one among the
"lost eyes." The eye was "lost" in the so-called "mythical source
of the Nile," the source of all waters. So it is surprising that Ovid
knew (Met. 2.254ff.) that because of Phaethon's fall, "Nile ran in
terror to the end of the earth to hide its head which now is still
unseen."5 Leaving the Egyptian case for the time being, it is appro-
priate here to cite two widely separated survivals concerned with
the Phaethon theme. They are useful because they come from
points far removed from the Greek landscape and consequently
cannot be connected with any local catastrophes which are sup-
posed to have made such a tremendous impression on the Greek
mind. The Fiote of the African Loango Coast, already mentioned,
say: "The Star Way [Galaxy] is the road for a funeral procession
of a huge star which, once, shone brighter from the sky than the
Sun."6 Conveniently short, and no technicalities. The Northwest
American version is broader. Because of the absence of chariots in
pre-Columbian America,7 the Phaethon figure of the Bella Coola
Indians, who had come to visit his father Sun by means of an
arrow-chain, wants to carry Sun's torches in his stead. Helios agrees,
but he warns his son not to make mischief and burn people. "In
the morning," he says, "I light one torch, slowly increasing their
number until high-noon. In the afternoon I put them out again
little by little." The next morning, "Phaethon," climbing the path
of the Sun, not only kindled all the torches he had, he did so much
too early, so that the earth became red hot: the woods began to
5 Nilus in extremum fugit: pererritus orbem/ occuluitque caput, quod adhuc
latet.
6 E. Pechuel-Loesche, Volksunde von Loango (1907), p. 155.
7 See H. S. Gladwin, Men out of Asia (1947), pp. 356-59, for this "feature."
Hamlet's Mill • 254
burn, the rocks split, many animals jumped into the waters, but the
waters began to boil, too. "Young woman," the mother of the Bella
Coola Phaethon, covered men with her coat and succeeded in sav-
ing them. But Father Sun hurled his offspring down to earth, telling
him: "From now on you shall be the Mink! "8
It is necessary to revive some other very ancient ideas lost to our
time. That Eridanus was the river Po in northern Italy was a com-
mon and simple notion in the Greece of Euripides. In one of his
great tragedies (Hippolytus), the chorus yearns for a flight away
from the world of guilt, to mountains and clouds, to lands far off:
Where the waters of Eridanus are clear
And Phaethon's sad sisters by his grave
Weep into the water, and each tear
Gleams, a drop of amber, in the waves.
Any hearer would have understood that Phaethon's sad sisters
were the poplars lining the banks of the river, and that the "drop
of amber" was an allusion to the riches of the "amber route" which
led from the Baltic Sea to the familiar reaches of the Adriatic. So
far so good. But what can be made of Strabo, a still later author
(5.215) who called Eridanus "nowhere on earth existing" and thus
referred clearly to the constellation Eridanus in heaven, and what
does Aratus (360) mean when he talks of "those poor remains of
Eridanus" because the river was "burnt up through Phaethon's
fall." Is this the very same river, ample and lined with poplars,
which runs into the delta of the Po?
Apollonios of Rhodes, in recounting the heroic travels of the
Argonauts, carefully preserved the double level of meaning, for the
adventures are set in an earthly context, yet they make, geographi-
cally speaking, no sense at all. The explorers do sail up the Po,
where they are confronted, as was said, with the stench of Phae-
8 W. Krickeberg, Indianermarchen aus Nordamerika (1924), pp. 224f., 396. Cf. E.
Seler, Gesammelte Abhandlungen, vol. 5, p. 19. A mere mink might appear to us,
today, as insignificant, like the tapir, or as the "Mouse-Apollo"—we fall for mere
"words" and "names" only too easily. This particular Mink introduces the tides,
steals the fire, fights with the "winds," playing Adapa, Prometheus, Phaethon all
at the same time.
255 • The Fall of Phaethon
thon's remains—but those might be located higher up in a waterfall
in the Alps, near the Dammastock, as one distinguished scholar
would like to suggest. For the Argo moves from the Po into Lake
Geneva and the Rhone, goes down it to the sea again and sails out
following the same longitude; then, by a considerable feat of por-
tage crosses the Sahara all the way to the coast of West Africa, and
reaches Fernando Po. This is at least how those who understand
the text as geography read it without blinking. Surely, it is closer
to common sense to treat Eridanus as a feature of the skies, where
it is already clearly marked together with Argo; and to treat the
other features accordingly will give at least a significant story, al-
though it will not dispel the mystery of the Argonauts.
Thus tradition holds that after the dreadful fall of Phaethon, and
when order was re-established, Jupiter "catasterized" Phaethon,
that is, placed him among the stars, as Auriga (Greek Heniochos
and Erichthonios); and at the same time Eridanus was catasterized.
Manilius hinted at this event only with the lines "The world took
fire, and in new kindled stars / the bright remembrance of its fate
it bears." Nonnos gave a more detailed report (38.424.-31) :9
But father Zeus fixed Phaethon in Olympus, like a charioteer, and
bearing that name. As he holds in the radiant Chariot of the heavens
with shining arm, he has the shape of a Charioteer starting upon his
course, as if even among the stars he longed again for his father's car.
The fire-scorched river also came up to the vault of the stars with
consent of Zeus, and in the starry circle rolls the meandering stream
of burning Eridanus.
Now, in times when myth was still a serious form of thought,
objects were not identified in heaven which did not belong there
in the first place. The problem which arose later is the one raised
by Richard H. Allen, who remarks that "the Milky Way was
long known as Eridanus, the Stream of Ocean,"10 and by the
translator of Nonnos, W. H. D. Rouse, who shortly annotated
Eridanus as "the Milky Way." It takes some nerve to say of the
9 Sec also F. X. Kugler, Sibyllinischer Stemkampf und Phaethon (1927), pp. 44,49.
110 Star Names (1963), p. 474.
Hamlet's Mill
256
Galaxy that it meanders—actually the Greek text has it that it
moves like a helix (helissetai). But apart from this incongruent
image of the "helixing" Milky Way, the myth of Phaethon was
meant by the Pythagoreans to tell of the departure of the Sun and
planets from their former path, and the enthroning of Eridanus,
which together with Auriga was to take over the function of the
Milky Way: that is why they were "catasterized" together. Ad-
mittedly, one faces a frightening confusion between the rivers in
heaven and those on earth, and the names which were given to both
kinds of streams, but with patience the threads can be disentangled.
Taking the rivers of our globe first, it was not only the Po that
received the name of Eridanus, but the Rhone,11 and the Nile and
the Ganges. Finally in Higgins' Anacalypsis there is a quote, with-
out the ancient source but reasonably reliable: "Ganges which also
is called Po."12 Thus it is not surprising that much later, in medieval
times, several redactions of the Alexander Romance show different
opinions about the river used by the king to travel to paradise in
order to win immortality. In a French prose novel of the 14th
century Alexander sails the Nile upstream, whereas in a Latin ver-
sion of the 12th century, he uses the Ganges: as the Indians had told
him, the Ganges had its source in paradise.13 So have, indeed, all
great rivers of myth.
In the sky, the number of candidates for election is three. Besides
the Milky Way, Eratosthenes' authoritative Catasterisms called the
constellation Eridanus Nile or Ocean.14 But the astrologers Teukros
and Valens listed Eridanus among the paranatellonta of Aquarius.
Paranatellonta are the constellations that "rise at the same time" as
a given one, i.e., in this instance, as Aquarius. That is, they called
the gush from the jug of Aquarius Eridanus. More awkward still,
11 For Po and Rhone and the joining of their waters, see A. Dieterich, Nekyia
(1893), p. 27, quoting Pliny and Pausanias.
12 (1927 repr.), p. 357: Ganges qui et Padus dicitur. As concerns the general idea
of Eridanus being in India, see O. Gruppe, Griechische Mythologie (1906), p. 394,
referring to Ktesias.
13 F. Kampers, Mittelalterliche Sagen vom Paradiese (1897), pp. 72f.
14No. 37 (Robert ed. [1878], pp. 176f).
257 • The Fall of Phaethon
this gush from Aquarius' jar was meant to join our constellation
Eridanus below Piscis Austrinus.15 Says Manilius (1 .438ff.):
Next swims the Southern Fish, which bears a Name
From the South-Wind, and spreads a feeble Flame.
To him the Flouds in spacious windings turn
One fountain flows from cold Aquarius' Urn;
And meets the other where they joyn their Streams
One Chanel keep, and mix the starry Beams.
Eratosthenes' Catasterisms bring one more complication into the
picture, but it is one which leads, finally, to the decisive insight.
Differing from those of Aratus (360f.) and from Ptolemy, it counts
Canopus in the constellation Eridanus, instead of Argo, and thus
gives the river a different direction.16 The whole "Gordian knot" of
misapprehensions hinges upon the name Eridanus, and one can do
nothing better than to follow the good example set by Alexander
and "pull out the pole pin." Eridanus, lacking a decent Greek
etymology, finds a reasonable derivation from Eridu, as was pro-
posed by Kugler, Eridu being the seat of Enki-Ea, Sumerian
mulNUNki = Canopus (alpha Carinae).17 Eridu marked, and meant,
the "confluence of the rivers," a topos of highest importance, to
which, beginning with Gilgamesh, the great "heroes" go on a
pilgrimage trying in vain to gain immortality—including Moses
according to the 18th Sura of the Koran. Instead of this unobtain-
able boon, they gain "the measures," as will be seen. "Eridu" being
known as the "confluence of the rivers," Eridanus had to join, by
definition so to speak, some "river" somewhere in the South, or it
had to flow straightaway into Eridu-Canopus, as the Catasterisms
claimed. There have been more drastic "solutions" still. The first is
given by Servius (to Aeneid 6.659) who pretends Eridanus and
15 F. Boll, Sphaera (1903), pp. 135-38.
16 See L. Ideler, Sternnamen (1809), p. 231; see also E. Maass, Commentariorum
in Aratum Reliquiae (1898), p. 259.
17B. L. van der Waerden, JNES 8 (1949), p. 13; see also P. F. Gossmann, Plane-
tarium Babylonicum (1950), 306; J. Schaumberger, 3. Erg. (1935), pp. 334f.
Hamlet's Mill • 258
Phaethon were one and the same.18 The second, presented by
Michael Scotus,19 agrees with Servius concerning the identity of
Phaethon and Eridanus, but does much more. He places into the
"sign" Eridanus the "Figura sonantis Canoni"—consisting of seven-
teen stars—which he calls Canopus and claims that Canopus touches
Argo. And about this enigmatic personage Scotus says that he "hin-
dered the work of the Sun by the tone of his lute, because the
horses listened to it, and enraged Jupiter pierced him with the
lightning."20
Eridanus was understood by the astrologers to be the whirlpool
(zalos), as has been seen, flowing through the underworld with
its many realms, including those from which one sees the celestial
South Pole. Virgil wrote in the Georgics (1.242f.): "One pole is
ever high above us, while beneath our feet is seen the other, of black
Styx and the shades infernal." But why was Auriga catasterized at
the same time as Eridanus, and what is the "function" which these
two constellations had to take over from the Milky Way? The
Galaxy was and remains the belt connecting North and South,
above and below. But in the Golden Age, when the vernal equinox
was in Gemini, the autumnal equinox in Sagittarius, the Milky
Way had represented a visible equinoctial colure; a rather blurred
one, to be true, but the celestial North and South were connected
by this uninterrupted broad arch which intersected the ecliptic at
its crossroads with the equator. The three great axes were united,
the galactic avenue embracing the "three worlds" of the gods, the
living and the dead. This "golden" situation was gone, and to Eri-
danus was bequeathed the galactical function of linking up the
"inhabited world" with the abode of the dead in the (partly) invis-
ible South. Auriga had to take over the northern obligations of the
18Fabula namque haec est: Eridanus Solis filius fuit. hie a patre inpetrato curru
agitare non potuit, et cum eius errore mundus arderet, fulminatus in Italiae fluvium
cecidit: et tune a luce ardoris sui Phaethon appellatus est, et pristinum nomen
fluvio dedit: unde mixta haec duo nomina inter Solis filium et fluvium invenimus.
19 Cf. appendix #10, Vainamoinen's Kantele.
20 See Boll, pp. 273-75, 540~42: Alii dicunt quodcum impediret opus solis sono
canoni, quia equi attendebant dulcedini sonorum, iratus Jupiter cum percussit
fulmine.
259 • The Fall of Phaethon
Galaxy, connecting the inhabited world with the region of the
gods as well as possible. There was no longer a visible continuous
bond fettering together immortals, living and dead: Kronos alone
had lived among men in glorious peace.
And here there is a proposition to be made. In order to evaluate it,
one has to consider the fact that alpha Aurigae is Capella, the Goat.
This remarkable figure was the nurse of infant Zeus in the Dictaean
Cave, and out of her skin Hephaistos was later to make the Aegis:
Amaltheia. Capella-Amaltheia's Horn was the Horn of Plenty for
the immortals, and the source of Nectar and Ambrosia. Mortals
called it "second table," dessert so to speak.21 But there are two
shreds of Orphic tradition which seem to be revealing, both handed
down to us by Proclus. The first says that Demeter separated the
food of the gods, splitting it up, as it were, into a liquid and a solid
"part," that is, into Ambrosia and Nectar.22 The second declares
that Rhea became Demeter after she had borne Zeus.23 And Eleusis,
for us a mere "place name," was understood by the Greeks as
"Advent"—the New Testament uses the word for the Advent of
Christ. Demeter, formerly Rhea, wife of Kronos, when she "ar-
rived," split up the two kinds of divine food having its source in
alpha Aurigae. In other words, it is possible that these traditions
about Demeter refer to the decisive shifting of the equinoctial
colure to alpha Aurigae.
But one should also look at some other traditions. Turning to
India, which is often helpful in its abundance, it was the Ganges
that stood for the Galaxy, almost as a matter of course,24 but the
Mahabharata and the Puranas tell at least how the link was con-
ceived: Ganga was born of the Milky Way. Says the Vishnu
Pur ana:25
21 See Athenaeus, Deipnosophistai 643a; also 783c, 542a.
22 Orphicorum Fragmenta, ed. O. Kern (1963), frg. 189, p. 216 (Proclus in
Cratylus 404b, p. 92, 14 Pasqu.); cf. G. Dumezil, he Festin d'Immortalite (1924),
p. 104. See also Roscher, in Roscher s.v. Ambrosia: sitos kai methy, sithos kai
oinos, etc.
23 Orphic orum Fragmenta, frg. 145, p. 188.
24 The same goes for the Jaxartes and Ardvi Sura Anahita of Iranian tradition;
sec H. S. Nyberg, Die Religionen des Alten Iran (1966), pp. 260f.
25.2,8 (Wilson trans,, p. 188).
Hamlet's Mill
260
Having the source in the nail of the great toe of Vishnu's left foot,
Dhruva (Polaris) receives her, and sustains her day and night devoutly
on his head; and thence the seven Rishis practise the exercise of
austerity in her waters, wreathing their braided locks with her waves.
The orb of the moon, encompassed by her accumulated current,
derives augmented lustre from this contact. Falling from on high,
as she issues from the moon, she alights on the summit of Meru (the
World Mountain in the North), and thence flows to the four quarters
of the earth, for its purification . . . The place whence the river pro-
ceeds, for the purification of the three worlds, is the third division
of the celestial regions, the seat of Vishnu.
It was, in fact, a colossal event to have "the stream Air-Ganges
fall down from Heaven," and its violence was only restrained by
Shiva's receiving it in the curls of his hair. One might add that he
bore it there "for more than 100 years, to prevent it from falling
too suddenly upon the mountain." The Indian imagination is free-
wheeling, and cares little for time sequence, but it is clear that the
flow is perpetual. Were it not for Shiva's hair acting as a catch-
ment, the earth would have been flooded by the Waters Above.
They come, as was just quoted, from the third region of the sky,
the "path of Vishnu" between Ursa Major and the Pole Star. Wil-
son stated in 1840: "The situation of the sources of the Ganges in
heaven identifies it with the Milky Way."26
But if the flow is perpetual, it still had a point of "beginning" and
this is found in the Bhagavata Purana (Wilson, p. 138, n. ii):
"The river flowed over the great toe of Vishnu's left foot, which
had previously, as he lifted it up, made a fissure in the shell of the
mundane egg, and thus gave entrance to the heavenly stream." How
can the Milky Way pour its waters over Polaris? And how can it
26 The Chinese report as given by Gustave Schlegel (L'Uranographie Chinoise
[1875; repr. 1967], p. 20) is shorter but it points to the same fanciful conception.
"La fleuve celeste se divise en deux bras pres du pole Nord et va de la jusqu'au
pole Sud. Un de ses bras passe par l'asterisme Nan-teou (lambda Sagittarii), et
l'autre par l'asterisme Toung-tsing (Gemeaux). Le fleuve est l'eau celeste, coulant
a travers les cieux et se precipitant sous la terre."
Nan-teou is the "Southern Bushel": mu lambda phi sigma tau zeta Sagittarii; the
Northern Bushel = the Big Dipper.
Although we agree with Phyllis Ackerman's view (in Forgotten Religions [1950],
p. 6): "The Nile, however, (like many, if not all sacred rivers originally—com-
pare the Ganges) is the earthly continuation of the Milky Way," we maintain
that the mere recognition docs nor help to restore sense and meaning to the myth.
261 • The Fall of Phaethon
flow to the four quarters of the earth? Indian diagrams remained
fanciful, in the same way as Western medieval ones. It takes some
time for one who looks at the great tympanon at Vezelay to realize
that here is a space-time diagram, as it were, of world history cen-
tered on the figure of Christ. The effect is all the greater for the
transpositions. It was not wholly absurd, either, for archaic cos-
mology to have double locations, one, for instance, on the ecliptic
and one circumpolar. If Tezcatlipoca drilled fire at the pole to
"kindle new stars," if the Chinese Saturn had his seat there too, so
could Vishnu's toe have bilocation: one "above" in the third region,
the other in beta Orionis-Rigel (the Arabian word for "foot"), the
"source" of Eridanus. (And might not Rigel-the-source stand also
for Oervandil's Toe, catasterized by Thor?) For Rigel marked the
way to Hades in the tradition of the Maori of New Zealand as well
as in the Book of Hermes Trismegistos.
Fanciful, assuredly, but neither the real Milky Way nor the ter-
restrial Ganges offered any basis for the imagery of a river flowing
to the four quarters of the earth "for the purification of the three
worlds." One cannot get away from the "implex" and it is now
necessary to consider the tale of a new skeleton map, alias skambha:
the equinoctial colure had shifted to a position where it ran through
stars of Auriga and through Rigel. Skambha, as we have said, was
the World Tree consisting mostly of celestial coordinates, a kind
of wildly imaginative armillary sphere. It all had to shift when one
coordinate shifted.
There are stylistic means other than "catasterizations," that is,
being promoted to heaven among the constellations, to describe
changed circumstances in the sky. Thus, a Babylonian cuneiform
tablet states: "The Goat-Star is also called the witch-star; the
divine function of Tiamat it holds in its hands." The Goat-Star
(mulUZA = enzu), apart from representing Venus, "rises together
with Scorpius" and has been identified with Vega.27 If one can rely
on this identification, it seems to describe the situation as seen from
across the sky: the shifting from Sagittarius to Scorpius, and Vega
27 Gossmann, 145; van der Waerden, JNES 8, p. 20.
Hamlet's Mill
262
taking over the northern part of the "function" of the Galaxy.
That Tiamat is the Milky Way, and no "Great Mother" in the
Freudian sense, any more than Ganga, Anahita and others, seems by
now obvious. And the same is true of Egyptian Nut,28 but the
story has different terms there: Mother Nut is changed into a cow
and ordered to "carry Ra." (It is, by the way, a "new" Ra: the
older Ra made it quite clear that he wanted to retire for good,
going somewhere "where nobody could reach" him) (appendix
#21).
28 The Arabian name of the Galaxy is sufficiently tale-telling: "Mother of the
Sky" (um as-sama), and in northern Ethiopia it is called "Em-hola," i.e., "Mother
of the Bend [Mutter der Kruemmung]." See E. Littmann, "Sternensagen und As-
trologisches aus Nordabessinien," ARW ; 11 (1908), p. 307; Ideler, p. 78.
Chapter XX
The Depths of the Sea
Hast thou entered into the springs of the sea?
Or hast thou walked in the search of the depth?
Job xxxviii. 16
It will help now to take a quick comparative look at the differ-
ent "dialects" of mythical language as applied to "Phaethon" in
Greece and India. The Pythagoreans make Phaethon fall into Eri-
danus, burning part of its water, and glowing still at the time when
the Argonauts passed by. Ovid stated that since that fall the Nile
hides its sources. Rigveda 9.73.3 says that the Great Varuna has hid-
den the ocean. The Mahabharata tells in its own style why the
"heavenly Ganga" had to be brought down.1 At the end of the
Golden Age (Krita Yuga) a class of Asura who had fought against
the "gods" hid themselves in the ocean where the gods could not
reach them, and planned to overthrow the government. So the gods
implored Agastya (Canopus, alpha Carinae = Eridu) for help. The
great Rishi did as he was bidden, drank up the water of the ocean,
and thus laid bare the enemies, who were then slain by the gods. But
now, there was no ocean anymore! Implored by the gods to fill the
sea again, the Holy One replied: "That water in sooth hath been
digested by me. Some other expedient, therefore, must be thought
of by you, if ye desire to make endeavour to fill the ocean." It was
this sad state of things which made it necessary to bring the
Galaxy "down." This is reminiscent of the detail in the Jewish
tradition about Eben Shetiyyah, that the waters sank down so
1 Mbh. 5.104-105 (Roy trans., vol. 2, pt. 2, pp. 23of.); see also H. J. Jacobi, ERE,
vol. 1, p. 181 a; S. Sorenson, Mahabharata Index (1963), p. i8a.
Hamlet's Mill
264
deeply that David had to recite the "fifteen songs of ascension" to
make them rise again.
Now Agastya, the great Rishi, had a "sordid" origin similar to
that of Erichthonios (Auriga), who was born of Gaia, "the Earth,"
from the seed of Hephaistos who had dropped it while he was
looking at Athena.2 In the case of the Rishi:
He originated from the seed of Mitra and Varuna, which they
dropped into a water-jar on seeing the heavenly Urvashi. From this
double parentage he is called Maitravaruni, and from his being born
from a jar he got the name Khumbasambhava."3 [Khumba is the
name of Aquarius in India and Indonesia, allegedly late Greek
influence.]
On the very same time and occasion there also was "born" as son
of Mitra and Varuna—only the seed fell on the ground not in the
jar—the Rishi Vasishtha. This is unmistakably zeta Ursae Majoris,
and the lining up of Canopus with zeta, more often with Alcor, the
tiny star near zeta (Tom Thumb, in Babylonia the "fox"-star) has
remained a rather constant feature, in Arabic Suhayl and as-Suha.
This is the "birth" of the valid representatives of both the poles,
the sons of Mitra and Varuna and also of their successors. To
follow up the long and laborious way leading from Rigvedic
Mitravaruna (dual) to the latest days of the Roman Empire where
we still find a gloss saying "mithra funis, quo navis media vincitur"
—"mithra is the rope, by which the middle of the ship is bound,"
would overstep the frame of this essay by far. Robert Eisler4 rely-
ing upon his vast material, connected this fetter of "rope," mithra,
2 Besides Greece and India, the motif of the dropped seed occurs in Caucasian
myths, particularly those which deal with the hero Soszryko. The "Earth" is re-
placed by a stone, Hephaistos by a shepherd, and Athena by the "beautiful Satana,"
who watches carefully the pregnant stone and who, when the time comes, calls in
the blacksmith who serves as midwife to the "stone-born" hero whose body is blue
shining steel from head to foot, except the knees (or the hips) which are damaged
by the pliers of the smith. The same Soszryko seduces a hostile giant to measure
the depth of the sea in the same manner as Michael or Elias causes the devil to
dive, making the sea freeze in the meantime.
3 RV 7.33.13-14; Brihad-Devata 5.15ff.; Sorenson, p. i8b. Let us mention that the
Egyptian Canopus is himself a jar-god; actually, he is represented by a Greek
hydria (sec RE s.v. Kanopos).
1 Weltenmantel und Himmelszelt (1910), pp. 175f.
265 • The Depths of the Sea
right away with the "ship's belt" from the tenth book of Plato's
Republic.
Of the inseparable dual Mitravaruna, Varuna is still of greater
relevance, particularly because it is he who "surveyed the first
creation" (RV 8.41.10), he who hid the Ocean—Ovid had it that
the sources of the Nile were hidden—and he who is himself called
"the hidden Ocean" (RV 8.41.8). Varuna states about himself: "I
fastened the sky to the seat of the Rita" (RV 4.42.2). And at that
"seat of Rita" we find Svarnara, said to be "the name of the celestial
spring . . . which Soma selected as his dwelling.5 This is no other
"thing" than Hvarna (Babylonian melammu) which the "bad
uncle" Afrasiyab attempted to steal by diving to the bottom of
Lake Vurukasha, although Hvarna belonged to Kai Khusrau (see
above, pp. 40, 201). Thus in whichever dialect the phenomenon is
spelled out, the fallen ruler of the Golden Age is held to dwell near-
est to the celestial South Pole, particularly in Canopus which marks
the steering oar of Argo, Canopus at the "confluence of the rivers."
This is true whether Varuna fastened the sky to the seat of the Rita
(and his own seat), whether Enki-Ea-Enmesharra, dwelling in
Eridu, held all the norms and measures (Rita, Sumerian me: Akka-
dian: parsu)—Thorkild Jacobsen called him very appropriately the
"Lord modus operandi"—or whether Kronos-Saturn kept giving
"all the measures of the whole creation" to Zeus while he himself
slept in Ogygia-the-primeval.
And there is little doubt, in fact none, that Phaethon (in the
strange transformation scenes of successive ages) came to be under-
stood as Saturn. There is the testimony of Erastosthenes' Catas-
terisms,6 according to which the planet Saturn was Phaethon who
5 See H. Luders, Varuna, vol. 2: Varuna und das Rita (1959), pp. 396-401 (RV
4.21.3; 8.6.39; tf.65.2f.; 5)70.6). Soma is addressed as "lord of the poles," and to
Agni is given the epithet svarnaram thrice (RV 2.2.1; 5.15.4; 8-19-1; cf. Luders,
p. 400). But we did hear before about "Agni, like the felly the spokes, so you sur-
round all the gods," and Soma and Agni supplement each other, as will come out
eventually, but not in this essay; the proportions Mitra: Varuna, Agni: Soma,
Ambrosia: Nectar are not as easily computed as wishful thinking might expect.
6 No. 43 (Robert ed., pp. 194f). E.g., Hyginus ii 42, dealing with the planets, be-
ginning with Jupiter: "Secunda stella dicitur Solis, quam alii Saturni dixerunt; hanc
Eratosthenes a Solis filio Phactonta adpellatam dicit, de quo complines dixerunt,
in patris inseienter curru vectus incenderit terras; quo facto ab love fulmine per-
cussus in Eridanum decidcrit et a Sole inter sidera sit perlatus."
Hamlet's Mill
266
fell from the chariot into Eridanus, and Stephanus of Byzantium7
calls Phaethon a Titan. There is, moreover, the Orphic wording of
the case: "After Kronos had emasculated Ouranos, Zeus threw his
father [Kronos] from the chariot and 'entartarosed' him" right
away, if we translate the word literally.8 Essential key words are
easily mistaken for petty details, as in this case the "chariot," from
which Kronos/Phaethon was thrown into "Tartaros." The vehicle
in question is the two-wheeled race car, Greek harma, Latin currus,
Babylonian narkabtu. It is the chariot of Auriga in Babylonia, sur-
viving in the "Sphaera barbarica" of astrologers,9 whereas in our
Sphere the Charioteer is bereft of any vehicle. And, indeed, no other
than Erichthonios (a Greek name for Auriga, besides Heniochos)
is claimed to have invented the two-wheeled race car drawn by four
horses (Erat. Catast. no. 13, pp. 98-101) which has to be distin-
guished carefully from the even more important four-wheeled truck,
the Big Dipper, that is, Greek hamaxa, Latin plaustrum, Sumerianmul
MAR.GID.DA = Charles' Wain.
Slightly perplexing traditions have come down in cuneiform
texts, but they clearly allude to the same "event." So, for in-
stance, "The Elamitic chariot, without seat, carries the corpse of
Enmesharra. The horses which are harnessed to it are the death-
demon of Zu. The king who stands in the chariot is the hero-king,
the Lord Ninurta." Leaving aside the two last sentences which are,
in reality, not so pitch dark as they look at first glance, the trans-
lator, Erich Ebeling,10 leaves no doubt that the "Elamitic chariot"
is identical with the constellation "Chariot of Enmesharra," which
the authorities on Babylonian astronomy have identified with beta
and zeta Tauri.11 This Enmesharra now has a "telling" name:
En.AfE.SARRA is "Lord of all the me" that is, he is Lord of
"norms and measures," also called "Lord of the World Order,"
7s.v. Eretria (Eretrios, "Son of Phaethon, and this was one of the Titans").
See M. Mayer, Giganten und Titanen (1887), pp. 70, 124.
8 Hieronymi et Hellanici theogonia (Athenagoras), see Kern frg. 58, p. 138; cf.
also R. Eisler, Weltenmantel und Himmelszelt (1910), p. 338.
9Cf. Boll, Sphaera, pp. 108ff. (Teukros and Valens).
10 Tod und Leben nach den Vorstellungen der Babylonier (1931), pp. 29, 33f.
11 Gossmann, p. 89; Schaumbcrger, 5. Erg., p. 327; E. F. "Weidner, in RI.A 3,p.77.
p.77.
267 • The Depths of the Sea
"Lord of the Universe = Ea" and, this is important, "the weighty
one in the underworld" and "the sovereign of the underworld."12
The "underworld" is misleading, though; the word is Arallu. The
experts generally—not the Assyriologists alone—prefer to talk of
names, in plural, given to the one "underworld," instead of trying
to find out the precise whereabouts of the several provinces of that
huge country, and to establish which name might properly fit every
quarter. As if one did not know of the plurality of "hells" and
"heavens." Here, however, it is not necessary to bring order into
the quarters of the Mesopotamian Hades, and for the time being, it
suffices that the Lord of the World Order, Enmesharra, is Enki-Ea,
because it is known anyhow that he dwells "at the seat of Rita":
Eridu-Canopus. And since "Enmesharra's chariot" is the vehicle of
Auriga, beta zeta Tauri, there can be little doubt that the tradition
of Phaethon's fall was already a Sumerian myth (appendix #22).
And as in Greece, where the drastic version of the Orphics, of
Hesiod and others are found side by side with those of Plutarch
and Proclus, according to which Kronos gives with paternal grace
"all the measures of the whole creation" to his son Zeus,13 so, too,
we have in Mesopotamia cruel-sounding variations besides "reason-
able" ones. For example, when Marduk builds his "world" and
receives fifty new names, his father Ea gives him his very own
name, stating (EE 7.141f.): "His name shall be Ea. All my com-
bined rites he shall administer; all my instructions he shall carry
out." And as concerns Ea under the name of Enmesharra, Edzard
states: "An incantation of Neo-Assyrian times, using an epithet of
Enmesharra 'Who transferred scepter and sovereignty to Anu and
Enlil' possibly hints to the voluntary abdication of the god."14
One of the questions begging answers is, which measures are
meant, and how does Saturn accomplish his assignment "to give
12 D. O. Edzard, "Die Mythologie der Sumerer und Akkader," Wb. Myth., vol.
1, p. 62; P. Michatz, Die Gotterliste der Serie Anu ilu A-nu-um (Phil. Diss.; 1909),
p. 12; K. Tallqvist, Sumerische Namen der Totenwelt (1934), p. 62, and Akka-
dische Gotterepitheta (1938), pp. 304, 437.
13 See also Lucian who makes Kronos say: "No, there was no fighting, nor docs
Zeus rule his empire by force; I handed it to him and abdicated quite voluntarily."
14 Edzard, p. 62.
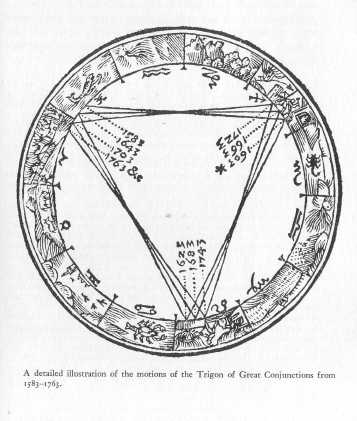
Hamlet's Mill • 268
them continuously" to Jupiter? And, even if it is accepted that his
"seat" is Canopus, how can he possibly give the measures from
there? Without pretending to understand the scheme well for the
time being, there are some explanations which seem to be the most
plausible ones.
Above (p. 136), attention was called to the significance of the
revolution of that Trigon which is built up by "Great Conjunc-
tions" of Saturn and Jupiter, and was still understood by Kepler
(see figure). Now, whoever tries to imagine the degree of difficulty
which faced the oldest "mythographers" will realize how welcome
it must have been to find periods which fitted into each other at
least approximately. This Trigon of Great Conjunctions presented
itself as the instrument by which one could "narrow down" the
almost imperceptible tempo of the Precession. To move through
the whole zodiac, one of the angles of the Trigon needs approxi-
mately 3 X 794.33 = 2383 years. That comes tolerably near to one
double-hour of the greatest "day" of the Precession of 25,900 years
(appendix #23). A new zodiacal sign was termed to "rule" start-
ing from the day of a great conjunction at the place of the "pas-
sage." The marginal point of Greek time-reckoning was the date
of the first Olympic Games: they had been founded in memory
of the wrestling of Kronos and Zeus, Pausanias said. The celestial
constellation, however, ruling the different traditional dates of the
first Olympic Games does not justify this claim; in other words, it
is not known yet which particular great conjunction it was in the
memory of which the Games were supposed to have been intro-
duced. Our own era, the Age of Pisces, started with a great con-
junction in Pisces, in the year 6 b.c.
By means of this Trigon, Saturn does give panta ta metra con-
tinuously to his "son" Zeus, and this same Trigon appears to be
called "genus" in the Orphic fragment already quoted (155 Kern),
where Zeus addresses Kronos with the words, "Set in motion our
genus, excellent Demon." And Proclus alluded to it in his statement
(ibid.), "And Kronos seems to have with him the highest causes of
junctions and separations." And still according to Macrobius he
269 • The Depths of the Sea
was the "originator" of time (Sat. 7.22.8: "Saturnus ipse qui auctor
est temporum.") ,15
So much for Saturn the unalterable planet gliding along his orb.
Saturn as the fallen ruler of the Golden Age and retired to Eridu
is a much harder proposition. Although there is also evidence to the
contrary, there are many indications that the South Pole—Canopus
—was taken for static, exempted from the Precession.16 And this
15 See R. Klibansky, E. Panofsky, and R. Saxl, Saturn and Melancholy (1964),
pp. 154f. Cf. pp. 333f., with quotations from the Latin translation of Abu Ma'shar,
where Saturn "significat . . . quantitates sive mensuras rerum," and where "eius est
... rerum dimensio et pondus."
16 We have neither time nor space to deal sufficiently with the relevant and
copious information on the "joyful" South Pole (see L. Ideler, Sternnamen,
pp. 265f.), the "Kotb Suhayl" of the Arabians, called thus after Canopus, which is
recognized in Fezzan as "l'etoile primordiale Sahel, identifie au premier ciel con-
tenant les constellations a venir" (V. Paques, L'arbre cosmique [1964], p. 36)—
the primordial star, "presented under the form of an egg that contained all the
things that were to be born" (Paques, p. 47). To begin discussing the static
South Pole, one might well start with the "Seven Sleepers of Ephesus," who were
thought to be on board the Argo—even if this is explicitly stated only in very
late Turkish tradition (16th century)—particularly from Louis Massignon's article,
"Notes sur les Nuages de Magellan et leur utilisation par les pilotes arabes dans
l'Ocean Indien: sous le signe des VII Dormants" (Revue des Etudes Islamiques
[1961], pp. 1-18 = part VII of Massignon's series of articles on the Seven Sleepers
in Islamic and Christian tradition; part I appeared in the same review in 1955,
part VIII in 1963), and in the very substantial review article by T. Monod,
"Le ciel austral et 1'orientation (autour d'un article de Louis Massignon)" (Bulle-
tin de rinstitut Frangais d'Afrique Noire [1963], vol. 25, ser. B, pp. 415-26). In
both articles one finds, besides the surprising notion of the happy South, note-
worthy information about human migrations directed toward the South in several
continents. Massignon derived the "lucky" significance of the Kotb Suhayl and the
Magellanic Clouds from historical events; i.e., from the expectations of exiled and
deprived peoples escaping from the perpetual wars and raids in the northern coun-
tries: "Nomades ou marins, ces primitifs expatries n'eurent pour guides, dans leur
migrations et leur regards desesperes, que les 'etoiles nouvelles du ciel austral"
(1961, p. 12). Monod (p. 422), however, pointed to the crucial key word as given
by Ragnar Numelin (Les Migrations Humaines [1939], p. 27cm.), who remarked:
"Il est possible que beaucoup de ces mysterieuses peregrinations se proposaient
comme but de trouver H'etoile immobile' dont parle la tradition. Le cultc de l'fetoile
Polaire peut avoir provoque de tels voyages," annihilating thus with the second
sentence the treasure which he had detected in the first. But Massignon and
Monod also missed the decisive factor, namely, that the South Pole of the ecliptic
is marked by the Great Cloud, and that Canopus is rather near to this south ecliptic
pole, whereas the immovable center in the North of the universe is not distin-
guished by any star, as has been said previously.
Hamlet's Mill • 270
would mean—at least it might mean, because it fits so well into
those notions of "time and the rivers"—that expired periods return
"home" into timelessness, that they flow into eternity whence they
came. Access to the Confluence of the Rivers, Mouth and Source
of aeons and eras, the true seat of immortality, has always been
denied to any aspect of "time, the moving likeness of eternity." For
eternity excludes motion. But from this desired motionless home,
source and mouth of times, the world-ruler has to procure the
normed measures valid for his age; they are always based on time,
as has been said. Again it is the same whether it was Marduk who
first "crossed the heavens and surveyed the regions. He squared
Apsu's quarter, the abode of Nudimud [=Ea]. As the lord mea-
sured the dimensions of Apsu," and then erected his palace as the
"likeness" of Apsu, or whether it was Sun the Chinese Monkey
who fetched his irresistible weapon from the "navel of the deep"—
an enormous iron pillar by means of which, once upon a time,
Yu the Great had plumbed out the utmost depth of the sea. In any
case, whether the description is sublime or charmingly nonsensical,
it is literally the "fundamental" task of the Ruler to "dive" to the
topos where times begin and end, to get hold of a new "first day."
As the Chinese say, in order to rule over space one has to be master
of time.
The reader may suspect by now that Hamlet has been forever
forgotten. The way has been long and circuitous, but the connec-
tion is still there. Even in so late and damaged a tradition as that
of Saxo Grammaticus, every motif once made sense in high and
far-off times. If it is difficult to recognize the central significance of
the "oar" of Odysseus,17 how much more difficult is it to spot the
For the fun of it, a note of Monod's should be quoted here (p. 421): "Quand
Voltaire nous dit que Zadig 'dirigeait sa route sur les etoiles' et que 'la constella-
tion d'Orion, et le brillant astre de Sirius le guidaient vers le pole de Canope', nous
retrouvons dans cette derniere expression un temoignage du role joue par Canopus
dans l'orientation astronomique. II n'y a pas lieu, bien entendu, de vouloir la cor-
riger en 'port de Canope'; cf. Voltaire, Romans et contes, ed. Gamier 1960, note
49, p. 621." Where shall we ever find security from the "improvements" of
philologists?
17 Sooner or later, one more object will have to be admitted to the assembly of
imperial measuring oars, or gubernacula: the enigmatical Egyptian hpt, the so-
271 • The Depths of the Sea
"steering oar of Argo" = Canopus-Eridu, in the childish riddle of
Amlethus? And yet, the "measuring of the depth of the sea" is there
all the time; infant-Kullervo dared to do it with a ladle, coming to
the startling result of "three ladles and a little bit more." And there
is an even less suitable measure to be had, a veritable stylus. Jacob
Grimm gives the story: "The medieval Dutch poem of Brandaen
. . . contains a very remarkable feature: Brandaen met on the sea
a man of thumb size, floating upon a leaf, holding in his right hand
a small bowl, in the left hand a stylus; the stylus he kept dipping
into the sea and letting water drip from it into the bowl; when the
bowl was full, he emptied it out, and began filling it again. It
was imposed on him, he said, to measure the sea until Judgment-
day."18 This particular kind of "instrument" seems to reveal the
surveyor in charge in this special case. Mercury was the celestial
scribe and guardian of the files and records, "and he was the in-
ventor of many arts, such as arithmetic and calculation and geom-
etry and astronomy and draughts and dice, but his great discovery
was the use of letters," as Plato has it (Phaedrus 274).
It remains to be seen whether or not all the measuring planets
can be recognized by their particular methods of doing the measur-
ing. It is known how Saturn does it, and Jupiter. Jupiter "throws,"
and Saturn "falls." But, as was said before, Saturn giving the meas-
ures as resident in Canopus is hard to imagine. Maybe all the avail-
able keys to this door have not been tried? Observing so many char-
acters occupied with measuring the depth of the sea, one stumbles
over the strange name given to Canopus by the Arabs: they call it
called "ship's device" (Schiffsgerat) of obscure literal meaning, which the Pharaoh
brought running to a deity in the ritual of the "oar-race." There was also a "jar-
race" and a "bird-race," the Pharaoh carrying a water jar or a bird, respectively.
In several Pyramid Texts the soul of the dead ruler takes this ship's device and
brings it to another celestial department, while the actual rowing of the boat is
done by the stars (Pyr. 2173A, d; see also 284A, 873D, 1346B). See Aeg. Wb., vol. 3,
pp. 67-71; A. Gardiner, Egyptian Grammar (1957), p. 581; M. Riemschneider,
Augengott und Heilige Hochzeit (1953), pp. 255f. For the different imperial races,
see the (unsatisfying) investigation by H. Kees, Der Opfertanz des Aegyptischen
Konigs (1912), pp. 74-90, the "oar-race."
18 Deutsche Mythologie (1953), pp. 420/373. The'English translation (TM, p. 451)
makes it "pointer" instead of "stylus"; Grimm has "Griffel." Cf. K. Simrock,
Handbuch der Deutschen Mythologie (1869), § 125, p. 415.

Hamlet's Mill • 272
"the weight," and the Tables of Alphonsus of Castile spell it "Suhel
ponderosus," the heavy-weighing Canopus.19 This "weight" is the
plumb at the end of the plumb line, by means of which this depth
was measured. So far so good. But where does Saturn come in? He
can be understood as the "living" plumb line.20 This would be hard
to believe if the story of this surveying were not told by the plumb
line itself, Phaethon. Only when he told it, he had another name,
as belongs to the manners and customs of celestial characters:
Hephaistos.21
In the first book of the Iliad (1.589ff.), Hephaistos tries to ap-
pease his mother Hera who is very angry with her husband Zeus,
and says to her:
"It is hard to fight against the Olympian. There was a time once
before now I was minded to help you and he caught me by the foot
and threw me from the magic threshold, and all day long I dropped
helpless, and about sunset I landed in Lemnos, and there was not much
life left in me."
Hephaistos mentions the event once more, when Thetis asks him
to forge the shield for her son Achilles (18.395ff.):
"She saved me when I suffered much at the time of my great fall
through the will of my own brazen-faced mother,22 who wanted to
hide me, for being lame. Then my soul would have taken much
19 "Suhail al wazn." The epithet "wazn" has been given also to other stars of
the southern sky. For ample discussions of this name, see Ideler, pp. 249-52, 263;
Allen, pp. 68f.; J. N. Lockyer, The Dawn of Astronomy (1964), p. 294; W. T.
Olcott, Star Lore of All Ages (1911), p. 133.
20 The strange "beacon" in Aeschylus' Agamemnon, which announced the Fall
of Troy, must have been something of this kind; the context excludes absolutely
any possible devices of the signal corps.
21 To avoid misunderstanding, we do not wish to insist upon the absolute identity
of the fall of Phaethon and the account of the fall as told by Hephaistos in the
first book of the Iliad. We suspect that the verbal image "Jupiter-hurls-down-
Saturn" describes the shaping of the Trigon of great conjunctions, not, however,
of the Trigon generally but of that new Trigon whose first angle was established
by a conjunction of the Big Two at the beginning of a new world-age. On the
other hand, this picturesque formula might cover the shifting of the Trigon of
conjunctions from one Triplicity to the next (cf. appendix #23); these highly
technical problems cannot be solved yet.
22 That is not what Homer says, it is kunopis, dog-eyed; Hera seems to have
been near Sirius at that time.

The Chinese picture illustrates in true archaic spirit (which means that only hints
are given, and the spectator has to work out for himself the significance of the
details) the surveying of the universe. The two characters surrounded by constel-
lations are Fu Hsi and Nu Kua, i.e., the craftsman god and his paredra, who
measure the "squareness of the earth" and the "roundness of heaven" with their
implements, the square with the plumb bob hanging from it, and the compass.
The intertwined serpent-like bodies of the deities indicate clearly enough, al-
though in a peculiar "projection," circular orbits intersect ing each other at regular
intervals. See also "The I Ching and the Genetic Code", Martin Schonberger, p. 9.
273 • The Depths of the Sea
suffering had not Eurynome and Thetis caught me and held me.
Eurynome, daughter of Ocean, whose stream bends back in a circle.
With them I worked nine years as a smith."
Indentured as a smith again, like Kullervo.
Krates of Pergamon23 explains this feature in the sense that Zeus
aspired to the measurement of the whole world (anametresin tou
pantos). He succeeded in determining the measures of the cosmos
by "two torches moving with the same speed": Hephaistos and the
Sun. Zeus hurled the former down from the threshold to earth at
the same moment when the latter was starting from point east on
his way to the west. Both reached their goal at the same time: the
Sun was setting when Hephaistos struck Lemnos.
Krates felt convinced that Homer spoke of a sphere, and since
he himself was most interested in the coordinate system of the
sphere he did not find it strange to interpret in his own sense the
shield of Agamemnon (Iliad 11.32f.) and of Achilles (18.468ff.).24
He also conceived Odysseus' sailing from Circe's island to Hades
as a voyage from the Tropic of Capricorn to the South Pole. The
idea is not so strange as it might seem. Zeus, establishing the equi-
noctial colure by hurling down the fictitious "Phaethon," intro-
duced a new skambha—one remembers Plato about this: "It has
the air of a fable . . ."25 But there is also Cornford's idea of the
23 It is to the credit of Hans Joachim Mette and his work, Sphairopoiia, Unter-
suchungen zur Kosmologie des Krates von Pergamon (1936), that we find
collected every relevant testimonial and fragment concerned with Krates and his
topics.
24 See Mette, pp. 30-42, and his introduction.
25 We cannot discuss here the Homeric wording of the topos from which Zeus
threw down Hephaistos: "magic threshold" means nothing, anyhow (apo belou
thespesioio); there were ancient scholars who claimed that Krates connected this
"belos" with the Chaldean "Bel"/Baal = Marduk. We leave it at Auriga's chariot,
Babylonian narkabtu, the more so, as Marduk, too, used it when tipping over
Tiamat. The "Babylonian Genesis" does not tell that Marduk hurled people
around, but there is a cuneiform text (VAT 9947) called by Ebeling (Tod und
Leben, 37f.) "a kind of a calendar of festivals," where it says: "the 17th is called
(day) of moving in, when Bel has vanquished his enemies. The 18th is called (day)
of lamentation, at which one throws from the roof Kingu and his 40 sons." Kingu
had the epithet "Enmesharra," i.e., "Lord of norms and measures"; he was the hus-
band of Tiamat—as Geb was husband of Nut—who gave him the "tablets of fate,"
which Marduk was going to take away from him after his victory, and 40 is the
Hamlet's Mill • 274
vision of Er,26 according to which Plato's "souls actually see in their
vision not the universe itself, but a model, a primitive orrery in a
form roughly resembling a spindle ..."
It is sad to observe, and certainly odd, how little scholars trust
their own eyes and words—as in the case of Jane Harrison who
remarked on the Titans: "They are constantly driven down below
the earth to nethermost Tartaros and always reemerging. The very
violence and persistence with which they are sent below shows that
they belong up above. They rebound like divine india-rubber
balls."27 It is rather evident that these divine india-rubber balls were
not really sent below: what was overthrown were the expired ages
together with the names of their respective rulers.
But now the galactical stage is empty and it is almost time to
watch the working of the next skambha grinding out the "destiny"
for the first postdiluvian generation. But before facing the hero of
the oldest, the most difficult, and by all means the oddest of epics,
there is an interval. We seize the occasion to insert a chapter on
methods, presented by means of a well-known episode.
number of Enki-Ea (see below, p. 288). The rest is easy to calculate. We are
hampered by our inappropriate ideas about "names," and by the misleading labels
settled upon celestial characters by the translators who make Tiamat, Kingu and
their clan into "monsters."
26 The Republic of Plato, p. 350.
27 Themis, p. 453f. Cf. for a similar sort of mistrusting one's own evidence, M.
Mayer, Giganten und Titanen, p. 97.
Chapter XXI
The Great Pan Is Dead
everyone has once read, for it comes up many times in litera-
ture, of that pilot in the reign of Tiberius, who, as he was sailing
along in the Aegean on a quiet evening, heard a loud voice an-
nouncing that "Great Pan was dead." This engaging myth was
interpreted in two contradictory ways. On the one hand, it an-
nounced the end of paganism: Pan with his pipes, the demon of still
sun-drenched noon, the pagan god of glade and pasture and the
rural idyll, had yielded to the supernatural. On the other hand the
myth has been understood as telling of the death of Christ in the
19th year of Tiberius: the Son of God who was everything from
Alpha to Omega was identified with Pan == "All."1
Here is the story, as told by a character in Plutarch's dialogue
"On why oracles came to fail" (419 b-e) :
The father of Aemilianus the orator, to whom some of you have
listened, was Epitherses, who lived in our town and was my teacher
in grammar. He said that once upon a time in making a voyage to
Italy he embarked on a ship carrying freight and many passengers.
1 O. Weinreich ("Zum Tode des Grossen Pan," ARW 13 [1910] pp. 467-73) has
collected the evidence for such strange notions, first found in 1549 (Guillaume
Bigot), then three years later in Rabelais' Pantagruel, and ridiculed in later times,
e.g., by Fontenelle, in the beginning of the 18th century: "Ce grand Pan qui
meurt sous Tibere, aussi bien que Jesus-Christ, est le Maistre des Demons, don't
l'Empire est ruine par cette mort d'un Dieu si salutaire a l'Univers; ou si cette expli-
cation ne vous plaist pas, car enfin on peut sans impietc donner des sens contraires
a une mesme chose, quoy qu'elle regarde la Religion; ce grand Pan est Jesus-Christ
luy-mesme, dont la mort cause une douleur et une consternation generale parmy les
Demons, qui ne peuvent plus exercer leuf tirannie sur les homines. C'est ainsi qu'on
a trouve moyen de donner a ce grand Pan deux faces bien differentes" (Weinreich,
pp. 472-73).
Hamlet's Mill
276
It was already evening when, near the Echinades Islands, the wind
dropped and the ship drifted near Paxi. Almost everybody was awake,
and a good many had not finished their after-dinner wine.
Suddenly from the island of Paxi was heard the voice of someone
loudly calling Thamus, so that all were amazed. Thamus was an
Egyptian pilot, not known by name even to many on board. Twice
he was called and made no reply, but the third time he answered;
and the caller, raising his voice, said, "When you come opposite to
Palodes, announce that Great Pan is dead." On hearing this, all,
said Epitherses, were astounded and reasoned among themselves
whether it were better to carry out the order or to refuse to meddle
and let the matter go. Under the circumstances Thamus made up his
mind that if there should be a breeze, he would sail past and keep
quiet, but with no wind and a smooth sea about the place he would
announce what he had heard. So, when he came opposite Palodes, and
there was neither wind nor wave, Thamus from the stern, looking
toward the land, said the words as he heard them: "Great Pan is
dead." Even before he had finished there was a great cry of lamenta-
tion, not of one person, but of many, mingled with exclamations of
amazement. As many persons were on the vessel, the story was soon
spread abroad in Rome, and Thamus was sent for by Tiberius Caesar.
Tiberius became so convinced of the truth of the story that he caused
an inquiry and investigation to be made about Pan; and the scholars,
who were numerous at his court, conjectured that he was the son
born of Hermes and Penelope.
Plutarch has not been accepted, and a "simple" explanation was
suggested. As the ship drifted along shore by a coastal village, the
passengers were struck by the ritual outcry and lamentations made
over the death of Tammuz-Adonis, the so-called grain god, as was
common in the Middle East in high summer. Other confused shouts
were understood by the pilot Thamus as directed to him.2 Out of
that, gullible fantasy embroidered the tale, adding details for credi-
bility as usual. This sounded good enough. The story had been
normalized, that is, disposed of as insignificant.
One is still allowed to wonder why such a fuss was made at the
time about exclamations which must have been familiar to contem-
poraries, and why, unless Plutarch be a liar, that most learned of
mythologists, the Emperor Tiberius himself, thought the matter
worth following up.
2 See F. Liebrecht, Des Gervasius von Tilbury Otia Imperialist (1856) pp. 179-80;
J. G. Frazer, The Dying God (Golden Bough 5), pp. 7f.
277
The Great Pan Is Dead
Therefore, with all due respect for the scholars involved, it is
worth trying a different tack. One can assume that it was not all
background noise, as we say today, but that there was an actual
message filtered through: "The Great Pan is dead," Pan ho megas
tethneke, and that it was Thamus who had to announce it.
It was enough of a message for Tiberius' committee of experts
(philologoi) to decide that it referred to Pan, the son of Penelope
and of Hermes, number 3 in Cicero's list given in De natura deorum
3.56. 3 Penelope, whoever she really was, must have had quite a life
after the events narrated in the Odyssey.4" Mythology seems to have
been a careful science in those circles.
If it is decided to credit the message, one is led to consider a num-
ber of similar stories, some of them collected by Jacob Grimm,
but the bulk by Mannhardt.5 They are strictly on the level of
folktale, which at least preserved their innocence from literate in-
terference. There is a whole set of stories from the Tyrol concerning
the "Fanggen," a kind of "Little People" (or giants), dryads or tree
spirits whose existence is bound to trees, so that the felling of such
a tree would annihilate a Fangga. They were once willing to live
with peasants in the form of servant maids and would bring bless-
ings to the home,6 but would also vanish unaccountably. A favorite
story is that of the master of the house coming home and telling
the family of a strange message that he has heard from a voice, such
as "Yoke-bearer, yoke-bearer, tell the Ruchrinden [Rough-bark]
that Giki-Gaki is dead on the Hurgerhorn," or "Yoke-bearer,
3Tertius Jove tertio natus et Maia, ex quo et Penelopa Pana natum ferunt. Cf.
also Herodotus 2.145.
4 As concerns the version according to which Pan was the son of Penelope and
all the suitors, Preller remarks (Griechische Mythologie [1964], vol. 1, p. 745): "the
repulsive myth."
5 J. Grimm, TM, pp. 453n., 1413f.; cf. pp. 989, 1011-12 ("The Devil's dead, and
anyone can get to heaven unhindered"); W. Mannhardt, Wald- und Feldkulte,
vol. 1 (1875), pp. 89-93; vol. 2 (1877), pp. 148ff.
6 Generally, however, they are claimed to show rather revolting habits, such as
eating children or disposing of them in another peculiar manner, as, for instance,
pulverizing them into snuff. Thus, of one Fangga it is said: "Wenn sie kleine Buben
zu fassen bekam, so schnupfte sie dieselben, wie Schnupftabak in ihre Nase, oder
rieb sie an alten durren Baumen, die von stechenden Aesten starrten, bis sie zu
Staub geraspelt waren." It seems to be a very deep-seated desire of "higher powers"
to change divine or human beings into powder and dust.
Hamlet's Mill
278
yoke-bearer, tell the Stutzkatze [also Stutzamutza, i.e., Docked Cat]
Hochrinde [High-bark] is dead." At which point the housemaid
breaks into a loud lament and runs away forever.
Or it might be that while the family was sitting at dinner, a voice
called three times through the window: "Salome, come!" and the
maid vanished. This story has a sequel: some years later a butcher
was coming home at midnight from Saalfelden through a gorge,
when a voice called to him from the rocky wall: "Butcher, when
you come to such and such a place [zur langen Unkener Wand],
call into the crack in the rock: 'Salome is dead.' " Before dawn the
man had come to that point, and he shouted his message three times
into the crack. And at once there came from the depths of the
mountain much howling and lamentations, so that the man ran
home in fear. Sometimes the message delivered is followed by the
"flyting" of whole tribes of Little People: it was their "king" whose
death had been announced.7 It is remarkable that in most of the
cases registered, the master was addressed as "Yoke-bearer." No
one knows why. But the wild woodmaid invariably vanished.
Felix Liebrecht speaks of the ways of certain ghostly were-
wolves, the "Lubins," that haunted medieval Normandy. These
timid ghosts hunted in a pack, but to little point, for instead of turn-
ing on the intruder, they would disperse at the slightest noise,
howling: "Robert est mort, Robert est mort."8 This meaningless
yarn gains perspective once its trail is followed back to the "Wolf-
Mountain" in Arcadia and the Lycaean "Wolf-games"—the parent-
festival of the Lupercalia in Rome—held on this Mountain Lykaios.
Pan is said to have been born here,9 and here he had a sanctuary.
Here also Zeus tilted a "table"—whence the place had the name
Trapezous—because Lykaon had served him a dish of human meat,
7 "No is Pippe Kong dod" (Schleswig); otherwise "Konig Knoblauch" (King
Garlic), "King Urban"; "Hipelpipel is dead" (Lausitz); "Mutter Pumpe is tot"
(Hessen). Cf. Grimm, p. 453; K. Simrock, Handbuch der Deutschen Mythologie
(1869), § 125, pp. 416f.; F. Liebrecht, Zur Volkskunde (1879), p. 257n., who gives
additional references. See also P. Herrmann, Deutsche Mythologie (1898), pp. 89f.
8 Liebrecht, Zur Volkskunde, p. 257n.
9 Pindar frg. 100 (68); Rhea had borne Zeus there also (Paus. 8.38.2f.), and on
top of the mountain was a temenos of Zeus, where nothing and nobody cast a
shadow.
279
The Great Van Is Dead
consisting of his own son. Zeus turned Lykaon into a werewolf, and
in tilting the "table" caused the Flood of Deukalion, the "table," of
course, being the earth-plane through the ecliptic. This is the sig-
nificant event of the tale, and the whole is so long no sensible person
would try to summarize it.
Next, there is the case of Robert, known as Robert le Diable,
allegedly a historical character who was supposed to have spells as
a werewolf and then to do penance by "lying in the guise of a dog
under the ladder." And thereby hangs the puzzle of the dynasty
of the Scaligeri in Verona (we all remember Prince Escalus in
Romeo and Juliet) whose powerful founder was Can Grande della
Scala, "Great Dog of the Ladder," who became a host to Dante
wandering in exile, and a patron of the Divine Comedy. His succes-
sors, Mastino, Cansignorio, had dog names too.10 Now, for the pur-
poses of this essay, this is the end of this line of approach, except
for two hints for the future. First, Pythagoras called the planets
"the dogs of Persephone." Second, there is only one huge ladder,
the Galaxy, and only one canine character lying under this ladder,
Sirius. But at this point we are only ringing bells at random.
What matters here is the tenacious survival of motifs in simple
surroundings. Moving one step down in folklore, there is a story
spread all over northern Europe (Mannhardt 1, 93) of which this
is the English version (the end is from a German variant). A
clowder of cats have met in an abandoned broken-down house,
where a man is watching them unobserved. A cat jumps on the wall
and cries: "Tell Dildrum that Doldrum is dead." The man goes
home and tells his wife. The house cat jumps up and yowls: "Then
I am king of cats!" and vanishes up the chimney.
This is how the "body" of tradition survives the death of its
"soul," fractured, with all ideas gone, preserved like flies in amber.
Greek gods have become cats and housemaids among illiterate folk;
the Powers pass, but the information remains. By checking on the
repeats, one has the message of the Voice in the canonic form:
"Wanderer, go tell Dildrum that the Great Doldrum is dead." The
10 Sec O. Holler, "Cangrande von Verona und das Hundesymbol der Lango-
barden," in Festschrift Fehrle (1940), pp. 107-37.
Hamlet's Mill
280
■/
bearer of the message may be an unknown pilot, a passerby, an
animal, a watcher. The substance is that a Power has passed away,
and that the succession is open. The cosmos has in its own way
registered some key event.
For another example of hardly credible survival, there are
also the findings of Leopold Schmidt on "Pelops and the Hazel
Witch,"11 a collection of tales from the Alpine valleys of South-
ern Tyrol. It is again about housemaids among peasants. The story
goes that a farm servant accidentally watches the dinner of some
witches, in which a housemaid is boiled and consumed by her
fellow witches. A rib is thrown at the young man, and when
after the meal the witches rebuild and revise the girl, this rib
is missing and has to be replaced by a hazel branch. At the very
moment that the farmhand tells his master that his housemaid is
a hazel witch, the housemaid dies. This is no witch hazel trick—
it is simply a rehearsing of the archaic tale of Pelops, son of Tanta-
los, the Titan, who had been boiled and served for dinner by his
evil father at the table of the gods. The gods, it is said, kept away
from the food that looked suspicious, all except for Demeter, who,
lost in her grief for the death of Persephone, absently ate a shoulder
blade believing it to be mutton. The gods brought the child back to
life. But a shoulder blade was missing and it was replaced by ivory.
Pelops went on to become a famous hero, from whom the Pelopon-
nesos was named, and he won the foot race at Olympia from King
Oinomaos, thus inaugurating the Olympian games. The two are
portrayed before the race on the metope of the temple of Zeus in
Olympia. Oinomaos stands there looking stuffy, Pelops relaxed, and
above the two the great figure of Apollo with arms outstretched,
as if to consecrate the event. But Olympia became holy because it
was the site where Zeus overcame his father Kronos12 and threw
him down out of the royal chariot. Near Olympia you can see the
11 "Pelops und die Haselhexe," Laos 1 (1951), pp. 67-78.
12Paus. 5.7.10. It is not from mere "religious" motifs that "in the hippodrome
the pillar which-marked the starting point had beside i: an altar of the Heavenly
Twins" (Pind. Olympian Odes 3.36; Paus. 5.75); cf. F. M. Cornford in Harrison
(Themis [1962], p. 228); see also above, pp. 206f. n. 5, for the Circus Maximus in
Rome.
28l
The Great Pan Is Dead
Kronion hill, which still bears the imprint of the celestial posterior.
Exeunt the official characters. Only the great Olympic Games re-
mained an "international" event which took place every four years
and became the Greek way of counting time. What has all that to
do with a little fairy housemaid in the Austrian Alps, thousands of
years later? Nothing at first glance, and yet, if one dug deeper into
the story of this shoulder blade, there would be a good case history
to be made.13 Tradition goes on tenaciously, even through ages of
submerged knowledge. At least, by now, some distance has been
made well away from the fertility rites of Frazer and others, which
accounted for things too patly. This is an important gain.
Returning to Plutarch's text the dialogue's chatty style gives an
impression of casualness, but in these matters Plutarch usually knew
more than he cared to discuss. There was a pilot, a kybernetes, giv-
ing an announcement from the stern deck (prumne) of his ship.
These details seem not to be casual. For there is one stern and one
pilot which cannot be overlooked in mythology. The stern is that
of the constellation Argo, a ship which consists of a stern and little
else. It is understood to be the Ship of the Dead with Osiris on
board (he is the strategos of the ship, according to Plutarch's his
and Osiris 359 ef), and the Pilot star in the stern is Canopus itself,
the site of the great Babylonian god Ea (Sumerian Enki), its name
in Sumerian being mulNUNki, and Enki is the father of Tammuz,
which might lead back to the trail.
But the striking thing is that Mesopotamian Canopus bears the
13 There is not only "moskhou omon chryseion," the golden shoulder of the ox
in the hands of Mithras (Egyptian Maskheti, the Bull's Thigh, Ursa Major), and
Humeri, an antiquated Latin name of Orion, as we know from Varro; the highest
god, Amma, of the West Sudanese Dogon (or the Clarias senegalensis, the shadfish,
an avatar of the Dogon's "Moniteur Faro," whose emblem is the very same as
that of ityphallic Min, the Egyptian Pan) carries in his humeri the first "eight
grains," and these 8 sorts of grain (stereotypically including beans) play their
cosmogonic role from the Dogon to China (cf. for another striking similarity of
West Sudan and China, the chapter on the "shamanistic" drums, but there are
many more). There is also the tale from modern Greece (see J. G. von Hahn,
Griechische und Albanische Marchen [1918], vol. 1, pp. 181-84) of the "Son of
the shoulder-blade," one of those "Strong Boys" who, after adventures in spirit
land, grinds his mother to porridge on a hand mill. How these and other traditions
arc connected with the shoulder blade oracle, if they are connected at all, cannot
be made out yet.
Hamlet's Mill
282
283
The Great Pan Is Dead
name "Yoke-star of the Sea"14—the "Yoke-star of the Sky" being
Draco. Here then there is a death fate, a pilot, and a yoke-bearer
in an unsuspected but suggestive complex. Dealing with such pro-
found experts of archaic myth as Plato and Plutarch, one is not
likely to overlook the "Egyptian king Thamus" in Phaedrus (274c-
275B, see below, chapter XXIII), who drives it home to Thoth-
Hermes, who was very proud of just having invented writing, that
this new art was an extremely questionable gain. It must have been
a mighty "king" who dared to criticize Mercury's merits. But then,
the chapter on the Galaxy and the fall of Phaethon will have shown
that geographical terms are not to be taken at their face value, least
of all "Egypt," a synonym of the ambiguous Nile.
To find something more about the substance of the message we
shall move many centuries back, to a text certainly ancient, but of
undetermined date. It is the so-called "Nabataean Agriculture"
which has little to do with farming but much to do with agrarian
rites. The author, Ibn Wa'shijja, claimed to have derived it from an
almost primordial Chaldean source.15 Modern critics have decided it
was a fabrication of uncertain origin, a so-called falsification. What-
ever else it may be, original it is not. Such things are built out of tra-
ditional material. Maimonides judged it worth quoting at length,
Chwolson and Liebrecht analyzed it, comparing it with An-
Nadim's report on the Tammuz festival of the Harranians, held in
the month of July and called el-Buqat, the "weeping women."16
Here first is a passage studied by Liebrecht:17
14See P. F. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum (1950), 281; J. Schaumberger,
in Kugler's 3. Erganzungsheft (1935), p. 325, and n. 2 (one version: the "yoke of
Ea"); P. Jensen, Die Kosmologie der Babylonier (1890), pp. 16ff., 25; F. Boll-
C. Bezold, Farbige Sterne (1916), p. 121.
15 Actually, he (and others) claimed that the book was written by three (or
even more) authors, namely Ssagrit, Janbushad, and Qutama. The first living in the
seventh thousand of the 7000 years of Saturn—which he ruled together with the
Moon—the second at the end of the same millennium, the third appeared after 4000
years of the 7000-year cycle of the Sun had passed; so that between the beginning
and the end of the book 18,000 solar years have passed (according to Maqrizi). See
D. Chwolson, Die Ssabier und der Ssabismus (1856), vol. 1, pp. 705f. (cf. p. 822 for
the special alphabet used by Janbushad). So we are up to another "Tris-megistos,"
three times great, not just "thrice." Time is involved. Hermes is repeated three
times historically.
16Chwolson, vol. 2, pp. 27f., 207, 209.
17 Zur Volkskunde, pp. 251f.
It is said that once the Sakain (angels) and the images of the gods
lamented over Janbushad, just as all Sakain had lamented over Tam-
muz. The tale goes that the images of the gods gathered from all
corners of the earth in the temple of the Sun, around the great golden
image, which hung between heaven and earth. The great image of the
Sun was in the middle of the temple, surrounded by the images of the
Sun from everywhere, and also by the images of the Moon, then
those of Mars, then those of Mercury, of Jupiter, of Venus, and
finally of Saturn.18
Chwolson's part of the text goes on:
This idol (that hung between earth and heaven) fell down at this
point and began to lament Tammuz and to recount his story of sor-
rows. Then all the idols wept and lamented through the night; but on
the rising of the morning star, they flew off and returned to their
own temples in all corners of the world.
Such is the story which, Liebrecht says, was rehearsed in the
temples after prayers, with more weeping and lamentations. This
is then the archaic setting. It concerns planetary gods, the great
cult of Harran. Two of them stand out, almost ex aequo: Tammuz
and Janbushad. Now this latter is no other than Firdausi's Jam-
shyd.19 It has been seen already (p. 146) that Jamshyd is in Avestic
Yima xsaeta, the name from which came Latin Saturnus. There is
no question then, this is about Saturn/Kronos, the God of the
Beginning, Yima (Indian Yama), the lord of the Golden Age. A
lament over the passing of Kronos would have been in order even
in Greece,20 since he had been dethroned and succeeded by Zeus.
18 Let us note that the planets are not given in the astronomical order of their
periods, but in the order given by the heptagram, which describes the days of the
week.
19 See Liebrecht, p. 251n: "The Babylonian Izdubar [= Gilgamesh] is called
by Ibn Wa'shijja's Book on the Nabataean Agriculture 'Janla-Shad' (Janbushad),
i.e. Jamshid . . . Thus Rawlinson in Athenaeum. December 7, 1872."
20 Cf. the report by Plutarch (his and Osiris 363E) on Egypt: "There is also a
religious lament sung over Cronus. The lament is for him that is born in the re-
gions of the left, and suffers dissolution in the regions on the right; for the
Egyptians believe that the eastern regions are the face of the world, the northern
the right, and the southern to the left. The Nile, therefore, which runs from the
south and is swallowed up by the sea in the north, is naturally said to have its
birth on the left and its dissolution on the right." Kronos having been the ruler
of "galactical times" ((Job "inside" Nut), this makes more sense than meets the
eye. See also chapter XIII, "Of Time and the Rivers."
Hamlet's Mill
284
285
The Great Pan Is Dead
But who was Tammuz? The grain god dying with the season, the
rural Adonis, would hardly fit into such exalted company. Now it is
clear he was astronomical first of all. So much has been written
about his fertility rites that it took time to locate the real date, given
by Cumont.21 The lament over Adonis-Tammuz did not fall simply
in "late summer": it took place in the night between July 19 and 20,
the exact date which marked the opening of the Egyptian year, and
remained to determine the Julian calendar. For 3000 years it had
marked the heliacal rising of Sirius.
Tammuz was extremely durable, for he is found in Sumer as
Dumuzi, already the object of the midsummer lamentations. It was
seen that he was worshiped as the son of Enki, who was the
Sumerian Kronos. The cult went on in Harran as late as the 13th
century, long after Mohammedanism had engulfed the Ssabian
population. Notwithstanding the severe displeasure of the Caliph
of Baghdad, it went through sporadic but intense revivals in an area
that spread from Armenia to Quzistan.22 As mentioned, the celebra-
tion was called el-Buqat, "the weeping women." And the lament
was mainly over the god who was cruelly killed by being ground
between millstones, just like John Barleycorn in the rhyme we
quoted earlier:23
They roasted o'er a scorching fire
The marrow of his bones
But a miller used him worst of all
For he ground him between two stones.
What kind of grinding could it have been? Surely, the lament
referred in popular consciousness to the death of a corn god, called
also Adonis (the Lord), slain by a wild boar, but the celestial aspect
21 "Adonis et Sirius," Extrait des Melanges Glotz, vol. 1 (1932), pp. 257-64. But see
for the different dates of the Adonia, F. K. Movers, Die Phonizier (1841), vol. 1,
pp. 195-218, esp. p. 205.
22 See Liebrecht, Gervasius von Tilbury, pp. 180-82; Zur Volkskunde, pp. 253ft.;
W. Robertson Smith, The Religion of the Semites (1957), p. 412 (lamentations
over "the king of the Djinns," and over "Uncud, Son of the grape cluster").
23 It was Felix Liebrecht who first felt reminded of John Barleycorn.
is predominant compared with the agrarian one, and more ancient,
too; the more so as that "wild boar" was Mars.24
This leaves a knotted story to untangle. It is hampered consider-
ably by too many "identifications" taken for granted by the scholars
who with magnificent zeal have extirpated the dimension of time in
the whole mythology. Actually, it is not known yet who Tammuz
is.25 He looks almost like a title, just as "Horus" was a title. There
is doubt of his "identity"—as taken in the current sense—with
Adonis, and with Osiris,26 Attis, Balder,27 and others. The "Naba-
taean Agriculture" leaves no doubt that there were lamentations
over Tammuz and Janbushad/Jamshyd. The Egyptians lamented
on account of Kronos and Maneros28 (Herodotus 2.79). Tammuz,
after all, is not the only star who came to fall in the course of the
Precession. (And was not King Frodhi a repetition of Freyr, Kai
Khusrau a repetition of Jamshyd, as Apis was the repetition of
Ptah [the Egyptian Saturn-Hephaistos], and Mnevis that of Ra?)
This is a long way from Great Pan, and it is not clear yet who
or what was supposed to have passed away in the time of Tiberius,
that is, which "Pan." Creuzer29 claimed right away that he was Sirius
—and any suggestion from Creutzer still carries great weight—the
first star of heaven and the kingpin of archaic astronomy. And
24 See Nonnos 41.208ff. on Aphrodite: "Being a prophet, she knew, that in the
shape of a wild boar, Ares with jagged tusk and spitting deadly poison was
destined to weave fate for Adonis in jealous madness." Cf. for the other sources,
Movers, vol. 1, pp. 222ff.
25 To give tiniest minima only: Tammuz = Saturn (Jeremias in Roscher s.v.
Sterne, col. 1443); Tammuz = Mars (W. G. Baudissin, Adonis und Esmun
[1911 ], p. 117, quoting the Chronicle of Barhebraeus). For the unheard-of number
of names given to "Tammuz" in Mesopotamia, see M. Witzel, Tammuz-Liturgien
(1935). For his name "Dragon of the Sky" (Usungal-an-na)= Sin (the Moon) see
K. Tallqvist, Akkadische Gotterepitheta (1938), p. 482; see also p. 464, where
Tammuz = "Mutterschafbild" ("mothersheep-image").
26 It is worth noticing that the death of Osiris, in his turn, was announced by
"the Pans and Satyrs who lived in the region around Chemmis (—Panopolh), and
so, even to this day, the sudden confusion and consternation of a crowd is called
a panic" (Plutarch: Isis and Osiris, c. 14, 356d).
27 All the gods of the North came together, in best "Nabataean" fashion, to weep
over Balder's death.
28 We leave aside, though, the cases Linos, Maneros, Memnon, Bormos, etc. See
Movers, vol. 1, p. 244.
29 Symbolik und Mythologie der Alien Volker (1842), vol..1, pp, 65ff.
Hamlet's Mill
286
Aristotle says (Rhet. 2. 24, 1401 a 15) that, wishing to circumscribe
a "dog," one was permitted to use "Dog-star" (Sirius) or Pan,
because Pindar states him to be the "shape-shifting dog of the
Great Goddess" (O makar, honte megalas theou kyna pantodapon
kaleousin Olympioi) .30 But this is far enough for now. The amazing
significance of Sirius as leader of the planets, as the eighth planet,31
so to speak, and of Pan, the dance-master (choreutes) as well as
the real kosmokrator, ruling over the "three worlds,"32 would take
a whole volume. The important point is that the extraordinary
role of Sirius is not the product of the fancy of silly pontiffs, but
an astronomical fact. During the whole 3000-year history of Egypt
Sirius rose every fourth year on July 20 of the Julian calendar. In
other words, Sirius was not influenced by the Precession, which
must have led to the conviction that Sirius was more than just one
fixed star among others. And so when Sirius fell, Great Pan was
dead.
Now, Creuzer had no monopoly on deriving from Egypt the
ideas connected with Pan, nor has the derivation been invented in-
dependently here. W. H. Roscher undertook this task in his article
on "The Legend of the Death of the Great Pan,"33 being convinced
30 See also Plato's Cratylus 408B: ton Pana tou Hermou einai hyon diphye echei
to eikos.
31 Creuzer takes Pan-Sirius for Eshmun/Shmun, "the eighth," great god of
Chemmis.
32 Cf. the Orphic Hymn to Pan (no. 11; see also Hymn 34.25): Pana kalo
krateron, nomion, kosmoio to sympan/ ouranon ede thalassan ide chthona pam-
basileian/ kai pyr athanaton . . . Echous phile . . . pantophyes, genetor panton,
polyonyme daimon/ kosmokrator ... As concerns his love for Echo, Macrobius
(Sat. 1.22.7) explains it as harmony of the spheres: quod significat harmoniam
caeli, quae soli arnica est, quasi sphaerarum omnium de quibus nascitur moderatori,
nee tamen potest nostris umqviam sensibus deprehendi. But then, Macrobius was
the first among the "sun-struck" mythologists, harmlessly claiming Saturn and
Jupiter and everybody else, including Pan, to be the Sun. It is not the echo itself
which is the harmony of the spheres but the syrinx—Pan makes it out of the reeds
into which his beloved Echo had changed—and the seven reeds of Pan's pipe are
indeed the seven planets, the shortest representing the Moon, the longest Saturn.
(It is worth consideration that in China the echo was understood as the acoustical
pendant to the shadow, so that under the pillar or tree, in the very center of the
world, the kien-mu, there is no echo and no shadow.)
33 "Die Legende vom Tode des Grossen Pan," in Fleckeisens Jahrbucher fur klas-
sische Philologie (1892), pp. 465-77. Referring to the "Panic" clement in Maim-
hardt's stories about the Fanggen, Roscher declares it "an accidentally similar
motif."
287
The Great Pan Is Dead
that the myth could not be understood by means of Greek ideas and
opinions, the less so, as Herodotus (2.145) informs us of the
following:
In Greece, the youngest of the gods are thought to be Heracles,
Dionysos, and Pan; but in Egypt Pan is very ancient, and once one
of the "eight gods" who existed before the rest;34 Heracles is one of
the "twelve" who appeared later, and Dionysos one of the third order
who were descended from the twelve. I have already mentioned the
length of time which by the Egyptian reckoning elapsed between the
coming of Heracles and the reign of Amasis; Pan is said to be still
more ancient, and even Dionysos, the youngest of the three, appeared,
they say, 15000 years before Amasis. They claim to be quite certain
of these dates, for they have always kept a careful written record of
the passage of time. But from the birth of Dionysos, the son of
Semele, daughter of Cadmus, to the present day is a period about 1600
years only; from Heracles, the son of Alcmene, about 900 years; from
Pan, the son of Penelope—he is supposed by the Greeks to be the son
of Penelope and Hermes—not more than about 800 years, a shorter
time than has elapsed since the Trojan war.35
These details are given, without meddling with them, in order to
draw attention to the modest numbers; whoever takes these elapsed
years for historical ones,36 presupposes a special Egyptian (and
Babylonian, Indian, etc.) frame of mind, a human nature, in fact,
which is fundamentally different from ours, forgetting that we are
all members of the very same species, Homo sapiens.
34 Archaiotatos kai ton okton ton proton legoumenon theon.
35 Cf. A. Wiedemann, Herodots ziveites Buch (1890), pp. 515-18.
36 See J. Marsham, Canon chronicus Aegypticus, Ebraicus, Graecus (1672),
p. 9: "Immensa Aegyptiorum chronologia astronomica est, neque res gestas sed
motus coelestes designat!" See also Ideler (Beobachtungen, 1806), p. 93. Apart from
the sensible 17th century, at the beginning of the 19th century still, the progressive
delusion was remarkably underdeveloped.
289 • The Adventure and the Quest
Chapter XXII
The Adventure and the Quest
he Epic of Gilgamesh in its first recorded version goes back
to Sumerian times.1 It has been rehearsed with variants by Hurrians
and Hittites, by Babylonians and Assyrians. Even in the best recen-
sions there are large gaps, many tablets are damaged beyond repair,
and to aggravate these detrimental conditions one must add the
efforts of a goodly number of specialists which have not helped to
clarify matters.
The story has been told many times over and it appears to be
fairly secure in its main lines, a patrimony of world literature.
Misleading as this appearance is—the way through those texts being
incredibly slippery—it is best to leave it at face value for the
present, giving only a brief outline of the accepted scheme in
Heidel's version. Then it will be possible to examine certain difficult
points which may eventually upset the scheme altogether.
Gilgamesh is claimed to have been one of the earliest kings of
Uruk (or Erech). The circumstances of his fabled birth make him
two-thirds god and one-third man, which makes him—in the sexa-
gesimal system of Mesopotamia—two-thirds of 60 (= Anu) == 40,
the number which characterized Enki-Ea, whence the latter's de-
nomination of "Shanabi (=2/3, i.e., of 60), and Nimin (Sumerian =
40)."2 Be that as it may, it is told that he lives in splendor and dis-
soluteness, and makes a nuisance of himself until the gods bring re-
lief to his people by rearing a human being, either twin or counter-
1 Sec, for example, S. N. Kramer, "The Epic of Gilgamesh and Its Sumerian
Sources," JAOS 64 (1944) p. 11: "the poem was current in substantially the form
in which we know it, as early as the first half of the second millennium b.c."
2 E. Weidner, RLA, vol.2, p. 379.
part,3 who can stand up to him. It is Enkidu, the man of the Wilds,
a kind of wolf-child as simple as the beasts he plays with, a happy
son of nature, hairy all over, grown to enormous strength. A harlot
is sent out to seduce him, and through her he learns love and the
ways of man, and is lured into the city (appendix #24).
His first encounter with Gilgamesh is a fierce battle which rocks
the community house and seems to damage the doorpost (appendix
#25) until the king manages to subdue Enkidu and decides he is
worthy of becoming his friend and playmate.
Together they plan an expedition to the great Forest, to over-
come the terrible ogre Huwawa or Humbaba,4 whom the god Enlil,
the so-called "god of storm" or "god of air," had appointed as its
guardian. Indeed, "Enlil has appointed him as a sevenfold terror
to mortals ... his roaring is (like that of) a flood-storm, his mouth
is fire, his breath is death! "5
Even if it is taken for granted that fights with dragons or ogres
were a popular subject once upon a time, some dry data on this
"monster" would do no harm. He "is invariably called a god in the
texts"6 and appears to correspond to the Elamitic god Humba or
Humban, who shares the title "the prevalent, the strong" with the
planets Mercury and Jupiter and with Procyon (alpha Canis Mi-
noris). He occurs, moreover, in a star list, carrying the determina-
tive mul (Babylonian kakkab) announcing stars, as mulHumba (appen-
dix #26). The identification with Procyon may eventually turn out
to be the decisive clue which will reconcile the Sumerian version
with the many others.
Ancient texts do not become more lucid if every strange-looking
aspect is silently omitted, and so it is well to mention that Humbaba
3 Actually, the goddess Aruru makes him "in the likeness of Anu," literally "a
zikru of Anu she conceived in her heart." But Enkidu is also said to look like
Gilgamesh "to a hair." See A. L. Oppenheim, "Mesopotamian Mythology," Orien-
talia 17 (1948), pp. 24, 28.
4 Huwawa in the Old Babylonian and Hittite versions, Humbaba in the Assyrian
version.
5Tabl. 3.136f., 109-11, Heidel trans., p. 35.
6Langdon, Semitic Mythology (1931), p. 253. See also F. Hommel, Ethnologic
und Geographic des Alten Orients (1926), pp. 35, 42, claiming hum to mean
"creator," and talking of Humbaba (= Hum-is-the-father) as of the "guardian of
the cedar of paradise." - <

Hamlet's Mill • 290
is some kind of a "god of intestines." More than that, his head or
face is built of intestines, and Langdon (MAR 5, 254) draws atten-
tion to the fact that "the face of this monster ... is designed by a
single winding line, except eyes." Bohl, moreover, in his inquiry
on the Babylonian origin of the labyrinth,7 pointed out the Babylo-
nian notion of the entrails as a labyrinthic "fortress of intestines."
This much about the "person" Humbaba, who is, evidently, no
primitive monster at all, the less so, as his unattractive face strik-
ingly resembles the features of Tlaloc, the so-called "rain-god" of
the Aztecs, whose face is built up of two serpents. Precipitate iden-
tifications lead only to mischief,8 and the "Gase Humbaba" is not
even partly solved, despite many efforts.
The only established features of the story seem to be that the
heroes reached the forest of cedars, which is said to extend for "ten
thousand double-hours" (say, 70,000 miles), and that they cut off
the head of Humbaba after having felled, apparently, the largest of
the cedars entrusted to Humbaba's guard by Enlil, but the feat is
not accomplished without the powerful help of Shamash-Helios
"who sends a great storm to blind the monster and put him at their
mercy."
Returned to Uruk, Gilgamesh washes his hair and garbs himself
in festive attire. As he puts on his tiara, Ishtar, the goddess of love
(in Sumerian, Inanna), is entranced with his looks and asks him to
marry her. Gilgamesh rejects her, reminding her in scornful words
of what happened to her previous mates, including the hapless Tam-
muz, later known as Adonis.
It is not unusual for a hero to refuse the love, and the unheard-of
presents, offered by a goddess. In every such case only two celestial
personalities are possible candidates for this role: the planet Venus,
and Sirius, alias Sothis, who has some of the reputation of a harlot.
7F. M. Bohl, "Zum babylonischen Ursprung des Labyrinths," in Festschrift
Deimel (1935), pp. 6-23.
8 Hommel, Ethnologie und Geographie, p. 35, dealing with an Elamitic star
list, makes "Amman-ka-sibar (derived from Chumban-uk-sinarra . . . i.e., Chum-
ban, king of the bolt? . . .) = Ninib-Mars." We would hazard a premature guess
that apart from Procyon, Mercury would be the safest bet, the second candidate
being Jupiter; but the latter "would never make a convincing lord of entrails, nor
would any other outer planet: their orbits do nor allow for such notions—and
Venus is much loo regular for this role.
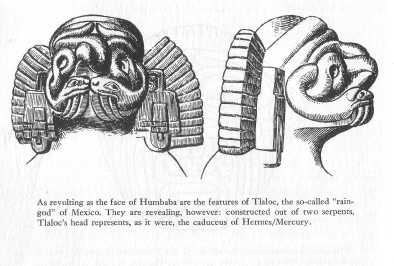



291 • The Adventure and the Quest
There is the story of Ugaritic Aqht, who shows mocking haughti-
ness to Anat;9 of Picus who flatly turns down the offer of Circe and
who is subsequently turned into the woodpecker by the angry god-
dess; there is Arjuna—a "portion of Indra"—who rejected the
heavenly Urvashi, whom he regarded as the "parent of my race,
and object of reverence to me . . . and it behoveth thee to protect
me as a son."10
There is also Tafa'i of Tahiti (Maori: Tawhaki) who went with
his five brothers courting an underworld princess. As a test, the
suitors "were told to pull up by the roots an ava tree which was
possessed by a demon, and which had caused the death of all who
had attempted to disturb it." Three of the brothers were devoured
by the demon; Tafa'i revived them, and then gladly renounced the
hand of the princess.11 (Ava = Kawa, and stands for the "next-best-
substitute" for Amrita, the drink of immortality which is the prop-
erty of the gods; mythologically Polynesian Kawa resembles almost
exactly the Soma of Vedic literature; even the role of the "Kawa-
filter" is an ancient Indian reminiscence; and, as befits the pseudo-
drink-of-immortality, it is stolen, by Maui, or by Kaulu, exactly as
happens in India, and in the Edda, and elsewhere).
Meanwhile Ishtar, scorned, goes up to heaven in a rage, and
extracts from Anu the promise that he will send down the Bull of
Heaven to avenge her.12 The Bull descends, awesome to behold.
9 See C. H. Gordon, Ugaritic Literature (1949), pp. 84-103. This "Legend of
Aqht" is the more relevant, in that the goddess wants nothing but "the Bow"
made by the Deus Faber and in Aqht's possession, and promises everything in-
cluding immortality, if the youth will hand over mulBAN, that being its fateful
name. Cf. above, pp. 2i5f.,t for this bow.
10 Mbh. 5.45-46. Urvashi, the goddess, "trembling with rage" condemned the
hero to pass his time "among females unregarded, and as a dancer, and desti-
tute of manhood and scorned as a eunuch." She raged the more, as she had, in
anticipation, before actually visiting Arjuna, "mentally sported with him on a
wide and excellent bed laid over with celestial sheets." Arjuna had to suffer the
curse of Urvashi in the thirteenth year of the exile of the Pandava, but he re-
gained his power on the expiration of that year.
11 T. Henry, Ancient Tahiti (1928), pp. 561ff.
12 Ugaritic Anat, after having been rebuked by Aqht, goes to her father too,
asking for revenge, and she goes "toward 'Il, at the course of the Two Rivers/
(at the midst of the streams) of the Two Deeps" (Gordon, p. 91). Ginsberg
translation (ANET, p. 152): "Towards El of the Source of the Floods (in the
midst of the headwaters) of the Two Oceans."
Hamlet's Mill
292
With his first snort he downs a hundred warriors. But the two
heroes tackle him. Enkidu takes hold of him by the tail, so that Gil-
gamesh as espada can come in between the horns for the kill. The
artisans of the town admire the size of those horns: "thirty pounds
was their content of lapis lazuli." (Lapis lazuli is the color sacred to
Styx, as we have seen. In Mexico it is turquoise.)
Ishtar appears on the walls of Uruk and curses the two heroes
who have shamed her, but Enkidu tears out the right thigh of the
Bull of Heaven and flings it in her face, amid brutal taunts (ap-
pendix #27). It seems to be part of established procedure in those
circles. Susanowo did the same to the sun-goddess Amaterasu, and
so did Odin the Wild Hunter to the man who stymied him.
A scene of popular triumph and rejoicings follows. But the gods
have decided that Enkidu must die, and he is warned by a somber
dream after he falls sick.13
The composition of the epic has been hitherto uncouth and repe-
titious and, although it remains repetitious, it becomes poetry here.
The despair and terror of Gilgamesh at watching the death of his
friend is a more searing scene than Prince Gautama's "discovery"
of mortality.14
"Hearken unto me, O elders, [and give ear] unto me!
It is for Enk[idu], my friend, that I weep,
Crying bitterly like unto a wailing woman
[My friend],my [younger broth]er (.?),15 who chased
the wild ass of the open country [and] the panther of the steppe.
Who seized and [killed] the bull of heaven;
13 Gen. xlix.5-7 is frequently brought into the play here—the "twins" Simeon
and Levi mutilating the bull—but we leave aside this whole chapter xlix bristling
with allusions to lost knowledge.
14 The quotation marks that enclose the word "discovery" are a measure of pre-
caution, advisable in our times ruled by Euhemerism; the most edifying among the
relevant model cases we found in Diakanoff's review article on Bohl's translation of
GE (see below): "F. M. Th. de Liagre Boehl shares the opinion of A. Schott that
the problem of human mortality was originally raised in the reign of Shulgi"
(= Third Ur Period, between 2400 and 2350 B.C., according to T. Jacobsen: The
Sumerian King List [1939], Table II). This "originally" is enough to show what
happens to Orientalists once evolutionist platitudes have taken hold of them.
15 Sec appendix #28.
293 • The Adventure and the Quest
Who overthrew Humbaba, that [dwelt] in the [cedar] forest—!
Now what sleep is this that has taken hold of [thee]?
Thou hast become dark and canst not hear [me]"
But he does not lift [his eyes].
He touched his heart, but it did not beat.
Then he veiled [his] friend like a bride [ . . . ]
He lifted his voice like a lion
Like a lioness robbed of [her] whelps . . .
uWhen I die, shall I not be like unto Enkidu?
Sorrow has entered my heart
I am afraid of death and roam over the desert. . .
[Him the fate of mankind has overtaken]
Six days and seven nights I wept over him
Until the worm fell on his face.
How can I be silent? How can I be quiet?
My friend, whom I loved, has turned to clay."16
Gilgamesh has no metaphysical temperament like the Lord
Buddha. He sets out on his great voyage to find Utnapishtim the
Distant, who dwells at "the mouth of the rivers" and who can pos-
sibly tell him how to attain immortality. He arrives at the pass of
the mountain of Mashu ("Twins"), "whose peaks reach as high as
the banks of heaven—whose breast reaches down to the under-
world—the scorpion people keep watch at its gate—those whose
radiance is terrifying and whose look is death—whose frightful
splendor17 overwhelms mountains—who at the rising and setting of
the sun keep watch over the sun."18
16Tabl. 8, col. 2; Tabl. 9, col. 1, 3-5 (Heidel, pp. 62-64); Tabl. 10, col. 2, 5-7,
11-12 (Heidel, p. 73).
17 The word which Heidel translates as "frightful splendor" and Speiser
(ANET) as "halo" is melammu, the Babylonian equivalent of Iranian hvarna, the
so-called "glory" for the sake of which the bad uncle Afrasiyab dived in vain,
because it belonged to Kai Khusrau.
18 That the Mashu mountain (s) does so "every day," as translated by Heidel,
Speiser, and others, is obviously wrong. Even if we stipulate, for the sake of peace,
the idea of a terrestrial mountain, the sun is not in the habit of rising on the
same spot every day, and it needs no profound astronomical knowledge to become
aware of this fact.
Hamlet's Mill
296
of him in the physical landscape of the Near East, ignoring the
work of equally learned scholars, experts in the heavens, whose
well-prepared and organized tool kits have long been available to
help in the search. One wonders whether the Orientalists, intent on
reconstructing texts, have ever even heard of Boll and Gundel and
men like them. Perhaps not, because they pass them by without a
word. In any case, it is appropriate here to mention once again two
valuable tool kits assembled by Franz Boll,25 who presents the whole
tradition on the constellations "Hades," "Acherusian lake," "ferry-
man," with many more details than are needed now, as they have
survived in astrological tradition. These topoi are found together
around the southern crossroads of Galaxy and ecliptic, between
Scorpius and Sagittarius. Boll points out that, instead of the Scor-
pion people,26 Virgil (Aeneid 6.286) and Dante posted centaurs
at the entrance of the underworld, representing Sagittarius. And so
back to the quest; Gilgamesh faces Urshanabi, expecting to be fer-
ried over the waters of death. The boatman demurs: the "stone
images" have been broken by Gilgamesh (appendix #31). But at
length he instructs the pilgrim to cut down 120 poles, each sixty
cubits (thirty yards) in length. With these he must punt the boat
along, so that his hands may not touch the waters of death. At last
they reach the far shore; there is Utnapishtim the Distant. The hero
is puzzled: "I look upon thee, thine appearance is not different, thou
art like unto me. My heart had pictured thee as one perfect for the
doing of battle; [but] thou liest (idly) on (thy) side, (or) on thy
back; [Tell me], how didst thou enter into the company of the
gods and obtain life (everlasting) ?"27
25 Sphaera, pp. 19f., 28, 48, 173, 246-51; Aus der Offenbarung Johannis (1914),
pp. 71ff., 143. See also W. Gundel, Neue Texte de Hermes Trismegistos (1936),
esp. pp. 235ff. (on p. 207 he votes for Centaurus as guardian of the netherworld
instead of Sagittarius).
26 The coronation mantle of Emperor Heinrich II shows woven in the statement:
Scorpio dum oritur, mortalitas ginnitur (=gignitur). E. Maass, Commentariorum
in Aratum Reliquiae (1898), p. 602; R. Eisler, Weltenmcmtel und Himmehzelt
(1910), p. 13; Boll, Aus der Offenbarung, p. 72. We might also point to Ovid's
description of the fall of Phaethon, according to which the son of Helios lost
his nerve, and let go the reins when Scorpius drew near, and to the death of
Osiris on Athyr 17, the month when the Sun went through Scorpius (Plutarch,
De Is, Os., c. 13, 356c).
27Tabl. 11, 3-7 (Heidel, p, 80).
297 • The Adventure and the Quest
Utnapishtim is spry enough to tell in great detail the story of the
Deluge. He tells how Enki-Ea has warned him of Enlil's decision to
wipe out mankind, and instructed him to build the Ark, without
telling others of the impending danger. "Thus shalt thou say to
them: [I will ... go] down to the apsu and dwell with Ea, my
[lor]d." He describes with great care the building and caulking
of the ship, six decks, one iku (acre) the floor space, as much for
each side, so that it was a perfect cube, exactly as Ea had ordered
him to do. This measure "i-iku" is the name of the Pegasus-square,
and the name of the temple of Marduk in Babylon, as is known
from the New Year's Ritual at Babylon, where it is said: "Iku-star,
Esagil, image of heaven and earth."28 Shamash had let Utnapishtim
know when to enter the ship and close the door. Then the cataracts
of heaven open, "Irragal [= Nergal] pulls out the masts [appendix
#32]; Ninurta comes along (and) causes the dikes to give way;
The Anunnaki29 raised (their) torches, lighting up the land with
their brightness; The raging of Adad reached unto heaven (and)
turned into darkness all that was light.30 . . . (Even) the gods were
terror-stricken at the deluge. They fled (and) ascended to the
heaven of Anu; The gods cowered like dogs (and) crouched in
28 Trans. A. Sachs, ANET, p. 332, 11. 275ff. Concerning the Rectangle of Pega-
sus, see B. L. van der Waerden, "The Thirty-Six Stars," JNES 8 (1949), pp. 13-15;
C. Bezold, A. Kopff, and F. Boll, "Zenit- und Aequatorialgestirne am babylonischen
Fixsternhimmel (1913), p. 11.
29 These divine beings of the "underworld" (their equivalent "above": the
Igigi) were also written A-nun-na-nunki (Deimel, PB, pp. 57f.), i.e., they belong to
NUNki = Eridu (Canopus), the seat of Enki-Ea. The Sumerian name Anunna
is interpreted as "(Gods who are) the seed of the 'Prince,' " according to A. Falken-
stein ("Die Anunna in der sumerischen Uberlieferung," in Festschrift Landsberger
[1965], pp. 128ff.). See also D. O. Edzard, "Die Mythologie der Sumerer und Ak-
kader," in Worterbuch der Mythologie, vol. 1, p. 42: "Die 'furstlichen' Samens
[sind]," the "Prince" (NUN) being Enki-Ea of Eridu. Concerning NUN =
"Prince," defined by T. Jacobsen as "one of authority based on respect only,
settling disputes without recourse to force," Falkenstein, politely, mentions: "Ganz
abweichend K. Oberhuber: Der numinose Begriff ME im Sumerischen, S.6f." The
title of this opus (Innsbruck 1963, Innsbruckcr Beitrage zur Kulturwissenschaft.
Sonderheft 17) expresses sufficiently the hair-raising propositions that it contains,
concerning ME, NUN, and other termini.
30 Speiser, ANET, p. 94, n. 207, remarks: "The term suharrartu . . . does not
mean 'rage,' but 'stark stillness, bewilderment, consternation,'" and he translates
11.105 06: "Consternation over Adad reaches to the heavens, Who turned to
blackness all thai had been Light."
Hamlet's Mill
298
distress (?).31 Ishtar cried out like a woman in travail; the lovely-
voiced lady of the g[ods] lamented . . . 'How could I command
(such) evil in the assembly of the gods! How could I command war
to destroy my people, For it is I who bring forth (these) my
people ...' The Anunnaki-gods wept with her; The gods sat bowed
(and) weeping."
The end of the story is almost exactly that of Noah's landing on
the mountain, except that Noah sends out a raven and twice the
dove, whereas Utnapishtim let fly dove, swallow, raven.32
When Enlil was still wroth because one family did escape,
Enki-Ea, "who alone understands every matter" (11.176), took
him to task: "How, o how couldst thou without reflection bring
on (this) deluge?" He added severely that Enlil could have pun-
ished only the sinful, and spared the innocent. The remark is one
that pious exegetes of the Bible are still left to ponder. Then Enlil
went up to the Ark and apologized. He granted Utnapishtim and
his wife "to be like unto us gods. In the distance, at the mouth of
the rivers, Utnapishtim shall dwell" (11.194-95).
"But now as for thee," the old man concludes his tale (11. 197ff.),
turning to Gilgamesh, "who will assemble the gods unto thee, that
thou mayest find the life which thou seekest? Come, do not sleep
for six days and seven nights."
We gather a gentle hint there from the Ancient of Days (Su-
merian: Ziusudra, with Berossos: Xisuthros), also called Atrahasis,
"the exceedingly wise." It amounts to this: "Young man, you have
come to the land where time has come to a stop, and the immor-
tality granted to us consists in remaining conscious and partaking
of truth while not being wholly awake. Now you try." But Gilga-
mesh cannot. "As he sits (there) on his hams, sleep like a rainstorm
blows upon him" (11.200ff.).
31 Speiser: "The gods cowered like dogs, crouched against the outer wall" (11.
115).
32 One is usually inclined to take such motifs as that of the sending out of birds
—not to mention the particular species—for minor matters, but A. B. Rooth can
teach us a remarkable lesson by means of her thorough inquiry: The Raven and
the Carcass: An Investigation of a Motif in the Deluge Myth in Europe, Asia, and
North America (1962).
299 •■ The Adventure and the Quest
One can imagine how Atrahasis-Utnapishtim would explain some
essentials during Gilgamesh's sleep. The Exceedingly Wise would
point to "his like," to Kronos sleeping in his golden cave in Ogygia,
as described by Plutarch,33 and yet continuously giving "all the
measures of the whole creation" to his beloved son Zeus, as de-
scribed by Proclus.34 The Exceedingly Wise would refer freely to
characters faraway in time35 and in geographical space, as only he is
entitled to do—to Kiho-tumu, for instance, creator god of the
Tuamotu islands, Kiho-tumu "the-All-Source" who sleeps, face
downward, in "Great-Havaiki-the-Unattainable," and yet takes
action when the "administration" oversteps the "laws" and measures
given by him. In the most amiable words Utnapishtim would ad-
monish the children of our century to perceive the divine mummies
of Ptah and Osiris—Osiris the "strategos" of the Ship Argo—and
to start to think about the mummies of gods, generally, about the
idea of the Seven Sleepers of Ephesus on board the Argo, about the
data given in the Liber Hermetis Trismegisti concerning the rele-
vant degrees (in Taurus, dealing with latitudes south of the Ship)
belonging to Saturn, meaning "continua vero delectatio, diminutio
substantiae, remissio malorum." Atrahasis would tell of the Chinese
"Ancient Immortal of the Celestial South Pole," of the numerous
sleeping Emperors in Mountain Caves (appendix #33)—and the
hours would pass like seconds, but one knows that Utnapishtim,
half-dreaming, half-teaching, had all the time an eye on the sleeping
"hero." He says to his wife: "Is this the strong man who wants life
33 De facie in or be lunae 941 a.
34 See frg. no. 55, Orphicorum Fragmenta, ed. O. Kern (1963).
35 The oldest and most exact traits have a perplexing talent of surviving, and of
turning up at unexpected places. Says R. S. Loomis (Arthurian Literature in the
Middle Ages [1959] pp. 70-71): "We have a unique version of Arthur's survival
alluded to by Godfrey of Viterbo, secretary to Frederick Barbarossa, about
1190. Merlin prophesies that though the king will perish from his wounds, he will
not perish wholly but will be preserved in the depths of the sea and will reign for
ever as before." How could the secretary to Frederick Barbarossa—an emperor
who was himself bound to that place where expired ages and their rulers sleep—
get hold of the "right" version? (We should be glad to learn, moreover, where
the archaeologist Pierre Plantard [quoted by Gerard de Sede: Les Templiers sont
parmi nous (1962), p. 280] got hold of the information on "Canopus, 1'oeui] su-
blime do L'architecte, qui s'ouvre tous les 70 ans pour contempler L'Univers.")

Hamlet's Mill • 300
everlasting?" And then, he wakens the man, on the seventh day, and
the startled Gilgamesh reacts thus: "Hardly did sleep spread over
me, when quickly thou didst touch and rouse me."
Les jeux sont faits. Gilgamesh is given a change of raiment and
told to go home; Urshanabi, the boatman, is told to escort him, and
there is, evidently, no return again for him to pi narati, to the mouth
of the rivers. But at the last minute, Utnapishtim's wife says to her
husband: "Gilgamesh has come hither, he has become weary, he has
exerted himself, What wilt thou give (him wherewith) he may re-
turn to his land?" Utnapishtim takes compassion and addresses the
hero:
"Gilgamesh, I will reveal (unto thee) a hidden thing . . . There is a
plant like a thorn . . . Like a rose (?) its thorn(s) will pr[ick thy
hands]. If thy hands will obtain that plant, [thou wilt find new life]"
11. 264-70).
"New life" sounds misleading, and Speiser remarks: "Note that the
process is one of rejuvenation, not immortality."36
To get hold of this plant, growing apparently in a tunnel leading
to the Apsu which the hero has to open, Gilgamesh dives deep,
weighting himself with stones. But then as he travels home with the
boatman, he stops to take a bath in a well, a serpent (literally, earth-
lion) comes up from the water, snatches the plant and, returning
into the water, sloughs its skin. The last hope is gone—at least so
it looks in the translations.
Since this is not a manual on the Epic of Gilgamesh, this whole
affair of the plant, the diving, the fateful bath in the well, must
stand as it is, even though every word in it is no better than a man-
trap (appendix #34), to come to the point which is of particular
relevance here.
Leaving the boat on the shore, Gilgamesh and the boatman walked
for another 50 double-hours on the way home.
When they arrived in Uruk, the enclosure, Gilgamesh said to him, to
Urshanabi, the boatman: "Urshanabi, climb upon the wall of Uruk
(and walk about); inspect the foundation terrace and examine the
brickwork, (to see) if its brickwork is not of burnt bricks, And (if)
the seven wise men did not lay its foundation!" (11.301-305).
3G Speiser, p. 96, n. 227.

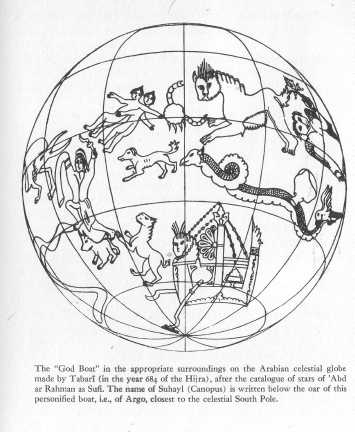
301 • The Adventure and the Quest
But before the Epic started (Tabl. 1, 19), it was said that "the
Seven Wise Ones" had laid the foundation of ramparted Uruk. So
the ring has been closed.
But what does it mean? Why is Urshanabi, of all people, asked
to survey Uruk, enclosed—according to the rule—-by seven walls?
And what have the Seven Sages to do with the foundation of Gilga-
mesh's city?
To take the latter question first: the Seven Sages are the stars
of the Big Dipper, the Indian Saptarshi, the Seven Rishis.37 The
solstitial colure, called the "Line of the Seven Rishis," happened to
run through one after the other of these stars during several mil-
lennia (starting with eta, around 4000 B.C.): and to establish this
colure is "internationally" termed "to suspend the sky"—the Baby-
lonians called the Big Dipper "bond of heaven," "mother bond of
heaven," the Greeks spelled it "Omphaloessa."
Next, why is it the business of the boatman from the "confluence
of the rivers" (that is what pi narati is) to check the measures of
Uruk? It is established that the boatman's name was "servant (or
priest) of 40 or of 2/3,"38 and that makes him a "piece," or what-
ever one prefers to designate it, of Enki-Ea, called Shanabi = 2/3
(of 60 = 40). Enki's residence is Eridu, at the confluence of the
rivers, at mulNUNki = Canopus (alpha Carinae), the seat of the me,
the norms and measures. From there these me have to be procured.
Urshanabi, however, seems to be bound with close family ties to
Enki-Ea, in fact to be his son-in-law, husband of Nanshe.39
Numerous texts and inscriptions show that Enki-Ea, Lord of
the Apsu, was responsible for the ground plan of "temples,"
whether celestial or terrestrial ones. The one who actually drew up
the plans, with the "holy stylus" of Eridu, was Nanshe, Enki's
37 And exactly as the Indian texts have a lot to say about the Seven Rishis with
their sister (and wife) Arundati, so the Mesopotamian ones talk about the "Sebettu
with their sister Narundi" (see H. Zimmern, "Die sieben Weisen Babylonians,"
ZA 51 [1923], p. 153; Edzard, vol. 1, p. 55; H. and J. Lewy, "The Origin of the
Week," HUCA 17 [1942-43], p. 44). Arundati = Alcor, the tiny star near zeta
Ursae Majoris.
38 Sec also Langdon, p. 213.
39T. Jacobsen, "Parerga Sumerologica," JNES 2 (1943), pp. 117f. See also
Edzard, p. 109.
Hamlet's Mill
302
daughter. And to her, the wife of Urshanabi the boatman, the "holy
stern of the ship was consecrated."40
Considering that Argo is a stern only, that Eridu-Canopus marks
the steering oar of Argo, it is fair to conclude that Gilgamesh,
bringing with him Urshanabi in person, had procured "the me from
Eridu." This is how it is styled in the Sumerian "dialect";41 in the
international mythical language the terminus technicus reads "to
measure the depth of the sea." (Odysseus, more advanced and ac-
cordingly considerably more modest than Gilgamesh, did not even
take over a veritable oar from Teiresias. He only procured the lat-
ter's advice, according to which he was, later, to take an oar and
carry it inland until he found people who had never heard of or
seen a ship) (appendix #35).
Now that Gilgamesh "surveys" the world is stated explicitly in
a text. (That this truth is uttered involuntarily by the translator
who meant to express "that he saw everything" makes it the more
enjoyable.) The invocation, quoted by Lambert, says:
Gilgamesh, supreme king, judge of the Anunnaki,
Deliberative prince, the ... of the peoples,
Who surveys the regions of the world, bailiff of the underworld,
lord of the (peoples) beneath,
You are a judge and have vision like a god.
You stand in the underworld and give the final verdict.
Your judgement is not altered, nor is your utterance neglected.
You question, you inquire, you give judgement, you watch and you
put things right.
Shamash has entrusted to you verdicts and decisions.
In your presence kings, regents and princes bow down.
You watch the omens about them and give the decision.42
40 Gudea Cylinder A XIV, in A. Falkenstein and W. von Soden, Sumerische und
Akkadische Hymnen (1953), p. 152; see also F. Hommel, Die Schwur-Gottin Esch-
Ghanna und ihr Kreis (1912), p. 57.
41 See, for example, S. Kramer's Sumerian Mythology (1944), pp. 64-88; and
his Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta (1952), p. 11. We feel strongly inclined to
accuse the much discussed "God Boat" (Dieu Bateau) of many seal cylinders of
"bringing the me from Eridu," particularly when the seals show a ground plan,
or a stage tower in the making. See P. Amiet, La Glyptique Mesopotamienne
Archaique (1961), pp. 177-86, plates 106-109; H. Frankfort, Cylinder Seals (1939),
pp. 67-70, plates xiv, xv, xix.
42 In Gilgamesh et sa legende (1960), p. 40. Cf. E. Ebeling, Tod und Leben nach
den Vorstellungen der Babylonier (1931), p. 127: "der die Weltraume uberschaut."
303 • The Adventure and the Quest
That neither this nor other clear hints make the slightest impression
upon "once-and-for-all Euhemerists goes without saying. Any un-
prejudiced student would at least ponder for some minutes about
that opened water-tunnel or the well in which the "hero" was tak-
ing a bath, once he comes to learn about a text, also mentioned by
Lambert (p. 43), dealing with the digging of wells, where "an in-
struction is given for the utterance of the words the 'well of Gil-
gamesh' .. ., as the well is being dug. Since, when water is reached,
it must be libated to Shamash, the Anunnaki, and any known spirit,
the well is thought of as a connexion with the underworld" (appen-
dix #36).
It seems obvious that sooner or later the data on Gilgamesh
—incompatible as they sound for the time being—have to be assem-
bled on a common denominator. But this is not likely to be accom-
plished unless the specialists renounce several of their firm precon-
ceptions and make up their minds to a thorough re-examination
of the whole case.
For the time being it is worth paying attention to information
such as that given by Strabo (16.1.5) on the tomb of Bel (ho tou
Belou taphos) in Etemenanki, the Tower of Babylon, and to mind
the baffling Mesopotamian texts dealing with gods cutting off each
other's necks and tearing out each other's eyes. It well might be
rewarding to look at the tombs of Anu and of Marduk,43 to consider
the fundamental role of the Abaton in Philae, tomb of Osiris,44 and
of divine sepulchers generally. The basic difficulty which has to be
43 Ebeling, pp. 25f., 39; see also G. Meier, "Ein Kommentar zu einer Selbstpradi-
kation des Marduk aus Assur," ZA 47 (1942), pp. 241-48. H. Zimmern, "Zum baby-
lonischen Neufahrsfest," BVSGW 58 (1906), pp. 127-36. S. A. Pallis, The Baby-
lonian Akitu Festival (1926), pp. 105-108, 200-43.
44 Apart from the Shabaka Inscription, the end of which is of the utmost rele-
vance, the highest Egyptian oath was taken by "Osiris who lies in Philae," as we
know from Diodorus; the Greek gods took their most solemn oaths by the waters
of Styx. We remember Virgil's information on Styx who sees the celestial South
Pole, and of the followers of Zeus who, before attacking Kronos, took their oath
by Ara. "Oath-stars" are to be found, rather regularly, among the southern circum-
polar constellations. As concerns swearing by Gilgamesh, sec Ebeling, p. 127. Com-
pare also Pallis (Akitu Festival, p. 238) who compares the "Mysteries of Osiris" in
Abydos with the Babylonian New Year Festival built around the "dead" Marduk
(who sirs during the ceremonies "in the midst of Tiamat").
Hamlet's Mill
304
overcome is our ignorance of the concrete meaning of the technical
term "tomb," whether one has to do with the Omphalos of Delphi,
grave of Python,45 with the "burial mound of dancing Myrina"
(Iliad 2.814), with the burial mound of Lugh Lamhfada's foster
mother, around which the Games of Taillte were performed, or
with many others.
What is haunting is the suspicion that "Uruk" stands for a "new"
realm of the dead, and that Gilgamesh is the one who was destined
to "open the way" to this abode and to become its king, and the
judge of the dead, like Osiris, and also Yama, of whom the Rigveda
states (10. 14.1-2): (1) "Him, who followed the course of the great
rivers, and who discovered the way for many, the Son of Vivasvat,
the gatherer of peoples—King Yama we honor with sacrifice.
(2) Yama is the one who first discovered the way; this trodden path
is not to be taken away from us; on that way that our forefathers
travelled when they left us, on that way the later born follow each
his trail."46
That neither Yama's nor Gilgamesh's "way" was, originally,
meant to last forever and ever, goes without saying. Again and
again the me must be brought from Eridu, the Depth of the Sea
must be measured respectively, and again and again the sky has to
be "suspended" by means of the "Line of the Seven Rishis"—the
huge precessional clock does not stop. What has been stopped, in-
stead, is the understanding among the heirs of the mythical language
who, out of ignorance, failed to adapt this idiom to "preceded" situ-
ations. Without thinking, they changed a movie into a set of stills,
projected a complex motion into conventional posters, and de-
45 Omphalos belongs among the words which are easily said and hard to
"imagine." Yet, during the Middle Ages, Jerusalem, with the Holy Sepulcher, was
understood as the Omphalos of the earth and, moreover, the tomb of Adam lo-
calized under the Cross in Golgatha, "in the middle of the earth." (See, for ex-
ample, Vita Adae et Evae, in F. Kampers, Mittelalterliche Sagen vom Paradiese
und vom Holze des Kreuzes Christi (1897), pp. 23, 106f.; W. H. Roscher, Omphalos
(1913), pp.24-28.
46 Cf. Atharva Veda 18.1.50 (Whitney trans.): "Yama first found for us a track,
that is not a pasture to be borne away; where our former Fathers went forth, there
(go) those born (of them), along their own roads."
305 • The Adventure and the Quest
stroyed, by this measure, all the sense of a carefully considered
system.47
This might be dismissed as a minor tragedy, but it is just one of
those "progressive measures" which violently interrupt the con-
tinuity of tradition. There must have been several such eruptive and
reckless "corrections of style"—otherwise it would be utterly in-
comprehensible that all our most ancient texts consist of "Scholia"
interpreting one or the other "antediluvian" "Book with seven
seals." In the case of that neglected tragedy just mentioned,48 a
tragedy coming from absentmindedness, the final blow was dealt
to the tradition that had established "us," mankind, as a unity. And
if we did not have Plato's Timaeus, it would be a hopeless task
altogether to understand the reason which made it obligatory in
those "archaic" times to watch the immense cosmic clock most
carefully. Plato himself, to be sure, started on the way of all intel-
lect—moving from thought to literature, from literature into phi-
lology, before flowing into nothing; but let us make it clear, this
official "trend" is not going to detract us from our own uncondi-
tional respect.
This essay could spend many chapters on the Timaeus, that
"topos" from which come and to which return all "rivers" of cos-
mological thought, and several more chapters on Phaedrus and
47 In our most unheeding times, nobody will even notice when in the not too
remote future Leo will be drowned in the sea when he arrives at the autumnal
equinox: the constellation of Leo, undisputed "king" of the hot plains, was
coined at a time when His Majesty of the Zodiac ruled the summer solstice, highest
and hottest "point" of the sun's orbit; and who will care for pitiable Aquarius
having no more water to shed from his jars, once he has arrived at the vernal
equinox—but, after all, who has considered poor Pisces, lying "high and dry"
since the times of Christ, the opener of the Age of Pisces? His title "Fish," i.e.,
Greek Ichthys, is officially explained as being the first letters of "Iesous Chreistos
Theou Yios Soter"—Jesus Christ God's Son Savior.
48 Without going into details, we think it possible that it was this very change
from "constellations" to "signs" and, more generally, the enthronement of that
astronomical language which alone is recognized as "scientific" by contemporary
historians, i.e., the terminology of "positional astronomy," which interrupted Ho-
meric tradition; the Greeks quoted Homer all day long, they interpreted him, they
broke their heads about the significance of details: his terminology had died long
ago.
Hamlet's Mill
306
Politikos, on the Epinomis (entartarosed by the label "Pseudo-"),
but we make it short. We leave aside the very "creation" which
Timaeus styles like the manufacturing of a planetarium—which is
exactly what makes this creation difficult for non-mathematicians.
But it can be done without here. What counts is this: When the
Timaean Demiurge had constructed the "frame," skambha, ruled
by equator and ecliptic—called by Plato "the Same" and "the Dif-
ferent"—which represent an X (spell it Khi, write it X) and when
he had regulated the orbits of the planets according to harmonic
proportions, he made "souls." In manufacturing them, he used the
same ingredients that he used when he had made the Soul of the
Universe, the ingredients however, being "not so pure as before."
The Demiurge made "souls in equal number with the stars (psychas
isarithmous tots astrois), and distributed them, each soul to its sev-
eral star."
There mounting them as it were in chariots, he showed them the
nature of the universe and declared to them the laws of Destiny
(nomous tous heimarmenous). There would be appointed a first in-
carnation one and the same for all, that none might suffer disadvan-
tage at his hands; and they were to be sown into the instruments of
time; each one into that which was meet for it, and to be born as the
most god-fearing of living creatures; and human nature being two-
fold, the better sort was that which should thereafter be called
"man."
And he who should live well for his due span of time should journey
back to the habitation of his consort star and there live a happy and
congenial life; but failing of this, he should shift at his second birth
into a woman; and if in this condition he still did not cease from
wickedness, then according to the character of his depravation, he
should constantly be changed into some beast of a nature resembling
the formation of that character, and should have no rest from the
travail of these changes, until letting the revolution of the Same and
Uniform within himself draw into its train all that turmoil of fire
and water and air and earth that had later grown about it, he should
control its irrational turbulence by discourse of reason and return
once more to the form of his first and best condition.
When he had delivered to them all these ordinances, to the end that
he might be guiltless of the future wickedness of any of them, he
sowed them, some in the Earth, some in the Moon, some in the other
instruments of time (Timaeus 41E-42D).
307 • The Adventure and the Quest
There is no need to engage in the futile task of arguing the
fairness of the Demiurge and his statement that all souls had the
same chances in their first incarnation. That God must needs be
innocent, and that man is guilty, anyway, is not a subject worth
arguing with Plato. In fact, this is the hypothesis upon which the
whole great edifice of Christian religion, and of our jurisdiction,
rests.
In any event, the faultless Demiurge sowed the souls, equal in
number to the fixed stars, in the "instruments of time" (i.e., the
planets), among which Timaeus counts the earth; he sowed, actu-
ally, "each one into that which was meet for it."
What does that mean? Timaeus alludes here to an old system of
connecting the fixed and the wandering members of the starry
community—and not only the zodiacal "houses" and "exaltations"
of the planets are meant, but fixed stars in general. One knows this
approach from astrological cuneiform tablets which contain a con-
siderable number of statements on fixed representatives of a planet,
and vice versa. But there is not enough to explain the rules of this
sophisticated scheme. To say it with Ernst Weidner: "In any case
we have to do with a very complicated system. Only a renewed
collection and revision of the whole material will perhaps allow us
to solve the still existing riddles."49 Ptolemy records the planetary
character of fixed stars in his Tetrabiblos (1.9 "Of the Power of the
Fixed Stars"), and so did all ancient and medieval astrologers. And,
one might add, so did Indian and Mexican astrologers. (See above,
p. 157, about the privilege enjoyed by Mars and the Pleiades of
representing each other in Babylonia and India.)
The souls were, then, taken away from their fixed stars and
moved to the corresponding planetary representatives, all according
to rules and regulations. The Demiurge retired—turning into the
character known under the title "Deus otiosus"—and the Time
Machine was switched on.
Cornford, in his translation and commentary on the Timaeus,
states (p. 146): "In the machinery of the myth it is natural to sup-
49RLA 3, pp. Kif. Cf. Bezold in Boll's Antike Beobachtung farbiger Sterne
(1916), pp. 102-25 (table, p. 138); A. Jeranias, HAOG (1929), pp. 200ff.
Hamlet's Mill • 308
pose that the first generation of souls is sown on Earth, the rest
await their turn, unembodied, in the planets."
With all the respect due to Cornford, this is hardly going to
work, and no "natural" suppositions can be admitted. The Demi-
urge of the Timaeus is too much of a systematist to allow for this
solution. On the contrary, it stands to reason—if one carefully
observes the manner in which the Craftsman God gradually and
systematically attenuates his original mixture of Existence, Same-
ness and Difference as described in Timaeus 35—that some new
principle, some new "dimension," has to be introduced right
here.
Eternity abides in unity highest and farthest "outside." Within,
Time, its everlasting likeness, moves according to number, doing so
by means of the daily turning of the fixed sphere in the sense of
"the Same," the celestial equator, and by means of the instruments
of time, the planets, moving in the opposite direction along "the
Different," i.e., the ecliptic. Taken together, they represent the
"eight motions." With the next step, from the planets to the living
creatures, the motion according to number is ruled out. The funda-
mentally different quality of "motion" by generation must replace
it (much to Plato's regret).
The planets, albeit "different" from the eternity abiding in unity
as well as from the regular motion of the sphere of constellations,
remain at least "themselves" and seven in number. The soul of man
is not only reincarnated again and again, but it is subdivided further
and further, since mankind multiplies, as does the grain to which
man is so frequently compared. This simile—misinterpreted time
and again by the fertility addicts—ought to be taken very seriously,
and literally. The Demiurge did not create the individual souls of
every man to be born in all future, he created the first ancestors of
peoples, dynasties, etc., the "seed of mankind" that multiplies and
is ground to mealy dust in the Mill of Time. The idea of "Fixed
Star Souls" from which mortal life started, and to which exception-
ally virtuous "souls once released" may return anytime, whereas
the average "flour" from the mill has to wait patiently for the "last
day" when it hopes to do the same—this idea is not only a vital part
of the archaic system of the world, it explains to a certain degree
309 • The Adventure and the Quest
the almost obsessive interest in the celestial goings-on that ruled
former millennia.
Although still, in our time, most children are admonished to be-
have decently, otherwise they may not have a chance to enter
heaven, the Christians have abolished the Timaean scheme. They
condemned as heresy the opinion of Origen according to which
after the Last Judgment, the revived souls would have an ethereal
and spherical body (aitherion te kai sphairoeides). This fundamen-
tal concept has been given voice in many tongues throughout the
"Belt of High Civilization." Sometimes the imagery is unmistakable,
sometimes it is ambiguous enough to mislead modern interpreters
completely, as when the starry "seed" of population groups comes
our way under the title of a "totem." But among the unmistakable
kind is a rabbinical tradition which says that in Adam were con-
tained the 600,000 souls of Israel like so many threads twisted
together in the wick of a candle; the more so, as it is also said: "The
Son of David [the Messiah] will not come before all souls that have
been on the body of the first man, will come to an end."50 Unmis-
takable, also, is the myth of the Skidi Pawnee of the Great Plains
dealing with "the last day": "The command for the ending of all
things will be given by the North Star, and the South Star will
carry out the commands. Our people were made by the stars. When
the time comes for all things to end our people will turn into small
stars and will fly to the South Star where they belong."51
As mentioned in the chapter on India (p. 77), the Mahabharata
reports how the Pandavas toiled up the snowy mountain and were
lost, and how Yudhishthira was finally removed bodily to heaven.
Although they were planetary "heroes," the wording of how they
came to their end is revealing with respect to mere human beings.
The said heroes are called "portions" of the gods, and when the
third world comes to its end and the Kali Yuga begins—it could
not begin "as long as the sole of Krishna's holy foot touched the
earth"—these "portions" are reunited with the gods of whom they
are a part. Krishna returns into Vishnu, Yudhishthira into Dharma,
50 J. A. K.Eisennmenger, Entdecktes Judenthum(1711), vol. 2, p. 16 (Emek ham-
elech).
51 H.B. Alexander, North American Mythology (1910), p. 117.
Hamlet's Mill
310
Arjuna is absorbed by Indra, Bala Rama by the Shesha-Serpent, and
so forth.
These examples will do. What they demonstrate is this: the
Timaeus and, in fact, most Platonic myths, act like a floodlight
that throws bright beams upon the whole of "high mythology."
Plato did not invent his myths, he used them in the right con-
text—now and then mockingly—without divulging their precise
meaning: whoever was entitled to the knowledge of the proper
terminology would understand them. He did not care much for
the "flour" after all.
Living in our days, where nothing is hidden from the press and
where every difficult science is "made easy," we are not in the best
condition to imagine the strict secrecy that surrounded archaic
science. The condition is so bad, indeed, that the very fact is often
regarded as a silly legend. It is not. The need for treating science
as reserved knowledge is gravely stated by Copernicus himself in
his immortal work, the Revolutions of Celestial Orbs. An adherent
of the Pythagorean conception since his student days in Italy, he
acknowledges the inspiration he owes to the great names of the
School, like Philolaos and Hicetas, that he had learned from the
classics, and who, he says, had given him the courage to oppose
the philosophical notions current in his own time. "I care nothing,"
he writes in his dedication to the Pope, "for those, even Church
doctors, who repeat current prejudices. Mathematics is meant for
mathematicians ..." It is the authority of these ancient masters
which gave him the independence of judgment to discover the cen-
tral position of the sun in the center of the planetary system. A shy
and retiring scholar, he appeals to that great tradition, which even
in the time of Galileo was called "the Pythagorean persuasion," to
advance what was commonly considered a revolutionary and sub-
versive theory. But if he did not bring himself to publish until his
last years, it was not from fear of persecution, but from an ingrown
aversion toward having the subject bandied around among the pub-
lic. In the first book, he quotes from a "correspondence" among
ancient adepts which is probably an ancient pastiche, but shows
their way of thinking: "It would be well to remember the Master's
3ii • The Adventure and the Quest
precepts, and to communicate the gifts of philosophy to those who
have never even dreamt of a purification of the soul. As to those
who try to impart these doctrines in the wrong order and without
preparation, they are like people who would pour pure water into
a muddy cistern; they can only stir up the mud and lose the water."
Creating the language of the philosophy of the future, Plato still
spoke the ancient tongue, representing, as it were, a living "Rosetta
stone." And accordingly—strange as it may sound to the specialists
on Classical Antiquity—long experience has demonstrated this
methodological rule of thumb: every scheme which occurs in
myths from Iceland via China to pre-Columbian America, to which
we have Platonic allusions, is "tottering with age," and can be ac-
cepted for genuine currency. It comes from that "Protopythago-
rean" mint somewhere in the Fertile Crescent that, once, coined the
technical language and delivered it to the Pythagoreans (among
many other customers, as goes without saying). Strange, admit-
tedly, but it works. It has worked before the time when we decided
to choose Plato as Supreme Judge of Appeals in doubtful cases of
comparative mythology, for example, when H. Baumann52 recog-
nized the myth of Plato's Symposium (told, there, by Aristophanes)
as the skeleton key to the doors of the thousand and one myths
dealing with bisexual gods, bisexual souls, etc.
Plato knew—and there is reason to assume that Eudoxus did, too
-that the language of myth is, in principle, as ruthlessly generaliz-
ing as up-to-date "tech talk." The manner in which Plato uses it,
the phenomena which he prefers to express in the mythical idiom,
reveal his thorough understanding. There is no other technique,
apparently, than myth, which succeeds in telling structure (again,
remember Kipling, and how he tackled the problem by telling of
the "ship that found herself"—see above, p. 49). The "trick" is:
you begin by describing the reverse of what is known as reality,
claiming that "once upon a time" things were thus and so, and
worked out in a very strange manner, but then it happened that . . .
What counts is nothing but the outcome, the result of the happen-
52 Das Doppelte Geschlecht. Ethnolonische Studicu zur Bisexualitaet in Mythos
und Ritus (1955).
Hamlet's Mill
312
ings told. Generally, it is overlooked that this manner of styling is
a technical device only, and the mythographers of old are accused
of having "believed" that in former times everything stood on its
head (see above, p. 292, n. 14, about the deplorable Mesopotamians
who were unaware of their own mortality before the Gilgamesh
Epic was written).
Since it is an actual language, the idiom of myth brings with it
the emergence of poetry. Every classical philologist has to admit,
for instance, that Hyginus and his like report the mythical plots
rather faithfully in 3-10 lines of "correct" idiom which sounds
hardly more interesting than average abstracts, whereas this instru-
mental language, when used by Aeschylus, remains soul-shaking
even to this day. But, however vast the difference of poetical rank
among the mythographers, the terminology as such had been coined
long before poets, whose names are familiar to us, entered the stage.
To say "terminology," however, sounds too dry and inadequate,
for out of this mint have come clear-cut types—surviving for ex-
ample, in the games of our children, in our chess figures and our
playing cards—together with the adventures destined to them. And
this spoken imagery has survived the rise and fall of empires and
was tuned to new cultures and to new surroundings.
The main merit of this language has turned out to be its built-in
ambiguity. Myth can be used as a vehicle for handing down solid
knowledge independently from the degree of insight of the people
who do the actual telling of stories, fables, etc. In ancient times,
moreover, it allowed the members of the archaic "brain trust" to
"talk shop" unaffected by the presence of laymen: the danger of
giving something away was practically nil.
And now, coming back for a while to "The Adventure and the
Quest," one should emphasize that it is, of course, satisfactory to
have cuneiform tablets and that it is reassuring that the experts
know how to read different languages of the Ancient Near East;
but Gilgamesh and his search for immortality was not unknown in
times before the deciphering of cuneiform writing. This is the result
of that particular merit of mythical terminology that it is handed
313 • The Adventure and the Quest
down independently from the knowledge of the storyteller. (The
obvious drawback of this technique is that the ambiguity persists;
our contemporary experts are as quietly excluded from the dia-
logue as were the laymen of old.) Thus, even if one supposes that
Plato was among the last who really understood the technical lan-
guage, "the stories" remained alive, often enough in the true old
wording. Accordingly, one can watch how the hero of the "Ro-
maunt of Alexander," in his own right an undisputed historical per-
sonality, slipped on Gilgamesh's equipment, while at the same time
slipping off whole chapters of sober history.
Alexander had to measure the depth of the sea, he was carried by
eagles up into the sky, and he traveled to the most unbelievable
"seas" in search of the water of immortality. Expecting it to be in
Paradise he sailed up the Nile, or the Ganges—but why repeat the
chapter on Eridanus? A true replica of Gilgamesh, Alexander sailed
to the magic place whence all waters come and to which they return.
And if it was, allegedly, a serpent ("earth-lion") who deprived
Gilgamesh of the rejuvenating plant, the Alexander of the fable
was defrauded unwittingly by a fish—just a salted one taken along
as travel supply. But he was consciously betrayed by the cook
Andreas (according to Pseudo-Kallisthenes), who had noticed the
fish coming to life when it fell into the brook and who drank of the
water himself without telling Alexander of this discovery. The
king, in his righteous indignation, had him thrown into the sea with
a millstone around his neck, thus effectually preventing the cook
from enjoying his immortality.
The range of significant variations of the many Alexander stories
precludes anything more than superficial remarks about them, but
they are relevant to Gilgamesh who has, perforce, been abandoned
in a darkness which is in large part artificial. It is possible to outline
some questions that may stir the problem of Gilgamesh out of its
stagnation. There is also one detail that points in the direction of
a proposition already put forward concerning Gilgamesh (p. 304).
Alexander, says the fable, interrogates the Oracle of Sarapis in
Egypt just as Gilgamesh interviewed Utriapishrini. Sarapis answers
Hamlet's Mill • 314
evasively as concerns the span of life allotted to Alexander, but he
points to the foundation of Alexandria and announces that the king
will last on in this city "dead and not dead," Alexandria being his
sepulcher. In another version Sarapis states: "But after your death,
you will be placed among the gods, and receive divine worship and
offerings by many, when you have died and, yet, not died. For your
tomb will be the very town which you are founding."53
The grotesque monster Huwawa appears to be the pointer.
Whatever approach is chosen, Huwawa's connection with Procyon,
Jupiter and/or Mercury54 should be taken into consideration, the
more so, as the Hurrian fragments seem to know the poem under
the title of "Epic of Huwawa."55 And along with this consideration,
the proper attention will have to be paid to the Babylonian name
of Cancer, namely Nangar(u), "the Carpenter." This is essential,
because in the twelfth tablet of the Gilgamesh Epic, preserved only
in Sumerian language, Gilgamesh complains bitterly of having lost
his "pukku and mikku," instead of having left them "in the house
53 Franz Kampers, Alexander der Grosse (1901), p. 93f.
The derivation of the name Sarapis from Enki-Ea's name sar apsi, as proposed
by C. F. Lehmann-Haupt (see also A. Jeremias in Roscher s.v. Oannes, 5.590)
makes sense; the more so as it does not exclude the connection of Sarapis with
Apis, since Apis has the title "the repetition of Ptah." Accidentally, a rather re-
vealing shred of evidence fell into our hands, contained in Budge's translation of
the Ethiopic Alexander Romance (London 1896, p. 9): "When Nectanebus, king
of Egypt and father of Alexander, had escaped to Macedonia, "the men of Egypt
asked their god to tell them what had befallen their king." That is what the
Ethiopian text says, and Budge adds: "In Meusel's text the god who is being asked
is called 'Hephaestus the head of the race of the gods,' and in Mueller's he is said
to dwell in the Serapeum."
The common denominator of Ea-sar apsi, Ptah-Hephaistos, "he who is south
of his wall," "lord of the triakontaeteris," is and remains the planet Saturn. Admit-
tedly, we knew this before, but we wish to stress the point that those despised
"late" traditions of the Romance represent useful "preservation tins"; i.e., if the
Romance replaces Utnapishtim of the confluence of the rivers with Sarapis we
can trust that there was a valid equation written down somewhere and known to
the several redactors—all of them closely related to some "Wagner" and hostile
toward any potential "Faust."
54 It is remarkable that the Tuamotuan "Hiro is said to be Procyon" (M. W.
Makemson, The Morning Star Rises [1941], p. 270). Hiro (Maori: Whiro), the
master-thief, is an unmistakable Mercurian character.
55 H. Otten, in Gilgamesh et sa legende (1958), p. 140.
315 • The Adventure and the Quest
of the carpenter,"56 where they would have been safe, apparently.57
Whoever reads the Epic in many translations is not likely to
overlook the indications of a "fence," or/and a "doorpost," or
frame of a door at such an improbable place as Huwawa's great
cedar "forest." Why not also try to look out for the "enclosing of
Gog and Magog" accomplished by Alexander and told still in the
18th Sura of the Koran, the same Sura which deals with the coming
to life of Moses' travel-supply-fish at the "confluence of the rivers?"
This "enclosure" is a great theme of medieval folklore, kept fear-
somely alive by the sudden appearance of Mongol invasions. The
story ran that Alexander had built iron gates over the mountain
passes, that the monstrous brood of the Huns, spawning over the
limitless plains of the East, had been kept in awe by trumpets sound-
ing from the pass betokening a seemingly immortal conqueror, the
"two-horned" hero who watched over the passes. But the trumpets
had suddenly fallen silent, and a dwarf from the horde risked his
way to the pass, and found the gate deserted. The trumpets were
nothing but aeolian harps, stilled by a tribe of owls which had
nested in them.58
The ancient story of Gog and Magog, revived from the Arabs,
plays such a decisive role in the Romance of Alexander that we
might rely upon the antiquity of the scheme: actually it ought to oc-
cur in our Epic. Considering that Gilgamesh appears to open a new
passage, the former one has to be closed. This also was done in the
case of Odysseus. Once he arrived in Ithaca with the stipulations for
a new treaty with Poseidon, the poor Phaeacians were done for.
56 A careful investigator has to be aware of the numerous traps along his way as,
for example, the naughty custom of exchanging Scorpius and Cancer (Cicero for
instance calls both constellations nepa) which seems to be on account of the simi-
larity between the scorpion and the landcrab (Geocarcinus ruricula).
57 "Pukku and mikku" (see below, p. 441) are lost "at the crying of a little girl"
(C. J. Gadd, "Epic of Gilgamesh," RA 50, p. 132): this sounds slightly improbable.
It is laughter, jf anything, that wrecks the old, and introduces the new age of the
world. Maui lost his immortality because his companions laughed when he passed
the "house of death" of the Great-Night-Hina.
58 Cf. the thorough investigation by A. R. Anderson, Alexander's Gate, Gog and
Magog, and the Inclosed Nations (1932). An early version of the story comes from
a much-traveled Franciscan, Ricoldo da Montecroce.
Hamlet's Mill
316
There was to be no Scheria anymore. This station being closed up,
growing mountains were to block off the beautiful island of Nau-
sikaa which was, henceforth, "off limits" for travelers. There are
some striking parallels available in Central Polynesia: when the
younger Maui stole the fire from "old Maui" (Mauike, Mahuike,
etc.) in the underworld, the passage which he had used was shut
from that day on. This is particularly remarkable because "it was
by the way of Tiki's hole that Maui descended into the home of
Mauike in search of fire." Tiki (Ti'i) was the "first man," and
"Tiki's hole had been the route by which souls were supposed to
pass down to (H) Avaiki." Thus, the souls had to find another way
"after this hole had been closed,"59 that is, after young Maui had
accomplished the theft of fire.
The notion of fire, in various forms, has been one of the recur-
ring themes of this essay. Gilgamesh, like Prometheus, is intimately
associated with it. The principle of fire, and the means of producing
or acquiring it are best approached through them.
59W. Gill, Myths and Songs from the South Pacific (1876), p. 57; cf. R. W.
Williamson, Religious and Cosmic Beliefs of Central Polynesia (1924), vol. 2, p.
252 (Austral Islands, Samoa).
Chapter XXIII
Gilgamesh and Prometheus
"... quand les esprits bienheureux
Dans la Voie de Laict auront fait
nouveaux feux . . ."
Agrippa d'Aubigne
Fire is, indeed, a key word, deserving a special inquiry. For the
time being, however, it is not essential to understand everything
about the different norms and measures, rules and regulations which
have to be procured by gods or heroes who are destined to open
"new ways." One can ignore here the true nature and identity of
the various "treasures," whether they are called "oar" or "ferry
man," or "hvarna-melammu," or "golden fleece," or "fire." This is
not to say that all these terms are different names for the same
thing, but that they identify several parts of the frame.1
It will be useful to recapitulate the ideas of the frame, as it has
been traced through the Greek precedents. It started out, inno-
cently enough, with the frame of a ship (see above, pp. 230f.), as the
Greeks did, and finally ended up with the bewildering "world tree"
called the skambha, which even Plato might have found intractable.
In the end, it is nothing more than the structure of world colures,
even if it rustles with many centuries of Hindu verbiage.
1 Even a superficial study of the Chinese novel Feng Shen Yen I (i.e., Popular
Account of the Promotion to Divinity) which, under the disguise of "historiogra-
phy" dealing with the end of the Shang Dynasty and the beginning of the Chou,
presents us with a fantastic description of a major crisis between world-ages, will
reveal to the attentive reader the amount of "new deities"—responsible for old
cosmic functions—who have to be appointed at a new Zero, beginning with 365
gods, 28 new lunar mansions, etc.
Hamlet's Mill
318
Another point to bear in mind is the cosmological relevance of
"way-openers" and "path-finders" like Gilgamesh. They are the
ones who bring the manifold measures from that mysterious center,
called Canopus or Eridu, or "the seat of Rita." One can illustrate
the general scheme by means of two adventures.
The Argonauts, with the Golden Fleece on board, had to pass
the Symplegades, the clashing rocks. Once a ship with its crew
came through unharmed2—so the "blessed ones" (makaroi) had
decided long ago—the Symplegades would stay fixed, and be clash-
ing rocks no longer.3 After that "accepting the novel laws of the
fixed earth," they should "offer an easy passage to all ships, once
they had learnt defeat."4 This is only one station on the long "open-
ing travel" of the Argonauts transporting the Golden Fleece (of a
ram), undertaken in all probability to introduce the Age of Aries,5
but it demonstrates best the relevant point, namely, "the novel
laws."
Another instance—in fact, a crucial one—of an Opening of the
Way comes to us from the Catlo'Itq in British Columbia.6 We
would call it a pocket encyclopedia of myth:
A man had a daughter who possessed a wonderful bow and arrow,
with which she was able to bring down everything she wanted. But
she was lazy and was constantly sleeping. At this her father was angry
and said: "Do not be always sleeping, but take thy bow and shoot at
the navel of the ocean, so that we may get fire."
2 The Symplegades cut off, however, the ornament of the ship's stern (aphla-
stoio akra korymba), where the "soul" of the ship was understood to dwell. We
do not know yet the precise meaning of this trait. Cf. H. Diels, "Das Aphlaston
der antiken Schiffe," in Zeitschrift des Vereins fur Volkskunde (1915), pp. 61-80.
It should be emphasized that, contrary to a widespread opinion, the planktai and
the symplegades are not identical.
3Apollonios Rhodios, Argonautica 2.592-606; Pindar, Pyth. 4.210: "but that
voyage of the demigods made them stand still in death."
4 Claudianus 26.8-11.
5 See the First Vatican Mythographer (c. 24, ed. Bode, vol. 1, p. 9) stating
about "Pelias vel Peleus" that he sent Jason to Colchis, "ut inde detulisset pellem
auream, in qua Jupiter in caelum ascendit," i.e., to fetch the Golden Fleece, in
which Jupiter climbs the sky. See also A. B. Cook, "The European Sky-God,"
Folk-Lore 15 (1904), pp. 271f., for comparable material.
6F. Boas, Indianische Sagen von der Nord-Pacifischen Kuste Amerikas (1895),
pp. 80f. Cf. Frazer, Myths from the Origin of Fire (1930), pp. 164f.; also L. Fro-
benius, The Childhood of Man (1960), pp. 395f.
319 • Gilgamesh and Prometheus
The navel of the ocean was a vast whirlpool in which sticks for mak-
ing fire by friction were drifting about. At that time men were still
without fire. Now the maiden seized her bow, shot into the navel of
the ocean, and the material for fire-rubbing sprang ashore.
Then the old man was glad. He kindled a large fire; and as he wanted
to keep it to himself, he built a house with a door which snapped up
and down like jaws and killed everybody that wanted to get in. But
the people knew that he was in possession of the fire, and the stag
determined to steal it for them. He took resinous wood, split it and
stuck the splinters in his hair. Then he lashed two boats together,
covered them with planks, danced and sang on them, and so he came
to the old man's house. He sang: "O, I go and will fetch the fire."
The old man's daughter heard him singing, and said to her father:
"O, let the stranger come into the house; he sings and dances so
beautifully."
The stag landed and drew near the door, singing and dancing, and at
the same time sprang to the door and made as if he wanted to enter
the house. Then the door snapped to, without however touching him.
But while it was again opening, he sprang quickly into the house.
Here he seated himself at the fire, as if he wanted to dry himself, and
continued singing. At the same time he let his head bend forward
over the fire, so that he became quite sooty, and at last the splinters
in his hair took fire. Then he sprang out, ran off and brought the fire
to the people.
Such is the story of Prometheus in Catlo'Itq. It is more than that.
For the stag has stood for a long time for Kronos. In the Hindu
tradition he is Yamawho has been met before as Yama Agastya,
and who, "following the course of the great rivers, discovered the
way for many." This stag is spread far and wide in the archaic
world, with the same connotations. And he is the archaic Prome-
theus-Kronos, "you who consume all and increase it again by the
unlimited order of the Aion, wily-minded, you of crooked counsel,
venerable Prometheus." In Greek, semne Prometheu. It leaves no
doubts. The Orphic invocation to Kronos, quoted in the very be-
ginning on p. 12, defines him as "venerable" and couples him with
the name of Kronos the Titan, and we did not go on to quote
the awful name of Prometheus so as not to confuse the issue. To
avoid confusing matters gratuitously, the name Prometheus has
so far been used sparingly. It summons up a formidable implex. The
Hamlet's Mill • 320
scholiast of Sophocles who gave the reference, quoting Polemon
and Lysimachides who are now lost sources, explains: "Prometheus
was the first and the older who held in his right hand the scepter,
but Hephaistos later and second."7
These are the underground regions of Greek mythology, still
barely noticed by the school of Frazer and Harrison in their search
for prehistoric cults and symbols in the classical world. Yet here
ancient Greek myth suddenly emerges in full light among Indian
tribes in America, miraculously preserved. The very unnaturalness
of the narrative shows how steps were telescoped or omitted
through the ages. In one moment the Whirlpool emerges as the
bearer of the fire-sticks of Pramantha and Tezcatlipoca. But why
should they be in the whirl? Myth has its own shorthand logic to
relate those floating fire-sticks to the cosmic whirl. And that logic
goes on tying together the basic themes, the bow and the arrow of
celestial kingship, the bow and arrow aimed at (or ending in)
Sirius, Stella marts (compare appendix #2 on Orendel).
The singing and dancing of the stag is intricately involved with a
proto-Pythagorean theme. And the theme appears full-fledged in
still another tale from the Northwest. The Son of Woodpecker,
before shooting his bow, intoned a song, and as soon as he had
found the right note, the flying arrows stuck in each other's necks
until they built the bridge of arrows to heaven; Sir James Frazer
himself identified this theme with that of the scaling of Olympus in
the Gigantomachy. But there is more. Although it is not stated
explicitly that the "clashing doors" (the precessing equinoxes) of
the old owner of fire ceased to clash, surely the stag opened a new
passage by passing the door at the predestined right moment in his
quest for the "fire."
There was little room for invention and variation in this solemn
play with the great themes, although imagination did retain some
freedom. Thus one might feel tempted to see pure imagination in
the feckless laziness of the Old Man's Daughter. And yet, was it
imagination, if one discovers in her the prototype of Ishtar, of
whom it was said (see above, p. 215) that she "stirs up the apsu
before Ea"? Lady-archers being a rare species, it is worth considera-
7 Schol. Soph. O. C. 56 (Mayer, Giganten und Titanen, p. 95).
321 • Gilgamesh and Prometheus
tion that the great Babylonian astronomical text, the so-called
"Series mulAPIN" (= Series Plough-Star, the Plough-Star being
Triangulum), states: "the Bow-star is the Ishtar of Elam, daughter
of Enlil." There has been mention of the constellation of the Bow,
built by stars of Argo and Canis Major, Sirius serving as "Arrow-
Star" (see above, p. 216 and figure on p. 290). It is no less signifi-
cant that the Egyptian divine archeress, Satit, aims her arrow at
Sirius, as can be seen on the round Zodiac of Dendera.
When one discovers a brief tale that miraculously encapsulates
great myths in a few words, one is led to the suspicion that such
tales are fragments of long and intricate recitals meant to hold their
audience for hours; that, actually they represent something like
"Apollodorus" or "Hyginus" who passed on the essential informa-
tion in brief abstracts. But behind them stood a fully shaped and
powerful literary tradition along with the Greek poets to give the
ideas flesh and blood, whereas with an illiterate neolithic people
such as the Catlo'ltq only the bare skeleton, even "Hygini Fabulae,"
appears to have survived, unless we assume the informants withheld
from the ethnologists the richer versions. (A colleague once told
us about a Tibetan minstrel who, bidden to recite the saga of Bogda
Gesser Khan, asked whether he should do the large version or the
small one: the large would have taken weeks to recite properly.)
It was stated earlier and should be re-stated here that "fire" was
thought of as a great circle reaching from one celestial pole to the
other, and also that the fire sticks belong to the skambha (Atharva
Veda 10.8.20), as an essential part of the frame. Among the things
which helped us to recognize "fire" as the equinoctial colure, only
one fact needs mention here, that the Aztecs took Castor and Pollux
(alpha beta Geminorum) for the first fire sticks, from which man-
kind learned how to drill fire. This is known from Sahagun.8 Con-
sidering that the equinoctial colure of the Golden Age ran through
Gemini (and Sagittarius), the fire sticks in Gemini offer a correct
8Florentine Codex (trans. Anderson and Dibble), vol. 7, p. 60. Sec also R.
Simeon, Dictionnaire de la Langue Nahuatl (1885) s.v. "mamalhuaztli: Les Ge-
nicaux, constellation," who does nor mention, though, that Sahagun identified
mamalhuaztli with "astijellos," fire sticks. Also, the Tasmanians felt indebted to
Castor and Pollux for the first fire (see J. G. Frazer, Myths of the Origin of
Fire [1930], pp. 3f.).
Hamlet's Mill
322
rhyme to a verse in a Mongolian nuptial prayer which says: "Fire
was born, when Heaven and Earth separated";9 in other words,
before the falling apart of ecliptic and equator, there was no "fire,"
the first being kindled in the Golden Age of the Twins.
There is no certainty yet whether or not there are fixed rules,
according to which one fire has to be fetched from the North, and
the other from the South; both methods are employed. The Finns,
for example, insist on the fire's "cradle on the navel of the sky,"
whence it rushes through seven or nine skies into the sea, to the
bottom if it, in fact.10 And Tezcatlipoca is claimed to be sitting at
the celestial North Pole also, when drilling fire in the year 2-Reed,
after the flood. Whereas it is said of the so-called fire-god of
Mesopotamia:
Gibil, the exalted hero whom Ea adorned with terrible brilliance
[ = melammu], who grew up in the pure apsu, who in Eridu, the place
of (determining) fates, is unfailingly prepared, whose pure light
reaches heaven—his bright tongue flashes like lightning; Gibil's light
flares up like the day.11
Gibil is also called, briefly, "hero, child of the Apsu." If the "fire,"
adorned with "terrible brilliance"—melammu/hvarna—is prepared
in Eridu, one should be permitted to conclude that it has to be pro-
cured from there, just as the Rigvedic Agni-Matarishvan, one
among the Agnis, "fires," had to be sought at the "confluence of
the rivers" (appendix #38).
But whether the "fire" comes from "above" or from "below,"
the divine or semidivine (or two-thirds divine as Gilgamesh) beings
who bring it from either topos could all be named after their com-
mon function, as is done in Mexico, where Quetzalcouatl is also
called "Ce acatl" = 1-Reed,12 and Tezcatlipoca "Omacatl (Ome
9 U. Holmberg, Die religiosen Vorstellungen der altaischen Volker (1938), p. 99.
10 K. Krohn, Magische Ursprungsrunen der Finnen (1924), p. 115.
11 W. F. Albright, "The Mouth of the Rivers," AJSL 35 (1919), p. 165; see also
K. Tallqvist, Akkadische Gotterepitheta (1939), p. 313.
12 Acatl/Reed represents, indeed, the arrow-stick, the drill stick of the fire drill
and the "symbol of juridical power." See E. Seler, Gesammelte Abhandlungen
(1960-61), vol. 2, pp. 996, 1102; vol. 4, p. 224.
323 • Gilgamesh and Prometheus
acatl) = 2-Reed. In the same way we might call the corresponding
heroes of the Old World "1-Narthex," "2-Narthex," and so forth,
after the "reed," in which the stolen fire was brought by the most
famous Titan, Prometheus, a "portion" of Saturn.
Without taking part in the heated discussion on the interpretation
of the very name Gilgamesh—dGIS.GIN.MEZ/MAS, and other
forms—one can mention that GIS means "wood, tree," and MEZ/
MAS a particular kind of wood,13 and that there are reasons for
understanding our hero as a true Prometheus.
Here it is worth turning briefly to a text recently translated anew
and edited by P. Gossmann, the tablets of the Era-Epos. This is a
grim poem, whose appalling fierceness emerges in almost every
word, dedicated as it is to the god of Death, Era (also spelled Irra),
a part of Nergal. The subject matter is wholly mythological, han-
dling the end of a world in terms which would hardly disgrace the
Edda, and dealing again with the Flood to end all floods in the
gloomy spirit of Genesis. But here something shines out unmistak-
ably that the commentators on Genesis have missed. They have
missed it so completely that even in our day some well-intentioned
Fundamentalists applied for permission to search for the remains of
the Ark on Mount Ararat. They were impatiently denied access
by the Soviet authorities, who suspected espionage with a CIA
cover name. No one, they figured, could be that simpleminded. The
simplemindedness obviously extends to the researchers of the Su-
merological Institutes, who went looking for Eridu in the Persian
Gulf, and for the dwelling of the divine barmaid Siduri on the
shores of the Mediterranean. But it is evident that the events of the
Flood in the Era Epic, however vivid their language, apply unmis-
takably to events in the austral heavens and to nothing else.
It becomes evident that all the adventures of Gilgamesh, even
if ever so earthily described, have no conceivable counterpart on
earth. They are astronomically conceived from A to Z—even as the
13 See R. Labat, Manuel d'Epigraphie Akkadienne (4th ed., 1963), nos. 296, 314;
also F. Delitzch, Assyrischisches Handworterbuch(1896), p. 420 s.v. miskannu;
Tallqvist, s.v. Gilgamesh. Albright calls Gilgamesh "torch fecundating hero"
(JAOS 40,p. 318).
Hamlet's Mill • 324
fury of Era does not apply to some meteorological "Lord Storm"
but to events which are imagined to take place among constella-
tions. The authors of Sumer and Babylon describe their hair-raising
catastrophes of the Flood without a thought of earthly events.
Their imagination and calculations as well as their thought belong
wholly among the stars. Their capacity for transposition seems to
have been utterly lost to us earthlings, of the earth earthy, who
think only of "primitive" images and primitive experiences, which
could account for the narrative so intensely and humanly projected.
Perhaps they are mutants from our type. In any case they seem be-
yond the comprehension of mature contemporary intellects, who
have adjusted comfortably to the mental standards of Desmond
Morris' Naked Ape of their own devising.
These phantoms being now laid to rest, one finds oneself dealing
with utterly unknown ancestors, whose biblical rages and passions
have to be read in an entirely new context. To be sure, the planets
are still neighbors: Mars, who is Era and Nergal, is only a few
light-minutes away, Marduk-Jupiter about eight minutes, Saturn an
hour. But they are all equally lost in cosmic space, their optical
evidence, like that of ghosts, equally unseizable, equally potent or
impotent in terms of present physical standards, equally and dread-
fully present according to those other standards.
Era is sternly reprimanded by Jupiter/Marduk for having sent
his weapons forth to destroy what remained after the Flood (Ea
once spoke in the same vein to Enlil after the earlier Flood) but
Marduk saved seven wise ones (ummani) by causing them to de-
scend to the Apsu or Abyss, and to the precious mes-trees by chang-
ing their places. "Because of this work, O hero, which thou didst
command to be done, where is the mes-tree, flesh of the gods,
adornment of kings?" "The mesu-tree," says Marduk, "had its
roots in the wide sea, in the depth of Arallu, and its top attained
to high heaven." He asks Era where are the lapis lazuli, the gods
of the arts, and the seven wise ones of the Apsu. He might well
ask where is Gilgamesh himself, that deceptively human hero, now
transformed into a beacon of light from a mes-tree of other-worldly
dimensions. Such is the fate of heroes, as they have been followed
325 • Gilgamesh and Prometheus
from Amlodhi onwards, whether they come as a spark hiding in a
narthex like Prometheus, or fire from the wood splinters in Stag's
hairs, or become a beam from Canopus-Eridu. Lost in the depths of
the Southern Ocean, they were capable of giving the Depths of the
Sea to our forefathers, and now are able to have the directional
systems of our missiles lock on them for interplanetary flight—they
remain points, circles, geometries of light to guide mankind past
and future on its way.
And so under the present circumstances it is necessary to leave
Era's somber prophecy unfulfilled, relating as it does to a coming
world age:
Open the way, I will take the road,
The days are ended, the fixed time has past.
But with it comes the clearest statement ever uttered by men or
gods concerning the Precession. Says Marduk:
When 1 stood up from my seat and let the flood break in,
then the judgement of Earth and Heaven went out of joint. . .
The gods, which trembled, the stars of heaven—
their position changed, and I did not bring them back.
Epilogue
The Lost Treasure
by Giorgio de Santillana
... while each art and science has
often been developed as far as
possible, and then again perished,
these opinions, with others, have
been preserved until the present
like relics (leipsana) of the an-
cient treasure.
Aristotle, Metaphysics
Bk. Lambda 1074b
A
I
AS we* were moving toward the conclusion of this essay, some
chance or accident or kind intention brought to our eyes, after
many years, the work of an author who was our guide when we
tried for a first understanding of the early consciousness of man. It
was Cassirer's opus on mythical thought. And with all the respect
one owes the great historian of Renaissance philosophy, we were
astounded. We went through the persuasive and limpid prose,
tracing the gradual growth of the concept from wild and uncouth
beginnings to the height of Kantian awareness. We gazed again at
the stately cortege of great scholars and researchers, Humboldt,
Max Muller, Usener and Wissowa, Frazer and Cumont and so many
others, the imposing phalanx in which philology, ethnology, his-
tory of religion, archaeology, and not least philosophy, display their
* Throughout the text the pronoun we has been used as little as possible because
it is so difficult to know what it means from one usage to the next. For the next
several pages, we necessarily will appear often and will refer solely to us, the
authors.
327
The Lost Treasure
well-knit progress in good order, to be finally sifted and cleared
up by the modern historian of culture. And then, as we reflected
further that here was the material that was going to provide ad-
vanced survey courses in the immense universities of the future, to
build the gleaming machinery of electronic-printed and audiovisual
General Humanities for the Masses, we were suddenly overcome
with the haunting memory of that unwearied, dedicated, and ridicu-
lous pair, Bouvard and Pecuchet. The merciless irony of Flaubert
was surely not called for in the case of Cassirer, but the same genius
who created Madame Bovary was suddenly showing us again the
shape of certain things to come. A noble enterprise was due to fail,
worse, was slated already for the coming Dictionnaire des Idees
Regues. What Flaubert's pathetic little self-taught characters had
in common with the sovereign cultural historian was clear: it was
intellectual pride, judging from the height of Progress, which tele-
scopes the countless centuries of the archaic past into artless primi-
tive prattle, to be understood by analogy with the surviving "primi-
tives" around us. Too much of that primitiveness lies in the eye of
the beholder. It took the uncanny penetration of trained observers
like Griaule to uncover suddenly the universe of thought which
remained hidden to generations of modern Africanists.
The great merit of Ernst Cassirer lies in his tracing the existence
of "symbolic forms" from the past in the midst of historic culture.
Who but he should have been able to discern the lineaments of
archaic myth? Yet he remained blinded by condescension. Evolu-
tion, a brilliant biological idea of our own past, construed into a
universal banality, held him in thrall. He could not follow up his
insight because of the fatal confusion which has established itself
between biological time, the time of evolution, and the time of man-
kind. The time of man, in which he has lived the life of the mind,
goes back into the tens of millennia, but it is not the same as biologi-
cal time. Again and again, in our text, we have adverted to this con-
fusion which has hardened to become worse confounded. If Cas-
sirer's idea of mythical thought is already dated, as arc his sources,
one must expect the survey courses of the future to go farther in
Hamlet's Mill
328
329
The Lost Treasure
the same direction with sociological psychology and anthropologi-
cal sociology, until all traces of the past have been wiped out. The
masses will then have a culture of commonplaces reared on the com-
mon ideas of the last two centuries of history. Even the gifts of a
Cassirer, who could discern the links between language and thought
in modern science, left him defenseless when he accepted the most
jejune reports of missionaries, and the most naive intuitions of the
obvious from the specialists of his own time. This makes his work
"passe." Those are the wages of the sin of intellectual pride. In the
very process of establishing an identity between non-discursive
symbolism and "primitiveness," he cut himself off from the Kantian
synthesis.
Where are the snows of yesteryear? In the very beginning of
Myth and Language, a curious equivocation, quite unintentional,
moves in with the words of Plato from the Phaedrus, a pleasant rail-
lery at the intellectual exercises of the oversubtle with myth and
"mythologemes." Clearly Professor Cassirer intends to take the
reader into camp, and remind him with the authority of the Master
that sober thought is in order, even concerning this "rustic science."
Does he expect one to forget about the Timaeus? For in this, among
his last Dialogues, Plato deals gravely and solemnly with first and
last things, with the universe and the fate of the soul. And yet the
Timaeus is, openly, explicitly, one great myth and nothing else. Is
it then "unserious," as Plato perversely would like to have certain
scholars believe? They have walked into the trap. For Plato not
only has put into his piece all the science he can obtain, he has
entrusted to it reserved knowledge of grave import, received from
his archaic ancestors, and he soberly adjures the reader not to be
too serious about it, nor even cultural in the modern sense, but to
understand it, if he can. The scholar is already in a hopeless tangle,
and Lord help him.
A simple way out would be to admit that myth is neither irre-
sponsible fantasy, nor the object of weighty psychology, or any
such thing. It is "wholly other," and requires to be looked at with
open eyes. This is what we have tried to do.
II
Wandelt sich schnell auch die Welt
Wie Wolkengestalten,
Alles Vollendete fallt
Heim zum Uralten.*
R. M. Rilke, Sonette an Orpheus
In order to find bearings, one can go back for a moment to the
thought of two fundamental moderns: Tolstoy, the last great epic
writer, and Simone Weil, the last great saint of Christendom, even
if a Gnostic one. Tolstoy, in his later years, was tormented with
the question whether a way could be found to make some sense
out of the events of history as he knew them. He concluded despair-
ingly that sense there is none, that whatever the justifications of
philosophers, the so-called makers of history are the puppets of fate.
The reality of war destroyed all semblance of rationality, and left
only a dreadful confusion. The modern consciousness is brought
to face the stark events, from which one can draw only pragmatic
inferences, starting from "what is ascertained as the fait accompli.
And here, maybe, we find ourselves facing one of the Tolstoyan
paradoxes driven to a point well-nigh unbearable. In his memorable
and desperate letter of 1908 to Gandhi, then an obscure lawyer,
which started the latter on his way to the teaching of nonviolence,
satyagraha, Tolstoy denounces the various forms of violence, mur-
der, and fraud on which society is based, which perpetuate educa-
tion and class distinctions as a whole. In it he included all the official
religions.
And then he pointed to science as the arch-culprit, because it
teaches man to do violence to himself and to nature essentially. Of
course, Tolstoy is thinking of the arrogant spirit of scientism with
its heartless, un-understanding doctrines. It would never have oc-
* So quickly the world doth change/Like shapes
Achieved remains/Cradled In Timeless Antiquity.
the clouds/Only the
Hamlet's Mill
330
curred to him that science is really something else, with its spirit
of pure research and serene dispassionateness. We would say now
that technology is the culprit. But the finger is pointed unequivo-
cally at our modern and vulgarizing idea of "science for the masses"
and the consumer society. Against that, Tolstoy holds the one
thing, Christian love—pure and simple—as wholly spontaneous,
natural, and compelling. We might say, keeping away from Tolstoy
and his illuminations, that what he asserts is respect for life and
spontaneity, a holy restraint for the arcane ways of the cosmos
itself, embodied in the community of beings with a conscience. He
forgot perhaps, also, his own striving for harmony, which makes
of him, in War and Peace, the legitimate successor of the great
K'wei, that singular "Master of Music" in the new Empire of Let-
ters. A reserved knowledge, that too, and far from our cliche of the
"common man," for Christ addressed himself to "those who have
ears to hear."
Simone Weil, lost in the turmoil of the Second World War,
thought she saw a retrospective answer in the Greeks, in Homer
himself, who had been called the Teacher of Greece. She called
the Iliad the "Poem of Force" because it showed Force at the center
of human history, a powerful and clear mirror of man's condition
—with no soothing nonsense added. Death for the vanquished,
nemesis for the conqueror—these are two members of the equation.
The strictly geometrical atonement that comes with the abuse of
force was the principal theme of Greek thought. It persisted
wherever Greek thought had reached. And yet, Western man, the
heir of the Judeo-Christian tradition, has lost it—so utterly that
in no Western language is there a word to express it. The notions
of limit, of measure, of commensurability, which guided the thought
of sages have survived only in Greek science and in the catharsis
of tragedy. This seemed to draw the boundary of understanding.
It is a strange truth, notes Simone Weil, that men today should be
geometers only with respect to matter. But Plato's famous lost lec-
ture on the Good is known to have been based on geometrical
demonstration. It had been so from the beginning in Greece. Not
only Anaximander's ethical statics of the cosmos, but the whole
331 • The Lost Treasure
Pythagorean theory had been based on those three mathematical
sciences: number, music, astronomy. Here lay the undeviating heart
of truth on which the Good can rest, and the rest concerned engi-
neers. Even in Thucydides, there is a kind of reductio ad absurdum.
And it shows that if the Greeks were no less miserable than we are
in life, still the great epic idea remains: no hate for the enemy, no
contempt for the victim. The measures of the cosmos unfolded the
facts. Force, Necessity, must be conceived as within an order. The
crucial word remains that of the Timaeus: "Reason overruled Ne-
cessity by persuading her to guide the greatest part of the things
that become towards what is best" (48A). There is a great idea
here. This is how far the mind could read, and yet be able to make
sense of reality. This is what the Greeks had accepted as the bound-
ary of thought. However original their minds, one might say that
the inheritance of archaic Measures had built up their patrimony,
indestructibly.
Man has moved beyond that, and has brought the marvelous
power of mathematics to the conquest of matter, as deep down as
the core of the atom, as far out as the outer-galactic nebulae. But
it is just as Simone Weil remarked, men are geometers only with
respect to matter and energy. The rest one has to leave to events,
and probabilities, to the physics of the dust. Man remains staring
at what in his own frame is the denial of thought, the fait accompli.
One dares not even examine the consequences of this geometry;
men feel their way apprehensively around such fate-laden corol-
laries as "information" or "overkill." They turn under one's eyes
into faits accomplis. The historical view of the past does not lend
itself to contemplation. But as man tries by means of contrast to
build up his experience of the true, he finds that truth is at odds
with his ancient faith in continuity. Scientific prediction moves
away from "instant catastrophes," on the subatomic level, breaks
against the perpetual resurgence of falsifiability. Whatever is au-
thentic expression in art, cleansed of context, scatters into the un-
ceasing variety of styles, of responses, of happenings and discov-
eries; not even the specious present, but the fractured instant is for
us the Now of Time.
Hamlet's Mill
332
333
The Lost Treasure
III
History is a nightmare from
which I am trying to awake.
James Joyce, Ulysses
In contrast with the present world, the archaic past has much to
speak for it. It was based on a very high culture, an artistic one of
a high order as everyone knows, and on a scientific culture too. It
brought the first technological Revolution, on which so-called an-
tiquity was to rest for millennia. Yet it lived on and flowered and
let the world live. People like to ignore this archaic science because
it started from the wrong foundations and drew any number of
wrong conclusions, yet historians know that wrongness is not a test
for relevance, that a course of reasoning may be scientifically im-
portant independent of its endpoints. Our forebears built up their
world view from the idea which today would be called geocentric;
they concluded with speculations about the fate of man's soul in a
cosmos in which present geography and the science of heaven are
still woven together. Worse, maybe, they built them up on a con-
ception of time which is utterly different from the modern metric,
linear, monotone conception of time. Their universe could have
nothing to do with ours, derived as it was from the apparent revolu-
tions of the stars, from pure kinematics. It has taken a great in-
tellectual effort on the part of many great scholars to transfer
themselves back to that perspective. The results have been aston-
ishingly fruitful. For those forebears did not only build up time
into a structure, cyclic time: along with it came their creative idea of
Number as the secret of things. When they said "things are num-
bers," they swept in an immense arc over the whole field of ideas,
astronomical and mathematical, from which real science was going
to be born. Those unknown geniuses set modern thought on its
way, foreshortened its evolution. But their ideas were at least as
complicated as our own have come to be.
Cosmological Time, the "dance of stars" as Plato called it, was
not a mere angular measure, an empty container, as it has now be-
come, the container of so-called history; that is, of frightful and
meaningless surprises that people have resigned themselves to calling
the fait accompli. It was felt to be potent enough to control events
inflexibly, as it molded them to its sequences in a cosmic manifold
in which past and future called to each other, deep calling to deep.
The awesome Measure repeated and echoed the structure in many
ways, gave Time the scansion, the inexorable decisions through
which an instant "fell due."
Those interlocking Measures were endowed with such a tran-
scendent dignity as to give a foundation to reality that all of mod-
ern physics cannot achieve; for, unlike physics, they conveyed the
first idea of "what it is to be," and what they focused on became
by contrast almost a blend of past and future, so that Time tended
to be essentially oracular. It presented, it announced, as it were; it
oriented men for the event as the Chorus was later to do in a Greek
tragedy. Whatever idea man could form of himself, the consecrated
event unfolding itself before him protected him from being the
"dream of a shadow."
Again and again, in the course of this essay, we have insisted on
the vanity of any attempt to give an "image" of the archaic cosmos,
even were it such an image as Rembrandt drew of the cabalistic
apparition to the Initiate, or as Faust suddenly saw in the sign of
the Spirit of Earth. Even as a magic scheme, it would have to be a
design of insoluble complexity. Far worse did our own scholarly
predecessors fare when they tried for a model, conceived mechan-
ically, an orrery, a planetarium maybe, such as Plato suggests teas-
ingly in his deadpan way with his whorls and spindles and frames
and pillars. A real model might indeed help, he goes on without
batting an eye, and one realizes it would come into the price range
of a Zeiss Planetarium, still true to the kinematic rigor of the Powers
of heaven, but blind to their moving soul in its action—and Plato's
machinery promptly dissolves into contradictions, no real "model"
at all. Plato will never yield on his "unseriousness," which for him
is a matter of principle, a way of leaving mystery alone while re-
specting reason as far as it can go. Another image suggested by the
past, still older than planetary models, would be the "tissue" woven
in the skies, the Powers working at the whirring loom of Time, says
Goethe, as they weave the living mantle <>l the Deity, But as in all
Hamlet's Mill
334
those images, the real terms are life and harmony, many harmonies,
such as Pythagoreans went on forever investigating. Our own "re-
construction," whatever it is, would come as close to a harmony as
our cat achieves by stretching out full length on a keyboard. Kep-
ler's mad attempt at writing out the notes of the "Harmony of the
Spheres" was bound to fail abysmally to express the, true lawful-
ness: what Plato called the Song of Lachesis.
Men have learned to respect it without thinking. Even today, as
one celebrates Christmas, one invokes the unique gift of that cyclic
time—the gift of not being historical; its opening into the timeless,
the virtue of mapping the whole of itself into a vital present, laden
with ancestral voices, oracles, and rites from the past. With what
sincerity is left to them, men invoke the remission of ancient sins,
the rebirth of the Soul even as was done many millennia ago. Peo-
ple beg from that Time the renewed strength to carry on against a
senseless reality—and still ask their children to aid their unbelief.
True history goes by myths. Its forces are mythical. As Voltaire
remarked coolly, it is a matter of which myth you choose.
The name of Revolutions is a true technical term of astronomic
knowledge and myth: that which ever returns to the same point.
It became insistently identified with the idea of the Great Change.
As soon as men began to misunderstand it, it set History on the
march with irreversible changes. But in the Middle Ages it still
promised a return to the undefined Origins, to the Golden Age,
when Adam delved and Eve span, or, more Christianly, to when
the Lord still walked on earth. Joachim of Flora (c. 1200) was still
the prophet of the Great Change that was to be a true accomplish-
ment of ancient prophecies. After the ages of the Father and the
Son men expected the Age of the Holy Ghost to follow imme-
diately, when all men would be brothers—a great revolutionary
moment sparked by the order of St. Francis. It lived on in the
shrunken horizon of Enlightenment, which set the span back to the
Greeks and Romans as semi-gods. And yet, in those classical times,
that dream was already there. It was of a return far back to the
birth of a Miraculous Child. And back far beyond that, to the
clearer idea of cosmic configurations such as they were when time
had not yet been set in motion. Here came the Timaeus.
335
The Lost Treasure
The idea lingered on. In the Apocalypses and Cosmogonies, in
the Vedic poems, time is scrambled artificially and deliberately into
elements, lunar stations, or proto-chess, to restore the vision, the
prophetic or sibylline vision. Out of this thoughtful scrambling of
elements came the Alphabet. A prodigious conquest, like the mak-
ing of iron, and a grievous gift unto men, as Hesiod might say.
There is no doubt that one is dealing with the creations of genius,
even if they were flashes in the darkness, which had found a way
to perpetuate and propagate themselves.
It stands to reason that the actual chronicle of the archaic ages
is full of "barbaric" events. What such migrations as those of the
Cimmerians, of the Mongols, of the Peoples of the Sea achieved
in the way of destruction and dispersal is beyond our imagination.
One calls this the primitive way of life, and blithely conjectures
extermination in the biological sense, forgetting what biology has
to say of real conflicts among animal tribes. It is only man, more
especially modern man, who knows the art of total kill, the quick
and the slow. But archaic cultures, devoid of history but steeped
in myth, did not find in events the surprise of the fait accompli,
stunning and shattering to the mind in the way Auschwitz is to us.
Mythical experience has its own ways of meeting catastrophe. Men
were able to see things nobly. Narration became epic.
The great epic of the Fall of the Nibelungen mirrors in its own
way the invasion of Attila and his Huns, the "Scourge of God."
Official history might counter the Mongol hordes with the Roman
victory on the Catalaunic fields, but the Attila of legend, chief of
Gog and Magog, remains more imposing, even as he passes silently
out of the scene, than Jenghiz or Tamerlane with their historic
conquests and pyramids of skulls. He has little to act, he is the
typical emperor of myth. Like Theodoric, like Arthur, like Kai
Khusrau, he is the unmoved chess king around whom figures move.
The Nibelungen story shows how mythical thought dealt with the
crisis. It is Nemesis who destroys the German warriors at the last.
Attila, "king Etzel," suffers in his turn, without losing the authority
of the conqueror. His child dies at the hands of Hagen, last of the
sinful brood who is cut down as a captive by the infuriated mother,
destroyed in turn by Hildebrand, reconciled to the conqueror, who
Hamlet's Mill • 336
brings the drama to a catharsis. Attila the Hun and Theodoric the
Goth, joined in the tale as allies, are left to weep together the death
of great heroes. No hatred, no terror left, except at the working of
Fate.
From the last night of Troy, extinguished in slaughter, what re-
mains in living myth is the flight of the few survivors toward new
shores. There they become mythical founding heroes in their turn,
contended for by the great cities of the West. This is how myth
deals with its own, and Nemesis is felt at last to catch up with the
Roman Empire. The spirit of Homer's epic impassiveness led the
ancient mind all the way up to the end of the classic world, purged
of resentment and hatred, but nowhere more impressively than in
Virgil's soul-stricken invocation, a vision of doom at a time when
Rome fancied itself established forever: "Please, gods, have mercy.
Have we not atoned enough for the original perjury of Troy?"
Iam satis luimus Laomedonteae periuria Troiae . . . But there is no
atonement in full measure within the unceasing rhythm of cycles
and megacycles, which builds up a living dialectic of mythical
imagination. The conquests and subversions which reshaped the
world with Alexander were surely more important than any feats
attributed to the legendary king of Uruk; but the latter's other-
worldly sheen reverberated on the Macedonian, and tradition
forced him into the pattern of another Gilgamesh, still bent on the
discovery and conquest of all earth, water, and air, down to the
end of the world and beyond, still questing in vain after immortal
life. The molding capacity of established myth created the historic
episodes that he needed to fit himself into the role, went beyond
him to build up the "two-horned" demigod, Dhul-Karnein, he who
erected a brazen wall against the path of destruction from the East,
the peril of Gog and Magog, a fable that even the later glory of
the Roman Empire could not imitate. For that kind of time always
tends to move off into the forms of timelessness.
Let us go back to the end of the wonderful adventure of Dante's
Odysseus, as he moves out of the straits of Gibraltar:
And having turned our poop towards the morning,
Our oars we turned to wings in crazy flight
Always gaming to the left-hand side.
337
The Lost Treasure
That is, he has "turned his poop to the east," and his prow directly
west; he proceeds "always gaining to the left-hand side." In other
words, it looks as if he were trying to circumnavigate Africa, not
as Columbus but as Vasco da Gama did, going to India. The gen-
eral direction of his "crazy flight" is actually south, across the
equator and then the Tropic of Capricorn, just as he has already
done in Homer under Circe's sailing directions: "follow the wind
from the North." He is still looking for the "experience, beyond
the sun, of the world "without people." But in Dante's world scheme,
he is clearly making for the Antipodes, which means, vaguely, the
unknown South Seas.
And, in fact, all the stars of the other pole had come into sight,
and those of ours had sunk so low that they did not rise from the sea;
five times the light of the moon had waxed and waned, when we
described a tall mountain, dim from the distance, so tall that I
had never seen any. We rejoiced, and soon it turned to tears . . .
for it "was, as we already know (see chapter XIV, "The Whirl-
pool"), the mount of Purgatory, denied to the living. Hence, Provi-
dence decreed a whirl that swallowed the ship and all its hands,
and that was the end.
What was Columbus' discovery? Hardly more.
Dante's description was not really an invention; it was derived
from texts of his own time, and we find it, bodily transcribed, in
Columbus' own extracts and notes, made in the years of waiting
in Spain, from his favorite readings: "subtle shining secrecies, writ
in the glossy margent of such bookes."1 It is still the land of Eden.
A long distance by land and sea from our habitable land; it is so high
that it touches the lower sphere, and the waters of the Flood never
touched it . . . . The waters which descend from this very high
mountain form an immense lake. The fall of such waters makes such
a noise that the inhabitants are born deaf. From that lake as the one
source flow the four rivers of Paradise: Physon which is the Ganges,
Gyon which is the Nile, Tigris and Euphrates .... A fountain there
is in Paradise which waters the garden of delights and which is dif-
fused in the four rivers. According to Isidore, John of Damascus,
Bede, Strabo and Peter Comestor . . . Pliny and Solinus, Marinus of
1Shakespeare, The Rape of Lucrece
Hamlet's Mill
338
339
The Lost Treasure
Tyre's corrections of Ptolemy show that the sea can be crossed with
favorable winds in a few days, going down per deorsum Africae,
along the back of Africa . . . for the earth extends from Spain to the
Indies more than 180 deg. And the proof is that Ezra says that 6/7ths of
the globe are land, Ambrosius and Augustine holding Ezra for a
prophet. . . the degree being equal to 52 2/3 Roman Miles ....
The sources of Columbus are well known, one of them being
Pierre d'Ailly's famous Imago Mundi of the 14th century, and an-
other Aeneas Sylvius' Historia Rerum ubicumque gestarum of the
15th. Pierre d'Ailly differs even more from Ptolemy by ruining his
celestial coordinates, whereas Aeneas Sylvius is no more than a
compilation, a vague miroir historial, and yet these are the books in
which Columbus put his trust, much more than in his maps, and
rightly so. Even Toscanelli's famous letter to Martius does no more
than emphasize Marco Polo's Cipango (Japan) and set it a thousand
miles east; which at least encouraged the lonely Genoese, who to
the end never suspected the existence of the Pacific, and made him
look for the golden homes of Cipango while he was discovering
Cuba. His never-never land, his own Island of St. Brandaen, must
have been in his mind somewhere between the Canaries and the
Empire of Prester John, along "the back of Africa," and this was
enough impetus for him to discover America, or rather invent it
out of his mythical enthusiasm, still bent on the Garden of Eden
and its nightingales. As for Toscanelli, the "cosmographer," his
impulse lay not so much in his geographical expertise on China as
in his vaticination of a new world-age. Columbus' and Toscanelli's
clear and very modern intention was "to search for the East by
way of the West"; but what did it amount to? One of the authori-
ties assured that Aryim, umbilicus marls, wherever it may be, was
not "in the middle of the habitable earth," but further, 900 off.
Another said that the distance between Spain and the eastern edge
of India was "not much." Once out in the Atlantic, Columbus had
to rely on his faith in timeless myth, from Gilgamesh to Alexander.
To be sure, he had the compass, but his cosmography had lost the
very idea of the heavens; and, like his Odyssean and medieval fore-
bears, he had to keep searching for the Islands of the Blessed.
It may be we shall find the Happy Isles,
and meet the great Achilles, whom we knew . . .
What led him to his discovery was his wonderful skill as a navi-
gator, which allowed him to ride out equinoctial storms and never
lose a ship as he threaded his caravels through the tricky channels of
the Indies. America was the reward for Paolo Toscanelli's2 and
Christopher Columbus' Archaic faith.
The relation of myth to history is very important indeed, but
the influence of one on the other often goes counter to the inter-
pretations of most debunkers. The famed nightingale from Eden
that Columbus wrote he heard when he landed on Watling Island
is only one striking counterexample. But there are more. For in-
stance, myth had influence on the geopolitics of great Eastern con-
querors like Tamerlane and Mohammed II. These two men of
action, and decisive action, were far from illiterate. They had the
cultures of two languages at their disposal, Turkish and Persian, and
their inquisitive minds liked to dwell on great plans of adventure
toward the West. Yet although they were obsessed with the destruc-
tion of the Empire of Rum (Rome), it has been shown (von
Hammer) that they had never so much as heard of Caesar and his
great successors. Their historical information did not go beyond the
"Romaunt of Alexander" in the Persian version. One is back again
with Gilgamesh as the prime source. The comparison is all in their
favor. While the potentates of Europe were loosing themselves in
miserable quarrels, frittering away their possibilities, and even seek-
ing an alliance with the Turk, only Pope Aeneas Sylvius, sick and
dying, was finding the words for the occasion: "The barbarians
have murdered the successor of Constantine together with his peo-
ple, desecrated the temples of the Lord, overthrown the altars,
thrown to the swine the relics of the martyrs, killed the priests,
ravished their women and daughters, even the virgins consecrated
to God; they have dragged along the camp the image of our cruci-
fied Savior, to the cry of 'there goes the God of the Christians' and
have defiled it with filth and spit—and we seem to care for nothing."
It was indeed the final tragedy of Christendom, vanishing first
West, then East. At that point only the conquering Sultan found
the words for the occasion. "The ruler of the world"—writes
2 Giorgio de Santillana, "Paolo Toscanelli and His Friends," in Reflections on
Men and Ideas (1968), pp. 33-47.
Hamlet's Mill
34°
The Lost Treasure
Tursum Beg, his chronicler—moved up like a spirit, to the summit
of Saint Sophia; he watched signs of the already coming decay, and
formed elegiac thoughts: "The spider serves as watchman in the
porticoes of the cupola of Khusrau. The owl sounds the last post
in the palace of Afrasiyab. Such is the world, and it is doomed to
come to an end."
IV
What time span did the archaic world embrace within our own
frame? Its beginning has already been placed in the Neolithic, with-
out setting limits in the past; let prehistoric archaeologists decide.
The astronomical system seems to conceive of the Golden Age, the
Saturnian Era, as already mythical, in the proper sense. One can
then say that it took shape about 4000 B.C.,3 that it lasted into proto-
history and beyond.4 The fearful loss of substance that tradition
suffered in the Greek Middle Ages (the same happened in Egypt
too, before the Middle Kingdom) has created an almost complete
gap with what we call Classical Antiquity, but enough did remain to
ensure a continuity with those ancestors whom Plato and Aristotle
liked to call "the men close to the Gods" and who were thought
of in this way even to our Renaissance. In Plato's philosophy, Ar-
chaic Time stayed intact; it was resolutely understood as "wholly
other" from extension, wholly incompatible with what Parmenides
had already grasped in his Revelation, with what Democritus coldly
theorized. But archaic time is the universe, like it circular and defi-
nite. It is the essence of definition, and so it continues to be through-
out Classical Antiquity, which did not believe in progress but in
eternal returns. In that world it was Space which, if taken by itself,
brought in indefiniteness and incoherence. Ultimately, in Plato,
space was identified with the nature of Non-Being. Plato called
space the "Receptacle." This idea, so puzzling for us who think in
spatial terms and cut up reality, as Bergson said, along dotted lines
drawn in space, must have been for Plato an easy and natural con-
clusion. He had inherited the idea that reality, or rather Being, was
3 See W. Hartner, "The Earliest History of the Constellations in the Near East
and the Motif of the Lion-Bull Combat," JNES 24 (1965), pp. 1—16, 16 plates.
'' But we do not know. These people could compute backward as well as forward.
defined in terms of Time above all. It was Space which brought in
confusion, multiplicity, the resistance to Order, what Plato called
the Unruly and Irregular which always resist the mind. In the
beginning, it would seem, space even resisted the mind of the
Creating Demiurge, for it presented him with the original chaos,
a kind of foreign body intractably plemmelos kai atakteos, unorga-
nized, devoid of any rhythm. Even the Demiurge must struggle to
force it into shape, within the limits of his power.
When did the archiac world come to an end? There are many
testimonials of the bewildering change. Plutarch, a true pagan, pon-
dered about a.d. 60, why it was "that oracles had ceased to give
answers." It is on this occasion that he told the tale of the voice
that came from the sea, telling the pilot that "the Great Pan was
dead." Recounting it on a previous occasion (above, chapter XX,
p. 277), it was noted that the experts of the Emperor Tiberius de-
cided that it must be Pan no. 3. Another world-age must be passing,
together with the gods who belonged to it. For traditionalists it was
indeed one more sign of the passing of the Age of Aries and the ad-
vent of the Age of Pisces. Historically, it is known as the advent of
the Christian revolution, marked in so many ways by the sign of the
Fish. It may have taken place with the Edict of Theodosius in
a.d. 390. It was to be a change so profound that it would have caused
Plutarch to lose his bearings. It was the end of the Parcae, the god-
desses who lived Fate. The Song of Lachesis had been silenced. In
a few centuries, it was as if new stars were shining over the heads of
men brought up in a classical culture. The introduction of new
gods from the East was certainly a contributory cause of the rapid
conversion of the Roman elite, which appeared to the Christians a
miracle in itself. Oracles and omens had been part of the texture of
circular Time, using the sibylline language which continuously
threw a rainbow bridge from the past into the future.
As later developments were to show, the great web of cyclical
time suffered irreparable harm from the doctrine of the Incarnation,
but did not snap asunder all at once. For a long time the belief in
the Second Coming among Christians kept rime together. But as it
became established that the supramundane advent of Christ into rhe
world had cleft time into an absolute Before and After, that it was
Hamlet's Mill • 342
a unique event not subject to repetition, then duration became
simple extension, a waiting for the day of judgment, increasingly
dependent on the vicissitudes of belief.
I tried to determine once, from the testimony of artistic experi-
ence, the period when the time frame of reality came to be felt and
described in terms of three-dimensional space.5 This first sign of the
Scientific Revolution, I suggested, coincided with the invention of
perspective in the 15th century. It arrived, as it were, surrepti-
tiously, originating in the minds of great artists and technologists
(artist being then the word for artisan). What is clear is that by
the end of the Renaissance time and space had become what we
mean by them.
Newton conceived of the frame of the universe as made up of
absolute space and time. The mode of thought became natural, and
not until Einstein did new and greater difficulties arise to resist the
imagination. Today one should begin to appreciate the divine sim-
plicity of the archaic frame, which took time as the one frame, even
at the terrible price of making the cosmos itself into the "bubble
universe." It was a decisive option. The choice went deep to the
roots of man's being. It conditioned Aristotelian theory and condi-
tioned Christian imagination. It constrained even Copernicus and
Kepler. They both recoiled from unboundedness. That is why
one sees Aristarchus, Bruno and Galileo not simply as bold gen-
eralizers or investigators of regularities, but as souls of superhuman
audacity.
Aristarchus remained a loner, neglected in his time even by the
sovereign mind of Archimedes. Twenty centuries later, Bruno was
less a thinker than an inspired prophet of God's infiniteness, identi-
cal with the Universe itself. Galileo, the true scientist, still remained
sufficiently dominated by the circularity he needed in his cosmos so
that he did not dare to formulate the principle of rectilinear inertia
which was already present to his mind. He held passionately to the
circular cosmos. The circle was to him a metaphor of Being that
he was still willing to accept even at the price of unacceptable epi-
5 G. de Santillana, "The Role of Art in the Scientific Renaissance," in Reflec-
tions on Men and Ideas (1968), pp. 137—66.
343 • The Lost Treasure
cycles. However much he supported perfect circularity by sober
and prosaic reasons, it remained to him first and last a "symbolic
form," much as the Seven-ringed cup of Jamshyd, the magic Cal-
dron of Koridwen, as the Cromlech of Stonehenge. The Untuning
of the World, the dissolution of the Cosmos, was to come only with-
Descartes.
It was said earlier concerning the Mayan astronomers that the
connections were what counted. In the archaic universe all things
were signs and signatures of each other, inscribed in the hologram,
to be divined subtly. This was also the philosophy of the Pytha-
goreans, and it presides over all of classical language, as distinct
from contemporary language. This was pointed out perceptively by
a modern critic, Roland Barthes, in Le degre zero de l'Ecriture.
"The economy of classical language," he says, "is rational, which
means that in it words are abstracted as much as possible in the
interest of relationship . . . No word has a density by itself, it is
hardly the sign of a thing, but rather the means of conveying a
connection." Today, the object of a modern poem is not to define
or qualify relations already conventionally agreed; one feels trans-
ported, as it were, from the world of classical Newtonian physics
to the random world of subatomic particles, ruled by probabilistic
theory. The beginning of this was felt in Cezanne, in Rimbaud and
Mallarme. It is "an explosion of words" and forms, liberated words,
independent objects—discontinuous and magical, not controlled,
not organized by a sequence of "neutral signs." The interrupted
flow of the new poetic language, Barthes remarks, "initiates a dis-
continuous Nature, which is revealed only piecemeal." Nature be-
comes "a fragmented space, made of objects solitary and terrible,
because the links between them are only potential." More, they are
arbitrary. They are supposed to be of the nature of the ancient
portentum. The only meaning to be drawn from those links is that
they are congenial to the mind that made them. The mind has
abdicated, or it shrinks in apocalyptic terror. In the arts we hear of
Amorphism, or "disintegration of form," of the "triumph of inco-
herence" in concrete poetry and contemporary music. The new
syntheses, if any arc still possible, arc beyond the horizon.
345
Conclusion
Conclusion
Honneur des Hommes, saint Langage
Discours prophetique et pare . . .
Valery, La Pythie
Starting from one theme chosen among many, this self-styled
first reconnaissance over uncharted ground has come a long and
tortuous way since the early introduction of the Hamlet figure.
The discussion has touched immense areas of myth whose probable
value was indicated by previous discoveries. The treasures of Celtic
tradition, of Egypt, China, tribal or megalithic India, and Oceania
have barely been sampled. Nevertheless, the careful, inductive ap-
plication of critical standards of form along the belt of High Civili-
zations has been enough to show the remnants of a preliterate "code
language" of unmistakable coherence. No apologies are needed for
having followed the argument where it led, but it is very much to
be hoped that what has been uncovered will eventually prove suffi-
ciently self-correcting to amend the inevitable errors of this essay.
What can the initial universe of discourse have been, that insen-
sate scattering of dismembered and disjointed languages of the re-
mote past, of earthy jargons and incommunicable experiences, from
which, by a stroke of luck, scientific man was born? Clearly, man's
capacity for attention, for singling out certain unattainable objects
in the universe, must have overcome the convolutions and horrors
of his psyche. There were some men, surely exceptional men, who
saw that certain wondrous points of light on high in the dark could
be counted, tracked, and called by name. The innate knowledge
that guides even migratory birds could have led them to realize that
the skies tell—yea, recount—the glory of God, and then to con-
clude that the secret of Being lay displayed before their eyes.
Their strange ideas, inscrutable to later ages, were the beginnings
of intellect, and in the course of time they grew into a koine, or
lingua franca, covering the globe. This common language ignored
local beliefs and cults. It concentrated on numbers, motions, mea-
sures, overall frames, schemas, on the structure of numbers, on
geometry. It did all this although its inventors had no experience to
share with each other except the events of their daily lives and no
imagery by which to communicate except their observations of
natural lawfulness.
Ordered expression, that is expression in accordance with laws
or rules, comes before organized thought. After that, the spon-
taneous creation of fables occurs when there is a fund of direct
experience to draw upon. For example, a prehistoric "tech talk,"
expressing only lawfulness in the grammatical or natural sense, may
have begun by using terms that came from the earliest technology.
Later, as experience increased, the same kind of talk using the same
terms may have been extended to include alchemy and other imag-
eries. In form, these exchanges would be transmuted tales, but
because of their terminology they would possess an ordering and
naming capacity that would diffuse stimuli over a sea of diversity.
Ultimately, they could produce a sign code whereby the stars of
Ursa became a team of oxen, and so on.
It is now known that astrology has provided man with his con-
tinuing lingua franca through the centuries. But it is essential to
recognize that, in the beginning, astrology presupposed an astron-
omy. Through the interplay of these two heavenly concepts, the
common elements of preliterate knowledge were caught up in a
bizarre bestiary whose taxonomy has disappeared. With the rem-
nants of the system scattered all over the world, abandoned to the
drift of cultures and languages, it is immensely difficult to identify
the original themes that have undergone so many sea-changes.
The language of the Vedas, for instance, which transposes a
dazzling wealth of metaphysics into the discourse of hymns, is as
remote from all other aspects of mythical thought as the stars of
Hamlet's Mill
346
347
Conclusion
Ursa themselves are from the verses which, as Masters, the Vedas
suppose those stars to have written. In these verses, the notion of
the way to transcendence and the absurdity and wild luxuriance of
the imagery are certain to confound the Western mind and lead it
far away from the subject of astronomical origins into a mystical
dialectic.
And yet the original life of thought, born of the same seeds as the
Vedas, worked its way in darkness, sent its roots and tendrils
through the deep, until the living plant emerged in the light under
different skies. Half a world away it became possible to rediscover
a similar voyage of the mind which contained not a single linguistic
clue that a philologist could endorse. From the very faintest of
hints, the ladder of thought leading back to proto-Pythagorean
imagery was revealed to the preternaturally perceptive minds of
Kircher and Dupuis. The inevitable process became discernible,
going from astronomical phenomena to what might be beyond
them. Finally perhaps, as Proclus suggested, the sequence leads from
words to numbers, and then even beyond the idea of number to a
world where number itself has ceased to exist and there are only
thought forms thinking themselves. With this progression, the as-
censional power of the archaic mind, supported by numbers, has re-
established the link between two utterly separate worlds.
The nature of this unknown world of abstract form can also be
suggested by way of musical symbols, as was attempted earlier.
Bach's Art of the Fugue was never completed. Its existing symme-
tries serve only as a hint of what it might have been, and the work
is not even as Bach left it. The engraved plates were lost and partly
destroyed. Then, collected once more, they were placed in approxi-
mate order. Even so, looking at the creation as it now is, one is
compelled to believe that there was a time when the plan as a whole
lived in Bach's mind.
In the same way, the strange hologram of archaic cosmology
must have existed as a conceived plan, achieved at least in certain
minds, even as late as the Sumerian period when writing was still a
jealously guarded monopoly of the scribal class. Such a mind may
have belonged to a keeper of records, but not of the living word,
still less of the living thought. Most of the plan was never recorded.
Bits of it reach us in unusual, hesitant form, barely indicated, as in
the wisdom and sketches of Griaule's teacher, Ogotemmeli, the
blind centenarian sage. In the magic drawings of Lascaux, or in
American Indian tales, one perceives a mysterious understanding
between men and other living creatures which bespeaks relation-
ships beyond our imagination, infinitely remote from our analytical
capacity.
"From now on," said Father Sun, grieving over Phaethon, his
fallen child, "you shall be Mink." What meaning can this have for
us? For such an understanding between men and men, and other
living creatures too, we would need the kind of help King Arthur
had at hand: "Gwryr Interpreter of Tongues, it is meet that thou
escort us on this quest. All tongues hast thou, and then canst speak
all languages of men, with some of the birds and beasts." This abil-
ity was also attributed to Merlin and Gwyon, those masters of
cosmological wisdom whose names resound through the legends
. of the Middle Ages. In general, all fabulous communication was
conceived as having such a range, not merely the Aesopian fable
with its flat, all-too-worldly wisdom.
Much of this book has been peopled with the inhabitants of a
Star Menagerie of profoundly meaningful animal characters. The
forms of animal life have varied from the Fishes who turned into
hairy Twins to the remarkable succession of doglike creatures
occurring around the world from Ireland to Yucatan. All of these
animals have been of great significance, and each was invested with
key functions in cosmological myth.
It would be possible, for example, to prepare a most informative
edition of the Romance of Reynard Fox illustrated entirely with
reproductions from Egyptian and Mesopotamian ritual documents.
For it is likely that these documents represent the last form of inter-
national initiatic language, intended to be misunderstood alike by
suspicious authorities and the ignorant crowd. In any case, the
language forms an excellent defense against the kind of misuse
which Plato speaks about with surprising earnestness in Phaedrus
(274D-275H). At the point in question, Thoth/Hermes is feeling
Hamlet's Mill
348
very proud of himself for having invented letters, and he claims
that the alphabet will make the Egyptians wiser and improve their
memory. Plato has the god Thamus, "king of all Egypt," speak to
him:
"Most ingenious Theuth," said the god and king Thamus, "one man
has the ability to beget arts, but the ability to judge of their useful-
ness or harmfulness to their users belongs to another; and now you,
who are the father of letters, have been led by your affection to
ascribe to them a power the opposite of that which they really pos-
sess. For this invention will produce forgetfulness in the minds of
those who learn to use it, because they will not practise their memory.
Their trust in writing, produced by external characters which are
no part of themselves, will discourage the use of their own memory
within them. You have invented an elixir not of memory, but of re-
minding; and you offer your pupils the appearance of wisdom, not
true wisdom, for they will read many things without instruction and
will therefore seem to know many things, when they are for the most
part ignorant and hard to get along with, since they are not wise, but
only appear wise."1
Now that Plato's apprehensions have become fact, there is noth-
ing left of the ancient knowledge except the relics, fragments and
allusions that have survived the steep attrition of the ages. Part of
the lost treasure may be recovered through archaeology; some of it
—Mayan astronomy, for instance—may be reconstructed through
sheer mathematical ingenuity; but the system as a whole may lie
beyond all conjecture, because the creating, ordering minds that
made it have vanished forever.
1 Translation by H. N. Fowler, LCL. The Jowett translation reads: "The specific
which you have discovered is an aid not to memory but to reminiscence, and you
give your disciples not truth, but only the semblance of truth" (oukcoun mnemes all'
hypomneseos pharmakon heures; Sophias de tois mathetais doxan, ouk aletheian
porizeis).
349
Conclusion
L'Envoi
From harmony, from heavenly harmony,
This universal frame began:
When nature underneath a heap
Of jarring atoms lay,
And could not heave her head,
The tuneful voice was heard from high,
"Arise, ye more than dead!"
Then cold, and hot, and moist, and dry,
In order to their stations leap,
And Music's power obey.
From harmony, from heavenly harmony,
This universal frame began:
From harmony to harmony
Through all the compass of the notes it ran,
The diapason closing full in Man. . . .
As from the power of sacred lays
The spheres began to move,
And sung the great Creator's praise
To all the Blest above;
So when the last and dreadful hour
This crumbling pageant shall devour,
The trumpet shall be heard on high,
The dead shall live, the living die,
And Music shall untune the sky!
Dryden, "A Song for St. Cecelia's Day"
Appendix
The only master of this kind of observation hitherto has been Marcel
Griaule (d. 1956) but he left an impressive cohort of disciples. They
have renewed the understanding of African studies, showing that such
systems are still alive with the Dogon, whom Griaule "discovered," in
the true sense of the word.
As Germaine Dieterlen writes: "The smallest everyday object may
reveal a conscious reflection of a complex cosmogony . . . Thus for in-
stance African techniques, so poor in appearance, like those of agri-
culture, weaving and smithing, have a rich, hidden content of signifi-
cance . . . The sacrifice of a humble chicken, when accompanied by
the necessary and effective ritual gestures, recalls in the thinking of
those who have experienced it an understanding that is at once original
and coherent of the origins and functioning of the universe.
"The Africans," she continues, "with whom we have worked in the
region of the Upper Niger have systems of signs which run into thou-
sands, their own systems of astronomy and calendrical measurements,
methods of calculation and extensive anatomical and physiological
knowledge, as well as a systematic pharmacopoeia. The principles un-
derlying their social organization find expression in classifications which
embrace many manifestations of nature. And these form a system in
which, to take examples, plants, insects, textiles, games and rites are dis-
tributed in categories that can be further divided, numerically expressed
and related one to another. It is on these same principles that the politi-
cal and religious authority of chiefs, the family system and juridical
rights, reflected notably in kinship and marriages, have been established.
Indeed, all the activities of the daily lives of individuals are ultimately
based on them."1
It goes without saying that we need not subscribe to the author's
opinion that the Mande peoples invented "their own systems of astron-
omy . .."
1 Introduction to Conversations with Ogotemmeli, Marcel Griaule (1965), p. xiv.
Hamlet's Mill
354
355 • Appendices
Appendix 2
The father of Saxo's Amlethus was Horvandillus, written also Oren-
del, Erentel, Earendel, Oervandill, Aurvandil, whom the appendix to
the Heldenbuch pronounces the first of all heroes that were ever born.
The few data known about him are summarized by Jacob Grimm:1
He suffers shipwreck on a voyage, takes shelter with a master fisher-
man Eisen,2 earns the seamless coat of his master, and afterwards
wins frau Breide, the fairest of women: king Eigel of Trier was his
father's name. The whole tissue of the fable puts one in mind of the
Odyssey: the shipwrecked man clings to a plank, digs himself a hole,
holds a bough before him; even the seamless coat may be compared
to Ino's veil, and the fisher to the swineheard, dame Breide's templars
would be Penelope's suitors, and angels are sent often, like Zeus's
messengers. Yet many things take a different turn, more in German
fashion, and incidents are added, such as the laying of a naked sword
between the newly married couple, which the Greek story knows
nothing of. The hero's name is found even in OHG. documents:
Orendil . . , Orentil ... a village Orendelsal, now Orendensall, in
Hohenlohe . . . But the Edda has another myth, which was alluded
to in speaking of the stone in Thor's head. Groa is busy conning her
magic spell, when Thorr, to requite her for the approaching cure,
imparts the welcome news, that in coming from Jotunheim in the
North he has carried her husband the bold Orvandill in a basket on
his back, and he is sure to be home soon; he adds by way of token,
that as Orvandil's toe had stuck out of the basket and got frozen,
he broke it off and flung it at the sky, and made a star of it, which is
called Orvandils-ta. But Groa in her joy at the tidings forgot her spell,
so the stone in the god's head never got loose (Snorri's Skaldskap. 17).
Powell,3 in his turn, compares the hero to Orion in his keen interpre-
tation:
The story of Orwandel (the analogue of Orion the Hunter) must
be gathered chiefly from the prose Edda. He was a huntsman, big
enough and brave enough to cope with giants. He was the friend of
Thor, the husband of Groa, the father of Swipdag, the enemy of the
1 TM, pp. 374f. See also K. Simrock, Der ungenahte Rock oder Konig Orendel
(1845), p.ix.
2 Also written Ise or Eise, and derived from Isis, by Simrock; considering that the
fisherman's modest home has seven towers, with 800 fishermen as his servants, Ise/
Eisen looks more like the Fisher King of Arthurian Romances.
3 In his introduction to Elton's translation of Saxo, p. cxxiii.
giant Coller and the monster Sela. The story of his birth, and of his
being blinded, are lost apparently in the Teutonic stories, unless we
may suppose that the bleeding of Robin Hood till he could not see,
by the traitorous prioress, is the last remains of the story of the great
archer's death. Dr. Rydberg regards him and his kinsfolk as doublets
of those three men of feats, Egil the archer, Weyland the smith, and
Finn the harper, and these again doublets of the three primeval artists,
the sons of Iwaldi, whose story is told in the prose Edda.
It is not known which star, or constellation, Orvandils-ta was sup-
posed to be. Apart from such wild notions as that the whole of Orion
represented his toe4—to identify it with Rigel, i.e., beta Orionis, would
be worth discussing—even Reuter tries to convince himself that Corona
borealis "looks like a toe,"5 because he could not free himself from the
fetters of seasonal interpretation of myth, nor dared he attack the ro-
mantic authority of Ludwig Uhland who had coined the dogma that
Thor carried the sign for spring in his basket; accordingly a constella-
tion had to be found which could announce springtime, and Reuter,
choosing between Arcturus and Corona, elected the latter.
It is not his toe alone, however, which grants to Hamlet's father his
cosmic background: some lines of Cynezvulfs Christ dedicate to the
hero the following words:
Hail, Earendel, brightest of angels thou,
sent unto men upon this middle-earth!
Thou art the true refulgence of the sun,
radiant above the stars, and from thyself
illuminest for ever all the tides of time.6
The experts disagree whether Earendel, here, points to Christ, or to
Mary, and whether or not Venus as morning star is meant, an identifica-
tion which offers itself, since ancient glosses render Earendel with
"Jubar,"7 and Jubar is generally accepted for Venus on the presupposi-
tion that "morning star" stands every single time for Venus, which is
certainly misleading: any star, constellation or planet rising heliacally
may act as morning star. With respect to juba, i.e., literally "the mane
4R. H. Allen, Star Names (1963), p. 310.
5 Germanische Himmelskunde (1934), p. 255.
6 Sec TM, p. 375; I. Gollancz, Hamlet in Iceland (1898), p. xxxvii; Reuter, p. 256.
7O jubar, angelorum splendidissime . . . See R. Heinzel, Uber das Gedicht von
Konig Orendel (1892), p. 15.
Hamlet's Mill
356
of any animal," jubar, "a beaming light, radiance," we have, however,
Varro's clear statement: "iuba dicitur Stella Lucifer."8 Nonetheless, sev-
eral experts are against the equation Orendel/Earendel = Venus.9
Gollancz abstains from precise identifications, but he procures the one
more existing piece of evidence concerning the word Earendel:
In Anglo-Saxon glosses "earendel" ... or "oerendil" is interpreted
jubar, but "dawn" or "morning star" would probably be a better
rendering, as in the only other passage known in old English litera-
ture, viz. the Blickling Homilies (p. 163, 1. 3): "Nu seo Cristes
gebyrd at his aeriste, se niwa eorendel Sanctus Johannes; and nu se
leoma thaere sothan sunnan God self a cuman wille"; i.e., And now
the birth of Christ (was) at his appearing, and the new day-spring
(or dawn) was John the Baptist. And now the gleam of the true Sun,
God himself, shall come.10
Orendel/Earendel, then, seems to be the foremost among those which
announce some "advent," not unlike the passage in the Odyssey (73.93f.)
dealing with Odysseus' arrival in Ithaca: "When that brightest of
stars (aster phaantatos) rose which comes to tell us that the dawn is
near, the travelling ship was drawing close to an island." That might
point, again, to Venus, but there are reasons to think of Sirius, the
brightest of all fixed stars, as will come out later.
Another subject of discussion has been the etymology of the name, and
since the identity of Orendel might depend on its etymology, we have
to look into the matter, at least superficially. Jacob Grimm admitted
freely:
I am only in doubt as to the right spelling and interpretation of the
word: an OHG. orentil implies AS. earendel, and the two would
demand ON. aurvendill, eyrvendill; but if we start with ON. orven-
dill, then AS. earendel, OHG. erentil would seem preferable. The
latter part of the compound certainly contains entil = wentil.11 The
first part should be either ora, eare (auris), or else ON. or, gen. orvar
(sagitta). Now, as there occurs in a tale in Saxo Grammaticus . . . , a
Horvendilus filius Gervendili, and in OHG. a name Kerwentil.. . and
8 See W. Gundel, De stellarum appellatione et religione Romana (1907), p. 106;
Reuter, pp. 256, 29ff.
9E.g., A. Scherer, Gestirnnamen (1953), pp. 79-81.
10 Gollancz, p. xxxvin.
II In a footnote, Grimm asks (and we wish we knew the answer!): "Whence did
Matthesius [in Frisch 2, 439a] get his 'Pan is the heathens' Wendel and head bag-
piper?' Can the word refer to the metamorphoses of the flute-playing demigod?
In trials of witches, Wendel is a name for the devil, Mones anz. 8, 124."
357 • Appendices
Gerentil . . , and as geir (hasta) agrees better with or than with eyra
(auris), the second interpretation may command our assent; a sight
of the complete legend would explain the reason of the name. I think
Orentil's father deserves attention too: Eigil is another old and ob-
scure name . . . Can the story of Orentil's wanderings possibly be so
old amongst us, that in Orentil and Eigil of Trier we are to look for
that Ulysses and Laertes whom Tacitus places on our Rhine? The
names show nothing in common.
Scherer (p. 179) states shortly: "Earendel does not belong to dusos
'dawn,' nor to OE. ear 'ear' (Ahre), but to OE. ae, ear m. 'wave, sea,'
ON. aurr 'humidity.' " Gollancz, who is inclined to connect Earendel
with Eastern (ushas, eos, aurora, etc.), mentions more current deriva-
tions, among which also that from aurr "moisture," and from the root
signifying "to burn" in Greek, euo, Latin uro, Ves-uvius, etc. Decisive
seems to us the derivation from or = arrow, suggested by Grimm, and
by Uhland, who explained Orendel as the one "who operates with the
arrow" (in contrast to his grandfather, Gerentil, who worked with the
ger = spear), and Simrock gives the opinion that the very gloss "Earen-
del Jubar" designates Earendel explicitly as "beam" (or "ray"), "which
still in MHG. and Italian means 'arrow.' "12
Simrock did more. Taking into consideration that in the Heldenbuch
Orendel is spelled Erendelle, and at some other place Ernthelle, he
thinks it probable that "Ern was dropped as epitheton ornans,13 and he
concludes from there that the story of Tell shooting the apple from the
head of his son was once told of Orendel himself. That the historical (?)
Tell was not the inventor of this famous shot, or even performed it,
seems rather certain. As Grimm aptly stated:
The legend of Tell relates no real event, yet, without fabrication or
lying, as a genuine myth it has shot up anew in the bosom of Switzer-
land, to embellish a transaction that took hold of the nation's inmost
being.14
Now there is no arrow to be found that could contest with Sirius in
mythical significance. We know mulKAK.SI.DI, the "Arrow-Star" from
12Handbuch der Deutschen Mythologie (1869), § 82, p. 233.
13 Ibid. Sec also Simrock, Die Quellen des Shakespeare (1870), pp. 129f: "Dies
ward aber wohl in Tell gwkurzt, weil man die erste Silbe fur jenes vor Namen
Stehende Ehren' ansah, das nach dem d. Worterb, III 52 aus 'Herr' erwachsen, bald
fur ein Epitheton ornans angesehen wurde."
14 'I'M 3, p. xxxiv.
Hamlet's Mill
358
359 • Appendices
Sumer, as well as "Tishtriya," the arrow from Ancient Iran—it is shot
from a bow built up by stars of Argo and Canis Major (Sumerian:
mulBAN). The very same bow is to be found in the Chinese sphere, but
there the arrow is shorter and aims at Sirius, the celestial Jackal, whereas
the same Egyptian arrow is aimed at the star on the head of the Sothis
Cow, as depicted in the so-called "Round Zodiac" of Dendera—Sirius
again. In India, Sirius is the archer himself (Tishiya), and his arrow is
represented by the stars of Orion's Belt. And about all of them manifold
legends are told. Thus, "Earendel, brightest of angels thou," might well
point to the brightest among the fixed stars, Sirius.
But even the derivation from the root aurr = moisture, ear = sea,
would not exclude Sirius. Quite the contrary. The Babylonian New
Year's ritual says: "Arrow Star, who measures the depth of the sea";
the Avesta states: "Tishtriya, by whom the waters count." And as
Tishtriya, "the Arrow," watches Lake Vurukasha (see p. 215), so
Teutonic Egil is the guardian of Hvergelmer, the whirlpool, and of
Elivagar, south of which "the gods have an 'outgard,' a 'saeter' which
is inhabited by valiant watchers—snotrir vikinger they are called in
Thorsdrapa, 8—who are bound by oaths to serve the gods. Their chief
is Egil, the most famous archer in the mythology. As such he is also
called Orvendel (the one busy with the arrow)."15
We had better stop getting diffuse concerning Sirius the Arrow and
his role as guardian and as "measurer of the depth of the sea"; the few
hints that were given here must suffice to show the level at which to
look for the father of Hamlet.
Since, however, we can never resist the temptation to quote beautiful
poems, we have still to confess our suspicion that the "Stella Maris" is
Sirius too. Enough is known about Isis/Sirius as guardian-deity of navi-
gators, to whom belongs the "carra navalis," and was it not "Mary or
Christ" who was addressed with "Hail, Earendel"? In the same manner,
the hymn "In Annunciatione Beatae Mariae" begins with the verses:
Ave, maris Stella
Dei mater alma
atque semper virgo
felix caeli porta
15 V. Rydberg, Teutonic Mythology (1907), pp. 424ff., 968ff.
Sumens illud Ave"
Gabrielis ore
funda nos in pace
mutans nomen Evae.
And there is another hymn which was sung, according to the Roman
Breviary, after Compline during Advent and Christmastide, and which
has been ascribed to Herimanus Contractus of Reichenau (d. 1054),
who would appear to have lived and died a cripple in his monastery:
Alma redemptoris mater, quae pervia caeli
porta manes et Stella maris, succurre cadenti,
surgere qui curat, populo, tu quae genuisti
(natura mirante) tuum sanctum genitorem,
Virgo prius et posterius, Gabrielis ab ore
sumens Mud Ave, peccatorem miserere.
"What I have been attempting to suggest," says the interpreter of this
hymn,16 "is that the attraction of this charming mediaeval prayer and
hymn would seem to come, in large measure, from the intentional am-
biguity, the different levels of meaning, and the sunken imagery . . .
The 'nourishing mother' is perhaps pictured as a fixed constellation in
the heavens, or perhaps as the morning star, guiding those on the sea.
She is a celestial passage-way, always passable and ever accessible . . .
The falling and rising has now (besides the constantly falling sinners)
perhaps the further overtones of heavenly bodies rising and falling,
perhaps of ships rising and falling on the sea, and lastly of tottering
children who need their mother's help to walk . . . The poem ... is a
very striking one, and its force derives, in my view, from the subtle
imagery of the first three lines . . . They offer us a symbol, a verbal
icon, of the entire situation of man on earth in his struggle to rise to
the stars, of his need of an otherworldly force which is at once strong
and loving."
16 H. Musurillo, S.J., "The Medieval Hymn, Alma Redemptoris," Classical
Journal 52 (1957), pp. 171-74.
Hamlet's Mill
360
Appendix 3
Now, apart from the circumstance that the snowy burial ascribed to
the followers of Kai Khusrau, Enoch, and Quetzalcouatl could hardly
be claimed to be an "obvious" feature, the fate of Quetzalcouatl's com-
panions might further our understanding; more correctly, the topos
where this event is supposed to have happened might do so. The "five
mountains" of Mexican myth, their "gods" respectively, the Tepicto-
ton,1 appear to represent the five Uayeb (== Maya; with the Aztecs:
Nemontemi), the Epagomena, those days gained by Mercury from the
Moon during a game of checkers, in order to help Rhea/Nut to days
"outside of the year," when she could bring forth the five planets. As a
matter of fact, in his chapter on the clothes and emblems of the gods,
Sahagun puts the "Mountain-Gods" at the end of the list.2
Worth mentioning might be two more traits which Quetzalcouatl
shares with his old-world brethren: Quetzalcouatl and Uemac, like Kai
Ka'us and Kai Khusrau, are said to have ruled together, and Quetzal-
couatl is accused of incestuous relations with his sister, as were Hamlet,
Kullervo, Yama and, we might add, King Arthur.3
Appendix
It is as yet too early in the day to deal with "Uncle Kamsa," whom
lexicographers make a "mura-deva" allegedly a "venerator of roots"
(mula/mura = root). In his Kleine Beitrdge (p. n), Jarl Charpentier
earnestly wishes us to accept as fact that "among the Indian natives fight-
ing against the invading Aryans, there were such," namely, "venerators
of roots" (and venerators of worms as well). Although we do not doubt
that the species Homo sapiens is capable of any "belief," we cannot
1 See E. Seler, Gesammelte Abhandlungen, vol. 2, p. 507, for an Aztec drawing
of the Tepictoton.
2 See T. S. Barthel, "Einige Ordungsprinzipein im Aztekischen Pantheon,"
Paideuma 10 (1964), pp. 80f., 83. In this paper, Barthel has established, in a
rather convincing manner, the presence of decans in Mexican astronomy.
8 See W. Krickeberg, "Mexicanisch-peruanische Parallelen," in Festschrift
P. W. Schmidt, p. 388.
361 • Appendices
perceive any cogent reason for subscribing to Charpentier's view.
Mula/mura, the "root," is a Nakshatra, a lunar mansion woven around
with tales: it is the sting of Scorpius, serving as Marduk's weapon in the
"Babylonian Genesis," and as Polynesian Maui's fishhook; with the
Copts it is "statio translationis Caniculae . . . unde et Siot vocatur," i.e.,
the Coptic table of lunar stations takes lambda upsilon Scorpii as the
precise opposite of Sirius/Sothis, as we are informed by Athanasius
Kircher, whereas Indian tables ascribe the role of exact opposition to
Betelgeuse, ruled by "Rudra-the-destroying-archer." Although we can-
not pursue these and other tales further here, we think it at least appro-
priate to mention the concrete problems arising with such characters as
"Uncle Kamsa," instead of accusing a true Asura of "veneration of
roots."
Appendix 5
Sem Snaebjoern krad:
Hvatt kveda hraera Grotta
hergrimmastan skerja
ut fyrir jardar skauti
Eyludrs niu brudir;'
thaer er, lungs, fyrir laungu
lid-meldr, skipa hlidar
baugskerdir ristr bardi
bol, Amloda molu
Her er kallat hafit Amloda Kvern.
Gollancz (Hamlet in Iceland, p. xi) retranslated his translation into
Old Norse so tjiat the original and the nolens volens interpreting transla-
tion might be compared. The retranslation runs thus: kveda niu brud-
ir eyludrs hraera hvatt hergrimmastan skerja grotta ut fyrir jardar skauti,
thaer er fyrir longu molu Amloda lid-meldr; baugskerdir ristr skipa
hlidar bol lungs bardi. Elton translates the passage:
"Men say that the nine maidens of the island-mill (the ocean) are
working hard at the host-devouring skerry quern (the sea), out beyond
Hamlet's Mill
362
363 • Appendices
the skirts of the earth; yea, they have for ages been grinding at Am-
lodi's meal-bin (the sea)."1
Rydberg, too, offers a translation:
"It is said, that Eyludr's nine women violently turn the Grotte of
the skerry dangerous to man out near the edge of the earth, and that
those women long ground Amlode's lid-grist."2
In spite of the trickiness and the traps of the text Gollancz tries to
solve the case; in fact, he tries too frantically (p. xxxvi): "The com-
pound ey-ludr, translated 'Island-Mill,' may be regarded as a synonym
for the father of the Nine Maids. Ludr is strictly lthe square case within
which the lower and upper Quernstones rest' hence the mill itself, or
quern."
With this we wish to compare O. S. Reuter's explanation: "ludr =
Miihlengebalk (dan. Luur = das Gerilst zu einer Handmuhley (Ger-
manische Himmelskunde, p. 239; he also includes a drawing of the mill).
On p. 242, note, he renders the lines of Skaldskap. 25: "Neun Scharen-
braute ruhren den Grotti des Inselmiihlkastens (eyludr) draussen an
der Erde Ecke (ut fyrir jardar skauti)," adding: "Das (kosmische?)
Weltmeer ist als 'Hamlets Muhle' gesehen." At least he thought, even if
within brackets and with a quotation mark, of "cosmic"—Rydberg is
the only one who has grasped this point completely.
"Ey-ludr," Gollancz continues, "is the 'island quern,' i.e., 'the grinder
of islands,' the Ocean-Mill, the sea, the sea-god, and, finally, Aegir.
'Aegir's daughters' are the surging waves of the ocean; they work
Grotti 'grinder,' the great Ocean-Mill (here called 'skarja grotti,' the
grinder of skerries, the lonely rocks in the sea), 'beyond the skirts of
the earth' or perhaps, better, 'off yonder promontory.' The latter mean-
ing of the words 'ut fyrir jardar skauti' would perhaps suit the passage
best, if Snaebjorn is pointing to some special whirlpool." Non liquet:
neither Aegir = eyludr, nor the nine maidens = waves, whether surg-
ing or not.
As concerns "off yonder promontory" which sounds ever so poetical
and indistinct, see J. de Vries:3 skaut n. Ecke, Zipfel, Schoss, Kopftuch,
eig. "etwas Hervorragendes" . .. Dazu skauti m. "Tuch zum Einhullen,"
ae. sceata "Ecke, Schoss, Segelschote." fyr. praep. praef. "vor," durch,
1 Saxo Grammaticus, Danish History, p. 402.
2 Teutonic Mythology, § 80, p. 568.
3 Altnordisches Etymologisches Worterbuch (1961).
wegen, trotz, fur ... —lat. prae "voran, voraus," lat. prior "der fruhere"
—which tells us either nothing at all or, if we take "prior" for the
proper translation, tells us the whole "story" by means of one single
word; in the same manner as the mere fact that the pillars of Hercules
were "fyr," called the pillars of Briareos, and before that time, the pil-
lars of Kronos.
We stick, however, to Gollancz for some more lines. "The real dif-
ficulty," he says, "in Snorri's extract from Snaebjoern is ... in its
last line; the arrangement of the words is confusing, the interpreta-
tion of the most important of the phrases extremely doubtful. 'Lid-
meldr' in particular has given much trouble to the commentators:
'meldr,' at present obsolete in Icelandic, signifies 'flour or corn in the
mill'; but the word Hid' is a veritable crux. It may be either the neuter
noun 'lid,' meaning 'a host, folk, people,' or ship, or the masculine
'lidr,7 'a joint of the body.' The editors of the Corpus Poeticum Boreale
read 'meldr-lid,' rendering the word 'meal-vessel'; they translate the
passage, 'who ages past ground Amlodi's meal-vessels = the ocean';
but 'mala' 'to grind,' can hardly be synonymous with 'hraera,' 'to
move,' in the earlier lines, and there would be no point in the waves
grinding the ocean. There seems, therefore, no reason why rneldr-lid
should be preferred to lid-meldr, which might well stand for 'ship-
meal' (sea-meal), to be compared with the Eddie phrase 'graedis
meldr,' i.e., sea-flour, a poetical periphrasis for the sand of the shore.
Rydberg [Teutonic Mythology (1907), pp. 570ff. = pp. 388-92 in the
1889 edition], bearing in mind the connection of the myth concerning
the fate of Ymer's descendant Bergelmer, who, according to an inge-
nious interpretation of a verse in Vafthrudnismal 'was laid under the
millstone,' advanced the theory that 'lid-meldr' means 'limb-grist.'
According to this view, it is the limbs and joints of the primeval giants,
which in Amlodi's mill are transformed into meal . . . Snorri does not
help us. The note following Snaebjoern's verse merely adds that here
the sea is called "Amlodi's kvern.' "
In a note Gollancz adds that in some other manuscript he found the
version: "Here the sea is called 'Amlodi's meal' " (Amloda melldur),
and concludes: "No explicit explanation is to be found in early North-
ern poetry or saga. 'Hamlet's Mill' may mean almost anything." It is
not as bad as that. Moreover, Gollancz (p. xvii, note) detected more
relevant figures of speech in the four lines cited below which he
Hamlet's Mill
ascribes to Snaebjorn: "The island-mill pours out the blood of the flood
goddess's sisters (i.e., waves of the sea), so that (it) bursts from the
feller of the land: whirlpool begins strong."
svad or fit jar fjoetra,
ftods asynju bolde
(roest byrjask roemm) systra
rytr, eymylver snyter.
To which he adds: "In no other drottkvoett verse does eymylver occur:
cp. eyludr above."
Appendix 6
It is not as easy to dispose of My sing, as the specialists pretend, e.g.,
by preferring to interpret his name as "mouse-gray" instead of the
equally possible "son of a mouse." Olrik (pp. 459f.) proposes to identify
straightaway "King Mysing who killed Frith-Frothi, and the cow that
struck down Frothi the Peaceful . . . King Mysing is merely a rational-
istic explanation of the ancient monster." (For the death of Frodi by
means of a sea cow, see also P. Herrmann's commentary on Saxo,
pp. 380-84. This "cow"—in Iceland they remain within the frame of
zoology and make it a stag—was, according to Saxo, a witch, who was
pierced through by Frodi's men. Afterwards they kept Frodi's death a
secret for three years, in the same manner as told by Snorri in his
Heimskringla about Frey.)
A. H. Krappe, more observant, compared Mysing with Apollon
Smintheus, the old "mouse-god" (ARW 55 [1936], pp. 40-56). He had
in his mind, however, only the connection—undeniable as it is—between
mice and rats and the plague, and the dragging-in of Smintheus does
not much further the understanding of Mysing. This state of things
was changed with the publication of the work by Henri Gregoire, R.
Goossens and M. Matthieu, "Asklepios, Apollon Smintheus et Rudra:
Etudes sur le dieu a la taupe et le dieu au rat dans la Grece et dans
l'lnde," although they do not even mention our Mysing, and although
they loudly praise (p. 157) the merit of "Meillet . . . d'avoir fait
365 • Appendices
descendre la mythologie du ciel sur la terre"; with Rudra, and with the
rat of Ganesha (who, by the way, acquired his elephant's head because
the planet Saturn, not being invited to the infant's "baptism," had
looked upon the baby with his evil eye, thus destroying his head which
was successfully replaced by that of an elephant), the mouse plot has
got much deeper background. Nevertheless, the identity and the role
of the mouse deity is hardly going to be settled without taking into
account (1) "the tailed Mus Parik, arrayed with wings; the Sun fet-
tered her to his own ray, so that she could not perpetrate harm; when
she becomes free, she will do much injury to the world, till she is
recaptured, having come eye-to-eye with the Sun"; this enigmatical
winged mouse comes from the world horoscope in the Iranian Bunda-
hishn (chapter V, A, Anklesaria translation, p. 63); (2) the colorful
Polynesian myths dealing with the rat that gnawed through the "Nets
of Makalii," i.e., Hyades and Pleiades; she could do so unpunished being
Makalii's very own sister; (3) the warriors, in the guise of mice, of
Llwyd, son of Cil Coed, "who cast enchantment over the seven cantrefs
of Dyfed ... to avenge Gwawl son of Clud," in the third branch of the
Mabinogi. There are more items, to be sure, but we have to leave it
at that.
Appendix 7
We want to stress the point that the haughty verdicts as given by
Genzmer, Olrik, and others on Snorri's tale are not unknown to us. Their
opinions run along these lines: "The last part of the story of Grotti and
Mysing is 'How the sea grew salt.' This is a different motif, in no wise
connected with the peace of Frothi."1 Genzmer's wording is more
arrogant still. The transportation of the mill by Mysing and the grind-
ing of salt aboard the ship is "die Anschweissung einer zweiten selb-
standigen Sage; der grossartig einfache, ahnungsvolle Schluss unserer
Dichtung wird durch ein solches Anhangsel todlich geschadigt."2
It would be more adequate to state that the myth has been "fatally
damaged" by the modern experts, and not by Snorri. When we come to
1 A. Olrik, The Heroic Legends of Denmark (1919), p. 460.
2 Edda trans. F. Genzmer (1922), Thule, p. 181.
Hamlet's Mill
366
the little salt-mill of Kronos, the reader will understand the plot better.
Olrik (pp. 457f.), however, has some pretty survivals to offer:
In 1895, Dr. Jakob Jakobsen, the well-known collector of the rem-
nants of the ancient "Norn" language of the Western Islands, was
informed by an old Shetlander, whose parents had come from the
Orkneys (Ronaldsey) that near the most northerly of these islands
there was an eddy called "the Swelki" [that is, Snorri's svelgr, "sea-
mill, where the waters rush in through the eye of the mill-stone"].
On that spot a mill stood on the bottom of the sea and ground salt;
and a legend of Grotti-Fenni and Grotti-Menni was connected with
it. In the course of later investigations in the Orkneys themselves
(South Ronaldsey) he learned about the sea mill in the Pentland
Firth grinding salt. In 1909, Mr. A. W. Johnstone was told by a lady
from Fair Isle that Grotti Finnie and Lucky Minnie were well known
in her native island, being frequently invoked to frighten naughty
children. Although the legend in those parts is in a fragmentary con-
dition, reduced to incoherent survivals, the tenacity of the oral tra-
dition shows how deeply rooted the legend is in these islands. Outside
of the Orkneys neither Mysing nor his salt mill are known to tradi-
tion except in the songs of the Edda which themselves bear the stamp
of Western provenience.
Appendix 8
Vafthrudnismal 35 is rendered by Gering: "Ungezahlte Winter vor
der Schopfung / geschah Bergelmirs Geburt. / Als fruhestes weiss ich,
dass der erfahrene Riese / Im Boote geborgen ward." Simrock translates
similarly, and he remarks (Hdb. Dt. Myth., § 9): "Das dunkle Wort
ludr fur Boot zu nehmen, sind wir sowohl durch den Zusammenhang
als durch die Mythenvergleichung berechtigt."
R. B. Anderson (The Younger Edda [1880], pp. 6of.) translates the
verse—quoted by Snorri (Gylf. 7)—as follows: "Countless winters /
Ere the earth was made, / Was born Bergelmer. / The first I call to
mind / How the crafty giant / Safe in his ark lay."
Neckel and Niedner (Die Jungere Edda, pp. 54f.) state that Bergel-
mer and his wife "stieg auf seinen Muhlkasten und rettete sich so." The
lines above they render with the words: "Als fruhestes weiss ich, dass der
vielkluge Riese in die Hohe gehoben ward," adding in a footnote: "Das
oben mit 'Mahlkasten' wiedergegebene Wort ubcrsctzt man gewohnlich
367 . Appendices
mit 'Boot' oder auch mit 'Wiege,' ohne Begrundung und gegen den
Wortlaut der Prosa. Gegen den gewohnlichen Wortsinn 'Mahlkasten'
(Muhlsteinbehalter auf Pfosten) spricht nichts. Freilich kennen wir
den angedeuteten Vorgang des Naheren nicht und wissen daher auch
nicht, warum der Riese gehoben ('gelegt') werden musste, und wer
ihn aufhob."
The ominous word ludr occurs again in Helgakvida Hundingsbana
11, 2-4, where Helge—seeking refuge from king Hunding—works in a
mill, disguised as a female, and almost wrecks the ludr.
In common with the mythologists who defend the "boat," in
Vafthrudnismal 35, feeling entitled to it on account of comparative
mythology (see Simrock, quoted some lines ago), and whom he fights
explicitly, Rydberg upholds the notion that the Ark was a ship. It will
come out later that this general notion is incorrect.
Appendix
As a matter of fact, Simrock already (Handbuch der Deutschen My-
thologie, pp. 240f.) ventured to interpret Fengo (Amlethus' evil uncle)
as "the grinding," and Amlethus as "the grain"; "wo selbst der Name mit
Amelmehl [Greek amylon], Starkemehl, Kraftmehl ubereinstimmt."
He even thought of the possibility (although taking this thought for
audacious, "gewagt") to derive the family name of Thidrek's clan, i.e.,
the name of the Amelunge, from "Amelmehl." We shan't dwell upon
the strange information given by Athenaeus (Deipnosophistai 3.114f)
about "Achilles, or very fine barley" (cf. Theophr. 8.4.2. Aristoph.
Eq. 819: Achilles cake), or on the surname of Ningishzida, namely
Zid-zi "Meal of Life" (K. Tallqvist, Akkadische Gotterepitheta, p. 406;
cf. Riemschneider, Augengott, p. 133), and we point only to Ras Shamra
texts, where the lady Anat ground Mot. (See C. Gordon, Ugaritic
Literature, p. 45.) H. L. Ginsberg (ANET, p. 140) translates 1 ab, col. ii:
She seizes the Godly Mot
With swords she does cleave him.
With fan she does winnow him
With fire she does burn him
Hamlet's Mill
368
369 • Appendices
With hand-mill she grinds him
In the field she does sow him.
Birds eat his remnants
Consuming his portions
Flitting from remnant to remnant.
An astonished footnote states: "But somehow Mot comes to life entire
in col. vi, and Baal even earlier." But there is absolutely nothing aston-
ishing enough to shake the firm belief of experts in "chthonic" deities.
Appendix 10
For the first Irish harp (cruit), see Eugene O'Curry, On the Manners
and Customs of the Ancient Irish, vol. 5 (1873), pp. 236f.; see also Ru-
dolf Thurneysen, Die irische Helden- und Konigssage bis zum 17.
Jahrhundert (1921),pp. 264f.
There once lived a couple . . . And the wife conceived a hatred to
him, and she was flying from him through woods and wilderness; and
he continued to follow her constantly. And one day that the woman
came to the sea shore of Camas, . . . she met a skeleton of a whale on
the strand, and she heard the sounds of the wind passing through the
sinews of the whale on the strand, and she fell asleep from the sounds.
And her husband came after her; and he perceived that it was from
the sounds the sleep fell upon her. And he then went forward into the
wood, and made the form of a Cruit;1 and he put strings from the
sinews of the whale into it; and that was the first Cruit that was ever
made.
Marbhan's legend about the beginnings of instruments and verses
continues:
And again Lamec Bigamas had two sons, Jubal and Tubal Cain were
their names. One son of them was a smith, namely, Jubal; and he dis-
covered from sounds of two sledges (on the anvil) in the forge one
day, that it was verses (or notes) of equal length they spoke, and he
composed a verse upon that cause, and that was the first verse that
was ever composed.
1 "The word Cruit . . . signifies literally, a sharp high breast, such as of a goose,
a heron, or a curlew" (O'Curry, loc. cit.).
The legend goes on to report, why the timpan—another stringed in-
strument, different from the cruit—was called Timpan Naimh (or
saint's Timpan), because "at the time that Noah, the son of Lamech,
went into the Ark, he took with him a number of instruments of
music into it, together with a Timpan, which one of his sons had, who
knew how to play it." When they finally left the ark, Noah caused
his son to name the instrument after his own name, and only under
this condition would he give it to him. "So that Noah's Timpan is its
name from that time down; and that is not what ye, the ignorant
timpanists, call it, but Timpan of the saints."
We introduce this legend for several reasons; first, because we felt
reminded at once, as O'Curry did (p. 237), "of Pythagoras, who is
said to have been led to discover the musical effect of vibrations of a
chord by observing the sound of various blows on an anvil, though the
Irish legend . . . does not appear to bear on the tones so much as on
the rhythm of music." Second, because here we learn again about two
successive stringed instruments, separated, so to speak, by a flood;
Vainamoinen lost his Kantele when going to steal the Sampo, and had
to construct a new one from wood, afterwards. These traditions must
be thoroughly compared, one day, with the different lyres of Greece;
we know that one was destroyed by Apollon—allegedly in a fit of
repentance—after he had flayed Marsyas, and that Hermes made an-
other one and presented it to Apollon; pike and whale of the northern
seas have apparently replaced the turtle of Greek myth. We also know
that the Pleiades, called the Lyre of the Muses by the Orphics, existed
side by side with Lyra. And Michael Scotus still knew about a turtle
figuring, so to speak, as prow of Argo, and "out of which the celestial
lyre is made."2 But before being trapped between the devil and the
deep sea, we prefer to stop, although this turtle seems to be placed
exactly there, where it "should" be, considering that upon its back the
Amritamanthana was accomplished. We shall hear more about that
considerable and mysterious man, Michael Scotus, later (see p. 258).
The long and the short of the various traditions is that with a new
age new instruments, new strings, or, as in the case of Odysseus, a new
peg are called for: a new "Harmony of the Spheres."
2 Testudo eius (navis) est prope quasi prora navis...
est lyra cacli. Cf. F. Boll, Sphaera, p. 447.
de qua testudine facta
Hamlet's Mill
Appendix 11
Christensen, in his work on the Kayanids,1 states: "La tradition na-
tionale fait grand cas du forgeron Kavag, qui s'insurgeait contre l'usur-
pateur Dahag (le Dahaka des Yashts) et hissait son tablier de cuir sur
une lance, ce qui fut l'origine du drapeau de l'empire sassanide, appele
drafs e kavyan, 'drapeau de Kavag.' Cette legende, nee d'un malentendu,
la vraie signification-du nom de drafs e kavyan etant 'le drapeau royal,'
est inconnue dans la tradition religieuse."
By means of such statements—apart from "modestly" insinuating that
Firdausi spun whole chapters of his Shahnama out of "malentendus"—
the way to relevant questions is effectively blocked. The story of the
smith Kavag—also written Kaweh,2 or Kawa—is told by Firdausi in
the book dealing with the 1,000 years' rule of Dahak, that fiendish tyrant
out of whose shoulders grew two serpents3 that had to be fed with the
brains of two young men every day. The predestined dragon-slayer,
and much expected savior, Faridun—Avestan Thraethona—a true pre-
decessor of Kai Khusrau, had been saved from the snares of Dahak as a
baby, and hidden away in the mountains. When the archdevil Dahak
claimed the sacrifice of the last son of Kaweh—seventeen sons had
already been fed to the dragon-heads—the smith started the revolution
for the sake of Faridun:
He took a leathern apron, such as smiths
Wear to protect their legs while at the forge,
Stuck it upon a spear's point and forthwith
Throughout the market dust began to rise . . .
He took the lead, and many valiant men
Resorted to him; he rebelled and went
To Faridun. When he arrived shouts rose.
He entered the new prince's court, who marked
1 A. Christensen, Les Kayanides (1932), p. 43.
2F. Justi, Iranisches Namenbuch (1895), p. 160. In the most recent translation of
the Shahnama (Firdousi: Das Konigsbuch [1967]—so far, only Pt. 1, Bks. 1-5 have
come out), H. Kanus-Crede boldly identifies the smith Kawa with "awestisch
Kawata," i.e., with Kai Kobad, the first Iranian ruler.
3 Dahak with his two additional serpent heads is the same as the "powerful, rav-
ing Dasa with his 6 eyes and 3 heads" of RV 10.99.6.: Visvarupa, son of Tvashtri,
and "Schwcstersohn der Asura"; cf. Mbh. 7.2.343 (Roy trans., vol. 10, p. 572).
371 • Appendices
The apron on the spear and hailed the omen.
He decked the apron with brocade of Rum
Of jewelled patterns on a golden ground,
Placed on the spear point a full moon—a token
Portending gloriously—and having draped it
With yellow, red, and violet, he named it
The Kawian flag. Thenceforth when any Shah
Ascended to the throne, and donned the crown,
He hung the worthless apron of the smith
With still more jewels, sumptuous brocade,
And painted silk of Chin. It thus fell out
That Kawa's standard grew to be a sun
Amid the gloom of night, and cheered all hearts.
Now, if there was only the "royal" flag to explain, why should Fir-
dausi (or his sources) invent a smith with the name Kaweh (Kavag,
Kawa), if there was no connection whatever between kingship and the
smith? Even if we leave out of consideration the widely diffused motif
of great smiths as foster-fathers and educators of the hero4 as well as
the Chinese mythical imperial smiths, and all the material collected by
Alfoldi in his article on smith as a title of honor among the kings of
Mongols and Turks:5 the very name of the dynasty of Iranian kings
which is of the greatest interest for us, i.e., the Kayanides, is derived
from Kavi/Kawi.6 The most "kawian" Shah is Kai Ka'us, whose
name even contains the relevant word twice, the "Kavi Kavi-Usan,"
who cannot be separated from Kavy Usa (or Usanas Kavya) of the
Rigveda and the Mahabharata,7 who shows several of the decisive char-
4 To mention only Mimir, Regin, Gobann. Kaweh's son Kama, by the way,
whose life was spared thanks to the rebellion, became a famous paladin of Faridun,
as Wittige/Wittich, son of Waylant the smith, became a strong paladin of Thidrek.
5 Cf., for Turkish traditions, R. Hartmann, "Ergeneqon," in Festschrift Jacob
(1932), pp. 68-75.
6 For the word kavi, see H. Lommel, Die Yashts des Avoesta (1927), pp. 171f.;
E. Herzfeld, Zoroaster and His World (1947), pp. 100-109.
7 See Lommel's article "Kavy Ucan," in Melanges linguistiques offerts a Charles
Bally (1939), pp. 210f. That C. Bartholomac (Altiranisches Worterbuch [1904],
col. 405) confesses that he is "unable to find relations" between Iranian Kavi
Usan and Rigvedian Kavy Usha is a precious gem in the collection of philological
atrocities. 'Tails meine Ktymologie richtig ist, entfallt auclh die Namensahnlich
keit." Similarity he calls it! It will come out in the course of this essay that his
Hamlet's Mill
372
373 • Appendices
acteristics of the Deus Faber. Not alone is he said to have forged the
weapon for Indra8—instead of Tvashtri—and to have given Soma to
Indra who, otherwise, has stolen (or has just drunk) the Soma in the
"House of Tvashtri" (e.g., RV 3.48.2f.), but we are told that, during
one of the never-ceasing wars between Asura and Deva for the "three
worlds," the Asura elected Kavya Ushanas for their "priest" or "mes-
senger,"9 the Deva elected Brihaspati (or Vrihaspati, i.e., Jupiter, in
Taittiriya Sanhita Agni). Many warriors were slain on both sides, but—
so the Mahabharata tells—"the open-minded Vrihaspati could not revive
them, because he knew not the science called Sanjivani (re-vivification)
which Kavya endued with great energy knew so well. And the gods
were, therefore, in great sorrow."10 The Bundahishn, in its turn, gives
the following report in chapter 32, dedicated to "the mansions which
the Kayans erected with glory, which they call marvels and wonders,"11
in verse 11: "Of the mansions of Kay Us one says: 'One was of gold
where-in he settled, two were of glass in which were his stables, and
two were of steel in which was his flock; there-from issued all tastes,
and waters of the springs giving-immortality, which smite old-age,—
that is, when a decrepit man enters by this gate, he comes out as a youth
of fifteen years from the other gate,—and also dispel death." According
to Firdausi, Kai Ka'us had a kind of balm by means of which he could
have restored Shurab to life, but he did not give it to Shurab's father
Rustem who implored him for this gift.12 To which Lommel remarks
proposition to derive the name Usan from "usa- m. (1) Quelle, Brunnen; (2) Ab-
fluss, Leek . . ," is no obstacle at all to the understanding of Kavy Usan. Kronos
too has been derived from Greek krounos, i.e., "source," "spring" (see Eisler,
Weltenmantel, pp. 3782, 385, reminding us also of the Pythagorean formula con-
cerning the sea: "Kronou dakryon, the tear of Kronos").
8RV 1.51.10; 121.12, 5.34.2. It is particularly the Shushna-myth, where K. U.
replaces Tvashtri.
9 Taittiriya Sanhita 2.5.8 (Keith trans., vol. 1, p. 198).
10Mbh. 1.76 (Roy trans., vol. 1, p. 185). For this role of Kavya Ushanas, cf.
Geldner, in R. Pischel and K. F. Geldner, Vedische Studien, vol. 2 (1897), pp.
166-70; for a life-restoring lake or well, owned by the "wicked Danavas," see Mbh.
8.33 (Roy trans., vol. 7, p. 83). In Ireland the Tuatha de Danann were able to
revivify the slain (in the Second Battle of Mag Tured), the Fomorians were not.
11 "Zand-Akasih: Iranian or Greater Bundahishn, trans, by B. T. Anklesaria
(1956), p. 271; cf. Christensen, p. 74.
12 In the same manner, Lug—the strength and heart of the Tuatha De Danann
as Krishna was that of the Pandava—denies the revivifying pig's skin to Tuirill
who, by means of it, could have restored to life his three sons, Brian, Juchair, and
Jucharba.
(Melanges Bally, p. 212): "Und das ist der hasslichste Zug im Bilde des
Kay Kaus, dass er die Herausgabe des Wunderheilmittels verweigert,
da Rostem und Sohrab, wenn beide am Leben waren, vereint ihm zu
machtig waren." It is a rather idle occupation to look for "ugly traits"
in the "character" of the Demiurge, even if he comes our way in the
disguise of a Shah.
These few hints must suffice for now; it is bad enough that the burden
of "proof" rests with the defenders of sense in our deteriorated century,
whereas everyone who presupposes non-sense and "malentendus" can
get away with the most preposterous claims. In other words: even if the
individual Kaweh/Kavag should have been "invented" by Firdausi, the
notion of the Deus Faber and Celestial Smith as the disposer and guard-
ian of kingship,13 as the original and legitimate owner of the "water of
life,"14 is by no means an accidental fancy,15 and the significance and
meaning of the smith's apron as "Kawian flag" would have been under-
stood from China to Ireland.
Appendix 12
It should be stressed that the disinclination of philologists to allow for
the "essential" connection of Chronos and Kronos rests upon the stern
belief that the "god" Saturn has nothing to do with the planet Saturn,
and upon the supposition that an expert in classical philology has
nothing whatever to learn from Indian texts. Were it not so, they might
have stumbled over Kala, i.e., Chronos, as a name of Yama, i.e., Kronos,
alias the planet Saturn.
13 To repeat: the "Lord of the Triakontaeteris," the period of thirty years, i.e.,
the Egyptian and Persian "Royal Jubilee" (Saturn's sidereal revolution), is Ptah-
Hephaistos.
14 Also of the intoxicating beverage replacing it; Soma belonged to Tvasthri; Irish
Goibniu brewed the ale which made the Tuatha De Danann immortal, and the
beer of the Caucasian smith Kurdalogon played the same role. When Sumerian
Inanna was almost lost in the underworld, it was Enki who gave to his messengers
the life-restoring fluid with which to besprinkle the goddess. And, last but not
least, it is Tanc/Kane, the Polynesian Deus Faber, whose are "the Living Waters."
15 Leo Frobenius, when accused—as happened sometimes—of having been de-
ceived by African informants who "made up" any amount of fairy talcs which
were not "true," used to smile benevolently, and to point to what he called
"stilgerechte Phantasie."
Hamlet's Mill
374
375 • Appendices
Indians have indeed, written more about their Kala—and the Iranians
about their Zurvan—than the Greeks about Chronos, but with the
translated Vedas being what they are, we won't claim the relevant texts
to be transparent, nor the scholarly interpretations to be particularly
elucidating, all of the experts starting, as they do, from the unfounded
conviction that "astrology" must be a "late" phenomenon.
To throw "identifications" around, does not lead anywhere, in our
opinion, so we do not mean to simplify by nailing down, once and for
all, Kala/Chronos as being the very same as Yama/Kronos/Saturn. To
recognize Kronos/Saturn as auctor temporum is quite sufficient for the
time being,1 and so are the Indian notions, according to which Yama is
often called Kala; in other passages he is the commander of Kala (and
Kala, in his turn, the commander of Mrityu, Death).2
Kala plays his unmistakable role already in Rigveda 164, but the
Atharva Veda dedicates to this "god" two whole hymns (19.53 and
19.54), and it is worth recalling Eisler's statement (Weltenmantel, p.
499): "Zu dieser Kala-Lehres des Atharvaveda ist spater nichts mehr
dazugekommen; die jungeren Quellen fuhren nur die Vorstellungen
weiter aus."
Here are some verses from these two hymns dedicated to Kala,
without the numerous notes and comparisons with other translations, as
treated by Bloomfield and Whitney (Atharva Veda, trans, by Bloom-
field [1964], pp. 224f.):
19.53: (1) Time, the steed, runs with seven reins (rays), thousand-eyed,
ageless, rich in seed. The seers, thinking holy thoughts, mount him, all
the beings (worlds) are his wheels.
(2) With seven wheels does this time ride, seven naves has he, immor-
tality is his axle. He carries hither all these beings (worlds). Time, the
first god, now hastens onward.
(3) A full jar has been placed upon Time; him, verily, we see existing
in many forms. He carries away all these beings (worlds); they call him
Time in the highest heaven.
1 We do not think it is an "accident" that this originator of time begins with the
letter X, representing the obliquity of the ecliptic in Plato's Timaeus.
2 See J. Scheftelowitz, Die Zeit als Schicksalsgottheit in der indischen und irani-
schen Religion (1929), pp. 18ff. See also Burgess (Surya Siddhanta, p. 5), who
generalizes: "To the Hindus, as to us, Time is, in a metaphorical sense, the great
destroyer of all things; as such, he is identified with Death, and with Yama, the
ruler of the dead."
(4) He surely did bring hither all the beings (worlds), he surely did
encompass all the beings (worlds). Being their father, he became their
son; there is, verily, no other force higher than he.
(5) Time begot yonder heaven, Time also (begot) these earths. That
which was, and that which shall be, urged forth by Time, spreads out.
(6) Time created the earth, in Time the sun burns. In Time are all
beings, in Time the eye looks abroad. . . .
(8) ... Time is the lord of everything, he was the father of Prajapati.
(9) By him this (universe) was urged forth, by him it was begotten,
and upon him this (universe) was founded. Time, truly, having become
the brahma (spiritual exaltation), supports Parameshtin (the highest
lord).
(10) Time created the Greatures (prajah), and Time in the beginning
(created) the lord of creatures (Prajapati), the self-existing Kashyapa
and the tapas (creative fervour) from Time were born.
19.54: (1) From Time the waters did arise, from Time the brahma
(spiritual exaltation), the tapas (creative fervour), the regions (of space
did arise). Through Time the sun rises, in Time he goes down again.
(2) Through Time the wind blows, through Time (exists) the great
earth; the great sky is fixed in Time. In Time the son (prajapati) begot
of yore that which was, and that which shall be.
(3) From Time the Rks (= the Rig Veda) arose, the Yajus (= the
Yaiur Veda) was born from Time; Time put forth the sacrifice, the
imperishable share of the gods.
(4) Upon Time the Gandharvas3 and Apsarases are founded, upon
Time the worlds (are founded), in Time this Angiras and Atharvan
rule over the heavens.
(5) Having conquered this world and the highest world, and the holy
(pure) worlds (and) their holy divisions; having by means of the
brahma conquered all the worlds, Time, the highest God, forsooth,
hastens forward.
3 See A. Weber (Die Vedischen Nachrichten uber die Nakshatras, Pt. 2, p. 278,
n. 3) about the Gandharvas as representing the days of the "year" of 360 days,
according to the Bhagavata Purana 4.29.21 (Sanyal trans., vol. 2, p. 145); the
Indians reckoned with several types of "years" at the same rime, and so did the
Maya.
Hamlet's Mill
376
Where we alternately read once "beings," and "worlds," the San-
skrit word is bhuvana, from the radical bhu- (= Greek phyo-) as dis-
cerned from the radical as-, bhu- meaning "to be" in the sense of per-
petual change, "coming to be and passing away," as- being reserved for
the changeless, timeless existence beyond the planetary "instruments of
time," the organa chronou of Plato's Timaeus. As a matter of fact,
Plato would have understood at once the verbs bhu- and as-, and he
might well have applauded the utterance of the vanquished Daitya
KingVali:4
"O Indra! Why are you vaunting so much? All persons are prac-
tically urged on by Kala in engaging themselves in an encounter. To
the heroes, glory, victory, defeat and death gradually come to pass.
This is the reason that the wise behold this universe as being guided
by Kala, and they therefore neither grieve nor are elated with joy."
Nor is there much "primitive belief" to be squeezed out of such
statements as "many thousand Indras and other divinities have been
overtaken by Kala in the course of world periods."5 But the classicists
usually prefer to keep silent about the most revealing sentence of Anaxi-
mander, handed down to us by Cicero (De Natura Deorum 1.25): "It
is the opinion of Anaximander, that gods are born in long intervals of
rising and setting, and that they are innumerable worlds (or the—much
discussed—innumerable worlds. Anaximandri autem opinio est, nativos
esse deos longis intervallis orientis occidentisque eosque innumerabiles
esse mundos)"; and if they do not keep silent, they claim it to be
"much more natural" to understand these intervals as being in space
than in time (Burnet), by which means every way to understanding is
effectively blocked.
This much only for the time being: a broader discussion of Iranian
Zurvan would wreck our frame; we do not think, however, that Zur-
van/Chronos represents a "Zoroastrian Dilemma"; to style it thus (with
Zaehner) is one more mistake: it is not the "beliefs" and "religions"
which circle around and fight each other restlessly; what changes is the
celestial situation.
4 Bhagavata Purana 8.11 (Sanyal trans., vol. 3, p. 126).
5 Quoted by Eisler, Weltenmantel, p. 501. What the author (pp. 385f.) has to say
about "anthropomorphic, most primitive empathies" (?Einfuhlungen), connected
with Ouranos, Ge, Helios and Selene, which are, allegedly, miles away from the
"step of highly abstract conceptions about eternal Time," is not only a contra-
diclio in adjecto, but plain thoughtlessness.
377 • Appendices
Appendix
Some say, he bid his angels turn askance
The poles of earth, twice ten degrees and more
From the sun's axle, they with labour pushed
Oblique the centric globe: some say, the sun
Was bid turn reins from the equinoctial road . . .
. . . else had the spring
Perpetual smiled on earth with vernant flowers
Equal in days and nights, except to those
Beyond the polar circles; to them day
Had unbenighted shone; while the low Sun
To recompense his distance, in their sight
Had rounded still the horizon, and not known
Of east or west; which had forbid the snow
From cold Estotiland, and south as far
Beneath Magellan. At that tasted fruit
The sun, as from Thyestean banquet, turned
His course intended; else how had the world
Inhabited, though sinless, more than now
Avoided pinching cold and scorching heat?
Milton, Paradise Lost, 10
Appendix 14.
The name Mundilfoeri (Mundel-fere) raises a cluster of problems, and
nothing is gained by evasive statements such as that given by de Vries
(Altnord. Etym. Wb., p. 395): uMundilferi. Name of the father of the
Moon . . . Mundill. Name of a legendary figure."
As concerns mund, feminine, it means "hand" (Cleasby-Vigfusson,
s.v.), but mund comprises the meaning of. tutelage, guardianship (cf.
German Von mund). Mund as a neutrum means "point of time, mood,
humor, measure, and the right time" (de Vries, loc. cit.).
Hamlet's Mill
378
Mundill (Mundell) is an unknown "legendary figure," certainly; we
should be glad to know what the name indicates precisely, but the spe-
cialists do not tell us. There is a small but promising hint: Gering, in his
commentary on the Edda (vol. 1, p. 168), remarked, "The name occurs
again among the saekonunga heiti Sn. E. II, 154." Heiti are a kind of
denominations (Neckel renders it "Furnamen") which the skalds used
side by side with kenningar (circumlocutions); the list of "heiti of sea-
kings" is to be found in the Third Grammatical Tract contained in
Snorri's Edda (ascribed to Snorri's nephew Olaf), and among the
twenty-four heiti, no. 11 is Mysingr, no. 15 is Mundill.1 Everyone who
is familiar with the many names given to the cosmic personae—specific
names changing according to the order of time—in Babylonian, Indian,
Chinese, etc., astronomy, is not likely to fall for the idea that these
heiti were names of historical kings.2 The consequences resulting from
the understanding of Mysing and Mundill (together with twenty-two
more heiti) as representatives of the same cosmic function will not be
worked out in detail here: he who keeps his eye on the different fords,
ferrymen, pilots, personified divine ships, and kings of the deep sea that
cross his path in the course of this essay may eventually work out his
own solution. As for the word fere (in Mundelfere), Gering feels cer-
tain that it is the same word as OHG ferjo, MHG verge, i.e., ferryman,
the name meaning "ferryman of Mundell." Gering refers to Finnur
Johnsson who understood the mund in the name as "time," and "ex-
plained the name which he took for the name of the moon, originally,
as 'den der bewaeger sig efter bestemte tider,' " i.e., somebody who
moves according to definite times, let us say: according to his timetable
(or schedule).
There is no reason at all to take Mundilfori for "originally" the name
of the moon, this luminary not being the only timekeeper at hand.
Vafthrudnismal 23 says of the Sun and Moon, the children of Mundil-
fori, that they circle around the sky serving as indicators of time.3
"Ferryman of Time" would make a certain sense, but not enough yet
to enlighten us about Mundill "himself." The same goes for Sim-
1 Den tredje og fjaerde grammatiske afhandling i Snorres Edda, ed. by Bjorn
Magnusson 61son (1884), III.15 (vol. 2, pp. 154f.).
2 Olson, apparently a hardened euhemerist, stated in a note: "Hoc versu me-
moriali viginti quatuor nomina archipiratorum sive regulorum maritimorum con-
tinentur."
3 Gering, loc. cit.: "himen hvcrfa . . . 'den Himmel umkreisen' . . . aldom at
artale, 'urn den Menschen die Zeitrechnung zu ermoglichen.' Daher fuhrt auch der
den Namen artale 'Zeitberechner.'"
379 • Appendices
rock's rather imaginative Mundilfoeri = "Achsenschwinger," i.e., "axis-
swinger," but Simrock has at least thought about a sensible meaning,
and maybe he has hit the mark quite unbeknownst. Ernst Krause, too,
racked his brains, modestly asking the experts to examine the relation of
this mundil with Latin mundus4 We do not mean to meddle earnestly
with this particular question, the less so as mundus translated into "the
world" has become an empty and insignificant word altogether, but it
certainly is depressing to watch the progressists working out their latest
"solutions" for Latin mundus, namely, (1) "ornament," (2) "jewel-
lery of women,"5 without recalling Greek kosmeo which does mean
also "to adorn," to be sure, but not "originally," and not essentially;
to establish order, especially in the sense of getting an army into line,
is what kosmeo means, whence kosmos. And we are not entitled to
give the silliest of all imaginable meanings to such a central word as
mundus.
We should like to approach the words in question by means of the
common objective significance underlying the vast family of word-
images engendered by the radical month, math, whence also (Mount)
Mandara, mandala, Latin mentula (penis), and also our mondull,6 which
is supposed to have replaced the older form mandull. True, mandull/
mondull is not yet mundill, and mundus is not identical with mandala,
yet the whole clan of words depends from a central conception stick-
ing firmly to mnt/mnd, and these consonants connote a swirling, drilling
motion throughout. We are, here, up to a veritable jungle of misunder-
standings, and the closer we look into the "ars interpretandi" of profes-
sionals, the more impenetrable the jungle becomes. But let us try to
get a shred of sense by laying bare the more or less "subconscious"
blunders accomplished by the interpreters dealing with the radical
manth, the heart and center of the Indian Amriumanthana, the "Churn-
ing of Ambrosia," i.e., the Churning of the Milky Ocean in order to
gain Amrita/Ambrosia, the drink of immortality. It is some sort of
case history, the "case" being that manth, math appears to have two
fundamentally,different meanings (and some more), for which we
4 Tuisko-Land (1891), p. 326; see also p. 321.
5 I.e., (1) "Schmuck," (2) "Putz der Frauen"; see Walde-Hofmann, Lat. Etym.
Wb., vol. 2, pp. 126f.
6Cf. A. Kuhn (Die Herabkunft des Feuers und des Gottertranks [1886], p. 116)
where he refers to Aufrecht: "mondull 111., axis rotarum, cotis rotatilis et similium
instrumentorum"; Ibid, note 2, quoting Egilson: "mondull m. lignum teres, quo mola
trusatilis circumagitur, mobile, molucrum; mondultre m. manubrium ligneum, quo
mola versatur."
Hamlet's Mill
380
quote Macdonell's Sanskrit dictionary (p. 218): "manth—a churning,
killing, mixed beverage (= the Soma mixture); mantha-ka m. churning
stick; manth-ana, producing fire by attrition." On page 214 we find
s.v. math, manth: "whirl around (agnim), rub (a fire stick), churn,
shake, stir up, agitate, afflict, crush, injure, destroy, . . . mathita bewil-
dered, . . . strike or tear off, . . . uproot, exterminate, kill, destroy, . . .
strike or tear off, drag away."7
So far, so good. But why insist on such misleading verbs as "striking"
or "tearing off," etc.? Did not we hear about Fenja and\Menja who
"ground out a sudden host" for Frodhi, i.e., Mysing? And this is not an
isolated instance. We know, for instance, of an extremely relevant Hit-
tite prayer to the Ishtar of Nineveh who is asked "to grind away from
the enemies their masculinity, power and health"8—the Hittites are
quite respectable members of the Indo-European family of languages.
Whether something is gained, or something is lost—peace, gold, health,
heads, virility, and what else—it is ground out, or ground away, when
the underlying image is a mola trusatilis; it is drilled out, or drilled
away, when the motion of the cosmos is understood as alternative mo-
tion, as in the case of the Indian churn. We have sufficient reasons to
take alternative motion for the older conception, but this is irrelevant
right here and now; relevant is the general conception, expressed by the
manifold words engendered by the radical manth/math, that every
event is due to the rotary motion (whether "true" or alternate, com-
pare appendix #17) of the celestial mill or churn,9 i.e., of the combined
motions of the planetary spheres and the sphere of fixed stars.
At the same moment, when we understand mill and churn as the
celestial machinery, the stumbling stone of "to drill" versus "to rob, to
destroy" becomes insignificant, and this is important enough, since it
helps to clear the decent name of the hotly debated Prometheus.
7 See also H. Grassmann, Worterbuch zum Rig-Veda (1955), col. <)j6i.
8 See L. Wohleb, "Die altromische und hethitische evocatio," in ARW 2$ (1927),
p. 209, n. 5: "Ferner mahle den Mannern (namlich des feindlichen Landes)
Mannheit, Geschlechtskraft(P) Gesundheit weg; (ihre) Schwerter, Bogen, Pfeile,
Dolch(e) nimm und bringe sie ins Land Chatti."
9 We touch only slightly the family of Amlodhi's kvern; it must be enough to
state that quairnus means "millstone, mill" in Gothic, whereas Old Norse kirna is
the churn. Jacob Grimm (Geschichte der deutschen Sprache [1848], p. 47) wanted
to derive quairnus from zarna, zrno, Lith. girna, Latv. dsirnus == corn, kernel, but
there seems to be no way from there to English churn, and kirna, the Old Norse
churn. Kuhn (p. 104) calls attention to Sanskrit curna, ground powder, derived in
the Pctersburgcr Wb. from carv, to crush, to chew.
381 • Appendices
Adalbert Kuhn, surely a great scholar, has dealt broadly with the
radical manth, with Mount Mandara, the churning stick used by the
Asura and Deva for the churning of the Milky Ocean, and he tried
hard to bring about a happy marriage between this manthana and Greek
manthano "to learn," confronting us with his rather strange opinion of
what is "natural." This is what he says (pp. i5ff.):
Mit der bisher entwickelten Bedeutung der Wurzel manth hat sich
aber schon in den Veden die aus dem Verfahren natiirlich sich ent-
wickelnde Vorstellung des Abreissens, Ansichreissens, Raubens ent-
wickelt und aus dieser ist die Bedeutung des Griech. manthano
hervorgegangen, welches demnach als ein an sich reissen, sich aneignen
des fremden Wissens erscheint. Betrachten wir nun den Namen des
Prometheus in diesem Zusammenhang, so wird wohl die Annahme,
dass sich aus dem Feuer entziindenden Rauber der vorbedachtige
Titane erst auf griechischem Boden entwickelt habe, hinlanglich
gerechtfertigt erscheinen und zugleich klar werden, dass diese Ab-
straktion erst aus der sinnlichen Vorstellung des Feuerm'&m her-
vorgegangen sein konne. Was die Etymologie des Wortes betrifft, so
hat auch Pott . . . dasselbe auf manthano in der Bedeutung von mens
provida, providentia zuriickgefiihrt . . . , aber er hatte, sobald er das
tat, das Sanskritverbum nicht unbenicksichtigt lassen sollen . . . Ich
halte daher an der schon friiher ausgesprochenen Erklarung fest, nach
welcher Prometheus aus dem Begriff von pramatha, Raub, hervorge-
gangen ist, so dass es einem vorauszusetzenden Skr. pramathyus, der
Rauberische, Raub liebende, entspricht, wobei jedoch wohl auch
jener oben besprochene pramantha—i.e. the upright drilling stick—
auf die Bildung des Wortes mit eingewirkt hat, zumal Pott auch noch
einen Zeus Promantheus . . . aus Lycophron 537 nachweist, so dass
in dem Namen auch der Feueranziindende zugleich mit ausgedriickt
ware.
It goes without saying that we do not think it either "natural" or "ob-
vious" to "develop" learning from robbing, or providence from learn-
ing: Prometheus (Lykophron's Promantheus)-pramantha drilled new
fire, at a new place, at new crossroads of ecliptic and equator; the
"gods" did not like that (about which more later).
Now, pramantha, alias the male fire stick, having the well-known
naughty connotations, and with the Fecundity-Trust standing around
the corner, classical philologists fought bitter battles against Kuhn's
proposition, for the sake of noble Prometheus who simply should not
be a fire stick or, worse, the fascinum. The highly emotional classicists
remained victorious upon the battlefield until very recently, when we
Hamlet's Mill
382
learn the newest tidings from Mayrhofer,10 who rules firmly: "manth,
'quirlen' ist etymologisch von math-, mathnati 'rauben' (offenbar nasal-
los) verschieden." After having dealt with the different meanings of
the words, already known to us, he continues: "An ausserindischen
Nachweisen der Vorstufe von ai. math- 'rauben' . . . besteht vorerst
nur die vorsichtig ausgesprochene, aber sehr glaubhafte Zusammenstel-
lung von ai. pra- math- mit griech. Prometheus, dor. Promatheus
(Narten)."
That is exactly what "progress" means nowadays: that we are offered
as a brand-new, "cautiously uttered, but very credible connecting of
Sanskrit pra-math with Greek Prometheus" in 1963, when Kuhn's sec-
ond edition had been published in 1886. We do not wish to dwell upon
the claimed "etymological difference" of the radicals manth and math:
if philologists do not understand a subject, they invent different radi-
cals, which are "mixed" in later times, allegedly, as here math- and
manth "in post-Vedic times."11
Prometheus was a "pramantha," as were Quetzalcouatl, Tezcatlipoca,
the four Agnis, and very many more, drilling or churning with "Mount
Mandara," or with Mondull: why not call him Mundilfoeri, the axis-
swinger? We have, indeed, Altaic stories about one or the other Mun-
dilfoeri "begetting" Sun and Moon. Uno Holmberg states {Die reli-
giosen Vorstellungen der altaischen Volker [1938], pp. 22, 63, 8pf.):
In the myths of the Kalmucks the world mountain—Sumeru, Meru,
alias Mandara—appears as the means of creation. The world came
into being, when four powerful gods got hold of Mount Sumeru,
and whirled it around in the primordial sea, just as a Kalmuck woman
turns the churning stick when preparing butter. Out of the vehe-
mently agitated sea came, among others, Sun, Moon, and stars. The
same significance has, doubtless, the story of the Dorbots, according
to which once upon a time, before Sun and Moon existed, some being
began to stir the primordial ocean with a pole of 10,000 furlongs,
thus bringing forth Sun and Moon. A similar creation is described
in a Mongolian myth, where a being coming from heaven—a Lama
it is supposed to have been, see Holmberg, Finno-Ugric Mythology,
p. 328—stirs up the primeval sea, until part of the fluid becomes solid.
10Kurzgefasstes Ety?nol. Worterbuch des Altindischen, vol. 2 (1963), pp. 567^,
578ff.
11 The worst among the relevant cases is the Greek radical lyk, which the experts
insist upon being two different ones, i.e., lyk = light, and lyk — wolf, without
spending a thought on Pythagoras, who taught us: "The planets arc the dogs of
Persephone"; all mythical canines have just everything to do with light.
383 • Appendices
These "creation stories" are more or less deteriorated survivals of the
Amritamanthana, "the incomparably mighty churn," in the course of
which one constellation after the other emerged from the wildly agi-
tated Milky Ocean.12 And the same goes for the "creation" brought
forth by the Japanese "parents of the world," who, standing upon the
Celestial Bridge, stirred with the celestial jewel-spear the primordial sea
until parts of it thickened and became islands. The Amritamanthana
survived also in Greece, in the beginning of Iliad 8, and in the myth of
Plato's Statesman, and Plutarch spotted it in Egypt: but this subject
would make another book. The relevant point was, here, to place
figures as Mundilfoeri, or some surviving Lama, or Vishnu Cakravartin
on the cosmological stage, where their modes of "creation" make sense.
12 The collector of merely funny survivals might enjoy the following yarn from
Switzerland (Grimm, TJVI, p. 697): "In the golden age when the brooks and lakes
"were filled with milk, a shepherd was upset in his boat and drowned; his body,
long sought for, turned up at last in the foamy cream, when they were churning,
and was buried in a cavity which bees had constructed of honeycombs as large as
town-gates."
Appendix
As concerns the removing of the Pole star, the most drastic version
is told by the Lapps:
When Arcturus (alpha Bootis, supposed to be an archer, Ursa Major
being his bow) shoots down the North Nail with his arrow on the
last day, the heaven will fall, crushing the earth and setting fire to
everything.1
Other legends prefer to deal with the fate of circumpolar stars, the
result being the same.
The Siberian Kirghis call the three stars of the Little Bear nearest the
Pole star, which form an arch, a "rope" to which the two larger stars
of the same constellation, the two horses, are fastened. One of the
horses is white, the other bluish-grey. The seven stars of the Great
Bear they call the seven watchmen, whose duty it is to guard the
horses from the lurking wolf. When once the wolf succeeds in killing
1 U. Holmberg, Finno-Ugric and Siberian Mythology (1964), p. 221. Sec the
drawing made by J. Tun in Das liuch des Lappc/i 'I'/iri (1912), plate xiv: Arc-
turns Favrna, Polaris/North Nail lloajc nastc, or Bohinavlle,
Hamlet's Mill
384
the horses the end of the world will come. In other tales the stars of
the Great Bear are "seven wolves" who pursue those horses. Just
before the end of the world they will succeed in catching them. Some
even fancy that the Great Bear is also tied to the Pole Star. When
once all the bonds are broken there will be a great disturbance in the
sky.2
According to South Russian folklore, a dog is fettered to Ursa Minor,
and tries constantly to bite through the fetter; when he succeeds, the
end of the world has come.
Others say that Ursa Major consists of a team of horses with harness;
every night a black dog is gnawing at the harness, in order to destroy
the world, but he does not reach his aim; at dawn, when he runs to
a spring to drink, the harness renews itself.3
A very strange and apparently stone-old story is told by the Skidi-
Pawnee about the end and the beginning of the world.4
Various portents will precede: the moon will turn red and the sun
will die in the skies. The North Star is the power which is to preside
at the end of all things, as the Bright Star of Evening was the ruler
when life began. The Morning Star, the messenger of heaven, which
revealed the mysteries of fate to the people, said that in the beginning,
at the first great council which apportioned to star folk their stations,
two of the people fell ill. One of these was old, and one was young.
They were placed upon stretchers, carried by stars (Ursa Major and
Ursa Minor),5 and the two stretchers wTere tied to the North Star.
Now the South Star, the Spirit Star, or Star of Death, comes higher
and higher in the heavens, and nearer and nearer to the North Star,
and when the time for the end of life draws nigh, the Death Star will
2 Holmberg, p. 425; cf. Holmberg's Die religiosen Vorstellungen der altaischen
Volker (1938), p. 40.
3 A. Olrik, Ragnarok (1919), pp. 309^ The author regards it as "ein neues Motiv,
dass der Hund am Himmel angebracht ist und mit den Sternbildern zu tun hat.
Sonst haben wir die Hunde in einem Berg am Ende der Welt. .."
4 H. B. Alexander, North American Mythology (1916), pp. n6f.
5 The Sioux take Ursa Major for a coffin, accompanied by mourners. This pic-
ture is not too "obvious," so it is significant that Ursa is banat na'sh with the
Arabs, i.e., the bier and its daughters; the bier is formed by the chest of the wagon,
El-na'sh, the handle of the Dipper being the daughters. See Ideler, Sternnamen,
pp. i9f. Kunitzsch, Arabische Sternnamen in Europa, p. 149, no. 71, adds that,
according to Athanasius Kircher, christianized Arabs recognized in the constella-
tion the coffin of Lazarus, followed by the mourners Maryam, Marta, and their
maid (al-ama). See also Henninger, ZfE 7^, p. 81. Due to Islamic influence, the
constellation is called bintang aVnash, star of the bier, by the people of Minangka-
bau, Southern Sumatra. (Sec H. Werner, "Die Vcrstirnung des Osiris-Mythos,"
lAfK, 16 I 1954I, p. 154.)
385 • Appendices
approach so close to the North Star that it will capture the stars that
bear the stretchers and cause the death of the persons who are lying
ill upon those stellar couches. The North Star will then disappear and
move away and the South Star will take possession of earth and its
people. The command for the ending of all things will be given by
the North Star, and the South Star will carry out the commands. Our
people were made by the stars. When the time comes for all things
to end our people will turn into small stars and will fly to the South
Star where they belong."
To return to better known provinces, Proclus informs us that the
fox star nibbles continuously at the thong of the yoke which holds to-
gether heaven and earth; German folklore adds that when the fox
succeeds, the world will come to its end.6 This fox star is no other than
Alcor,7 the small star g near zeta Ursae Majoris (in India Arundati, the
common wife of the Seven Rishis, alpha-eta Ursae; see p. 301 about
Arundati and Elamitic Narundi, sister of the Sibitti, the "Seven"),
known as such since Babylonian times.8
The same star crosses our way again in the Scholia to Aratus9 where
we are told that it is Electra, mother of Dardanus, who left her station
among the Pleiades, desperate because of Ilion's fall, and retired "above
the second star of the beam . . . others call this star 'fox.' "
This small piece of evidence may show the reader two things: (1)
that the Fall of Troy meant the end of a veritable world-age. (For the
time being, we assume that the end of the Pleiadic age is meant;
among various reasons, because Dardanos came to Troy after the third
flood, according to Nonnos.); (2) that Ursa Major and the Pleiades
figuring on the shield of Achilles, destroyer of Troy, have a precise
significance, and are not to be taken as testimony for the stupendous
ignorance of Homer who knew none but these constellations, as the
6 (Proklos ad Hesiod, opp. 382) Boll and Gundel, in Roscher s.v. Sternbilder,
col. 876.
7 For the name Alcor, and its tradition, see Kunitzsch, pp. i25f.
8 See F. X. Kugler, S.J., Erga'nzungsheft zum 1. u. 2 Buck (1935), pp. 55L; P. F.
Gossmann, Planetariypi Babylonicum: "The star at the beam of the wagon is the fox
^star: Era, the powerful among the gods. In astrological usage, it represents above
all the planet Mars/Nergai." See also E. F. Weidner, Handbuch Babyl. Astr.
(1915), p. 141; E. Burrows, S.J., "The Constellation of the Wagon and Recent
Archaeology," in Festschrift Deimel (1935), pp. 34, 36. The said Nergal, i.e., Mars,
- to whom "belongs" Alcor in the Series mulAPIN, starts the first flood, as we
learn from Utnapishtim—see p. 297—under the name of Era, he succeeds in starting
a new one, according to tire ftra-Kpos.
!) 257; I1'.. Maass, Comment ariorimi in Arawm RcHquac (iK<>H), p. 591, II. (IF.
Hamlet's Mill
386
specialists want us to believe. There are, indeed, too many traditions
connecting Ursa and the Pleiades with this or that kind of catastrophe
to be overlooked. Among the many we mention only one example from
later Jewish legends, some lines taken out of a most fanciful description
of Noah's flood, quoted by Frazer:10
Now the deluge was caused by the male waters from the sky meeting
the female waters which issued forth from the ground. The holes in
the sky by which the upper waters escaped were made by God when
he removed stars out of the constellation of the Pleiades; and in order
to stop this torrent of rain, God had afterwards to bung up the two
holes with a couple of stars borrowed from the constellation of the
Bear. That is why the Bear runs after the Pleiades to this day; she
wants her children back, but she will never get them till after the
Last Day.
10 Folk-Lore in the Old Testament (1918), vol. /, pp. i43f.
Appendix 16
For Hallinskidi see Reuter, p. 237; Simrock, Handbuch, p. 277;
Gering (Edda trans., p. 320): "gebogene Schneeschuhe habend." Much
(in Festschrift Heinzel, p. 259), connecting -skidi with Celtic sketo,
skeda (English: humerus, scapula) and taking halle for "stone," ventures
to propose the reconstruction "he with the stone shoulder . . . which
would presuppose a similar story as that about Pelops and his ivory
shoulder."
As concerns mjotvidr, A. V. Strom renders vol. 2:1
lch erinnere mich neun Welten
Neun im Baume (oder neun Heime),
des ruhmvollen Massbaums
unter der Erde.
And he quotes Hallberg's statement: "Der Baum selbst ist das Mass fur
die Existenz der umgebenden Welt—in der Zeit."2 The last remark goes
1 "Indogermanisches in der Voliispa," Numen 14 (1967), pp. 173.
2 Why the author, in this excellent article, drags in "ecstatic visions," remains
incomprehensible, unless we prefer to call every account of astronomical situa-
tions "ecstatic visions," which would be a true miotvidr to measure the vast abyss
between sciences and humanities in our time.
387 • Appendices
without saying, mythic measures are time measures, generally, but this
fact is so seldom recognized that this white raven has to be welcomed
enthusiastically. The "localization under the earth" points to the (in-
visible) South of the world, as will come out later. By which we do not
mean to say we understood the enigmatical picture of this measuring
tree.
Now, Heimdal and Loke, perpetual enemies as they are, kill each
other at Ragnarok, but Heimdal's death is accomplished by means of
a very strange weapon, i.e., by a "head." Snorri's Skaldskaparmal 8 (see
also 69) offers an ambiguous kenning: "Heimdal's head is the sword,
or, the sword is Heimdal's head,"3 or we learn that the sword was
called "miotudr Heimdaler," and that is, according to Jacob Grimm,4
"the measurer (sector, messor)." Thus, Heimdal measures—or is he
measured?—by means of a sword that is also said to be his very own
head. Strange goings-on, indeed. Ohlmarks5 declared the sword to be
the Sun—a pleasant change for once, otherwise everything and every-
body is the Moon, with him—but although the measuring instrument,
whether the "golden rope" or not,, usually is the sun (see p. 154 on Va-
runa, and p. 246 on Theaethetus 153c [the latter is by Plato]), we have
the suspicion that the case of Heimdal's head/sword is more compli-
cated, and that it may not be settled until we know much more about
Loke.
3 Heimdalur hoefut heitir sverdh; cf. Simrock, Handbuch, pp. 272^
4TM, p. 22 (see also p. 1290); the English translation says "the wolf's head,
with which Heimdal was killed," but the original (Deutsche Mythologie, p. 15)
does not mention a wolf.
5 Heimdalls Horn (1937), p. 151.
Appendix
To prevent rash critics from hurling into our faces the—maybe they
will style it th*us—"complete absence of technological knowledge," we
hasten to assert that the relevant inquiries are not as foreign to us as
they might assume.1 Curwen might point to his enlightened sentence:
1 To mention only a few useful titles: Joseph Necdham, Science and Civilisation
in China, vol. 4, Pt. II, (1965); Gordon Childc's chapter on "Rotary Motion," in
Singer et al., eds., A History of Technology, vol. / (1954), pp. 187(1.; 1 lugo Theo-
dor Horwitz, "Die Drehbewegung in ihrer Bedeutung fiir die Knrwicklung der
Hamlet's Mill • 388
We are, happily, emerging from that state of blissful ignorance of the
subject which made possible such an anachronism as Decamps' well-
known picture of "Samson grinding in the Prison-house," wherein
Samson is seen turning a huge mill-stone by means of a long lever
like a capstan-bar, after the fashion of the Roman slaves a thousand
years later.2
There are, indeed, "a number of reasons for questioning the common
belief that grainmills were rotary," as Moritz states (p. 53). And
whereas Forbes (Studies in Ancient Technology, vol. 5, p. 155, n. 3)
votes for "rotary querns ... in Assyrian times," Lynn White (p. 108)
says: "But while continuous rotary motion was used in this large mola
versatilis and, of course, in the water mill which appears in the first
century b.c, it is by no means clear how early such a motion was used
with querns," which is certainly true. That true rotary motion was
used with the potter's wheel much earlier is unquestionable, which is
the more relevant, as the potter's wheel, too, belongs to the cosmological
instrumentation, e.g., in the hands of Ptah and Khnum. Decisive is the
Ancient Egyptian instrument for drilling out stone vessels, which was
perhaps even cranked, but there is no unanimity among the historians
of technology as to the real nature of this device. In this case and in
that of the mill, the accent goes with "true" rotary motion, because
there are two kinds of rotary motion, to which we quote Gordon
Childe (Singer, p. 187) on the difference "between continuous, true and
complete rotary motion, and partial or discontinuous rotary motion.
For true rotary motion, the revolving part of the instrument must be
free to turn in the same direction indefinitely. There are, however, a
number of processes which involve a partial turn of the instrument, such
as boring and drilling by hand. There are even machines like the bow-
drill or the pole-lather which allow a number, but only a limited num-
ber, of complete revolutions of the revolving part. Partial rotary motion
of this sort has been used by man much longer than true rotary motion."
Now, we do not wish to suppress White's footnote (p. 109), where
he claims Fenja's and Menja's Grotte to have been an apparatus involv-
ing alternative motion, "no doubt." This might be the case, although we
materiellen Kultur," Anthropos 28 (1933), 29 (1934). John Storclc and Walter
Dorwin Teague, Flour for Man's Bread: A History of Milling (1952); Lynn
White, Medieval Technology and Social Change (1962)—this title is a grotesque
understatement!
2 "Querns," Antiquity 11 (1937), pp. 133f. Sec also L. A. Moritz, Grain-Mills and
Floitr in Classical Antiquity (i<>sK), p. ■ *■■ he makes it :i medieval mill.
389 • Appendices
do not agree with the "no doubt": several doubts are permitted. We
shall abstain, however, from discussing this and similar questions as long
as we do not understand precisely and thoroughly how the "Churning
of the Milky Ocean" was thought to work, in India, and in Egypt,
where the specialists insist upon calling the celestial churn a "symbol of
uniting the two lands," and in the survivals in Homer and Plato. For the
time being we do think that the oldest technological device used in
cosmological terminology was, indeed, a churn or a drill, implicating
alternative motion.
The point is this: whether or not Samson, or Fenja and Menja, waited
on an oscillating quern or on a true rotary mill is a cosmological ques-
tion, and will hardly be decided by historians of technology. To illus-
trate this, we have a look at that "mill" of the Cherokee Indians, men-
tioned in the chapter on the Galaxy, where it is told that "people in the
South had a corn mill," from which meal was stolen again and again;
the owners discovered the thief, a dog, who "ran off howling to his
home in the North, with the meal dropping from his mouth as he ran,
and leaving behind a white trail where now we see the Milky Way,
which the Cherokee call to this day . . . 'Where the dog ran.' " In his
supplementary notes (p. 443), Mooney explains: "In the original ver-
sion the mill was probably a wooden mortar, such as was commonly
used by the Cherokee . . ." Well, in the "original version," as told by
the Cherokee, we may rely on their talking of a mortar—but certainly
not in the truly "original" myth. There is no possible way whatsoever
of "developing" out of "primitive" mortars (or grindstones) cosmologi-
cal imagery; in other words: the Cherokee mortar is a "deteriorated"
mill (whether oscillating or not).
The cosmic machine (mill, drill, or churn) produces periods of time,
it brings about the "separation of heaven and earth," etc. Along the way
of diffusion into unfamiliar surroundings, particularly tropical ones
(lacking grain, plow culture, etc.), the Mill (or churn) ceases to be
understood, while the memory sticks to an instrument for crushing
foodstuff. And, suddenly, we are told in several continents how Heaven,
who once was lying closely upon Earth, withdrew in anger because
of women who, busy with their mortars, kept bumping with their
pestles against Heaven's body. An extremely pointless idea, the origin
of which is only to be understood when we-follow it back to the highly
complicated machinery which stood at its beginning- (historically as
well as "sinngeiniiss"), and begot quite innocently such strange off
shoots.
Hamlet's Mill • 390
Although we do not like to apply strictly scientific models to his-
torical phenomena, here we abuse the case of entropy: to derive Grotte
(the Amritamanthana, etc.) from those utterly nonsensical females
bumping their pestles against "Heaven" would be on the same level as
to derive the original substances from the state of randomly mingled
gases.
These minima only for the technological problem. We keep these
questions under lock and key on purpose, and not because it has not
dawned upon us that the technological aspect is a very important one.
On the contrary, we nurse the suspicion that next to nobody has an
idea of the huge difficulties that arise with churn, mill, and fire drill, if
one understands them properly as machines which were meant to de-
scribe the motions of nested spheres.
Appendix 18
Compare Popol Vuh: The Sacred Book of the Ancient Quiche Maya
(Eng. trans, by D. Goetz and S. Morley, [1951], pp. 99-102). As con-
cerns the escape of Zipacna, compare the distribution map, given by
Frobenius (Paideuma 1 [1938], p. 8, map 3—"Der Lausbub im Haus-
pfeiler").
For the whole motif of pillars and houses pulled down, compare
Eduard Stucken, Astralmythen (1896-1907): pp. 73^ for the death of
Nebrod, according to Cedrenus—of Cain, according to Leo Gram-
maticus Chron. p. 8 (Kain, hos legei Moyses, tes oikias pesouses ep'auton
eteleutesen); pp. 329^ for the case of Susanowo; p. 348 for Turkish
Depe Ghoz; pp. 402^ for Zipacna; there, he also wants to incorporate
Job 1.18. Stucken's complete blindness to the mere existence of planets
has prevented him from better understanding; thus, he claims for the
case of Job 1.18: "Auch hier ist die Orion-Gottheit (Satan-Ahriman),
welche den Hauseinsturz verursacht, um die Plejaden-Gottheit (Hiob)
zu ziichtigen." This blindness is the more astonishing as Stucken has
read Eisenmenger's huge opus, "Entdecktes Judenthum" (1711), where
he should have detected the identity (as claimed by rabbinical litera-
ture) of the planet Mars with the serpent in Paradise, with Kain, Esau,
Abimclcch, Goliath, Sammael, the Scape-Goat, and many others.
391 • Appendices
Appendix 19
A remarkable amount of information about submarine creatures is
contained in Mansikka's inquiry into Russian magic formulae, already
mentioned;1 intermingled as the material is with the author's rather vio-
lent "interpretatio Christiana," it is well-nigh impossible to lay one's
hands on the bare facts. This much can be said, however: in the middle
of the "Blue Sea" (or "the middle of the whole earth"), there is either
(a) an island—most of the time called Bujan, from the same radical as
buoy—"the center of celestial power," upon which there is a tree, or
a stone, or a tree upon a stone, sometimes the cross or the "mountain
of Zion" itself;2 or there is (b) the "White Altar-Stone," which is a
"fiery" one, lying in the navel of the sea without being supported by
an island; under this stone, there is "a green fire, the king of all fires,"
or an "eternal, unquenchable fire" that "has to be procured from under
the stone" (Mansikka, p. 188—we are not told for what purpose the
fire has to be fetched from there; the text says only "for burning").
Sometimes it is said that upon this stone—regardless of its being "holy"
and the "Stone of the Altar," and even "Christ's Throne"—was the
"habitation of the Devil himself";3 in other formulae the point is stressed
that this fire "scorches and burns the decayed and impure power of
the. devil" (i.e., "die verfallene, unreine Macht des Teufels," where "ver-
fallen" may mean either "decayed" or "forfeited"). As long as this
unquenchable fire remains safely under a stone, nothing dangerous is
going to happen; accordingly, a German formula (Mansikka, p. 37)
says: "In Christ's Garden there is a well, in the well there is a stone,
under the stone lies a golden snake." That snake can also be a scorpion,
as we have just seen (footnote 3).
1 Vber russische Zauberformeln (1909), pp. 168-213: "The Sea, the Stone, the
Virgin Mary."
2 Thus it is said that "upon the mountains of Zion, upon the white stone stands
the pillar and the altar of Christ," or, "a pillar from the earth to heaven." In a
prayer Christ is addressed: "O, thou deadly stone pillar" (o, du todliche Steinsaule,
Mansikka, p. 187).
3 Mansikka, p. 189; see also the formula on pp. 35^.: "Es gibt cin hciligcs
Mccr Ozean, in seiner Mittc liegt cin wcisscr stein, aus dem wcisscn Stein kommt
cine grimmige Schlangc, dor Skorpion, hcrvor . . . In dem tcuflischcn Sumpf licgt
dcr wcissc Stein Lntyr; auf dem weissen Stein Latyr aber sii/.t der leibhaftige
Tcufel."
Hamlet's Mill • 392
The Mordvinians4 have a long story to tell about God, Tsham-Pas,
who was rocking to and fro upon a stone in the primordial sea, thinking
deeply about how to create the world and how to rule it afterward, and
complaining: "I have neither a brother nor a companion with whom to
discuss the matter." Angrily he spat into the sea, the spittle turned into
a large mountain from which emerged Saitan and offered himself as part-
ner in the discussion. Tsham-Pas sent his new companion to the bottom
of the sea to fetch sand, admonishing him to mention his (God's) name
before touching the sand. Saitan did not do so, and was burned heavily
by the flames which came out of the bottom of the sea; this happened
twice, and Tsham-Pas warned Saitan that, should he not mention the
divine name when diving for the third time, the flames would consume
him completely. The bad companion obeyed and brought, finally, the
sand necessary for the creation. But since he could not abstain from
playing tricks, God chased him away, saying: "Go away to the bottom
of the sea, to the other world, in that fire that burned you when you
were too proud to mention the name of your creator. Sit there and
suffer for all eternity."
In India, where the word "eternity" is not applied as thoughtlessly
as in European legends, the Harivamsa tells us the following about the
offspring of the sage Aurva (i.e., "born from the thigh," uru), as we
hear from Dowson:5
The sage was urged by his friends to beget children. He consented,
but he foretold that his progeny would live by destruction of others.
Then he produced from his thigh a devouring fire, which cried out
with a loud voice, 'I am hungry; let me consume the world.' The
various regions were soon in flames, when Brahma interfered to save
his creation, and promised the son of Aurva a suitable abode and
maintenance. The abode was to be at Badava-mukha, the mouth of
the ocean; for Brahma was born and rests in the ocean, and he and the
newly produced fire were to consume the world together at the end
of each age, and at the end of time to devour all things with the gods,
Asuras, and Rakshasas. The name Aurva thus signifies, shortly, the
submarine fire. It is also called Badavanala and Samvarttaka. It is
represented as a flame with a horse's head, and it is also called Kaka-
dhwaya, from carrying a banner on which there is a crow.
In the Mahabharata,6 this story is told by the Rishi Vasishtha (zeta
Ursae Majoris) in order to appease his grandson, who likewise wished
4 O. Dahnhardt, Natursagen (1907-1912), vol. /, pp. 60-62.
5 J. Dowson, A Classical Dictionary of Hindu Mythology (8th cd. 1953), pp. 3zf.
(J Mbh. /.iKn H;t (Roy nans., vol. /, p|>- 410-14).
393 • Appendices
to destroy the whole world without delay: "Then, o child, Aurva cast
the fire of his wrath into the abode of Varuna.7 And that fire which
consumeth the waters of the great Ocean, became like unto a large
horse's head which persons conversant with the Vedas call by the name
of Vadavamukha. And emitting itself from that mouth it consumeth
the waters of the mighty ocean."
This fiery horse's head guides the curious straight into the mazes of
the Mahabharata and the Shatapatha Brahmana where they are most im-
penetrable because they deal with the enigmatic story of the Rishi
Dadhyafik, whose horse's head was dwelling in Lake Saryanavant, after
it had revealed the "secret of madhu" (madhuvidya; madhu = honey
mead) to the Ashvins, the Dioscures,8 and out of whose bones (the
bones of the horse's skull) Tvashtri forged the thunderbolt for Indra,
thus enabling him to slay "the 99 vritras"9—as Samson killed the Philis-
tines with the jaw-bone of an ass—whereas Vishnu used this head to
reconquer the Vedas that had been carried away by two Daityas during
one of those time-swallowing "Yoga-sleeps" of Vishnu. Bereft of the
Vedas, Brahma, to whom they served as "eyes," was unable to continue
the work of creation, so that he implored the Lord of the universe to
awake. "Praised by Brahma, the illustrious Purusha . . . shook off his
slumber, resolved to recover the Vedas (from the Daityas that had
forcibly snatched them away). Applying his Yoga-puissance, he as-
sumed a second form . . . He assumed an equine head of great efful-
gence, which was the abode of the Vedas. The firmament, with all its
luminaries and constellations, became the crown of his head . . . Having
assumed this form endued with the equine head . . . the Lord of the
universe disappeared then and there, and proceeded to the nether
regions"10—to return with the Vedas, successfully, and resuming his
sleep, as goes without saying.
In other words, the "equine head" is as important a "form" of Vishnu
as an enigmatical one, so much so, in fact, that the more "popular" tra-
dition seems to ignore it, although the Great Epic tells us the following:
7 "The water from which the world took its origin," according to H. G. Jacobi,
Mahabharata (1903), p. 20.
8Cf. RV /.116.12; SB 74.1.1.18-25 (Eggeling trans., vol. 5, pp. 444f.); Saunaka's
Brihad Dcvata 5.16.25 (Macdoncll trans., vol. 2, pp. 82-85).
9Cf. RV / .84.13; Mbh. 7.2.343 (Roy trans., vul. to, p. 578). Compare for the
whole tradition, K. Ronnow, "Zur Erkliining des Ptw.irgya, dos Agnicayana und
des SautrimanI," In Le Monde Oriental (1929), pp. 113 73; sec also A. Keith, "In-
dian Mythology," M Al< 6 (1917), |>|»- <">", 64.
l0M!)h. /.v;.|K (Roy trans., vol. /«, p. 605).
Hamlet's Mill
394
In days of yore, for doing good to the world, Narayana [Vishnu]
took birth as the great Rishi Vadavamukha [see above, Aurva's son,
the mouth of the ocean, Vadavamukha]. While engaged in practising
severe austerities on the breast of Meru, he summoned the Ocean to
his presence. The Ocean, however, disobeyed his summons [Greek
Okeanos, too, was in the habit not to make his appearance, when Zeus
summoned everybody to assemble.] Incensed at this, the Rishi, with
the heat of his body, caused the waters of the Ocean to become as
saltish in taste as the human sweat. The Rishi further said, 'Thy
water shall henceforth cease to be drinkable. Only when the Equine-
head, roving within thee, will drink thy waters, they will be as sweet
as honey.'—It is for this curse that the waters of the Ocean to this
day are saltish to the taste and are drunk by no one else than the
Equine head.11
The translator, Pratap Chandra Roy, remarks in a footnote (p. 583),
without referring to the first book of the epic:
The Hindu scriptures mention that there is an Equine-head of vast
proportions which roves through the seas. Blazing fires constantly
issue from its mouth and these drink up the sea-water. It always makes
a roaring noise. It is called Vadava-mukha. The fire issuing from it
is called Vadava-nala. The waters of the Ocean are like clarified but-
ter. The Equine-head drinks them up as the sacrificial fire drinks
the libations of clarified butter poured upon it. The origin of the
Vadava fire is sometimes ascribed to the wrath of Urva, a Rishi of
the race of Jamadagni. Hence it is sometimes called Aurvya-fire.
None of the authorities quoted hitherto thought it worth mentioning
where this Vadava-mukha was supposed to be. Only when checking the
word in Macdonell's Practical Sanskrit Dictionary (p. 267) did we learn
—exactly as foreseen, although Macdonell means a terrestrial South
Pole, presumably—that "vadaba, f. = mare; Vivasvat's wife, who in
the form of a mare became the mother of the Ashvins . . . vadaba-agni,
m. submarine fire (supposed to be situated at the south pole) . . .
vadaba-mukha, n. mare's mouth = entrance of hell at the south pole."
We are not likely to change these dark plots into a lucid and coherent
story by dealing, here and now, more closely with Dadhyafik, whose
name is said to mean "milk-curdling," and who is a "producer of Agni,"
and by comparing the several characters who are accused of swallowing
up the ocean: we only hope to guide the attention to one among the
many unperceived concrete problems.
-
11 Mhh. 72.345 (Roy trans., vol. 10, p. 583).
395 • Appendices
We might be suspected of proposing to identify the sea-swallowing
horse's head with the equally thirsty Agastya-Canopus,12 just to simplify
the situation, and there are factors which invite such a "solution."13 But
the horse is the animal of Mars, and it is "the khshatriya Apam Napat
with the swift horses" who "seizes the hvarnah," hiding it in the "bot-
tom of the deep sea, the bottom of the deep lake":14 the "nephew"
(napat) of the waters (apam), and not the original (and highest) ruler
of the "mouth of the ocean," alias pi narati, "the confluence of the
rivers," i.e., Canopus, which the Tahitians of old called "Festivity-from-
whence-comes-the-flux-of-the-sea" (T. Henry, Ancient Tahiti [1928],
p. 363). Aurva's frightening son is, moreover, a "newly produced fire,"
as we have heard, and Apam Napat is by no means the one and only
"Agni"; the Rigveda knows of four "fires," Agnis, allegedly consumed
by the sacrificial service, one after the other. No valid insight is likely
to be gained before we cease to disregard the only mythical dimension
that counts: time.
Horses' heads not being connected with deep waters quite "natu-
rally," we might close with some stories collected by Jacob Grimm
(TM, pp. 597f.) which go to show that
Lakes cannot endure to have their depth gauged. On the Mummelsee,
when the sounders had let down all the cord out of nine nets with a
plummet without finding a bottom, suddenly the raft began to sink,
and they had to seek safety in a rapid flight to land ... A man went
in a boat to the middle of the Titisee, and payed out no end of line
after the plummet, when there came out of the waves a terrible cry:
"Measure me, and I'll eat you up!" In a great fright the man desisted
from his enterprise, and since then no one has dared to sound the
12 See p. 263. Cf. also Varahamihira, The Brihad Sanhita, trans, by H. Kern, in
JRAS $ (1871), p. 24. For a related and very peculiar legend of the Maori, see
The Lore of the Whare-wananga, trans, by S. Smith, in Mem. Polynesian Soc. 5
(1913), pp. i56f., 164, and M. Makemson, The Morning Star Rises: An Account
of Polynesian Astronomy (1941), p. 157, for a summary. There, the heavenly
waters of Rangi-tamaku (i.e., the sky which lies directly above the visible one) be-
came overheated and evaporated, so that whole tribes of celestial fish had to emi-
grate by descending on the "Road of the Spider," where they met Tawhaki
ascending on his expedition to avenge his father.
13 E.g., Stephanus of Byzantium mentions a temple of Poseidon-Canopus; see P.
Casanova, "De quclques Legendes astronomiqucs Arabes," in BIFAO 2 (1902), p. 11.
14Yasht /.9.51; see E. Hcrzfeld, Zoroaster and His World (1947), p. 571; to tin-
Iranian conceptions one lias to compare the Rigyedian hymn dedicated to Apam
Napat (RV 2.25), where he is said to "shine in (he waters," blazing iiiiqiiau'hably,
-the driver of horses (j.35.5: "K.r hat sit li in <\<:\\ (iVwiiv.ei 11 ap-.u auS
,\. i.35.6: "Don ist (lei- (leburtsorl des Rosses und dii'scr Sonnc").
Hamlet's Mill
396
depth of the lake . . . There is a similar story . . . about Huntsoe, that
some people tried to fathom its depth with a ploughshare tied to the
line, and from below came the sound of a spirit-voice: "i maale vore
vagge, vi skal maale jeres lagge!" Full of terror they hauled up the
line, but instead of the share found an old horse's skull fastened to it.
Appendix 20
Such stories are no jokes, although they make this impression when
they cross our way in Eurasian folklore. "Air" is a strictly astronomical
and, therefore, also a "religious" term. Thus, we hear from Rabbi
Eleazar b. Pedath (ca. a.d. 270): "Als der Pharaoh aus Agypten auszog,
die Israeliten zu verfolgen, erhoben sie ihre Augen gen Himmel und
sahen den Engelsfiirsten Agyptens in der Luft fliegen."
"That signifies the fall of Egypt," adds Bertholet, who mentions this
case in his article on the "guardian angel of Persia" (Festschrift Pavry,
p. 38), starting from Isa. xxiv.21 and its rabbinical interpretations. He
also points to the utterance of Rabbi Chanina (ca. a.d. 225): "Nicht
bestraft Gott eine Nation eher, als bis er zuvor ihren Engelfiirsten im
Himmel bestraft hat," to which he compares Ps. xxiv.21: "On that day
the Lord will punish the host of heaven, in heaven, and the kings of the
earth, on the earth."
These "guardian angels" will be identified sooner or later, insofar as
this has not yet been accomplished in older literature which our con-
temporaries disdain as "obsolete"; one among them, the "angel-lord" of
Esau/Edom, with whom, according to the Zohar, Jacob wrestled (Gen.
xxxii.24-33), is the planet Mars.1 How the whole system really works—
e.g., these punishments first in "heaven," subsequently "on earth"—will
not be understood before Plato's Timaeus is taken as earnestly as it was
taken by the Pythagorean Timaios himself, whom Plato introduced as
1 See J. Eisenmenger, Entdecktes Judenthum 1 (1711), pp. 844-46; cf. The Zohar,
144a, 146a (trans, by H. Sperling and M. Simon, [1956], vol. 2, pp. 63, jof.): "For
Jacob conquered the serpent with prudence and craft, but chiefly by means of the
he-goat; and although the serpent and Sammael are the same, yet he also conquered
Sammael by another method, as described in the passage, saying: and there wrestled
a man with him until the breaking of the day (Gen. xxxii.25-26)." And: "Another
blessing he [Jacob] received from that angel, the chieftain of Esau." A. Jeremias
(ATAO, p. 324) maintains that the wrestling took place at "Nibiru," which he
identifies, here, with the solstice, but sec appendix #39. For angels as stars, see also
M. Knapp, Antiskid (1927), pp. 33-36.
397 • Appendices
"astronomikotaton hemon," i.e., the most astronomically-minded among
us, and before it is accepted as the foundation from which to proceed
further. (See below, chapter XXII, for a superficial touching on this
cosmic system.)
Appendix 21
A faint, though rather pleasant, echo of such huge events, comes from
an Esthonian story about the Lake Eim changing his bed (Grimm,
TM,p. 599):
On his banks lived wild and wicked men, who never mowed the
meadows that he watered, nor sowed the fields he fertilized, but
robbed and murdered, so that his bright wave was befouled with the
blood of the slain. And the lake mourned; and one evening he called
his fish together, and mounted with them into the air. The brigands
hearing a din cried: "The Eim has left his bed, let us collect his fish
and hidden treasure." But the fish were gone, and nothing was found
at the bottom but snakes, toads and salamanders, which came creep-
ing out and lodged with the ruffian brood.
But the Eim rose higher and higher, and swept like a white cloud
through the air; said the hunters in the woods: "What is this murky
weather passing over us?" and the herdsmen: "What white swan is
flying in the sky?" All night he hung among the stars, at morn the
reapers spied him, how that he was sinking, and the white swan be-
came as a white ship, and the ship as a dark drifting cloud. And out
of the waters came a voice: "Get thee hence with thy harvest, I come
to dwell with thee." Then they bade him welcome, if he would
bedew their fields and meadows, and he sank down and stretched
himself in his new couch. They set his bed in order, built dikes, and
planted young trees around to cool his face. Their fields he made
fertile, their meadows green; and they danced around him, so that
old men grew young for joy.
In a note, Grimm quotes F. Thiersch's opinion on this lake:
Must not Eim be the same as Embctch (mother-beck, fr. emma
mother . . . ) near Dorpat, whose origin is reported as follows? When
God had created heaven and earth, he wished to bestow on the beasts
a king, to keep them in order, and commanded them to dig for his
reception :i deep broad beck, on whose banks he mighi walk; the
earth dug out of it was to make a hill for the king t<> live on. All the
Insists set to work, the hare measured the land, Che fox'l bruih tailing
Hamlet's Mill
398
after him marked the course of the stream; when they had finished
hollowing out the bed, God poured water into it out of his golden
bowl.
How tough the life of tradition is! And how obvious—here, we mean
it—that more is meant than the changing of the bed of a river or a lake;
that rivers have their own method of establishing a new course, instead
of flying, fish included, in the air and hanging among stars, is a fact that,
we trust, was not unknown to our ancestors, whether Esthonians or not.
Appendix 22
A survival, vague as it is, and evidently mistaking a chariot for a wain,
we find in India. The Silrya-Siddhanta states: "In Taurus, the 17th
degree, a planet of which the latitude is a little more than two degrees,
south, will split the ivain of Rohini."1
According to Burgess (p. 214), Rohini's (= Aldebaran) wain "con-
tains five stars, in the grouping of which Hindu fancy has seen the fig-
ure of a wain," i.e., the Hyades, containing epsilon, delta, gamma, nu,
alpha Tauri. Burgess continues (p. 249): "The Siddhanta does not in-
form us what would be the consequences of such an occurrence; that
belongs rather to the domain of astrology than of astronomy. We cite
from the Pancatantra (vv. 238-241) the following description of these
consequences, derived from the astrological writings of Varahamihira:
'When Saturn splits the wain of Rohini here in the world, the
Madhava rains not upon the earth for 12 years.
When the wain of Prajapati's asterism is split, the earth, having as
it were committed a sin, performs, in a manner, her surface being
strewn with ashes and bones, the Kapalika penance.
If Saturn, Mars, or the descending node splits the wain of Rohini,
why need I say that, in a sea of misfortune, destruction befalls the
world?
When the moon is stationed in the midst of Rohini's wain, the men
wander recklessly about, deprived of shelter, eating the cooked flesh
of children, drinking water from vessels burnt by the sun.'
By what conception this curious feature of the ancient Hindu astrol-
ogy is founded, we are entirely ignorant."
1 Sfirya-Siildhanta, 11:111s. by V. Burgess (i860; repr. 1935), #.13, pp. i.\V>iX.
399 • Appendices
The bad experiences which Saturn had with Auriga's vehicle—
whether beta zeta Tauri, or the Hyades—seem to have left a trace in
the memory of Indian astrologers.
Appendix 23
See J. Kepler, "De Stella Nova in Pede Serpentarii et qui sub ejus
exortum de novo iniit Trigono Igneo," in Opera Omnia, ed. C. Frisch
(1859), v°l- 2> P- 636- See also J. Kepler, "De vero anno quo Aeternus
Dei Filius humanam naturam . . . assumsit," in Opera Omnia (1863),
vol. 4, pp.
Kepler was less interested in the revolution of one angle of the trigon
through the whole zodiac than in the span of time which the conjunc-
tions needed to pass through all four "elements," particularly between
conjunctions in the "fiery triplicity." The zodiac is divided into four
"elementary" trigons or triplicities in the following manner:
Fire: Aries, Leo, Sagittarius
Earth: Taurus, Virgo, Capricornus
Air: Gemini, Libra, Aquarius
Water: Cancer, Scorpio, Pisces
The "great conjunction" of Saturn and Jupiter, occurring every
twenty years, remains about 200 years within one triplicity; it moves
through all four "elements" in 800 years (more exactly: in 794!^ years).
By means of the average of 800 years which it took the conjunction to
pass from one "fiery triplicity" to the other, Kepler reconstructed
history:

Hamlet's Mill • 400
As concerns the—faraway—2400 a.d., Kepler remarks: "Ubi tune
nos et modo florentissima nostra Germania? Et quinam successores nostri?
An et memores nostri erunt? Siquidem mundus duraverit." ("Floren-
tissima Germania": this was written before the Thirty Years' War
started.)
Compare H. H. Kritzinger (Der Stern der Weisen [ 1911 ], pp. 35, 44,
59), who deals broadly with the significance of "great conjunctions,"
and who adds: "The same table was repeated, with more precise data,
by Riccioli in his Almagestum Novum (Tom. 1, 672-75), beginning
with the verses:
Ignea Triplicitas, coniunctio Maxima dicta
Saturniq. Jouisque, annis redit Octingentis."
What is called here "great conjunction"—occurring every twenty
years—has been styled in earlier times, i.e., in Sasanian and Arabian
astrology, "small conjunction," as we learn from E. S. Kennedy:1
After about 12 such small conjunctions the next conjunction will pull
forward into the next triplicity. This event, called the shift or transit
(intiqal al-mamarr) is also known as the middle conjunction . . . Four
middle conjunctions carry the phenomenon through all the triplicities
and make up a big conjunction. But in order that the entire cycle
recommence from a particular initial sign, taken as Capricorn, three
big conjunctions are required, these making up a mighty conjunction.
A "mighty conjunction" thus corresponds to the revolution of one
angle or corner of the trigon of Jupiter-Saturn conjunctions—built up
in sixty years (more correctly: 59.6 years)—through the whole zodiac,
completed in 2400 years (2383 years, respectively).
For one particular reason why the "big conjunction" of 800 years
should be multiplied by 3, see Oscar Marcel Hinze's article:2 within the
frame of archaic "Gestalt-Astronomie," it was the revolution of the
trigon as a whole that "counted." (Hinze deals also with the hexagon,
i.e., the "Gestalt" of Mercury—revolution of one corner about twenty
years—and with the famous "Pentagramma Veneris.")
As concerns the role of Saturn-Jupiter conjunctions in Iran and India,
cf. also D. Pingree ("Astronomy and Astrology in India and Iran,"
1 "The Sasanian Astronomical Handbook Zij-i Shah, and the Astrological Doc-
trine of 'Transit' (Mamarr)," JAOS 78 (1958), p. 259.
2 "Studien zum Verstandnis der archaischen Astronomic," in Symbolon, Jahr-
buch fur Symbolforschung f (1966), pp. 162-219, csp. pp. 2o3fF.
401 • Appendices
ISIS 54 [1963], p. 244), and the forthcoming paper by B. L. van der
Waerden on "the conjunction of 3102 B.C."—this very conjunction
introduces the flood of the Mahabharata. Allegedly, there is no trace of
big conjunctions in Hindu and Hellenistic astrology. Astrology, how-
ever, is not found in texts only which are recognizable as such at first
glance. Apart from Greece, where we have—besides the wrestling of
Kronos and Saturn at Olympia—also the Daidalia, held in the interval
of sixty years—sixty-year cycles in India, or in the West Sudan, are not
likely to be understood, if the scholars prefer to inhibit the trigon of
the Saturn-Jupiter conjunction; this inhibition being the logical out-
come of the persistent refusal to recognize Saturn and Jupiter as Saturn
and Jupiter.
The decisive conjunction of 6 b.c. (that "opened" our age of Pisces)
having been near zeta Piscium, it is slightly surprising to learn from
Burgess (Siirya-Siddhanta, p. 14) the following—he explains the Indian
notion of nutation (also called libration): "The vernal equinox librates
westwards and eastwards from the fixed point, near zeta Piscium, as-
sumed as the commencement of the sidereal sphere," the "libration"
moving in eastern and western directions for twenty-seven degrees from
this fixed point. On p. 230 he states about zeta Piscium that "it coin-
cided in longitude with the vernal equinox in the year 572 of our era."
Appendix 24
Eduard Stucken (Astralmythen, pp. 1906°.) and, later, F. W. Albright
(JAOS 40, pp. 329L) drew attention to the very same method em-
ployed when Rishyasringa, son of Vibhandaka (son of Kashyapa) and
a hind, was lured by a courtesan, ordered by King Lomapada, into the
latter's town, because only with Rishyasringa present would the coun-
try have rain. (Compare H. Liiders, "Die Sage von Rsyasrnga," in
1 Philologica Indica [1940], pp. 1-42; also Liiders, "Zur Sage von
Rsyasrnga," Philologica Indica, pp. 43-73.)
The major difference between GE and the story told in the Mahab-
harata 3.110-13 (R°y trans., vol. 2, pp. 242-48) is that Father Vibhan-
daka is the one "whose body vv;is covered with hair down to (he lip of
the nails... and whose lift- was pure and \\;is passed in religious medita
Hamlet's Mill
402
403 • Appendices
tion"; seduced is the son, not a hairy one, apparently, but "there was a
horn on the head of that magnanimous saint." "Saints" they were both
—those Indians of "high and far-off times" were in the habit of building
up tapas, "ascetic heat," an instrument of the utmost cosmic "effi-
ciency," if we may style it thus.
Appendix 25
It is not yet securely established what the word sippu means.
(See W. Baumgartner, "Untersuchungen zu den akkadischen Bauaus-
driicken," ZA 36 [ 1925], pp. 27, 63; A. Schott, "Zu meiner tibersetzung
des Gilgamesh-Epos," ZA 42 [1934], pp. 105^) For the style of this
battle, characterized by Cyrus Gordon as "Beltwrestling" (JNES 7,
p. 264), see A. Oppenheim, Or. 77, pp. u)f. "They seized each other
(by their girdles), like experts/ they wrestled./ They destroyed
the doorpost/ The wall shook." See also E. A. Speiser, "Akkadian
Myths and Epics," ANET, p. 78. This "doorpost" is no quantite
negligeable, because some similar "object" comes our way again at the
"entrance" of the Cedar Forest, and does the most devilish things to
poor Enkidu. (Compare J. Friedrich, "Die hethitischen Bruchstiicke des
Gilgamesh-Epos," ZA 35) [1929-30], pp. 48f., dealing with the Hittite
fragments; he established at least that it was not the bolt.) In fact, were
we to have started from GE, instead of paying it a casual visit, the
several "doors" with their "posts," or "pillars," with their "fillings" and
"thresholds" would have had as much of a paralyzing effect upon us as
the eye of Medusa. Meanwhile, detrimental translations are quite enough
to turn the reader to stone.
Appendix 26
See P. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum (1950), 99: ""Dapinu,
'the prevalent, the strong,' surname of Nusku (passim), of Nabu, of
Marduk ... As star-god ''Dapinu is the Marduk-star Jupiter, identical
with dSUL. PA.lv, . . . , """UD.AL.TAR . . . Since UD.AL.TAR can
also mean the fixed star Procyon, also "Dapinu should have this signifi-
cance (Jensen, "der Furchtbare, Gewaltige (= Humbaba)," ZDMG
67, S. 517)." (For the identification of Nusku with Mercury, see H. and
J. Lewy, "The God Nusku," Or. ij [1948], pp. 146-59.) See also
Gossmann, 137 s.v. mulUD.AL.TAR: "I. Akkadian as much as umu
dapinu . . . the full name of Jupiter, II. Procyon. Procyon seems to have
been counted with Jupiter's hypsoma, Cancer." See also E. Weidner,
Handbuch der Babylonischen Astronomie (1915), p. 25. (For Procyon
as part of Cancer, see RLA 3, p. 77; for al. lu5, representing sometimes
the zodiacal sign Cancer, otherwise Procyon, see B. van der Waerden,
"The Thirty-Six Stars," JNES 8 [1949], p. 21.)
Langdon (Semitic Mythology [ 1931 ], p. 268) mentions the identifica-
tion Humbaba == Procyon, without giving the source, and without pay-
ing heed to such notion.
As concerns Humba with the determinant mul (BabyIonian kakkab, re-
spectively), Weidner (RLA 2, p. 389) informs us of the existence of
two lists dealing with "7 astralen Enlil-Gottheiten." List 1 states—we
give it according to Weidner, since it is not essential, right here, to es-
tablish whether or not his identifications are right throughout: "Perseus
is the Enlil of Nippur, g Ursae Majoris is the Enlil of Enamtilla, alpha
Cassiopeiae is the Enlil of Hursag-kalama, Columba is the Enlil of Kul-
lab, Taurus is the Enlil of Aratta, kHumba ( = ?) is the Enlil of Suba
(?)-Elam, Arcturus is the Enlil of Babylon." List 2 omits mulHumba
(compare also Weidner, Handbuch, pp. 58-60). Gossmann 188 states,
pointing to F. Boll-C. Bezold (Antike Beobachtungen farbiger Sterne
[1916], p. 121), that, according to VAT 0418 III 3, "mulHUMBA re-
places mulAPIN." The latter, the "plow constellation," is triangulum and
gamma Andromeda^ (see van der Waerden, JNES 8, p. 13).
Now it is of considerable interest to learn from Hiising (Die ein-
heimischen Quellen zur Geschichte Elams [1916], pp. 11, 95) that "the
highest god of Elam . . . Humban (Hanubani, Hamban—Umman,
Imbi)" is (supposedly) the same as Hanuman, the monkey-god, the
crafty adviser of Rama (Hiising also takes Humban for a monkey);
and from Charles Dupuis (Origine de tous les cultes et toutes les re-
ligions [1795], vol. 3, p. 363) the following: "Dans l'explication
des Fables Indienncs, nous avons toujours trouve que Procyon etoit lc
fameux singe Hanuman. II fixe le lever du Sagittairc, avcc Icqucl le
singe cst en aspect (Kirchcr: Oedipus 2 II, p. 201)."
Considering thai Procyon hus been counted among the stars of O,\\\-
fcer, :i constellation which had the name Hangar Carpenter, ilu-
m
Hamlet's Mill
404
Twelfth Tablet of GE, of pure Sumerian origin, might gain a com-
pletely new significance. Gilgamesh does, there, a lot of "wailing" and
"lamenting" about some objects that he left (or failed to leave) there,
where they might have been in safety, in "the house of the Carpenter,"
nangar. Apart from Procyon, the fixed representative of Jupiter and
Mercury, once Humbaba is purged from his "ogrish" reputation, the
time will have come to approach Kombabos and his doubles in Iranian
and Indian mythology.1 The story of young Kombabos, who castrated
himself as a precaution when he was appointed the traveling companion
of "Caesar's wife," has been hitherto incompatible with the "monster" of
the cedar forest, although the scholars agree that the names Humbaba
and Kombabos are identical. It would be worth investigating whether
or not the proposed equation Humbaba = Mercury might also fit Kom-
babos. F. K. Movers, however, was inclined to take Kombabos for
Saturn.2
Appendix 27
405 • Appendices
they see it. Yet it is there: Maskheti, the thigh of the bull, Ursa Major,
depicted on the astronomical ceilings in the tombs of Senmut, Seti, in
the Ramesseum, etc. In Altaic mythology, Ursa turns into the leg of a
stag; in Mexico we find it as the lost "foot" of Tezcatlipoca.
The constellations are named according to a system, and if we meet
"incomplete" or mutilated characters among them, we have to ask for
the sufficient reason, e.g., why the ship Argo is a stern only, why
Pegasus is barely half a horse—apart from its standing on its head
and having wings—and why Taurus is the head and first third of a
bull, his "thigh" turning around in the circumpolar region. Thus, it
might be something to think about that in the Round Zodiac of Dendera
(Roman period), the circumpolar "thigh" shows a ram sitting on it,
looking back, moreover, as befits the zodiacal Aries (see F. J. Lauth,
Zodiaques de Denderah [1865], p. 44). G. A. Wainwright, in "A Pair
of Constellations," Studies presented to F. L. Griffith (1932), p. 373,
with reference to Benedite, mentions a thigh with the head of a ram
from Edfu, called the "Foreleg of Khnum" (cf. Monumenti deWEgitto
e delta Nubia, Ippolito Rosellini, ed. [1844], vol. 5, plate 24).
See A. Oppenheim, "Mesopotamian Mythology," Or. 77 (1948),
p. 40: "After Enkidu tossed towards her . . . what is euphemistically
termed the 'right thigh' of the bull, the goddess and her devotees per-
formed age-old rites over the part of the bull."
True as this statement certainly is, it does not explain much—nor is
it even asked why it must be the right thigh (imittu; compare H.
Holma, Die Namen der Korperteile im Assyrisch-Babylonischen [ 1911 ],
pp. 13 if. See for the "euphemism" Holma, pp. 96f.).
The consensus of the experts, in overlooking that the GE talks ex-
plicitly of the celestial bull, keeps them from asking relevant questions,
and their conviction that Mesopotamians and Egyptians had not much
in common prevents them from recognizing the "bull's thigh" when
1 Lucian, "De Dea Syria," in Lucian, trans, by A. M. Harmon, vol. 4, cols. 19-27,
LCL. Lucian claims that Kombabos was the prototype of the galloi, i.e., that after
his example the priests of the Great Goddess castrated themselves and put on fe-
male garments. See also F. Liebrecht, Des Gervasius von Tilbury Otia Imperialia
(1856), pp. 2i6f.; Ganschinietz, in RE //, cols. 1132-39; E. Benveniste, "La Legcnde
de Kombabos," in Melanges Syriens offerts a Rene Dussaud (1939), pp. 249-58.
2 Die Phonizier (1841/1967), vol. /, pp. 154, 306-09, 686-89.
Appendix 28
In the GE Enkidu appears later on the stage of events than Gilga-
mesh. This does not entitle us to take him for the prototype of the
"younger brother" (see, e.g., W. Albright, "Gilgamesh and Engidu,"
JAOS 40 [1920], pp. 312, 318). Actually, the hairy partner of the
Twins, the "Dog," is the prototype of the older one who is cheated out of
his primogeniture in various ways. Esau, the hairy, is the first born; so is
Hono-susori no Mikoto (Nihongi, trans, by W. G. Aston [repr. i960],
pp. 92-108; K. Florenz, Die historischen Quellen der Shinto-Religion
[1919], pp. 204-21) who, together with his offspring, after having been
passed by the Japanese "Jacob," had to serve as "dogs," as clowns,
playactors, guardians of the imperial palace for eighty generations; at
New Year and during coronation ceremonies these Hayahito had to
bark three times.
Particularly obvious is the case in F.gypf, where we learn from II.
Kits (Der Ciottcrgltiiibc im Allen A'gylrtcn | 1956 |, p. i<;<, 11. \): "wrw
Hamlet's Mill • 406
means 'jackal' and 'the eldest,' " and it happens that Kees made this re-
mark when dealing with a classical case of cheating: when Geb/Kronos
declared Horus the eldest, cutting out Seth/Typhon completely, as
reported in the Shabaka Inscription. Actually Geb claims Horus to be
Upuaut, the Opener of the Way—Upuaut being the Upper Egyptian
Jackal or Wolf. The complex of the "Dog-Twin" is, however, of such
a size and weight that it cannot be attacked here.
A particularly relevant and revealing case of inseparable "twins"
comes our way in Cherokee mythology, where the thunder-boys are
called "Little Men." At the beginning we hear of one boy only, born
in proper wedlock by "The Lucky Hunter" and "Corn," but soon the
boy "finds" his "Elder Brother" in the river, and the latter has the name
"He-who-grew-up-wild." These two arrange the world and human
life as it is now, model cases of what ethnologists call "heroes of cul-
ture." Gilgamesh and Enkidu all over, they were asked to give "ver-
dicts," alias oracles, after they had finally left the "earth."1
Appendix 29
We might call it Lethe, and feel happy about it, were it not for the
deplorable uncertainty of Lethe's localization, with respect to the celes-
tial itinerary of the soul particularly. The Milky Way being as large
as it is, it does not help to state that one has to look for a galactical
section. Worse, it remains unclear at which occasion the souls were
supposed to drink from the water of this river of forgetfulness, whether
they did so shortly after having arrived in Hades or before their re-
incarnation, or at both times. Although the supposition of an intake of
Lethe right at the entrance of Hades would deprive the underworld
jurisdiction, together with the good or bad recompenses for former
conduct, of its significance, both views were upheld. (See Stoll, in
Roscher s.v. Lethe, col. 1957; O. Gruppe, Griechische Mythologie
und Religionsgeschichte [1906], pp. 403-405, 1036-41. On p. 760, n. 8,
Gruppe quotes a passage, according to which a soul which has not yet
crossed the river Lethe comes back to molest the living.)
Our most competent witnesses for Orphic-Pythagorean tradition take
Lethe for the last "station" before rebirth, e.g., Plato in the myth of Er
1 J. Mooncy, "Myths of the Cherokee," 19th ARBAE 1897-98 (1900), pp. 243-50.
407 • Appendices
(Republic 10.620), and Virgil in the sixth book of the Aeneid (748-
51), but only Macrobius (Commentary on the Dream of Scipio, trans,
by W. Stahl [1952], /.12.8) pretends to know the source of the drink:
the constellation Crater, the "bowl of Bacchus." This does not make
sense1 but, anyhow, he makes the souls descend through the northern
intersection of Galaxy and zodiac, taking the southern crossroads, be-
tween Scorpius and Sagittarius for the entrance, which fits the "Hades-
constellations" of the Sphaera barbarica. Yet we have observed, in
other parts of our globe (see pp. 242L), some uncertainty concerning
entrance and exit: the Nicaraguan "Mother Scorpion at the end of the
Milky Way" receives the souls of the dead, and takes care of the babies
going to be reborn, whereas the Cherokee appear to assume the entrance
at the "Northern End" of the Milky Way (Gemini-Taurus), from
where the souls migrate to the "Spirit-Star" in Scorpius. We are not
informed precisely whether the souls follow the Milky Way for a
whole half-circle, either turning to the north or to the south, or whether
they go first in one direction and return later on the same way. The
latter seems to be expressed in the Vishnu Purana which restricts the
"Way of the Fathers" to the region on the north of Canopus, and south
of three lunar mansions in Sagittarius and Scorpius; the "Road of the
gods" (devayana) runs north of three lunar stations in Taurus and
Aries, and south of the Seven Rishis, the Big Dipper. Vishnu Purana 2.8
(Wilson trans. [i96i],p. 186) reads:
On the north of Agastya, and south of the line of the goat [Ayavithi,
i.e., the said three nakshatras in Scorpius and Sagittarius] lies the road
of the Pitris. There dwell the great Rishis, the offerers of oblation
with fire, reverencing the Vedas, after whose injunctions creation
1 Macrobius' "uranography" is most embarrassing. He claims that "so long as the
souls heading downwards still remain in Cancer they are considered in the com-
pany of the gods, since in that position they have not yet left the Milky Way. But
when in their descent they have reached Leo, they enter upon the first stages of
their further condition . . . The soul, descending from the place where the Zodiac
and the Milky Way intersect, is protracted in its downward course from a sphere,
which is the only divine form, into a cone . . ." We have remarked already
(p. 242) that Macrobius, in calling the "Gate of Cancer" the crossroads of
Galaxy and zodiac, talks of signs, not of constellations. And so he does, when
pinning down the "bowl of Bacchus"—Crater—"in the region between Cancer and
Leo": Crater is "between" Leo and Virgo, i.e., south of these constellations. How
the souls, coming "down" from those crossroads, of Galaxy and ecliptic, i.e.,
between Taurus and Gemini, should get hold of Lethe in Crater, south of 1,10 and
Virgo, remains a mystery. Marrolmis was, Apparently, not in tin' habit of looking
at the sky, ami in this respect in- was a very modern character.
Hamlet's Mill
408
commenced, and who were discharging the duties of ministrant
priests: for as the worlds are destroyed and renewed, they institute
new rules of conduct, and reestablish the interrupted ritual of the
Vedas. Mutually descending from each other, progenitor springing
from descendent, and descendent from progenitor, in the alternating
succession of births, they repeatedly appear in different houses and
races along with their posterity, devout practices and instituted ob-
servances, residing to the south of the solar orb, as long as the moon
and the stars endure.
In a similar direction might point the report given by Pausanias about
the oracle of Trophonios in a deep cave (5^.39.8): the visitor comes first
to "fountains of water very near to each other.2 Here he must drink
water called the water of forgetfulness (Lethes hydor), that he may
forget all that he has been thinking of hitherto, and afterward he drinks
of another water, the water of memory (hydor mnemosynes) which
causes him to remember what he sees after his descent." Not enough,
after the oracle has been given, and the inquirer ascended from the
chasm (9.39.13), "he is again taken in hand by the priests, who set him
upon a chair called the chair of memory (epi thronon mn.) and they
ask of him, when seated there, all he has seen or learned. After gaining
this information they then entrust him to his relatives. These lift him,
paralyzed with terror and unconscious both of himself and of his sur-
roundings . . . Afterwards, however, he will recover all his faculties,
and the power to laugh will return to him."3
Nor does this "chair of memory" remain without its partner: Apollo-
dorus (Epit. z.24) tells us of the "Chair of Forgetfulness," to which
Theseus and Pirithous "grew and were held fast by coils of serpents."
That we learn also of "houses" of Lethe (Plutarch, Consolatio ad Appo-
lonium, ch. 15, iioe, quoting an unknown poet) does not make this
quarter more lucid. On the Etruscan Bronze Liver of Piacenza, letham,
the river, divides the lower—otherwise empty—side into approximately
equal parts—the invisible southern arch of the Milky Way?
2 So are the rivers of lust and mourning (Hedone and Lype) of Theopompus
(Book 8 of his Philippika) which have been compared to our rivers by E. Rohde
("Zum griechischen Roman," Rh. Mus. 48 [1893], pp. 123^). In Polynesia we meet
near together the "water of life" and the "water of death" (see R. Williamson,
Religious and Cosmic Beliefs of Central Polynesia [1924], vol. /, pp. 334, 344; vol.
2, pp. i69f.).
3 Of considerable interest are several terrestrial rivers called Lethe, mentioned
by Gruppe (Griechische Mythologie [1906], p. 817): they arc flowing at the foot
of several "White Rocks" (Leuketis skopelos), one among which lias the name
agelastos pare, the laughterless rock.
409 • Appendices
Considering this state of confusion and uncertainty, we abstain from
calling it rightaway either the drink of forgetfulness or the drink of
memory, although one or both of them could very well be found upon
the shelves of Ishara tamtim, alias Mother Scorpion.
Appendix 30
See P. F. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum (1950), 94: "mulGIR2-
TAB dIshara tam-tim. Anton Deimel (Pantheon Babylonicum [1914],
pp. i48f.) takes mulGIR.TAB for beta delta alpha Scorpii only: 'Ishara
est dea quaedam partus, quae relationem habet ad Gestin anna, Adad.'':
See also W. J. Hinke, A New Boundary Stone of Nebuchadnezzar I
from Nippur (1907), pp. 223, 243; A. Jeremias, HAOG (1929), pp.
223, 385; F. Hommel, Ethnologie und Geographie des Alien Orients
(1926), pp. 563, 770-74, 783; and D. O. Edzard, "Die Mythologie
der Sumerer und Akkader," in Worterbuch der Mythologie, vol. /,
p. 9.
We might be accused of a clumsy contradiction because of having
claimed Sirius to be the "Sea-Star" in appendix #2, when here it is evi-
dent that Ishara tamtim, the goddess of Scorpius, is entitled to this dig-
nity. We are not only aware of this apparent "contradiction," but we
also hope to unravel the mystery in the future. It is a mysterious
scheme, but not a hopeless case. Clue number one is contained in the
Coptic list of lunar mansions, already mentioned in appendix #4 (cf. A.
Kircher, Oedipus Aegyptiacus [1653], vol. 2, pt. 2, p. 246), where it is
stated with respect to the twentieth lunar mission, the sting of the scor-
pion (lambda upsilon Scorpii): "Aggia, Sancta, Arabice al-Sa'ula [i.e.,
"the sting" ]; statio translationis caniculae in coelum, unde et siot vocatur
. . . Longitudo huius stationis est a quarto Sagittarii usque ad decimum
septimum eiusdem. Haec statio ab Aegyptiis quoque vocatur soleka sive
Astrokyon . . . statio venationis." Eduard Stucken (Der Ursprung des
Alphabets und die Mondstationen [1913], p. 7) identified this soleka
immediately with Egyptian Selket/Serqet, the Mesopotamian Ishara
tamtim, the Scorpion goddess. Whether or not this is permissible under
the stern laws of linguists, it is a fact that we find regularly on the
F-gyptian astronomical ceilings Selkct standing above, i.e., beyond, tin-
Hamlet's Mill
410
411
Appendices
o
bull's thigh (Big Dipper), which means that Selket represents the oppo-
sition to the perpetual center of attention: Sirius/Sothis. (Yes, we are
aware of the circumstance that fourteen degrees is no ideal opposi-
tion to one star.) Clue number two are the stories spun around Indian
mura, "the root" (or "tearer out of the root"), again lambda upsilon
Scorpii—compare appendices #4 and #39—which have to be combined
with the ocean of most atrocious yarns dealing with Mandragora
(Alraun), the famous root that can be pulled out only by a dog that
dies immediately after having completed this feat. Clue number three is
carefully hidden away in the Mexican traditions concerned with the
hunting festival Quecholli (statio venationis, and Quecholli is not to
be separated from the "hunt" for hikuli, the peyote, as undertaken by
Huichol and Tarahumare), which rehearses the great "fall" of the gods
who had plucked the forbidden flowers, in Tamoanchan, "the house of
descending."
Appendix
These unknown factors, crucial as they are, resist successfully every
decoding for the time being. Su-ut abne, "those of stone," represent "an
expression which recurs and has not been explained" (S. Langdon,
Semitic Mythology [1931], pp. 213^, 405). Alexander Heidel (The
Gilgamesh Epic and Old Testament Parallels [1963], p. 74, n. 157) re-
marks: "The Hittite Version has 'two images of stone.' These images
may perhaps have been idols of an apotropaic character enabling
Urshanabi to cross the waters of death." Speiser ("Akkadian Myths and
Epics," ANET, p. 91, n. 173) makes it "apparently stone figures of
unusual properties ..."
According to Speiser (Assyrian version, Tabl. 10, col. 3, 37^, ANET,
p. 92; cf. Heidel, p. 76) Urshanabi states: "Thy hands, Gilgamesh, have
hindered [the crossing]: Thou hast broken the Stone Things . . . ,"
which can hardly be correct, since they do cross, after all.
F. M. Th. de Liagre Bohl, in his translation of GE, seems to have
boldly claimed that the "stone objects" were "part of the fence of
Siduri's yard," to which I. M. DiakonofT (Review article on the GE
translations of F. M. Th. Bohl and P. L. Matous, Bibliotheca Orientalis
18 [1961], p. 65) remarked: "The sut abne cannot have any connection
with Siduri's yard (indeed, no such yard is mentioned)."
Luckenbill (AJSL 38 [1922], pp. 96-102) seems to have voted for
anchors (see Gilgamesh et sa legende, ed. by P. Garelli [1958], p. 17,
item 146). Orally, three years ago, Florence Day proposed "load
stones." For further keen propositions, see A. Salonen, Die Wasserfahr-
zeuge in Babylonien (1939), pp. 13if.
Some new light falls upon these objects through a Neo-Babylonian
fragment published by D. J. Wiseman (Gilgamesh et sa legende,
pp. 128-30), but the author himself states that the new reading (u su-ut
NA4.MES) "appears at present to help little towards the understanding
of this much discussed term. The restoration of parts of 11.3 5-41, now
possible, shows that the end of this column describes the manner in
which Gilgamesh met Ur-shanabi and obtained the boat and its equip-
ment for his journey over the 'waters of death.'
When Gilgamesh heard this,
he took up the axe in his hand,
drew the dagger from the belt,
crept along and went down . . .
Like a lance he fell among them . . .
within the forest he sat down and . . .
Ur-shanabi saw the flashing of the dagger,
heard the axe and . . .
Then he smote his head . . . Gilgamesh
seized the wings ... its breast
and the sutabne .. . the boat. .."
More annoying still, these stone-things are not the only vexing items
to be found in the neighborhood of Urshanabi. Heidel simply drops
them, and renders line 29 of the Assyrian version (Tabl. 10, col. 2,
p. 74): "With him are the stone images (?), in the woods he picks . . . , "
and accordingly he deals with column 3, 38f.: only the stone-things are
mentioned. Speiser (ANET, p. 91) continues after the "Stone-Things":
"In the woods he picks ['mTzz/'-snakes]." And column 3 he renders:
"Thou hast broken the Stone Things, hast picked [the 'urnu'-snakes |.
The Stone Things arc broken, the 'urnu' is not I in the woods |."
Hamlet's Mill
412
In note 174 Speiser refers to Landsberger (Die Fauna des Alien Meso-
potamien [1934], P- 63)> who "points out that the urnu snake has long
been supposed to be a favorite with sailors. At all events, whatever the
meaning of the term may be in the present connection, its properties
seem to be on a par with those of the Stone Things."
Now, let us first express our disapproval of Urshanabi's lack of "fair-
ness," just in case this translation might be correct: Siduri states it as
well known that "Urshanabi, with whom are the stone-things, picks
urnu-snakes" in the woods, and here he accuses Gilgamesh of having
done so, taking it, evidently, for an improper thing to do! In the second
line, B. Landsberger (Fauna, p. 63; cf. pp. 45^, 52, 60) identified tenta-
tively the "urnu-snake" (maybe also "the yellow (green) snake," mus.
sig7. sig7) with the waran, and considers, since even today warans are
eaten, that the urnu were collected in order to serve as roast meat for the
sailors. He thinks it possible that in later times "urnu" was meant as
"land-crocodile." If urnus belonged to the usual travel provisions, why
should the picking of these animals be an impediment for the crossing
of the waters of death? Although one should not criticize others, least
of all scholars of the rank of Landsberger, if one has no positive propo-
sitions to offer, reading through this learned work, it becomes less and
less comprehensible how he could misapprehend these animals, particu-
larly the snakes, for a veritable terrestrial fauna, these seven-headed,
one-eyed, unicorned creatures belonging to Anu, Nergal, Ningishzida,
etc.
Appendix 32
Considering that removed posts or pegs, pulled-out pins, wrecked
axles, and felled trees have accompanied this whole investigation as a
kind of basso ostinato, we cannot pass in silence over these superimpor-
tant posts; considering, on the other hand, that technical details are not
likely to make pleasant reading, we prefer to deal with this specimen
outside the main text, although we deem it essential indeed.
The object that Irragal is tearing out is called tarkullu, Sumerian
DIM.GAL, which has been translated into "(Anchor-)post," "ship's
mast," "mooring-post" (Hcidcl), also "anchor" itself, and even "stccr-
413 • Appendices
ing-oar" (Jensen).1 In the Era Epic, Era (=Irragal=Nergal), when
announcing a new catastrophe, threatens that he is going to tear out the
tarkullu, that he will make the ship drift off, break the steering oar so
that the ship cannot land, and remove the mast and all that belongs to it.2
We meet the word also in names given to temples, as we learn from
Burrows,3 who considers "the evidence for the relation of the temples
to (1) heaven, (2) earth, (3) underworld," and tells us what follows:
(1) The idea of the Bond of Heaven and Earth is given explicitly.
Dur-an-ki, was the name of sanctuaries at Nippur, at Larsa, and prob-
ably at Sippar. Also in Semitic markas same u irsiti, Bond of Heaven
and Earth, is used of the temple E-hursag-kur-kur-ra and of Babylon.
(2) Idea of Bond of the Land. Probably by extension of religious
use the royal palace of Babylon is called markas (bond) of the Land.
An ancient Sumerian temple-name, which probably expresses an
analogous idea, is "dimgal of the Land." This was the name of the
temple of Der, an old Sumerian center beyond the Tigris; a name
given to Gudea's temple at Lagash; a temple of Sauska of Niniveh;
and probably the temple of Nippur was another "dimgal of the
Land." The pronunciation and meaning of dimgal are disputed.
"Great binding-post" is perhaps a fair translation. The religious terms
udimgal of the Land" and the like perhaps indicate the temple as a
kind of towering landmark which was a center of unity by its height.
(3) Idea of the bond with the underworld. Gudea uses dimgal also
with reference to the abzu, i.e., the waters of the underworld: he laid
two temens, ritual foundations—the temen "above" or "of heaven"
and the temen "of the abzu," and the latter is called "great dimgal."
The idea may be that the temple is as it were a lofty column, stretch-
^ing up to heaven and down to the underworld—the vertical bond of
the world. The same passage mentions, it seems, a place of libation
1See P. Jensen, Die Kosmologie der Babylonier (1890), pp. 377, 422f.; K. Tall-
qvist, Akkadische Gotterepitheta (1934), p. 244 (see also p. 283; Dim gul-ah-na /
"Himmelspfahl" == Ninurta, and Dim gulkalam-ma "Weltpfahl" = Ninurta). Sy
C. Bezold, Babylonisch-Assyrisches Glossar (1926), p. 296: "Pfahl, Priigel, Schiffs-
pfahl, Mast"; A. Salonen, Nautica Babyloniaca (1942), p. 85; "(Anker)pfahl." On p.
104 Salonen explains tarkulla as "the mast," and it is the mast of Ea's ship: "sein (des
Ea-Schiffs) Mast ist in der Schiffsmitte aufgestellt, schwebt am Himmelsband." See
also R. Labat, Manuel d'Epigraphie Akkadienne (1963), no. 94, p. 81: DIM riksu,
lien; dimmu, colonne; DIM-GAL tarkullu, mat; no. 122a, p. 93: DIM GUL tar-
kullu, mat. Cf. B. Meissner, Beitrage zum Assyrischen Worterbuch / (1932), pp.
58f., and A. Schott, Das Gilgamesch-Epos (1958), p. 90, n. 19: "Das Weltenruder?"
2 For the explanation of the several termini, see P. F. Gossmann, Das Era-Epos
(1956), p. 55; see also Ebeling, AOTAT, p. 227.
3 Eric Burrows, S.J., "Some cosmological patterns in Babylonian religion," in
The Labyrinth, ed. by S. II. Hooke (1935), pp. 46ft. (Thai we do nor share the
author's too simple opinions gO63 without Baying.)
Hamlet's Mill
414
to the god of the underworld. Drains or pipes apparently destined
for libations to the underworld have been discovered at Ur. Thus, if
these interpretations are right, the temples expressed not only, in
their height, the idea of the bond with heaven but also, in their depth,
that of union with the netherworld.
Were we to hear less of "towering landmarks" and "lofty columns,"
for the sake of being presented with one single thought dedicated to the
fact that these alleged "temples" and "columns" were torn out in order
to start a deluge, we would be better off. Much more astonishing, how-
ever, is the circumstance that nobody seems to have taken the trouble
of looking for relevant enlightenment in Egypt, i.e., of dealing with the
Egyptian mnj.t.
According to Erman-Grapow (Wdrierbuch der Aegyptischen
Sprache [1957], vol. 2, pp. 721T.) the word is used as (1) symbolical
expression for the king (als Lenker des Staatsschiffes); (2) symbolical
expression for Isis and Nephthys who fetched Osiris from the water.
It is a constellation, the instrument for impaling, the post to which a
person to be punished is bound. The transitive verb (mnj) means to
bind to a post, to tether (anpflocken); the intransitive verb means to
land, from persons, and from ships, and to die, sometimes supplemented
"at Osiris" (bei Osiris landen).
This mnj.t ivr.t—Mercer writes it min.t—the "great landing stick,"4
is said "to mourn" for the soul of the dead in the Pyramid Texts,5 and
Mercer comments6 that "the great stake ... is personified as a 'mourn-
ing woman' in reference here to Isis." The "mooring-post" being a con-
stellation, as even the Worterbuch der Aegyptischen Sprache has to ad-
mit, the question is where to look for this mnj.t. The constellation—
transcribed menat by Brugsch,7 mnit by Neugebauer8—occurs in two
categories of astronomical monuments, namely (1) in the Ramesside
4See W. Max Miiller, Egyptian Mythology (1918), p. 376, n. 79.
5 Pyramid Texts, ed. by S. Mercer (1952), p. 794c: "The great min.t (-stake)
mourns for thee"; cf. 876c, 884b ("the great min.t laments for thee, as for Osiris
in his suffering"), and 2013b.
6 Pyramid Texts, vol. 2, p. 399; see also p. 361. See pp. 371, 398 for mini "to
pasture, to land (i.e., to die)," and for min.iv, derived from mini, as an epithet of
Anubis 793c: "he who is upon the min.iv"). "The min.w here seems to indicate a
cask for the limbs of Osiris."
7H. Brugsch {Thesaurus lnscriptionum Aegyptiacorum [1883-91; repr. 1968],
pp. 122, 130, 188) takes it for a "knife" or "sword"; later {Die Aegyptologie
[1891], p. 343) he spelled it "ship's peg" ("Schiffspflock" and "Doppelpflock").
8O. Neugebauer and R. Parker, The Raines side Star Clocks (1964), p. 7.
415 • Appendices
Star Clocks,9 and (2) in the ceiling pictures of royal tombs, in the
zodiacs of Dendera, etc. In every case the peg or post rests in the hands
of Isis disguised as a hippopotamus; fastened to the mooring-post is a
rope or chain, to the other end of which is tied Maskheti, the bull's
thigh, i.e., the Big Dipper, and in one of the texts it is stated (Brugsch,
Thesaurus, p. 122) that "it is the office of Isis-Hippopotamus to guard
this chain."
According to the Ramesside Star Clocks, mnj.t included six different
parts,10 and only after these six parts follow rrt "female hippopotamus,"
comprising eight positions. Boll (Sphaera [1903], p. 222) remarks that
this constellation must be thought of as being parallel to either the
equator or the zodiac, and as being rather "long," because otherwise it
could not need more than four hours of ascending.
Most of the scholars dealing with the Egyptian astronomical ceilings
took it for granted that the main scenery represented the northern cir-
cumpolar constellations, because the Big Dipper, Maskheti, holds the
"determinant" position upon the stage, and they tried their hardest to
identify Isis-Hippopotamus holding the mooring-post, and carrying
upon her back a crocodile, with a constellation very near the Pole.
Now, we do not mean to go into details of the Egyptian sphere as
represented in these ceiling decorations, which is an extremely difficult
task, and nothing has been gained in the past by the different efforts to
settle the affair by simply looking at the sky (worse, at sky-maps) try-
ing to imitate Zeus by "catasterizing" on one's own account, and giv-
ing keen verdicts. Let us say only this much: (1) as yet no single
proposition concerning the Hippopotamus holding the mooring-post is
satis/ying;11 (2) that the determinative group of the ceiling pictures
9 Formerly they were called "Theban hour-tables" {Thebanische Stundentafeln,
or Thebanische Tafeln stundlicher Aufgange).
10 Neugebauer and ParkgfT^The Ramesside Star Clocks," p. 7: (1) the "prede-
cessor," or the "front of the moorjing post," (2) "is not translatable," (3) "follower
of the front of the mooring post,' (4) "mooring post," (5) "follower of the moor-
ing post," (6) "follower which comes after the mooring post."
11 We hope for enlightenment to be contained in the third volume of Neuge-
bauer's Egyptian Astronomical Texts. In vol. 2, p. 7 he states, with respect to the
hour-stars: "To what extent, if at all, the constellations of the lion, the mooring
post, the hippopotamus, and perhaps others, can be identified with similar figures
in the so-called 'northern' constellations as depicted on many astronomical ceilings
... is a problem into which we do not intend to enter until all the evidence can
be presented in <>ur final volume. Thai the problem is more complex than would
appear at first glance a< Least In so far as the two hippopotami are concerned
is sufficiently iiulicsiuul by the fact thai <m the ceilings the hippopotamus is -newt
1
Hamlet's Mill • 416
show decisive factors of the "frame": Leo, Scorpius, Taurus,12 serving
thus as a kind of "key" of the whole presentation.13 But, if our "frame"
is meant, i.e., the structure of colures, where is the southern celestial
landscape? We do not dare to molest the reader with the impenetrable
text (Brugsch, Thesaurus, p. 122), out of which we quoted only one
sentence which states that Isis-Hippopotamus is guarding the chain; this
much at least is recognizable, that this text jumps from the Big Dipper—
via "the middle of the sky"—to positions "South of Sah-Orion."
And here Casanova14 comes in quite handy with his proposition to un-
derstand mnj.t (he writes it menat) as Menouthis, the wife of Canopus,
steersman of Menelaus, whom we know from late Greek texts (also writ-
ten Eumenouthis). Epiphanius15 talks of the tomb of both, i.e., Canopus
and his wife, in Alexandria. Stephanus of Byzantium knows of a village
"at Kanobos" which had the name Menouthis.16 It would lead us too far
to deal with Canopus-steersman-of-Menelaus, and the Canopic mouth
named rrt, never is shown with two feathers as a headdress, and very frequently
has a crocodile on its back." (We are only too grateful for everybody who recog-
nizes that the problems are "more complex"—a hundred times more complex,
indeed—"than would appear." The underlining of "so-called 'northern'" is ours;
that of the two "never's" is Neugebauer's.)
12 That the Dipper is said to be the thigh of a bull indicates Taurus clearly
enough; we have mentioned that there is also a "foreleg of Khnum" available, i.e.,
that of a ram, and that in Dendera a ram is sitting on the Ursa-Leg: whose leg it is
depends from the constellation marking the vernal equinox. To the objection that
the constellation as depicted in Egyptian pictures clearly shows the hindleg of an
ox, we have to answer that the texts insist on talking about the bull's foreleg; in
other words, the real resemblance does not count so much, apparently (cf. appen-
dix #27).
13 Even if we had no other evidence, the Ramesseum would be good enough,
showing in the center, precisely below Maskheti, the baboon sitting upon the
Djed-pillar—we know from Horapollo (/.16) that the squatting baboon indicates
the equinoxes; whereas the third, lowest register shows the sitting dogs at both ends,
and we know from Clemens Alexandrinus (Strom. 5.7, 43.3) that these represent
the Tropics.
14 P. Casanova, "De quelques Legendes astronomiques Arabes," BIFAO 2 (1902),
p. 18.
15 Quoted by P. E. Jablonski, Pantheon Aegyptiorum (1752), vol. 3, pp. 141L
16 Casanova, p. 153. Cf. H. Kees in RE s.v. Menuthis, cols. 968f., who also men-
tions a dedication to "Eisidi Pharia, Eisin ten en Menouthi," and who points to a
sanctuary of Menouthis famous as "sanatorium" and replaced, later, by a monastery.
W. Max Miiller, in his turn (Egyptian Mythology [1918], p. 397, n. 94), in-
forms us thus: "In the Greek period the name Menuthias ('Island of the Nurse')
was given to a mythical island in the South as being the abode of the divine nurse
[of Horus], and later this was identified with Madagascar as the most remote
island in the south, i.e., the lower world." Miiller seems CO take Menouthis for the
417 • Appendices
of the Nile: the modern Homo occidentalis is bound to shrink back from
the mere idea that the Nile represented a circle, where "source" and
"mouth" meet, so that there is nothing preposterous in the notion that a
Canopic mouth can be found in the geographical North, and here it
is not necessary to discuss the question. It is sufficiently striking to see
the mooring-post "married" to Canopus in a similar manner as Ur-
shanabi is "married" to Nanshe, Enki's daughter, to whom is con-
secrated the holy stern of the ship.
Admittedly, we know as little as before where precisely the mnj.t of
the star clocks has to be looked for,17 but we have at least made it more
plausible that DIM.GAL/'tarkulluj'mnj.t must be the decisive plumb line
connecting the inhabited world with the celestial South Pole or, let us
say, with the orbis antarcticus: Osiris being depicted as a circle (see
Brugsch, Religion und Mythologie, plate facing p. 216), the verb mnj.t,
"to land (at Osiris)," points in this direction. (We recall once more
Virgil's statement that the "shades infernal" and Styx see the South
Pole.) It has not escaped our attention that GE //.101 seems to talk
of posts, in the plural: as, in some Egyptian texts, we have the "double
mnj.t." We do not know yet why: the Era Epic uses the singular, but
Era is going to pull out a different post from the one he had torn out
previously in GE under his name Irragal. There are possible solutions,
but we leave alone this question as well as the next difficult problem
arising with the suspicious similarity of the ship's peg with the nose-
bone of the Horus-Eye (numerical value 1/64), however tempting this
problem is.
same as Thermouthis, the daughter of that Pharaoh who found Moses in the Nile
(cf. Josephus, Jewish Antiquities 2.9.5-7, 224; Bk. Jub. XLvii.5: Tharmuth),
without giving sources or reasons for doing so. We should very much like to know
whether or not mnj.t is identical, or has something to do at all with "Menat or
Heliopolis," wrTom\Brugsch identified with Satit of Elephantine (of all deities!);
it would be (decisive; to know it. (Cf. Brugsch, Religion und Mythologie [1891],
p. 3or; Brugsch, Thesaurus [1883-91; repr. 1968], p. 107.)
17 Some years ago, a mathematician in Frankfurt, who had invested much com-
puter time in the star clocks, felt sure that mnj.t must end in alpha Centauri. As
concerns the astronomical ceilings, we have presumably to mind the manner in
which the late zodiacs of Dendera and Esne (Roman time) "project" the Big
Dipper/'Maskheti, the bull's thigh (together with Isis-Hippopotamus and the
chain) into the zodiac, namely, between Scorpius and Sagittarius (Esne), and
between Sagittarius and Capricornus (Dendera). There is, moreover, a remarkable
Arabian survival (R. Bokcr, quoting Chwolson [1859V in A. Schorr's tninsl.ition
of Aratus, Sternbildcr und Wcticrzcichcu [ 1958], p. 119) staring 10 Sagittarius
30: "To the right of tjic degree is Alcshkcdai, the moulder of divine images."
Hamlet's Mill • 418
Appendix 33
The mere notion of the emperors sleeping makes it clear that they are
expected to awake and to return one day;1 be it Quetzalcouatl (in the
heart of the sea), Ogygian Kronos himself, or Arthur, "ruler of the
lower hemisphere," who announces in a fictitious letter "that he has
come, with a host of antipodean subjects"2—according to Etienne de
Rouen (c. 1169; see R. S. Loomis [ed.], Arthurian Literature in the
Middle Ages [1959], p. 69); that Geoffrey of Viterbo placed Arthur
straightaway into the depth of the sea has been mentioned on p. 299,
n. 35.
Few scholars only, among them Franz Kampers and Robert Eisler,
have recognized the awe-inspiring age of such traditions, and even they
have been incapable of calling the much-expected "redeemer" and "kos-
mokrator" by his very own name: Saturn. Says Kampers, concerning
the apocryphal Apocalypsis of Daniel:3
Alexander wird hier . . . nicht mit seinem Namen genannt, sondern
er wird als Johannes eingefiihrt. Nach all dem Gesagten wird es nicht
mehr allzu kiihn erscheinen, in diesem Namen Johannes eine pro-
phetische Chiffre zu erkennen. Wenn Nimrod in einer altslawischen
Sage auch Johannes heisst, wenn der erdichtete Erretterkonig der
Kreuzfahrer, wie wir sehen werden, Johannes genannt [=Prester
John] und auch in Beziehung gesetzt wird zu dem Weltenbaum, so
diirfte die Annahme, dass hier fortlebende altorientalische Oannes-
Erwartungen sich aussern, nicht von der Hand zu weisen sein.
And right here, he refers to Robert Eisler's chapter, "John-Oannes?"
which states:4
We should not hesitate even to presuppose that the same syncretism
of John and Oannes, which seems so natural with Neo-Babylonian
Gnostics [the Mandaeans are meant], existed also among the more
immediate Jewish followers of the Baptist, seeing that an influence
1 See for the rich theme of "heroes inside hills," J. Grimm, TM, pp. 951-62; Axel
Olrik, Ragnarok (1922), pp. 353-62.
2 This role is otherwise ascribed to Beli (or Bilis), brother of Bran, "the dwarf
King of the Antipodes"—later he had the name Pelles. "In Welsh poetry the sea is
referred to as Beli's liquor and the waves as Beli's cattle" (R. S. Loomis, The Grail
[1963], pp. 110-12). "Elsewhere he is implored as 'victorious Beli . . . that will
preserve the qualities of the honey-isle of Beli' " (McCulloch, in ERE 3, p. 290).
3 F. Kampers, Vom Werdegange der abendlandischen Kaisermystik (1924),
p. 109; Kampers, Alexander der Grosse und die Idee des Weltimperiums in Pro-
phetie und Sage (1901), pp. 145-48.
1 Orpheus /he Fisher (1921), pp. 151 62, csp. p. 155.
419 • Appendices
of the Babylonian belief in ever new incarnations of the primeval
Oannes—Berossos knows as many as six such reincarnations in past
times—on the Messianic hopes of the later Jews is far from credible.
In ch. 12L of IV Esra (temp. Domitian, 81-96 a.d.), the redeemer of
the world, the celestial "Man" is expected to rise from the "heart of
the Ocean" before his coming, as Daniel (7.13) says, with the clouds
of the sky, for: "As no man can search or discover that which is in
the depths of the Ocean, even so no mortal can see the Son of God
nor his hosts except in the hours of His day."
Accordingly, we find in 4 Ezra xm.3 (in E. Kautzsch [ed.], Pseudo-
epigraphen des Alien Testaments [1900]) the sixth vision of the pro-
phet: "Ich schaute, siehe da fiihrte jener Sturm aus dem Herzen des
Meeres etwas wie einen Mann hervor." In a note (p. 395) the Latin
translation of the Syriac version is quoted: "Et vidi et ecce ipse ventus
ascendere faciebat de corde maris tanquam similitudinis hominis."
We know well enough that the Oannes of Berossos is Ea, i.e., Saturn,
whose "town" is Eridu/Canopus, the very depth of the sea. That Ogy-
gian Kronos is unmistakably the planet Saturn is not to be overlooked
by anyone who reads Plutarch's report (De facie quae in orbe lunae
apparet 941) of the "servants" of Kronos who—every thirty years,
when Saturn is standing in Taurus—sail to Ogygia to remain there in
service for thirty years, after which they are free to go; but most of
them prefer to stay, because there, in Saturn's island, the Golden Age
lasts on and on. The servants spend their whole time on mathematics,
philosophy, and the like, and there is no reason to worry about food,
it is all conveniently at hand.
"The reluctance at recognizing the almost uncanny power of the old-
est traditions is a very modern invention. Kampers still knew very well
that the "type" of the medieval emperor was coined in the most ancient
Nfear East, Alexander being a "repetition" of Gilgamesh, and the em-
peror repeating Alexander again and again. (Cf. Kampers, Vom Werde-
gange, pp. 2 if., 35, and passim.)
Appendix 34.
Actually, we arc up against a completely incomprehensible narrative
of events which occurred during ;i sen voyage. The plunt, nccording lo
Albrighi < AJSI ;6, p. zHi, n. .•) literally "thorny tfmpevine,1 is sup
Hamlet's Mill • 420
posed to grow in the apsu, and to be accessible by way of a "water-
pipe." This pipe, ratu, however, is a conjecture right here: the word
occurs only later when, after his bath in a well, and the following loss
of the plant, Gilgamesh complains bitterly about his frustration, i.e.,
about having obtained a boon for the "earth lion" instead of for himself.
The "earth lion," identified with the thievish serpent, is assumed in its
turn to live "in a well which communicated with the apsu" (Albright,
AJSL 35, p. 194). It is then (GE 77.298) that the hero says: "When
I opened the water-pipe and [. . .] the gear, I found that which has
been placed as a sign for me: I shall withdraw and leave the boat on the
shore" (Speiser trans., ANET, pp. 96L). Heidel makes it: "When I
opened the ... I have found something that [has been s]et for a sign
unto me; I will withdraw!" Instead of that "sign," Albright (RA 16,
pp. 175f.) recognized a flood rising out of the pipe (if so, why does
Gilgamesh talk about it only after his bath in the well?): "When I
opened the water-pipe, I overturned the cover (?). Let not the sea rise
to my side, b[efo]re (it) let me retire"; and so did Ungnad-Gressmann
(pp. 63f.) and Schmoekel (p. in). From this passage the translators
derive the occurrence of the word ratu in the earlier passage, where
Gilgamesh dives for the plant. Speiser alone1 refers to another occasion
where the word is used, and it is a decisive occasion; namely, in the
(wrongly called) "Eridu creation story" (v. n), where it is told that
before anything was created and when all lands were sea (tamtim),
then "the spring which is in the sea was a water pipe; then Eridu was
made, Esagila was built" (Heidel, The Babylonian Genesis [1963],
pp. 6if.). Sayce (ERE 4, p. 129) makes it a "current" within the sea;
with Jensen (Assyrisch-Babylonische My then und Epen [1909], p. 41)
it is a "Wasserbecken"; with Ebeling (AOTAT, pp. 130^) a "Schoepf-
rinne." Considering that Eridu is Canopus, and Esagila is "1-Iku"—
the Pegasus-square between the two Fishes that ruled the hibernal sol-
stice during the Age of Gemini—this particular ratu seems to have been
the connection between the two depths of the sea, between Pisces as the
depth of the salt sea and Canopus as the depth of the apsu, the sweet
water ocean.
1 ANET, p. 96, n. 232. The conclusions drawn from this footnote by N. K.
Sandars in his rendering of the GE in the form of a "straightforward narrative"
are, as is his whole undertaking, a willful misrepresentation of the truth, unless one
accepts the whisking away of the iooi stumbling blocks and obscurities and the
fabrication of a "Gilgamesh made easy" for a praiseworthy progress (Gilgamesh
Epic [i960], pp. 53, 113).
421 • Appendices
Although it is probable that the conception of one or more such
"pipes" is the same as the Jewish one of the "channels," shithim, that
went down to the tehom and were dug by God during the creation,
this is not the place to deal broadly with this plot. In any case, Gilga-
mesh opening one or the other ratu comes close to David, who, when
digging such a channel, found the Eben Shetiyyah. The relevant (and
revealing) material has been assembled by D. Feuchtwang in his article,
"Das Wasseropfer und die damit verbundenen Zeremonien," Monats-
schrift jiir Geschichte und Wissenschaft des Judentums 54 (1910), pp.
535-52, 7i3-29; 55 0911), PP- 43-63-
Of remarkable interest are pieces of information dealt with by Lang-
don (MAR j, pp. 227-29) coming from Nicander, and Aelianus (De
natura animalium ^.51), who in his turn refers to Sophocles,2 and several
poets whose works are lost. Aelianus—to whom, by the way, we are
indebted for the only mention of our hero's name in^Greek literature
(De natura animalium 12.21: Gilgamos)—when dealing with a particu-
larly fiendish small snake called Dipsas (literally "thirst")-,i:ells the fol-
lowing:
It is said that Prometheus stole fire, and the myth goes that Zeus was
angered and bestowed upon those who laid information of the theft
a drug to ward off old age. So they took it, as I am informed, and
placed it upon an ass. The ass proceeded with the load on its back;
and it was summer time, and the ass came thirsting to a spring in its
need for a drink. Now the snake which was guarding the spring
tried to prevent it and force it back, and the ass in torment gave it
as the price of the loving-cup the drug that it happened to be carry-.
- ing. And so there was an exchange of gifts: the ass got his drink and
the snake sloughed his old age, receiving in addition, so the story
goes, the ass's thirst. [The Sophocles fragment says that since then,
snakes slough their old skin every year, kath'hekaston eniauton.]
Nicander, as quoted by Langdon, supplements the story by telling us
of the date when this "exchange of gifts" took place, namely, on the
occasion of a new distribution of the "Three Ways," reporting "that
when Cronus' eldest son became master of Heaven, he divided up in
his wisdom glorious governments among his brethren, and gave youth
as a reward to short-lived men; so honouring them, because they dis-
closed the thief of fire, fools that they were! for they got no gain from
their evil counsel."
aFrg. 56-! (Pearson ed.) = frg. ^^ Tragicorwn Qtaecoruw Frctginenta, ed. A.
N;ui(l< (1964), pp. 2<>9f., from Kdphoi Saluroi.
/
Hamlet's Mill • 422
Appendix 3$
There are a few dim and blurred signals to be received from the
regions of Styx flowing, as we have heard, in sight of the celestial South
Pole. Photius1 tells us about Hyllos, son of Herakles, who had a small
horn growing out of the left side of his head, and how Epopeus2 of
Sikyon broke off this horn, after having killed Hyllos in a duel, fetched
Styx water with this horn, and became king of the country. Why should
he have procured this much dreaded water, if it did not enable him to
become king?
Allegedly "late" are the legends claiming that Thetis made the child
Achilles invulnerable by means of Styx water—his heel excepted, as we
know. On the other hand it was fabled that Alexander was killed with
water from the Styx, as Pausanias, who remained skeptical, reported (see
also p. 201, n. 8). Thus, both of them were brought in touch with
Stygian water, the one almost at the right moment, but only almost,
and the other at a completely wrong time, far away from that unknown
day in the year, where this fluid was supposed to make the drinker
immortal, whereas it brought inevitable death on every other day.
Appendix 36
For related conceptions in Rome, see Festus (128M, BT [1965],
p. 115): u Manalem fontem dici pro eo, quod aqua ex eo semper manet
. . . Manalem lapidem putabant esse ostium Orci, per quod animae
inferorum ad superos manarent, qui dicuntur manes." (Cf. F. Bomer,
"Der sogenannte Lapis Manalis," ARW 55 [1936], p. 281; Kroll, RE
16 s.v. mundus, cols. 56if. To prevent one-sided conceptions from steal-
ing into the picture, see also Festus 156M, p. 147: "Manes di ab auguri-
bus vocabantur, quod eos per omnia manere credebant, eosque deos
superos atque inferos dicebant.)
To this one should compare the rich material offered by F. M. Corn-
1 Bibliotheque, ed. R. Henry (1962), vol. 2, p. 56.
2 M. Riemschneider (Augengott und Heilige Hochzeit [1953], p. 59) interprets
the name: "dcr Hinaufschaucr, der 1 linaufwiiiflcr."
42 3 • Appendices
ford ("The Eleusinian Mysteries," in Festschrift Ridgeivay [1913], pp.
i6off.) about Greek underground structures, "phrear, the equivalent of
the Latin puteus." And about the "Curtius-Lake," Lacus Curtius—repre-
senting a mundus—which was to be found, according to Dion. Hal.
2.42, en meso tes Romaion agoras, i.e., right in the middle of the Forum
(see also Festus 49M, p. 42). Cornford explains (p. 162, note):
The legend of Curtius, whose self-devotion stopped a flood, and who
was honoured with dona ac fruges thrown into his lakkos, may throw
light on the custom at Athens of throwing wheatmeal kneaded with
honey into the cleft in the ground at the precinct of Ge Olympia
where the water ran away after Deukalion's flood, Paus. 7.18.7.
The well, closed by a stone—here even by a veritable Roman general
and his horse—is not unfamiliar to us, meanwhile, after all that we heard
about Eben Shetiyyah, the well of the Ka'aba, etc. There are more
curious connections between wells and stones that ask for consideration
in future investigations, such as the following three items:
(1) The stone that was given by the Child to the Wise Men of the
East, according to a legend picked up by Marco Polo. "The Magi did
not understand the significance of the stone and cast it into a well. Then
straightaway there descended from Heaven a fire which 'they carried
into their own country and placed it in a rich and beautiful church.' "
L. Olschki1 mentions also the Uigur version of this story, where "the
stone is detached by the Child from His crib and thrown into a well
because of its overwhelming weight which frustrated all human and
animal efforts to carry it away. A column of fire reaching the blue sky
is said to have risen from the well into which the stone had fallen and
to have kindled the fire worshiped by the Magi 'up to our days.' "
(2) The star of the Magi which fell into the well of Bethlehem,
according to Gervase of Tilbury,2 after it had served its purpose to
guide the Wise Men to the "new way."
(3) The falling star that opened the abyss, according to Revelation
—a future event, for a change. Out of this well ascends smoke which
darkens the sun and air, and Franz Boll pointed aptly to the "smoke-
1 "The Wise Men of the East in Oriental Traditions," in Festschrift Popper
(i95i),p. 386.
2 Sunt qui diclinr, stcllam Mafoonmi suo eomplcto minisic-iio in piitoum cecidilSC
Bcthlchcmicum ct illic cam intro videri aurumanr. Sec F. Liebltcht, DtS QerVttsiui
von Tilbury Otia Intperialia (1856), pp. 1, S?.
Hamlet's Mill • 424
barrel," south of Sagittarius and Scorpius: Ara, the Altar in the Galaxy,3
and under this very Altar are the souls of the witnesses of God waiting
for the last day (Rev. vi.o). According to Eratosthenes' catasterisms, at
this Altar Zeus and his followers took their oath before attacking
Kronos.4
The reader is likely to react unkindly claiming that there is no reason
for whichever connection between legends about the Three Wise IVIen,
Revelation, and the "Well of Gilgamesh." Yet, Franz Boll (Ojfenbarung,
pp. 6off.) has recognized in those strange locust demons of Revelation—
they come out of the well of the abyss—who resemble horses with
human heads, and have wings, and tails of scorpions, the Sagittarius-
Centaur of Mesopotamian boundary stones, also to be found on the
rectangular zodiac of Dendera. Revelation also states that they had
wreaths as if of gold on their heads: the Egyptian Sagittarius wears a
double crown, the Teukros tradition ascribes to the constellation "the
royal face" (to prosopon basilikon, Boll, Sphaera, pp. 18if.). In the
Gilgamesh Epic Scorpion men watch the way to the other world; Virgil
(Aeneid 6.286) makes it centaurs.
We must leave it at that: the chapter "Sagittarius and Saturn" would
take us too far. We merely wanted to show that Gilgamesh's well and
the opening of new ways are not "prehistoric drivel" that has nothing
to do with our post-Greek, Christian civilization. It was with veritable
awe that Boll stated (Ojfenbarung, p. 73, n. 4): "Von der Konstanz
aller wesentlichen Charakteristiken in diesen Sternbildtypen maCht sich
der Fernerstehende schwer einen Begriff."
Although all this must remain posterior cura, we would like to men-
tion the suggestion offered by Cornford, namely, "that one of these
phreata ( = wells) in Eleusis was closed at its mouth by the agelastos
petra" i.e., the laughterless rock; Demeter was agelastos because of
the loss of Persephone, and she was sitting upon this laughterless rock,
3 Thymiatherion, or thyterion. Michael Scows still made it "puteus sive sacrarius."
See F. Boll, Sphaera (1903), p. 446; Boll, Aus der Offenbarung Johannis (1914),
P-75-
4 It remains to be seen whether Ara has something to do with that enigmatical
well of Gen. xxi.31, 33, called Beer-sheba, which is either "Well of Seven" or "Well
of the Oath." The Septuaginta votes for the Oath," xxi.31: phrear horkismou;
xxi.33: kai ephyteusen Abraam arouran epi to phreati tou horkou kai epekalesato
ekei to onoma Kyriou Theos aionios. (Compare also T. Noldeke, "Siebcn Brunncn,"
ARW 7 [1904], pp. 340-44.)
425 • Appendices
which Cornford ("The Eleusinian Mysteries," p. 161) proposes to take
for "the double of the anaklethra at Megara, which, as its name implies,
was the place where Kore was 'called up.' " This might be, but it does
not throw much light on the whole plot, whereas it seems important to
recall how the "laughterless" state of the goddess was altered, namely,
by the rather improper jokes of Baubo/Iambe. This very trait, now,
occurs frequently within the scheme of world-ages. The Japanese sun
goddess, Amaterasu, who, enraged by Susanowo's misdemeanor, had
withdrawn into a rocky cave leaving the world in utter darkness, was
caused to come out again only by the lascivious dances of "the ugly
sky-female," Uzumue, dancing with the celestial jewel-tree upon her
head, amidst the 800,000 gods assembled in the Milky Way, and produc-
ing fire afterward. Egyptian Ra, who had retired from a world which
he did not like anymore, was "persuaded" by the same kind of jokes by
Isis to take up again his duties ("And then the great god laughed at
her"). The motif emerges again in the Edda, where Loke and a he-goat
make the angry Skadi laugh, preventing her, thus, from avenging the
murder of her father, Thiassi.5 The story has also survived, although in
dull disguise, in the Polynesian Marquesas Islands and, in excellent shape,
with the Cherokee Indians; there the sex appeal is missing, admittedly,
but the agelastos character is Mother Sun, desolate about the death of
her only daughter: a true Demeter (her daughter resembling Eurydice:
she had been brought back half of the way already, when the psycho-
pompoi made a mistake that permitted her to return to Hades); the
indecent dance is replaced by the concert of a juvenile orchestra.
"We have heard (appendix #29) of an allegedly terrestrial agelastos
petra with a river flowing at its foot, called Lethe. We also mentioned
that Eleusis means "Advent," pointing to the circumstance that Demeter
arrived there and that, before having borne Zeus, Demeter had the name
of Rhea (Orph. frg. 145, Kern p. 188).
The moving of Rhea-Demeter to Eleusis is a huge and perplexing
story, indeed, involving honeybees, a woodpecker—whose daughters
were promoted to priestesses of Eleusinian Demeter—goats, and what
else, and we are not likely to cover this event here and now. That we
are up to a major change of residence can be taken from the parallel
case of Amaterasu who, after having been caused by Uzumuc's dance to
5 Sec I'. R. Schroder, .S'/W/ riml ilic Goiter Skandinavian (1941), pp. u> 25.
Hamlet's Mill
426
leave her cave, was respectfully guided into a "New Hall," as we hear
in the Kogo-shui,6 and "then Ama no Koyane no Mikoto and Futo-tama
no Mikoto suspended an exalted Sun-rope around this Hall."7
Not being specialists in Eleusinian matters, topography, etc. (they
remained secrets to the end), we do not feel entitled to deal earnestly
with these items beyond raising some questions, such as which well was
closed—if Cornford's suggestion is right—by the laughterless rock?
Was it a former lapis manalis? What happened to the agelastos petra
after Demeter had been moved to laugh? And how could this rock,
closing a well connected with the underworld, be combined with the
legends that hold Demeter responsible for the coming into being of the
Stygian spring (Aelianus, De natura animalium 10.40), or for her having
caused the waters of Styx to become black (O. Waser, Roscher 4.1572)?
Demeter is supposed to have changed the color of the Stygian waters
when she, on her search for Persephone, fleeing from Poseidon and
changing into a mare, arrived at the Arcadian spring of Styx and per-
ceived in the water her own mis-shape. And how,* on the other hand,
could the bringing into being of Styx and her sitting on the laughter-
less rock be combined with the Orphic claim, according to which
Demeter "separated the double nourishment of the gods," splitting it up
into Nectar and Ambrosia,8 both of which come out of the "horn of
Amaltheia," i.e., alpha Aurigae?
Considering the amount of testimonies for stones, shards, trees, plugs
which close the one or the other well, abyss, whirlpool, or, by being
pulled out or just removed announce major changes and great catastro-
phes, we might be expected to wrap up this whole parcel, from the
"Holiest of Holies" replacing the Ark—its function, respectively, to
cover the tehom—to Tahaki tearing up the tree of Tane-of-holy-waters,
and to Alexander pulling out the pole-pin, or to mischievous Monkey
who removed the basket. But apart from the fact that there are many
more instances, unmentioned in this essay, which should also find their
place in the said parcel, behind every tree, stone, and well lurks, as it
6 K. Florenz, Die historischen Quellen der Shinto-Religion (1919), p. 423; see
also pp. 37ff., 153-62; and Nihongi, trans, by W. Aston (1956), pp. 40-49.
7 The question remains whether the "exalted Sun-rope" is the same as the "left
rope"—being called thus because plaited from left to right—and the "rope whose
root-ends are plaited together" by means of which Amaterasu was cut off from
ever reentering that (laughterless) cave, according to Nihongi and Kojiki (see
Florenz, Quellen der Shinto-Religion, p. 40, n. 22).
8 Orph. frg. 189, Kern p. 216: Demeter prote kai tas dittas trophas dicilcn.
42 7 • Appendices
were, the danger of simplification and of ruthless identifying; to sim-
plify, however, is the very danger that we most wish to avoid. In other
words, we do not mean to make comparative mythology "easier," by
procuring simple denominators upon which all these items could be
brought; we think, on the contrary, that we are faced with an almost
uncountable number of x's for which the fitting equations have to be
worked out in long and cumbersome future investigations.
Appendix 37
A sidelight falls upon the notions connected with the stag by Hora-
pollo's statement concerning the Egyptian writing of "A long space of
time: A Stag's horns grow out each year. A picture of them means a
long space of time."1 Chairemon (hieroglyph no. 15, quoted by
Tzetzes) made it shorter: "eniautos: elaphosP Louis Keimer, stressing
the absence of stags in Egypt, pointed to the Oryx (Capra Nubiana)
as the appropriate "ersatz,"2 whose head was, indeed, used for writing
the word rnp = year, eventually in "the Lord of the Year," a well-
known title of Ptah.3 Rare as this modus of writing the word seems to
have been—the Worterbuch der Aegyptischen Sprache (eds. Erman
and Grapow), vol. 2, pp. 429-33, does not even mention this variant—
it is worth considering (as is every subject dealt with by Keimer), the
more so as Chairemon4 continues his list by offering as number 16:
"eniautos: phoinix" i.e., a different span of time, the much-discussed
"Phoenix-period" (ca. 500 years). There are numerous Egyptian words
for "the year," and the same goes for other ancient languages. Thus, we
1 The Hieroglyphs of Horapollo, trans, by G. Boas (1950), p. 89 = Horap. 2.21.:
"pos polychronion. Elaphos kat'eniauton blastanei ta kerata, zographoumene de,
polychronion semaiei."
2 "Interpretation de plusieurs passages d'Horapollon," in Suppl. 5 jxux Annales
du Service des Antiquites de Pfigypte (1947), pp. 1-6. "Les figyptiens avaient re-
marque la resemblance existant entre les cornes d'un Bouquetin, caracterisees par
de nombreux noeuds, et le signe . . . qui est originairement une branche de dattier"
[this branch being the main part of the hieroglyph for "year"—rnp].
3M. Sandman Holmberg, The God Ptah (1946),. pp. 22, 64L, 77, 17K K<>.
4 F. J. Lauth, "Horapollon,/ SBAW (1876), p. <">K. It remains :i tragedy ih.it
only nineteen of Chairemon'i explanations have been preserved l>y Tzetzes,
only stated thai Chairemon had given "Uai lu'tcra inyria."
Hamlet's Mill
428
propose to understand eniautos as the particular cycle belonging to the
respective character under discussion: the mere word eniautos ("in
itself," en heauto; Plato's Cratylus 410D) does not say more than just
this. It seems unjustifiable to render the word as "the year" as is done
regularly nowadays, for the simple reason that there is no such thing
as the year; to begin with, there is the tropical year and sidereal year,
neither of them being of the same length as the Sothic year. Actually,
the methods of Maya, Chinese, and Indian time reckoning should teach
us to take much greater care of the words we use. The Indians, for in-
stance, reckoned with rive different sorts of "year," among which one
of 378 days, for which A. Weber did not have any explanation.5 That
number of days, however, represents the synodical revolution of Saturn.
Nothing is gained by the violence with which the Ancient Egyptian
astronomical system is forced into the presupposed primitive frame.
The eniautos of the Phoenix would be the said 500 (or 540) years;
we do not know yet the stag's own timetable: his "year" should be
either 378 days or 30 years, but there are many more possible periods
to be considered than we dream of—Timaios told us as much. For the
time being the only important point is to become fully aware of the
plurality of "years," and to keep an eye open for more information
about the particular "year of the stag" (or the Oryx), as well as for
other eniautoi, especially those occurring in Greek myths which are,
supposedly, so familiar to us, to mention only the assumed eight years
of Apollo's indenture after having slain Python (Plutarch, De defectu
oraculorum, ch. 21, 421c), or that "one eternal year (aidion eniauton),"
said to be "8 years (okto ete), that Cadmus served Ares (Apollod. 5.4.1;
see also .2.5.11 with long note by Frazer).
Appendix 38
See RV 7046.2, ed. K. Geldner (1951); cf. V. Rydberg, Teutonic
Mythologie (1907), p. 587. Geldner, vague as ever, spells it "der
Gewasser Behausung." Agni, however, is a title, and the Rigveda stresses
time and again that three Agnis already have gone away, "consumed"
5 A. Weber, "Die Vedischen Nachrichtcn von den Naxatra," APAW 2 (1862),
pp. 281-88, csp. pp. 286-87.
429 • Appendices
by the "sacrificial service." Agni, too, is not only coming from the con-
fluence of the rivers like Gibil, but is also born in the "highest sky"
(RV 6.8.2): "Im hochsten Himmel geboren wachte Agni iiber die
(Opfer) regeln als ihr Hiiter. Der Klugsinnige mass den Luftraum aus."
In fact, he has three birthplaces as a rule, in the "three worlds." (We
have mentioned already that one of the Agnis had "seven mothers,"
like Heimdal.)
But wherever one of the Agnis is "found," he is a very busy surveyor.
Says RV 6.J.6: "Durch das Auge des Vaisvanara, durch das Wahr-
zeichen der Unsterblichkeit sind die Hohen des Himmels ausgemessen.
Auf seinem Haupte (stehen) alle Welten, wie die Zweige sind seine
sieben Arme (?) gewachsen." RV 6.J.1-2 calls the same Agni Vaisvanara,
"head of the sky, leader1 of the earth, born at the right time ... the
navel of the sacrifice." Stanza 5 of the same hymn states: "Vaisvanara!
Diese deine hohen Anforderungen hat noch keiner angetastet, o Agni,
der du im Schosse der beiden Eltern geboren, das Wahrzeichen in der
Reihenfolge der Tage fandest." It is of another Agni, "just born," "the
best path-finder," that RV #.103.11 states: "Der bei (Sonnen-) aufgang
die angebundenen Schatze erkundet." Whoever minds the "implex" is
not going to think of the daily sunrise, if it is the sun at all: this is a
conjecture of Geldner; we are up either to the heliacal rising of the
"Agni-in-charge" at the vernal equinox, or at the rising day of Sirius.
We wonder when the glorious day will finally arrive when the philolo-
gists begin to realize the purely cosmological significance of "sacrifices,"
and of "victims" chained to a "sacrificial post" or to a mountain.
The overwhelming amount of evidence on Agni and Soma ("lord of
the world poles") as colures will have to be dealt with in the fitting
frame, by means of an investigation of the so-called Shunashepa Hymns
of the first Mandala of the Rigveda, Shunashepa being literally the same
as Cynosoura, "Dog'sTail," i.e., Ursa Minor. In the present context we
wish to point to only one more name of Agni—being himself a title—
that is, Apam Napat, a designation which belongs also to Iranian Tish-
triya, Sirius. Usually it is translated into "child of the waters," but we
1 Geldncr's rendering of Sanskrit arati into "Lenker" (Wagenlenker) has been
contested by P. Thicme {Untersuchungen zur Wortkunde und Auslegung des
Rigveda I 1949], pp. 26-35). Arati (fcni.) from ara, the spoke, being the totality
of spokes, according t<> Thirmc, he translates RV 6-7.1: "(den Agni), das Ilaupt
des Himmels, den Speichenkranz der Erde," pointing also to /.59.2s "Agni isi das
! taupt des I linmuls, der Nabel der Krde. So ward it der Speichenkran/. der beiden
Welten,"
Hamlet's Mill
cannot agree to this interpretation of napat (whence also Neptunus)
as "child." Not only does Boissacq allow only for nephews and nieces
in connection with this radical, but we are always dealing with nephews
in mythology, beginning with our own hero Amlethus; with Horus,
nephew of Seth; with Kullervo, nephew of Untamo; with Reynard Fox,
nephew of Isengrim; and so forth. What counts is a kind of "broken"
relation, a subject deserving an extensive chapter, but since the under-
standing of the graphical sign that expresses best this "relation" ( )
comes from Mande tradition, West Sudan (where it marks circumcision,
and the star of circumcision: Sirius), we postpone investigation of the
whole complex.
Appendix 3$
Excursus on Gilgamesh
There are many points from which to start new trips of exploration
into the Gilgamesh Epic, once it is conceded that reasonable questions
have to be asked. Among the many we single out two, without intend-
ing to "get at the bottom of the matter"; the first concerns the "ferry-
man," the second concerns "trees."
Face to face with the ferryman Urshanabi, a kind of personified me
who was dragged away from the "confluence of the rivers" to check
the proper measures of Uruk, it can hardly be taken for a farfetched
idea that we ask for comparative "individuals" or "places" in other
Mesopotamian texts. There is, indeed, no need for a frantic search: the
Enuma elish offers us an equally decisive item from which depends the
whole skeleton map, namely Nibiru (or neberu).
There are three passages of the so-called "Babylonian Genesis" that
give—recognizable at first glance—details of the surveying of the new
world as accomplished by Marduk/Jupiter. In Speiser's translation they
read thus (ANET, pp. 67, 69):
4.i4iff. He crossed the heavens and surveyed the regions.
He squared Apsu's quarter, the abode of Nudimmud [Ea],
As the lord measured the dimensions of Apsu.
The Great Abode, its likeness, he fixed as Esharra
The Great Abode, Esharra, which he made as the firma-
ment.
Anu, Enlil, and Ea he made occupy their places.
431 • Appendices
j. 1-8 He constructed stations for the great gods,
Fixing their astral likenesses as constellations. [Heidel: The
stars, their likeness(es), the signs of the zodiac, he set
up]1
He determined the year by designating the zones:
He set up three constellations for each of the twelve
months.
After defining the days of the year (by means) of (heav-
enly) figures,
He founded the station of Nebiru to determine their {heav-
enly) bands,
That none might transgress or fall short.
Alongside he set up the stations of Enlil and Ea.
6.62f. They raised high the head of Esagila equaling Apsu.
Having built a stage-tower as high as Apsu,
They sat in it an abode for Marduk, Enlil (and) Ea.
Leaving aside the specific charm of these passages—i.e., the circum-
stance that the places of Anu, Enlil, Ea in 4.146, and their stations in
j.8 are not the same—we concentrate on EE 5.6: "He founded the
station of Nibiru to determine their (heavenly) bands" (Speiser), or:
"He founded the station of Nibiru to make known their duties" (Hei-
del), or: "Er setzte ein den Nibirupunkt, um festzusetzen ihre Verkno-
tung" (= riksu; Weidner, Handbuch Baby 1. Astr., p. 33), and on j.8:
"Alongside he set up the stations of Enlil and Ea" (Speiser), or: "He
established the stations of Enlil and Ea together with it" (Heidel), or:
"Den Enlilpunkt und den Eapunkt setzte er bei ihm fest" (Weidner).
That means the position of the "Ways of Anu, Enlil, Ea" was a func-
tion of Nibiru; that only the setting up of the points, or stations, of
1 The terminus is "Lumashi"-stars, and it is not yet certain which stars are meant.
F. Kugler (Sternkunde und Sterndienst in Babel. [1907-13], vol. /, p. 259) voted for
zodiacal signs; E. Weidner (Reallexikon der Assyriologie [1932], vol. 3, p. 83) con-
fined this signification to the 5th century b.c. and later, whereas O. Neugebauer
(The Exact Sciences in Antiquity [1962], p. 140) stated that the zodiacal signs
(instead of constellations) were not yet introduced at 418 B.C. There are texts
which include among the Lumashi-stars Cygnus, Cepheus, Aquila, Orion, Sirius,
Centaurus (A. Jeremias, HAOG, p. 200; P. Gossmann, Planetarium Babylonicum,
250), and this appears to rule out the zodiac. C. Bezold (Boll-Bezold, Antike
Beobachtungen farbiger Sterne [1916], p. 149; sec also Bezold, Babylonisch-As-
syrisches Glossar [1926], p. 160) proposed to understand the Luniashi-stars :is
"Jupitcr-srars"; this was accepted by 15. Mcissncr (Babylonian und Assyricn \ i<)\i |,
vol. 2, p. 40H) bin Weidner (Ul.A ;, p. Ho) claimed chat lie/old had started from
erroneous premises.
Hamlet's Mill
43 2
Enlil and Ea is mentioned suggests that Marduk/Jupiter claims the
"Ami-ship" for himself.2 The experts seem to be quite happy with the
equation "Nibiru = Jupiter" (see below). But what is his "station,"
or point? Considering that upon this very station of Nibiru rests the
whole tripartition of the universe during the age ruled by Marduk/
Jupiter, it is surprising how little the professionals care.
The plain meaning of nibiru is "ferry, ferryman, ford"—mikis nibiri
is the toll one has to pay for crossing the river—from eberu, "to cross."3
Alfred Jeremias insisted that Nibiru "in all star-texts of later times"
indicated Canopus, taking this star for the provider of the meridian of
the city of Babylon.4 There have been other identifications (including
even a comet!)—the summer solstice,5 or the celestial North Pole;6 the
opinions and verdicts collected by Gossmann (Planet., 311) show clearly
that Nibiru remains an unknown factor for the time being.
This deplorable situation is not improved by means of the next occa-
sion, when the ominous word is hurled at us anew, in EE 7.1241!.,
where fifty names are given to the new ruler, Marduk/Jupiter, among
which is Nibiru.
Speiser translation:
Nebiru shall hold the crossings of heaven and earth;
Those who failed of crossing above and below,
Ever of him shall inquire.
Nebiru is the star which in the skies is brilliant.
Verily, he governs their turnings, to him indeed they look
Saying: "He who the midst of the Sea restlessly crosses,
Let 'Crossing' be his name who controls its midst.
May they uphold the course of the stars of heaven;
May he shepherd all the gods like sheep."
2 This dignity must have got lost after the first (?) flood (or by means of it?),
otherwise Marduk could not ask reproachfully for the whereabouts of "Ninigi-
nangargid, the great carpenter of my Anu-ship" (Era Epic, tabl. /.155; Goss-
mann, Das Era-Epos [1956], p. 98).
3Cf. C. Bezold, Glossar, p. i3f.; E. Ebeling, RLA 3, p. if.; P. Jensen, Kosmo-
logie, p. 128; E. Weidner, Handbuch, p. 26; P. Gossmann, Planet., 311: "Nibiru ist
eigentlich die 'Uberfahrtsstelle.' Der 'Stern der trberfahrtsstelle' ist der Marduk-
stern Jupiter, wenn er den Meridian iiberschreitet."
4HAOG, p. 134; Weidner (RLA 2, p. 387): "Ob der Stern Marduk-Nebiru
wirklich = Canopus, bleibt freilich ebenfalls unsicher." On p. 247, n. 2, Jeremias
generalizes without much ado: "Kulminationspunkt der Sterne im Ortsmcridian."
5 Weidner, Handbuch p. 33, but that was written at least thirty years earlier
than his articles in RLA.
0 Meissncr, Bab. und Assyr. 2, p. 40H.
43 3 • Appendices
Heidel translation:
Nibiru shall be in control of the passages in heaven and on earth,
For everyone above and below who cannot find the passage inquires
of him.
Nibiru is his star which they caused (?) to shine in the sky.
He has taken position at the solstitial point (?), may they look upon
him,
Saying: "He who crosses the middle of the sea without resting,
His name shall be Nibiru, who occupies the middle thereof;
May he maintain the course of the stars in heaven;
May he shepherd all the gods like sheep ..."
Von Soden (ZA 47, p. 17):
Nebiru soil die tibergange von Himmel und Erde besetzt halten,
denn droben und drunten fragt jeder, der den Durchgang nicht findet,
immer wieder ihn.
Nebiru ist sein Stern, den sie am Himmel sichtbar werden lieBen;
er fasste Posten am Wendepunkt, dann mogen sie auf ihn schauen
und sagen: "Der die Mitte des Meeres (Tiamat) ohne Ruhe iiber-
schreitet,
sein Name sei Nebiru, (denn) er nimmt die Mitte davon ein.
Die Bahn der Sterne des Himmels sollen sie (unverandert) halten..."
How secure and unshakable the ground is upon which we walk,
according to the inscrutable decree of the experts, may be guessed from
the translation of lines 128-32 by Albrecht Gotze7 who starts from
the conviction that eberu = "to bind, to enclose" which, combined
with the "solution" that tam-tim means "struggle," apparently permits
him to get rid of the "midst of Tiamat"
Who enclosed (in his net) indeed amidst the struggle without loos-
ening,
May his name be "encloser," who seizes amidst (it).
Of the stars of heaven may he uphold their courses
May he shepherd the gods, all of them like sheep.
F. M. Th. Bohl8 was at least perplexed enough to admit: "Der Passus
gehort zu den sachlich schwierigsten der Tafel, ohne dass der ziemlich
vollstandig erhaltene Kommentar hierbei wesentliche Hilfe leistet." But
he did not further the case by upholding opinions incompatible among
themselves since based upon doubtful identifications. On the one hand,
he claimed Nibiru to be the name given to "the planet and his hyp-
soma"; on the other hand, he took Nibiru for a star or constellation
7 "Al<l<;uli;ni d/t:imtiim," jn Festschrift Dcimcl (1935), |>|>. 1K5 <>i.
8"Die fiinfzig Namen dei Marduk," Afo // (1936), p. 110.
Hamlet's Mill • 434
marking the point where Jupiter entered the "Way of Ami," to which
he adds: "The time of observation is the night of the Vernal Equinox,
when the Sun stands at the crosspoint of Equator and Ecliptic in the
constellation Aries." He does not reveal from where he has this sur-
prising knowledge; he seems to rely on the identification of "1-Iku"
with Aries/Cetus, which is not the case: the Pegasus-square it is,9 but
the constellation is not mentioned in 7.1241!., so what? Apart from this,
we do not know whether, in the time of the Enuma elish, Aries was
taken for Jupiter's hypsoma; there seem to be reasons for recognizing
—already at this time—Cancer (more precisely: Procyon) == Nangar =
the Carpenter, as Jupiter's exaltation.10 In the third place, if Bohl takes
1-Iku for Aries ruling the vernal equinox, how could Jupiter enter
there the "Way of Ami"?11 The "Way of Ami" represents a band, ac-
companying the equator, reaching from 15 (or 17) degrees north of
the equator to 15 (or 17) degrees south of it; the "Way of Enlil" runs
parallel to that of Anu in the North, the "Way of Ea" in the South.12
That, due to the precessional shifting of the crossroads of ecliptic and
equator, the stars standing in these three "Ways" are not the same all
the time, goes without saying.
9 Bohl mentions this identification, with reference to Bezold and Schott, p. 211,
n. 47.
10 See E. Weidner, "Babylonische Hypsomatabilder," OLZ 22 (1910), cols. i4fT.;
Weidner, Gestirn-Darstellungen auf Babylonischen Tontafeln (1967), pp. 9f., 134,
n. 166, and plates V, VI (VAT 7847). A passage from the Taittiriya Brahmana
(j.i.i) also has to be considered: "When Jupiter was first born, he defeated the
nalcshatra Pushya by his brilliance." P. Sengupta, who quoted the line in his intro-
duction to Burgess' translation of the Surya Siddhanta (1935, p. xxxiv), misinter-
preted it thoroughly by claiming it described "the discovery of Jupiter," and by
adding, "the star group of Pushya (delta eta gamma Cancri) has no bright stars
in it and the planet Jupiter was detected when it came near to this star group."
To the fully initiated expert who sternly points with outstretched finger to the
circumstance that the nakshatra Pushya was formerly called Tishya (see, e.g.,
Scherer, Gestirnnamen, p. 150), and that means, Sirius, we can, for the time being,
only answer that we are aware of this particular circumstance. Premature "solu-
tions" are of no avail.
11 To be sure, Bohl does not say so explicitly, his wording being as unprecise as
possible. He claims that at the time of New Year (vernal equinox) "the orbit of
Jupiter was observed particularly carefully." "Man beobachtete—so diirfen wir
annehmen—wie er (wohl von der ausseren Ea-Sphire her [sic!]) in den Anu-
Bereich eintrat, diesen Bereich durchquerte (eberu, itburu) und ihn dadurch
gleichsam feierlich in Besitz nahm."
12 For these much discussed "Ways," see van der Wacrdcn, "The Thirty-Six
Stars," JNES 8 (1949), p. 16; Weidner, Hand bitch, pp. 46-49; Mcissncr, Bab. und
Assyr. 2, pp. 4<>7f.; Ik/old KopfT Boll, "Zenit- und Aqunforialgesrirnc," SHAW
(1913); ScliauinberKcr, >\ Erg., pp. 521-30.
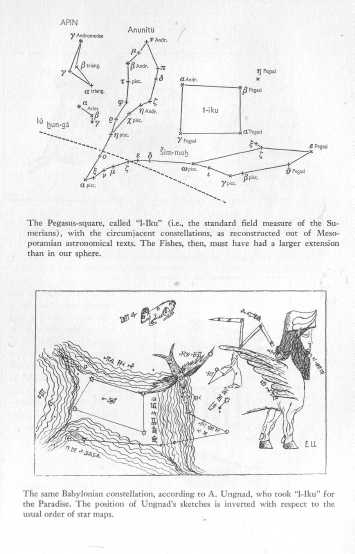
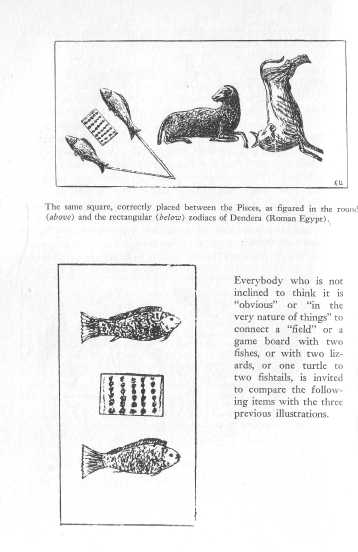
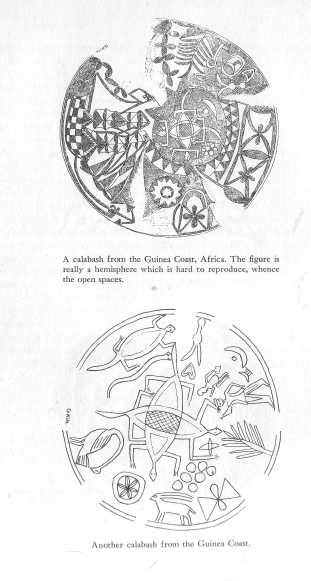
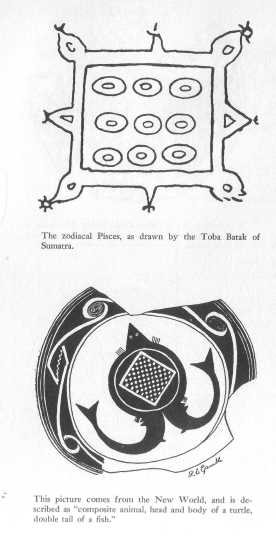
43 5 * Appendices
But, as a matter of fact, "1-Iku," darkly hinted at by Bohl, does come
into play, namely, in EE 6.62, quoted above: "They raised high the
head of Esagila equaling Apsu." And concerning this Esagila (or Esagil)
we hear in the ritual text of the New Year festival in Babylon13 that
the Urigallu-priest "shall go out to the Exalted Courtyard, turn to the
north and bless the temple Esagil three times with the blessing: 'Iku-star,
Esagil, image of heaven and earth.' " "1-Iku," the Pegasus-square (= al-
pha beta gamma Pegasi, alpha Andromedae) is, indeed, of the utmost
importance, 1-Iku representing the fundamental field measure,14 and
Ungnad (Das iviedergefundene Paradies [1923], p. 11) understood the
constellation, enclosed by Pisces, for the "Paradise," the primordial field,
so to speak. More important, Utnapishtim tells Gilgamesh (GE J/.57)
about his ark, which was, like the apsu, an exact cube: "One iku was
its floor space."15 (Before, / 2.31, Ea had ordered Utnapishtim: "Like the
apsu thou shalt ceil her.") Remembering what we heard above: "Since
the ark disappeared there was a stone in its place . . . which was called
foundation stone," i.e., Eben Shetiyyah, that covered the abyss, this
cubic ark, the floor space of which was one iku, cannot be without
interest for us, the less so, when the gods "raised high the head of
Esagila (= 1-Iku) equaling Apsu."
To be sure, this does not teach us where Marduk was supposed to be
when he received the title Nibiru—it might have been decisive for the
planet to rise heliacally together with 1-Iku, the celestial model of Esa-
gil (representing the "foundation-stone-covering-the-apsu," maybe?),
but when?16 The heliacal rising of "1-Iku"—precisely, beta Pegasi—
13 See Sachs translation, ANET, p. 232,1. 274^
14 About 3,600 square meters-, see Heidel, GE, p. 82, n. 173.
15 A. Schott translation: "Ein 'Feld' gross war seine Bodenflache." Compare for
details, Schott, "Zu meiner tlbersetzung des Gilgamesch-Epos," ZA 42 (1934),
pp. 37f., 40.
16 One clue, at least (probably many more), to the situation is contained in the
Cuneiform Tablet K 3476 dealing with the Babylonian New Year festival, trans-
lated and commented on by Heinrich Zimmern ("Zum babylonischen Neujahrs-
fest," BVSGW 58 [1906] 5, pp. 127-36), which says that "Marduk lies with
his feet within Ea" (lines 20-21: "(Das ist) Marduk [ . . . ] [der (?) mit (?)]
seinen Fiissen innerhalb (?) Eas liegt"). In a note, Zimmern proposes to under-
stand this line as an "allusion to a constellation connected with Marduk (Auriga?)
that reaches into a constellation connected with Ea (Aries?)." S. A. Pallis, not
tending to astronomical notions, made it that - "Marduk lies (?) before (?)
Ea"j the unmistakable presence <>f the planet Venus in the second part of the
sentence (k"ulu'lMll)l!,. HAT) forced him to the concession: "perhaps ii rclcr. tO
certain astronomical conditions" (The HabyIonian Ak'ilit Festival I 1 «j.'f>|, p 117)
In 1926, sufficient literature about the "Tlirrc W:i) ■■" \\ ;is ;i\ nibble.
Hamlet's Mill
436
coincided with the winter solstice of 4000 B.C.; around 1000 B.C. it took
place on January 25.17 "1-Iku," the Pegasus-square, is called "the habita-
tion of the deity Ea, the leader of the stars of Ami"18 in the "Series
mulAPIN" (Plow-star, Triangulum), called by Weidner "a Babylo-
nian compendium of astronomy."19 According to van der Waerden
("The Thirty-Six Stars," p. 17) this series is a compilation "made about
700 b.c. or somewhat earlier20—in which material from different periods
between -1400 and -700 was used": thus, 1-Iku as "leader" of the stars
standing in the "Way of Ami" would rise in the end of January, quite
a time away from the vernal equinox when the New Year's festival was
held.
This is all very nice so far, and certainly not without highest interest,
but do we know meanwhile what Nibiru, "ferry, ferryman, ford," was
supposed to be? Even without worrying about Jupiter and his where-
abouts? We know it not, and we feel tempted to say: "quod erat
demonstrandum," namely, that the many verbose translations, eloquent
articles, and books have not cleared up the decisive points of the cos-
mological system ruling the Enuma elish, the Gilgamesh Epic, the Era
Epic and the other alleged "poems." Nibiru is only one case among
many, but it is a rather significant model case for proving that no con-
crete problem is going to be solved as long as the experts of astronomy
are too supercilious to touch "mythical" ideas—which are firmly be-
lieved to be plain nonsense, of course—as long as historians of religion
swear to it that stars and planets were smuggled into originally "healthy"
fertility cults and naive fairy tales only "very late"—whence these un-
healthy subjects should be neglected by principle—and as long as the
philologists imagine that familiarity with grammar replaces that scien-
tific knowledge which they lack, and dislike.
But even when the different specialists would condescend to renounce
their common haughtiness, we do not think that there is much chance
to arrive at a satisfying solution of concrete details, and the adequate
understanding of the system as a whole, without taking into account
comparable systems of other parts of the earth: Mesopotamia is by no
means the only province of high culture where the astronomers worked
17 See W. Hartner, "The Earliest History of the Constellations in the Near East,"
JNES 24 (1965), pp. 13, 15.
18 Bezold-Kopff-Boll, p. 23.
19 "Ein babylonisches Kompendium der Himmelskunde," AJSL 40 (1924), pp.
186-208.
20 See also A. Schott, "Das Werden dor babylonisch-assyrisrlu-n Posicions-Astro-
nomic und cinige seiner lU'diiir.nni'.cii," ZI)M(i <V,V (1934), pp. 331, 333,
437 • Appendices
with a tripartition of the sphere—even apart from the notion allegedly
most familiar to us, in reality most unknown—that of the "Ways" of
Zeus, Poseidon, and Hades as given by Homer. The Indians have a very
similar scheme of dividing the sky into Ways21 (they even call them
"ways"). And so have the Polynesians, who tell us many details about
the stars belonging to the three zones (and by which planet they were
"begotten"); but nobody has thought it worth listening to the greatest
navigators our globe has ever seen; nor has any ethnologist of our
progressive times thought it worth mentioning that the Polynesian
megalithic "sanctuaries" (maraes) gained their imposing state of "holi-
ness" (taboo) when the "Unu-boards" were present, these carved Unu-
boards representing "the Pillars of Rumia," Rumia being comparable to
the "Way of Ami," where Antares served as "pillar of entrance" (among
the other "pillars": Aldebaran, Spica, Arcturus, Phaethon in Columba).
But now, is Nibiru as important as all that? We think so. Or, to say
it the other way around: once this astronomical term, and two or three
more, are reliably settled, one can begin in earnest to get wise to, and
to translate, Mesopotamian "poetry."
II
The epics of Gilgamesh and Era offer too many trees for our modest
demands. The several wooden individuals have, however, the one ad-
vantage that the expert's delight in uttering deep words about "the
world-tree" wilts away.
There is, first, the mesh-tree, contained in the hero's name,22 about the
location of which Marduk asks stern questions of Era, followed by the
cedar of Huwawa/Humbaba which was—as we have been taught by
21 See W. Kirfel, Die Kosmographie der Inder nach den Quellen dargestellt
(1920), pp. i4of. At first glance, it looks as if only the circle of lunar mansions
was subdivided into these three ways, but the domains are extended far beyond
the limits of the "inhabited world" in both directions, north and south, as are the
Ways of Enlil and Ea.
22 The identity of the tree is not settled. R. Labat (Manuel d'Epigraphie Akka-
dienne [1963], no. 314) proposes "cedre (Pmicocoulier?) [Celtis australis, "ge-
meiner Ziirgelbaum"—Celtis occidentalis is the American nettle tree] glsMEZ-MA-
GAN-(NA) musskanu-murier (Pmicocoulier de Magan?)" (Cf. Labat, no. 296:
"GIS, bois, arbre. Determinatif prccedant les noms d'arbres et d'objets en bois.")
See also F. Delitzsch, Assyrisches Handivorterbuch (1896), p. 410 s.v. miskanu,
musukanu, "cin Bauni . . . , v/cchselt mit mis-ma-kan-na, d.i. MIS-Holz von
Makan."
(Even this mes-wood from Magan cannot he dismissed ai "nm applicable" for
the GE< because [n the Sumerian myth "Gilgameih and the I.and <>i the Living"
(Knuner, ANKT, |>. .|<>, /......, >, when I he hero is allegedly .i<lm<>mslmi|', liikidii
Hamlet's Mill
438
the specialists—felled by Gilgamesh and Enkidu. Yet, according to the
"latest news" available to us,23 Huwawa is "the guardian monster of the
'land of the cut cedar.' " Admittedly, also at an earlier occasion, Kramer
stressed his opinion that "the far distant 'Land of the Living' was also
the 'Land of the Felled Cedar,' "24 but we have not yet found evidence
of any thought, any consequence which should follow such alarming
statements. But one cannot expect earnest thoughts to be wasted on
Sumerian conceptions from a scholar who wrote about the fathers of
hydraulic engineering (irrigation) that "to the Sumerian poets and
priests the real sources of the Tigris and Euphrates in the mountains of
Armenia were of little significance. They did not understand, as we do,
that the volume of the waters of the two rivers depended upon 'feeding'
from their tributaries, or that it was the melting winter snows which
produced the annual overflow, or that the Tigris and Euphrates 'emp-
tied' their swollen waters into the Persian Gulf. Indeed, their view was
not to shrink away from Humbaba, Gilgamesh utters the most enigmatical words:
"Do thou help me [and] I will help thee, what can happen to us? After it had
sunk, after it had sunk, After the Magan-boat had sunk, After the boat 'the might
of Magilum' had sunk.")
See also F. Hommel, Ethnologie und Geographie des Alien Orients (1926), pp.
539, 783. According to Meissner, quoted by Weidner ("Gestirn-Darstellungen auf
Babylonischen Tontafeln," SOAW 254 [1967], p. 18), sisMES = mesu is the rowan.
As concerns the astrological system of connecting trees (and stones, and animals,
etc.) with the zodiac, the tablets translated by Weidner put the mes-tree two times
with Aquarius (pp. 18, 35), once with Aries (p. 31). Wood of the mesu-tree and of
the huluppu-tree occurs as building material for the chariot (narkabtu) of Ningirsu,
in the Gudea Cylinder A VII, 16-18 (cf. A. Salonen, Prozessionswagen [1946],
p. 6; Salonen, Die Landfahrzeuge des Alten Mesopotamien [1951], pp. inf.).
This tree is also part of the name of MES.LAM.TA.E3.A, taken for the oldest
name known of the god Nergal (see J. Bollenriicher, Gebete und Hymnen an
Nergal [1904], p. 7) and the name of the one of the Gemini, MES.LAM.TA.E.A.,
means "who comes forth from MES.LAM." MES.LAM was the name given to
Nergal's sanctuary in Kutha, and means "the luxuriantly growing MES-tree,"
according to Gossmann (Das Era-Epos, p. 67), who continues with respect to the
name MES.LAM.TA.E.A.: "Spater diente der Name in erster Linie als Bezeich-
nung eines der beiden Zwillinge (Planetarium Babylonicum, 271), bezw. als Tum-
melplatz philologischer Spielereien. Auf Grund solcher Philologeme wurde der
Name auf Marduk und Gilgamesh iibertragen (Tallqvist, 374)." It is not in the
best scientific style to dispose of difficult formulae by declaring them philological
pastimes. Since MES.LAM appears to be a "fixed" topos, we can hardly expect
that "to come forth from MES.LAM" has been a monopoly of Nergal-Mars. But
see below, p. 449.
23 S. N. Kramer, The Sumerians (1963), p. 277.
„ 24In Gilgamesh et sa legende, ed. by P. Garclli (1958), p. 64. In "Gilgaiiirsh and
the Land of the Living," JCS 1 (1947), p. 4, lie had styled it more modestly: "the
far distant Land of the Living (also known as cedar land)."
439 • Appendices
just the opposite; it was the Persian Gulf which was responsible for
the waters of the Tigris and Euphrates and for their all-important over-
flow. Mythologically expressed, it was Enid who filled the Tigris and
Euphrates with sparkling water, and who, by riding the sea, makes its
waters and those of the Tigris and Euphrates, turbulent and violent
... In short, as the Sumerians saw it, it was not the rivers that 'fed' the
sea,... but rather the sea that 'fed' the rivers."25
Apart from the mes-tree and the unexplained cedar of Huwawa/
Humbaba—whether it was felled by our heroes or not—the Gilgamesh
Epic confronts us with the huluppu-tree, taken for a willow by Labat
(nos. 371, 589), for an oak by the Assyrian Dictionary (vol. 6, pp. 55f.),
for a kind of Persea by Salonen (Landfahrzeuge, pp. 11 if.)—all the
identifications decently equipped with a question mark. This specimen
crosses our way in the Sumerian version of the Gilgamesh Epic, part
of which was incorporated as Tablet XII in the Akkadian Epic; the
Sumerian text has been translated by C. J. Gadd,26 and by S. N. Kramer.27
We quote the summary given by Kramer in his first translation (1938,
p. 12) for the simple reason that it is shorter than the one offered in
JAOS 64 (1944), pp. 19-21. In the meantime, this text had been given
a different name, i.e., "Gilgamesh, Enkidu, and the Nether World." The
first half of the first sentence is, of course, no quotation, and it is not
likely to be subscribed to by the author.
On occasion of a new distribution of the "Three Ways,"28 "on that
day," it happened that "a huluppu tree (very likely a willow) which
had been planted on the bank of the Euphrates and nourished by its
waters was uprooted by the South Wind and carried off by the Eu-
phrates. A goddess wandering along the bank seized the floating tree,
25 "Dilmun, the Land of the Living," BASOR 96 (1944), p. 28; we pass in silence
the identification of this "Land of the Living" with Dilmun, as claimed in this
article, and as upheld in all later publications.
26 "Epic of Gilgamesh, Tablet XII," in RA 30 (1933), pp. 129-43.
27 "Gilgamesh and the Huluppu-Tree," Assyriological Studies 10 (1938). Cf.
Kramer, Sumerian Mythology (1944), pp. 33-37, and From the Tablets of Sumer
(1956), pp. 222-26.
28 As concerns the beginning of this text, one shock after the other receives the
reader who studies eagerly the various "translations": it is hard to believe that they
are meant to render the same Sumerian original. Out of the first lines Kramer
(Sumerian Mythology, pp. 3off.) built up the Sumerian creation story which he
took (and takes?) for unknown; in JAOS 64, p. 19, he stressed again: "The first
thirteen lines of this passage contain some of our basic data for the analysis of the
Sumerian concept of the creation of (he universe." Of the following lines i.| 's
he constructed a dragon ii)-,ht. By means of hitherto unpublished pieces, Kraniei
claimed, in 195H (<iih\,unc\h <•/ ui Ivxvmlv, iy'•<■>), thai "the lirsi seven lines <>l il»
Hamlet's Mill
440
and at the word of Arm and Enlil she brought it to Inanna's [i.e., Ish-
tar's] garden in Uruk. Inanna tended the tree carefully and lovingly,
hoping to have made of its wood a throne and bed for herself. After
ten years had passed and the tree had matured, Inanna, to her chagrin,
found herself unable to realize her hopes. For in the meantime a dragon
had set up its nest at the base of the tree, the Zu-bird had placed his
young in its crown, and in its midst the demoness Lilith had built her
house. But Gilgamesh, informed of Inanna's distress, rushed to her aid.
Making light of his weighty armor, the giant slew the dragon with his
huge bronze ax, seven talents and seven minas in weight. Thereupon
the Zu-bird fled with his young to the mountain, while Lilith, terror-
stricken, tore down her house and escaped to the desert. After Gilga-
mesh had uprooted the liberated tree, his followers, the men of Uruk,
cut down its trunk and gave part of it to Inanna for her throne and bed.
Of the remainder—i.e., root and crown—"Gilgamesh makes for himself
the pukku and mikku, two wooden objects of magic significance."
poem can now be completely restored." He added, however: "Unfortunately, the
meaning of the passage is by no means certain and the mythological implications
are rather obscure, as is obvious from the following tentative translation:
The days of creation, the distant days of creation,
The nights of creation, the far-off nights of creation,
The years of creation, the distant years of creation,—
After in (?) days of yore everything needful had been brought into existence,
After in (?) days of yore everything needful had been commanded,
After in the shrines (?) of the land bread (?) had been tasted (?)
After in the ovens of the land, bread (?) had been baked (?)."
Nobody is likely to contradict the stated uncertainty of the meaning; it would
be advisable to mind the utterance of Margarete Riemschneider (Augengott und
Heilige Hochzeit [1953], p. 190): "So lange sie sinnlos sind, stimmen unsere Uber-
setzungen nicht." The objections raised by stern expert reviewers (T. Jacobsen,
"Sumerian Mythology," JNES $ [1946], pp. 128-52; M. Witzel, "Zur sumerischen
Mythologie," Or. 77 [1948], pp. 393-415) remain throughout within the usual frame
of specialists on grammar and "religion," and it is hard to decide who carries off
the laurels in this race of arbitrary interpretations. The remarkable point of the
new "distribution" seems to be that Ereshkigal belongs henceforward to the "nether
world." (In 1938 Kramer translated line 12: "After Ereshkigal had been presented
(?) as a gift (?) to (?) the netherworld"; in his Sumerian Mythology, after having
"discovered" the dragon-fight, he made it: "After Ereshkigal had been carried off
into Kur as its prize." Witzel (Or. 77, p. 402) rendered the line: "Als (dcr)
Ereshkigal mit der Unterwelt Geschenk 'aufgewartet' worden war.") Since we do
not know yet which star or constellation Ercskigal was meant to represent, this
does not tell us more than that the (unknown) astcrism had "entered" the Way of
' Ea, i.e., that it had sunk below the 15th (or 17th) degree of southern latitude.
441 • Appendices
(It goes without saying that there is no whiff of "magic significance"
to be found in the text.) Here, the summary of 1938 comes to its end,
and we continue with JAOS 64, p. 20: "Follows a passage of twelve
lines which describes Gilgamesh's activity in Erech with this pukku and
mikku, with this 'drum' and 'drumstick' [see below]. Despite the fact
that the text is in perfect condition, it is still impossible to penetrate its
meaning. It is not improbable, however, that it describes in some detail
the overbearing and tyrannical acts which, according to the first tablet
of the Epic of Gilgamesh, brought woe to the inhabitants of Erech, and
which, again according to the Babylonian epic only, led to the creation
of Enkidu."
According to this verdict, Kramer does not even try to translate lit-
erally the lines 24-35 which are allegedly in "perfect condition." Gadd
(RA 50, p. 131) renders the passage as follows:
22. He makes its root into his pukku [ gisRIM (ellag) ]
23. Its top he makes into his mikku [gisE.AG]
24. He says "ellag," except (?) "ellag" let him not speak
25. Saying . . . except (?) ... let him not speak
26. The men of his city say "ellag"
27. He viewed his little company which did not...
28. ? ? his lament they make [a-gestin-nu a-gestin-nu]
29. He that had a mother, (she) brought bread for her son
30. He that had a wife, (she) poured out water for her "brother"
31. The Wine (?) was taken away [dgestin-an-na]
^32. (In) his place where the pukku was set he draws a circle
33. The pukku he raised before him and went into the house
34. In the morning his place where the circle was drawn he viewed
35. The adults (?) do not...
36. (But) at the crying of a little girl. . .
Kramer continues: "When the story becomes intelligible once again,
it continues with the statement that 'because of the outcry of the young
maidens,' the pukku and mikku fell into the nether world. Gilgamesh
put in his hand as well as his foot to retrieve them, but was unable to
reach them. And so he seats himself at the gate of the nether world and
laments:
O my pukku, O my mikku.
My pukku whose lustiness was irresistible,
My mikku whose pulsations could not be drowned out.29
29In From, the Tablets of Sumcr (1956), p. 224, Kramer irunslutcd: "My pukku
with lustiness irresistible, h\y mikku with dance rhythm umi\ ;iled."
Hamlet's Mill
442
(With the following line, representing line 1 of Tablet XII, the Ak-
kadian translation sets in):30
In those days when verily my pukku was with me in the house of the
carpenter,31
(When) verily the wife of the carpenter was with me like the mother
who gave birth to me
(When) verily the daughter of the carpenter was with me like my
younger sister,
My pukku, who will bring it up from the nether world,
My mikku, who will bring it up from the "face" of the netherworld?
His servant Enkidu, his constant follower and companion, thereupon
volunteers to descend to the nether world and bring them up for him
... Hearing his servant's generous offer, Gilgamesh warns him of a num-
ber of the nether world tabus which he is to guard against . . . But
Enkidu heeds not the instructions of his master and commits all those
very acts against which Gilgamesh has warned him. And so he is seized
by Kur and is unable to reascend to the earth."
We can do, here, without the following description of the goings-on
in the "underworld," a description which is common to the Sumerian
myth of the huluppu-tree, and to Tablet XII of the Akkadian Epic.
Kramer (JAOS 64, p. 23) closes his inquiry on the Sumerian sources
of the Gilgamesh Epic: "In conclusion, a comparison of the text of the
'twelfth' tablet of the Epic of Gilgamesh with that of our Sumerian
poem Gilgamesh, Enkidu, and the Nether World, proves beyond all
doubt what has long been suspected, that is, that the 'twelfth' tablet is
an inorganic appendage attached to the Babylonian epic whose first
eleven tablets constitute a reasonably well-integrated poetic unit." We
do wish neither to consent nor to disagree; we do not like those "beyond
all doubt's," and similar verdicts, considering how frightfully little we
know of the Epic. (If there is something that is, really, "beyond all
doubt," it is only this, that the eleven tablets of the Epic do not "con-
30Thus, directly after Urshanabi's checking of the measures of Uruk (//.307),
there follows as catchline line 308 = 12.1: "In those days, when ..."
31 A. Heidel (p. 95) translates lines 1-3: "O that today I had left the pukku in
1 lie house of the carpenter! O that I had left it with the wife of the carpenter, who
was to me like the mother who bore me! O that I left it with the daughter of the
CftTpenter, who was to me (like) my younger sister." In a footnote he explains:
"I lad Gilgamesh left his pukku and his mikku in the house of the carpenter, they
would have been safe and would not have fallen into the underworld." He adds:
"The translation of the first three lines is somewhat tentative." Of only the first
1 luce lines?
443 • Appendices
stitute a reasonably well-integrated poetic unit," not the translated
Epic.)
Of course, it would be to our great advantage were we to know
more about the objects "pukku" and "mikku," that have withstood the
honest efforts of several scholars, first among whom is Sidney Smith
("b/pukk/qqu and mekku," RA 50 [1933], pp. 153-68). Nets have been
proposed, wind instruments (pipes and horns), and Margarete Riem-
schneider (Augengott, pp. 5of.) voted for a particular trap, the very
same rather uncanny trap which is known to us from the Pyramid Texts
(representing the "palace" of Upper Egypt). Most interpreters have
accepted Landsberger's first proposition "drum" and "drumstick";32
there is nothing to say against this solution per se, as long as the signifi-
cance of celestial drums is recognized (see chapter VIII, "Shamans and
Smiths"), and under the condition that comparable celestial drums are
properly investigated—e.g., those of the Chinese sphere. For the time
being there is no cogent reason to stick to "drum" and "drumstick,"
the less so as Landsberger dropped his earlier notion—about which he
states explicitly that he never substantiated it—for the sake of "hoop"
and "driving stick."33 In the present situation, however, we know
nothing of the function of pukku and mikku, and this fact should pre-
vent idle speculations.
No less lamentable than the loss of these objects is the circumstance
that we do not know more about Inanna's unwelcome subtenants in her
huluppu-tree, about Lilith, and about the dragon at the root; that he
corresponds to Nidhoggr of the Edda does not enlighten us concerning
his identity. The Zu-bird, at least, is known to us: the planet Mars it is,34
but we do not yet risk drawing specific conclusions from this ideritifica-
32 Marius Schneider votes for "drum" (Rahmentrommel) and "harp" or "lyre,"
in his article "Pukku und Mikku. Ein Beitrag zum Aufbau und zum System der
Zahlenmystik des Gilgamesh-Epos," Antaios 9 (1967), pp. 28of.
33 "Einige unerkannt gebliebene oder verkannte Nomina des Akkadischen,"
WZKM $6 (i960), pp. 124-26. It is advisable to take into consideration that Lands-
berger does not recognize the occurrence of the word pukku in GE 7.II.22, be-
cause Schott and Schmoekel brought the alleged drum pukku into the first tablet
of their translations without hesitating. At first glance, it might seem irrelevant
whether or not pukku occurs in the first tablet. A little concentrated thinking will
correct this impression: pukku having been made from the wood of the felled
huluppu-tree, the whole timetable of the Epic, particularly the appropriate alloca-
tion of the 12th tablet and the Sumerian poem of the huluppu-trcc, might hinge
upon the valid answer to this very question: whether or nor pukku docs make its
appearance in the first tablet.
;il See C'ossmann, I'lavclariuni llabyloniaivi, 195: ""ll 'MMDIK .'Ul )"'""<•».
Hamlet's Mill
444
tion to the "nest" or "house" of the planet that was taken away from
him.
The deadlock is hardly to be overcome by Mesopotamian texts alone,
and this goes for the huluppu-tree, the mes-tree, Huwawa's cedar, and
that tree in the Era Epic of which Era announces (Tablet 4.123-26,
Gossmann, pp. 3of.; Langdon, MAR 5, p. 144): "Irkalla will I shake
and the heavens shall tremble. The brilliancy of Jupiter [USUL.PA.E3]
will I cause to fall and the stars will I suppress.35 The root of the tree
will I tear up and its sprout will not thrive."
In case we wished to go on this errand in the future we should start
from two Indian nakshatras (lunar mansions) and the legends connected
with them: mula (or mura), "the root," also called "the tearer out of
the root" (see also appendices #4 and #30), and even "Yama's two un-
fasteners," i.e., the Sting of Scorpius,36 (lambda upsilon Scorpii)—in
Babylonian astronomy mulSAR.UR and mulSAR.GAZ, the weapons of
Marduk in the "battle" against Tiamat; and the nakshatra containing
Antares (alpha Scorpii) which bears the names "the oldest," or "who
slays the oldest"37—in Tahiti: "parent pillar of the world."
From India we should turn to the hero Tahaki of Tuamotuan texts,38
already mentioned, because he represents the almost "professional"
avenger of his father. Right from the beginning of events, Tahaki's
mother laments that the hero is destined to die in a faraway country;
35 Langdon (MAR 5, pp. 144^) points to the prophecy against Babylon and its
king, in Isa. xm, xiv, "clearly reminiscent of this passage ... 'I will make the
heavens to tremble and the earth shall be shaken out of her place.' So prophesied
the Hebrew writer, and even more obvious is his borrowing from the Irra myth
when he compares the king of Babylon to Helel: 'How art thou fallen from
Heaven, O Helel, son of morning!' In the cuneiform text of the Irra myth Marduk
is called Shulpae, the name of Jupiter in the early morning, and there can be little
doubt that Helel is a transcription of a Babylonian title of Marduk-Jupiter, elil,
'the shining one.'"
36 The Indians claim that exactly opposite to mula was Betelgeuse, ruled by
"Rudra-the-destroying-archer," whereas the Coptic list of lunar mansions (Kircher,
Oedipus Aegyptiacus 2 [1653], pt. 2, p. 246) calls the Sting of Scorpius (al-Sha'ula)
"Soleka statio translationis caniculae in coelum . . . unde et Si6t vocatur, statio
venationis," which is of the utmost importance since it elucidates the role of a
"sea-star" common to Sirius and the Scorpion-goddess.
37 A. Weber ("Die Vedischen Nachrichten von den Naxatra," APAW 2 [1862],
pp. 2$>if.) renders Jyesthaghni: "die altesten (Geschwister) todtend" which re-
minds us, nolens volens, of Mercer, who translates Pyramid text 399 ab: "It is N.
who judges with him whose name is hidden (on) this day of slaying the eldest
(gods), and N. is lord of offerings, who knots the cord."
38J. F. Stimson, The Legends of Maui and Tahaki, Bull. BPB Mus. (1933),
pp. 50-77.
445 • Appendices •
and again and again throughout the unfolding of the legend, Tahaki
sings: "I go to the night-realm of Kiho, the last bourne of repose."
When still a child, his cousin, with whom he plays diving for pearls,
kills and dismembers him; but his foster brother saves the vital parts
(unlike the case of Osiris), from which his mother revives him again.
He sets out with this brother to free his father from the "goblin
myriads" (see above, p. 175). When reaching the home of his grand-
parents, he wins the love of Hapai, daughter of Tane, the Deus Faber.
When Hapai tells her father about the young man, he answers: "If he
is really Tahaki go and say to him: 'Tane-of-ancient-waters told me
that if you can pass before his face you must be Tahaki; if you can sit
upon his four-legged stool, you must be Tahaki; if you can pull up his
sacred tree by the roots then you are surely Tahaki.' Then Tahaki went
to Tane-of-ancient-waters and stood beside him; and immediately he
passed before his face; he sat upon his high four-legged stool—and it
broke to pieces under him; then Tahaki pulled up his sacred tree by the
roots—and Tahaki looked down and saw the entrance to Havaiki
beneath.39 Then Tahaki and Tane-of-ancient-waters chanted a song
about the death of Tahaki."40 Nonetheless, with Tane's consent, the pair
39 Compare Handy, on Marquesas (Bull. BPB Mus. 69, p. 132): "When Vaka-Uhi
had reached a certain spot in the sea, he could see Havaiki down at the bottom
of the ocean." We seem to be still circling the spot beneath the whirlpool, de-
scribed by Adam of Bremen, and by the Cherokee (see pp. io6f.).
40 Stimson, p. 73. The antiphony of the chant does not allow for a summary:
there are "First Voice," "Second Voice," "Chorus," "Refrains" sung by Tane, and
Tahaki gets some lines in between, also. Noteworthy is the mentioning of a "way-
opener," but we do not know who he is, the Polynesians being more prone to
"titles" and kenningar than other mythographers. Sung by (a) Tahaki, (b) the
first voice, (c) the second voice, we hear (a) "It was Puga-ariki-tahi-"; (b) "The
first Puga-ariki who came at last"; (c) "To Fare-kura-templed abode of the vener-
ated learning of the gods—there in the spirit-world where thou dwellest." This
Fare-kura (fare = house, kura = red, or purple; Maori: Whare kura; Samoa: Fale
ula, etc.) was, according to the "Lore of the Whare-wananga" of New Zealand, a
temple "at Te Hono-i-wairua ... in the spot where the teaching of the Whare-
wananga originated" (i.e., remarks S. Smith, p. 82, "where man was first taught
the doctrines brought down from Heaven by Tane"). The Te Hono-i-wairua (the
gathering place of the spirits) was in Hawaiki, the so-called "primordial home"
of the Polynesians, and the sage states (Smith, p. 101): "Whakaahu, a star (Castor,
in the constellation Gemini) was appointed (or set up) at Te Hono-i-wairua in
Hawaiki . . . whilst Puanga (Rigel of Orion) was fixed at the cast of Rarohcnga
(Hades)." Later he explains (p. 113) that "those spirjts which by their evil con
duct on this earth . . . left the temple [Whare kura] by the Takeke-rOfl (<>r long
rapid, descent) to Rarohengft, or I lades," while- the others MCended slowly to the
"realm of lo the Supreme Cod," i.e., the same as Kiho tutnu, Kiho ihe All SOUKI,
ol Tuiimoi u. -\ /
Hamlet's Mill
446
still lived together "many months until a certain day when trouble arose
between them ... So Tahaki went far far away to a distant land hop-
ing that he might be killed there. And the land where Tahaki was slain
at last was known as Harbor-of-refreshing-rain."
After an extended excursion into Mexico and the "broken tree," the
symbol of Tamoanchcm, "the house of descending," where the gods
were hurled down for having plucked the forbidden flowers, the broken
tree being claimed to be the Milky Way (W. Krickeberg, "Der mittel-
amerikanische Ballspielplatz und seine religiose Symbolik," Paideuma 3
[1944-49], P- J32)> we should return once more to the storehouse of
magnificent survivals, Finland, particularly to the many variants of the
"cutting of the large oak" (K. Krohn, FFC 52 [1924], pp. 183-99).
This was by no means an easy task to accomplish, but the oak had made
trouble right from the start. When (in the second rune of the Kalevala)
Sampsa Pellervoinen had sowed trees, it was the oak alone that would
not grow until four or five lovely maidens from the water, and a hero
from the ocean, had cleared the ground with fire and planted an acorn
in the ashes; and once it had started, the growth of the tree could not
be stopped:
And the summit rose to heaven
And its leaves in air expanded,
In their course the clouds it hindered,
And the driving clouds impeded,
And it hid the shining sunlight,
And the gleaming of the moonlight.
Then the aged Vainamoinen,
Pondered deeply and reflected,
"Is there none to fell the oak-tree,
And o'erthrotu the tree majestic?
Sad is now the life of mortals,
And for fish to swim is dismal,
Since the air is void of sunlight,
And the gleaming of the moonlight."
"One sought above in the sky, below in the lap of the earth," as we
are informed by variants, but then Vainamoinen asked his divine mother
for help.
447 • Appendices
Then a man arose from ocean
From the waves a hero started,
Not the hugest of the hugest,
Not the smallest of the smallest.
As a man's thumb was his stature;
Lofty as the span of woman.
The "puny man from the ocean," whose "hair reached down to his
heels, the beard to his knees," announces, "I have come to fell the oak
tree/And to splinter it to fragments." And so he does. In several variants
the oak is said to have fallen over the Northland River, so as to form the
bridge into the abode of the dead. Holmberg (quoted by Lauri Honko,
"Finnen," Wb. Myth., p. 369) took the oak for the Milky Way.
Considering that the same puny character was alone able to kill the
huge ox—we might call it "bull" quietly—whose mere sight chased all
heroes to the highest trees, we can hardly overlook the possibility that
we are up to some kind of "grandson" of hairy Enkidu, and the oak
would be a faint reflection of the cedar. Whereas an Esthonian variant
sounds—although suffering from atrophy—more like the story of the
huluppu-tree. A damsel plants the acorn—it is typical that Krohn
(p. 187) calls the versions of Russian Karelia "disfigured," where this
acorn is called "taivon tahti," i.e., sky-star—the growing tree endangers
the sky, trying to "tear the celestial luminaries, or to darken them."
The maiden, therefore, asks her brother to cut off the tree. Out of its
wood presents are made for the relatives of the bridegroom, and for
the virgin herself a chest is fabricated.
Since we do not mean to undertake the expedition into comparative
tree-lore here and now, we have to leave it at that. That mythical
"trees" are not of terrestrial provenance, and that we cannot cope with
the different specific tree individuals under the heading "the world
tree"—not although, but because they are "cosmic" trees—could have
been expected by everybody who has spent time and thought on
the tree of the Cross; on Yggdrasil (and Ashvatta); on the "Saltwater-
tree" of the Cuna Indians; on Zeus' oak, part of which was built into
Argo; on the fig tree at the vortex which saved Odysseus; on the laurel
which did not yet mark the omphalos of Delphi, when Apollo slew
Python ("nondum laurus erat," Ovid)—it had to be brought from
Tempe after Apollo's indenture of eight great years; on Ullcr's yew 1 ree
(belonging to Sirius) by means of whose juice Hamlet's father was
Hamlet's Mill
448
murdered; on—apart from the mentioned Mesopotamian tree individ-
uals—the "dark kishkannu-tree" growing in Eridu, where no mortal is
ever admitted; on the tamarisk at Be'ersheba in Genesis xxi; on the
heather tree that "enfolded and embraced the chest with its growth and
concealed it within its trunk," the "chest" being the coffin of Osiris
(Plutarch, De hide et Ostride, ch. 14-15, 256E-357A); and on the king of
the country who "cut off the portion that enfolded the chest, and used
it as pillar to support the roof of his house," until Isis carried off this
"pillar." Those who prefer to overlook these items (and very many
more) might recall the many times that we hear of much sighing and
crying over trees cut down, sawed in two, and the like41—after all, our
very Yima-Jamshid was sawed in two, by Azhi Dahak—as Tammuz
"the lord of the great tree, overcome by the rage of his enemies," and
the numerous comparisons of Mesopotamian temples with trees (cf.
M. Witzel, Texte zum Studium Sumerischer Tempel und Kultzentren
[1932], pp. 37f.; Witzel, Tammuz-Liturgien und Veriuandtes [1935],
pp. io8f.).
It would be an imposition to expect the reader to listen to such
endless rambling on without telling him the aim that we hope to attain,
sooner or later, by digging into these trees and posts: we do want to
know which "New Way" it was that has been "opened" by Gilgamesh
who was "wood" from the mes-tree, and we wish to find out the chrono-
logical sequence of the celestial events as told in the Enuma elish, the
Gilgamesh Epic and the Era Epic. The irrelevancy of the scholarly
quest for "poets" (and who cribbed from whom) has been understood,
meanwhile: it is the celestial phenomena that move and change, and not
the "mythopoetic fantasy" or the "doctrines" of poets and pontiffs.
We have to find out, therefore, who came first as ruler of "the under-
world," Nergal or Gilgamesh, or whether these two should really be
the same, which we doubt for the time being. Yet, we have already
heard (pp. 437f., n. 22) that Nergal's name MES.LAM.TA.E.A. was
given to Gilgamesh. As Lambert states (La Legende de Gilgamesh, pp.
39f.): "After his life on earth Gilgamesh became king of the under-
41 See R. Eisler, Orphisch-Dionysische Mysterien-Gedanken in der christlichen
Antike (1925; repr. 1966), pp. 246, 248. Compare also the "epitheton" of Ugaritic
Baal, 'aliyn, and its possible derivation from Hebrew 'allon ('elon), Oak, There -
bynth, holy tree, and allanati as name of the fourth month, i.e., the month of
Tammuz. (H. Birkeland, Norsk Tidskrift for Sprogvidenskap 9 [1938], pp. 338-45;
W. Robertson Smith, The Religion of the Sewitcs [1957], p. 196, n. 4.)
449 • Appendices
world, a Babylonian Osiris. A formal statement of this is given in a late
religious text: 'Meslamtaea is Gilgamesh, Gilgamesh is Nergal, who
resides in the underworld.' This comes from one of the texts which
explain the functions of deities by equating them with other gods or
goddesses, a very significant type of exposition."
This "significant type of exposition" is, in fact, the technique of the
Old Norse skalds, and we have some perfect kenningar from Meso-
potamia, such as "Ninurta is the Marduk of strength," "Nergal is the
Marduk of battle," "Nabu is the Marduk of business,"42 "Enzak is the
Nabu of Tilmun."48 Now, the passage quoted by Lambert says: "dgil-
games dnergal (u.gur) asib (dur) ersetimtim." In the text (quoted above)
that addresses Gilgamesh as "supreme king, judge of the Anunnaki . . .
you stand in the underworld and give the final verdict," it is again
ersetu, and according to GE 72.56 it is ersetu that has seized Enkidu.
Thus, that line might try to tell us "Gilgamesh is the Nergal of Ersetu,"
whereas Nergal's own "underworld" is Arallu (Aralu). Says Albright:44
"Eridu is employed as a name of the apsu, just as Kutu (Kutha), the
city of Nergal, is a common name of Aralu." Thus, it would be the
very confidence in the custom of giving many names to the same topos
—and in "synonyms" in general—which enforces, so to speak, distorted
translations. It is a matter of course that the final decision will rest with
those who know Sumerian and Akkadian, in the future: spontaneous
angry refusals should not be accepted. Taught by bad experience
with the Egyptian dictionary (Aegyptisches Worterbuch) that renders
thirty-seven Egyptian special termini with the one word Himmel, we
suspect the Assyriologists to handle their "underworld" accordingly—
and their "heaven," of course. The authors of the Assyrian Dictionary
do try to be as specific as possible, admittedly, so they deliver several par-
ticular significations of ersetu (vol. 4, pp. 308-13): "(1) the earth (in
cosmic sense); (2) the nether world; (3) land, territory, district, quarter
of a city, area; (4) earth (in concrete sense), soil, ground, dry land";
but translations being a function of the expectations of the translator,
the categories are bound to look fundamentally different, once several
of them are expected to represent sections of the sphere.
42 Jeremias, HAOG, p. 190; see also Meissner, Babylonien und Assyrien 2, p. 133;
Witzel, Tammuz-Liturgien, pp. 47of. •
43 D. O. Edzard, "Die Mythologic der Sumcrcr und Akkadcr," Worterbuch der
Mythologie 1, p. 130.
""l'lic Mouth of the Rivers," AJSL 1$ (1919)1 p. 1655 sec also K. Tallqvist,
Sumerisch-Akkadische Namen der Totenweh (1934)1 P< 15'
Hamlet's Mill
450
But where does the proportion, Gilgamesh belongs to Ersetu, Nergal
to Arallu, lead us to? This is not yet to be made out properly; too many
riddles lurk behind every word. About the mes-tree, Marduk knew to
tell (in the Era Epic) that it "had its roots in the wide sea, in the depth
of Arallu, and its top attained High Heaven," asking Era reproach-
fully "Because of this work which thou, o hero, didst command to
be done, where is the mes-tree, flesh of the gods, adornment of kings?"
(S. Langdon, Semitic Mythology [1931], p. 140). Concerning the
Mashu mountain (Mashu = twin) watched by the Scorpion-men, the
GE says: "Whose peaks reach to the vault of heaven (And) whose
breast reach to the nether world below," this "nether world" being
Arallu. We knew all the time, certainly, that we were up to Scorpius
(probably with a part of Sagittarius), but the huge constellation offers
sufficient space for more than one way of descending. It is for this reason
particularly that we hope for a better understanding from the Indian
lunar mansions (1) lambda upsilon Scorpii, alias "the root," alias "the
tearer out of the root," alias "Yama's two unfasteners," and (2) Antares,
"the eldest," alias "who slays the eldest": in the sense of Precession, the
sting of the Scorpion antecedes Antares.
If we knew the precise "extension" of the Scorpion-goddess (Ishara
tamtim, Egyptian Selket) we should be better off. And this is the
reason: GE Tablet 7, col. 4, iof., dealing with Enkidu's alleged sick-bed
hallucinations, makes Enkidu prophesy to that "harlot"—in the texts of
Boghazkoi it is she who has the name Siduri—who had lured him into
the city: "[On account of thee (?) ] the wife, the mother of seven, shall
be forsaken." (Speiser: "[On thy account] shall be forsaken the wife
(though) a mother of seven." Ebeling, AOTAT, p. 105: "[Urn deinet-
willen soil] verlassen werden die Mutter der sieben, die Hauptgattin.")
This "mother of seven" should be Ishara tamtim, the Scorpion-goddess
whose seven sons are notorious with her45—it is preposterous, anyhow,
to associate one or the other righteous housewife in Uruk or elsewhere;
but whenever well-bred scholars meet a "harlot" they accept it as their
duty to discover moral lectures in the text surrounding her, very touchy
they are! The first part of the line, however, is not in existence, and it
is, again, their expectation that urges the philologists to supply "[On
account of thee (?)]." Here, for a change, Freud would come in handy,
but for the sake of the translators, not for the text. The readable part of
45 Meissner, Babylonien und Assyrien 2, p. 16; Edzard, Wb. Myth., p. 90.
451 • Appendices
the line states nothing else but that "the wife, the mother of seven shall
be forsaken." But since we do not know yet the whole extension of
the Lady Ishara tamtim who was going to be forsaken, we still do not
know the position of Gilgamesh's "new way"—to ersetu, as we assume,
or by way of ersetu. Ersetu might have replaced Ishara tamtim, because
we learn right in the beginning of the Era Epic (Tablet 2.28-29, Goss-
mann, p. 8) that Anu begets "the Sevengods" (USIBIU) on Ersetu, trans-
lated "the Earth," as companions for Era. The one who doubts that
"begetting" is done up there might begin to ponder over the Hurrian
texts, where MAR.GID.DA, the Big Dipper (alias the Seven Rishis),
begets twins on "the Earth."48 It is evident that we are still far away
from the first among the proposed goals, but we prefer to confess to
this state of things rather than fall into the bottomless pit of speculation
—the very many inviting pits, respectively.
46 The Big Dipper does it on the order of Ea. See H. Otten, My then vom Gotte
Kumarbi. Neue Fragmente (1950), pp. ji.
