- 8 Talk
-
Water pasteurization
Redirected from Water pasteurisation

 Added by Tom Sponheim
Added by Tom SponheimA good introduction to solar water pasteurization and food safety is this interview with microbiologist and SCI-founder Dr. Bob Metcalf.
Millions of people become sick each year from drinking contaminated water. Children are especially susceptible. An estimated 1.5 billion cases of diarrhea occur each year, resulting in the death of nearly 2 million children. Worldwide, about 1.3 billion people do not have access to safe drinking water, including nearly half the population of sub-Saharan Africa. Yet, in many of the most severely affected regions, sunshine is an abundant source of energy that can not only cook food but can also heat water to temperatures that kill harmful microbes, making water safe to drink. This procedure is called solar water pasteurization.
 Added by Tom Sponheim
Added by Tom SponheimIt has been known since the late 1880s, when Louis Pasteur conducted groundbreaking research on bacteria, that heat can kill pathogenic (disease-causing) microbes. Most people know contaminated water can be made safe by boiling. What is not well known is that contaminated water can be pasteurized at temperatures well below boiling, as can milk, which is commonly pasteurized at 71°C (160°F) for 15 seconds.
The chart below indicates the temperatures at which the most common waterborne pathogens are rapidly killed, thus resulting in at least 90 percent of the microbes becoming inactivated in one minute at the given temperature. (The 90 percent reduction is an indicator frequently used to express the heat sensitivity of various microbes.) Thus, five minutes at this temperature would cause at least a 99.999 percent (5 log) reduction in viable microbes capable of causing disease.
| Microbe | Killed Rapidly At |
| Worms, Protozoa cysts (Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Entamoeba) | 55°C (131°F) |
| Bacteria (V. cholerae, E. coli, Shigella, Salmonella typhi), Rotavirus | 60°C (140°F) |
| Hepatitis A virus | 65°C (149°F) |
| (Significant inactivation of these microbes actually starts at about 5°C (9°F) below these temperatures, although it may take a couple of minutes at the lower temperature to obtain 90 percent inactivation.) | |
Solar water pasteurization Edit
Edit
Solar cooks know how easy it is to heat foods in a solar cooker to temperatures well above 60°C (140°F). Knowing this, Dr. Bob Metcalf and a graduate student of his in the early 1980s, David Ciochetti, studied solar water pasteurization for the latter's master's thesis. They found that when contaminated water was heated in a black jar in a solar box cooker, both bacteria and rotaviruses -- the main cause of severe diarrhea in children -- were inactivated by 60°C (140°F). In the paper published this work (Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 47:223-228, 1984) it was concluded that if contaminated water were heated to 65°C (149°F), all pathogenic microbes would be inactivated. This includes the hepatitis A virus, which has a 90 percent reduction after two minutes at 60°C (140°F).
Another student, Negar Safapour, found contaminated water could be pasteurized in a black metal or glass container in a CooKit (Solar Cookers International's simple solar cooker) without using the clear plastic bag that is required for cooking. In our experiments it took about three minutes for each 1°C increase from 55°C to 65°C when heating 2 liters of water, and four to five minutes for each 1°C increase when heating 4 liters. Thus, water is at lethal temperatures for several minutes as it is solar heated to 65°C (149°F), and it remains in the lethal zone for many more minutes as the water slowly cools back down to 55°C (131°F).

 Added by Tom Sponheim
Added by Tom Sponheim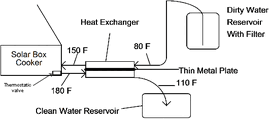
 Added by Tom Sponheim
Added by Tom Sponheim
 Added by Paul Hedrick
Added by Paul HedrickAnother technique that has developed from seeking a simple solution to water pasteurization is the SODIS approach. Basically it involves leaving sealed transparent bottles of clear, but untreated, water in direct sunshine from two to four hours. The time will depend on the surfaces below the bottles, and the intensity of the sunshine. Often the bottles are placed on a flat corrugated metal roof. When the water reaches 65°C(150°F) it is suitable for drinking. As mentioned earlier, a need developed to find a simple device, a WAPI, to indicate when the water was safe. Several designs use a melting wax method. A recent version, called the SPADE, is designed to be fitted directly to the cap on a water bottle. After drilling a 1/4" hole through the cap. The slender clear tube, with wax at one end, is submerged into the bottle. Reaching a safe temperature, the wax runs to the bottom of the tube. A compact approach to providing water pasteurization using existing bottles.
During numerous trips to developing countries, Dr. Metcalf has had the opportunity to conduct numerous solar water pasteurization experiments. In Meatu district, Shinyanga region, Tanzania, water most often comes from open holes dug in the sand of dry riverbeds, and it is invariably contaminated. Indeed, the water that was provided in Dr. Metcalf's guesthouse was heavily contaminated. Bacteriological tests of the water during solar pasteurization repeatedly showed indicator bacteria (key bacteria whose presence indicates faecal contamination) becoming inactivated at temperatures just below 60°C (140°F). During all of Dr. Metcalf's fieldwork, he has heated his own drinking water in a solar cooker using a WAPI as a temperature indicator and he has had no intestinal problems.
Pasteurizing water in a solar cooker Edit
Edit
A standard solar cooker can be used to pasteurize water by simply replacing the food to be cooked with the water to be heated.
Other simple solar pasteurization devices Edit
Edit
Water testing Edit
Edit
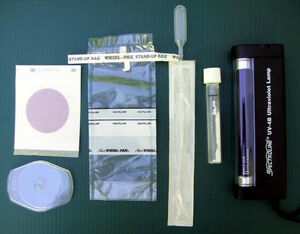
 Added by Tom Sponheim
Added by Tom SponheimDr. Bob Metcalf, a microbiology professor at California State University at Sacramento has prepared a portable water testing kit. Contact information for Dr. Metcalf can be found on his biography page.
See main article: Portable Microbiology Laboratory
Frequently-asked questions Edit
Edit
How is pasteurization accomplished? Edit
Edit
Traditional fuels can be used to pasteurize water, but on sunny days solar energy can be used as well. Simple solar cookers can pasteurize water for a family at a rate of about one liter per hour. Solar Cookers International's reusable water pasteurization indicator (WAPI) can be used to determine when water heated by solar or conventional means has been heated to a high enough temperature to make it safe.
Don’t you need to boil water for 20 minutes to sterilize it and make it safe to drink? Edit
Edit
No, it is only necessary to heat water to 65° C to pasteurize it.
What is the difference between sterilization and pasteurization? Edit
Edit
Sterilization kills all of the organisms in the water, while pasteurization kills only those organisms that can cause harm to humans.
What common disease organisms are killed by pasteurizing water? Edit
Edit
Giardia, cryptosporidium, entamoeba, the eggs of worms, cholera, shigella, salmonella bacteria and those that cause typhoid, the enterotoxogenic strains of E. Coli, Hepatitis A, and also rotavirus which is a major cause of disease in children are all killed or inactivated at 65°C.
How can water be tested in the field? Edit
Edit

 Added by Wsiegmund
Added by WsiegmundTo test whether water has been heated enough to make it safe to drink you can use a thermometer or a water pasteurization indicator.
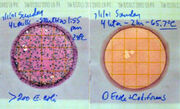
To test a water source for human or animal fecal contamination, it is best to test for the bacterium Escherichia coli, which is always present in human faeces at a level of about one hundred million E. coli per gram. The presence of E. coli in water indicates recent fecal pollution and a public health threat. Water containing one E. coli per milliliter is considered heavily contaminated. In order to do world-class microbiology in developing countries where there is no lab, since 2000 SCI has used two complementary tests extensively.
The first test is a presence/absence test using Colilert, the most widely used test in the water industry (IDEXX Laboratories, Westbrook, Maine). SCI uses the Colilert MPN tube, which is inoculated with 10 ml of water, and incubated at body temperature for 10-24 hours. If the liquid in the tube turns yellow, and fluoresces blue when illuminated with a battery-operated, hand-held ultraviolet light, the presence of E. coli in the water sample is confirmed. If the tube remains clear, or is yellow but does not fluoresce blue under UV light, it indicates that there were no E. coli cells in the 10 ml sample, and there is a low risk of disease from the water.

 Added by Tom Sponheim
Added by Tom SponheimRecent news and developments Edit
Edit
- September 2011: Research study now available online: Social Return on Investment (SROI), the value added for families before and after using SOLVATTEN in the Bungoma district in western Kenya
- March 2011: Solar water pasteurization is a great success with the school children
- November 2010: Retired 3M engineers create a solar water pasteurizer for use in Third World countries. Inspired by the potential capacity for heat transfer they saw in plastic political signs, Bob Nepper and Bill Stevenson living in Minnesota, USA, set about designing their version of a water purifier. Water is first filtered, then passes through a field of channels in a black corrugated plastic collector. When the water reaches 160°F, and is suitable for drinking, a thermostat will open and allow the potable water to flow into an adjacent bucket. Capacity for the system is approximately four gallons of pasteurized water per hour.
Commercial water pasteurization devices Edit
Edit
SODIS Edit
Edit
To see information on solar water disinfection (without the use of heat), see main article: SODIS
Topics needing research Edit
Edit
Nitinol as a temperature indicator Edit
Edit
Nitinol (Nickel-Titanium) is a memory metal which can be designed with a temperature transition threshold. It can be designed with two memory shapes: straight for below 65°C and circular for above 65C. Nitinol wire can be manufactured on a mass scale to provide an accurate indicator. The wire can be submerged into the water without a glass enclosure. When the wire becomes circular, the water temperature will have reached the 65°C threshold.
See also Edit
Edit
- Nepper and Stevenson water pasteurizer
- Water pasteurization indicator (WAPI)
- Flow-through pasteurization device
- Safe Water Project
- Safe Household Water Storage
- A Summary of Water Pasteurization Techniques - Dale Andreatta
- Solar Water Disinfection in the northeast of Brazil: Kinetics of the Microbiological Process and the Study for the Development of the Pilot Plant - Paulo Mário M. Araújo
- Dr. Bob Metcalf
- Using beeswax to indicate pasteurization temperature
- Boil 3, Add 1 Method - A method of mixing an amount of cold water with boiling water to pasteurize more water with less fuel
- Solar puddle
- Solar Kettle-Thermos Flask
- Soda bottle pasteurizer
- Solar Water Disinfection (SODIS)
- Another soda bottle pasteurizer
- Simple Solar Water Pasteurizer
- Solar Water Boiler with Tracking System - Yousif Abakr
- Jompy Water Boiler
External links Edit
Edit
- May 2010: EPA Water Disinfection Project A grant awarded by the Environmental Protection Agency will provide funding for the research and development of a solar water pasteurizer.
- January 2009: Dr. Dale Andreatta speaking on water pasteurization at the 2009 ETHOS conference - Dale Andreatta describes the development of the WAPI, a simple device for determining whether water has been heated to a temperature that makes it safe to drink. He also discusses flow-through pasteurization devices and strategies to pasteurize water with the waste heat from a wood-burning cookstove. Slides from presentation are also available.
- September 2007: Bob Metcalf interviewed on Sacramento NPR program
- September 2007: Safe Water from Sunshine - Patricia McArdle
- July 2006: Bob Metcalf's Granada conference presentation on solar water pasteurization. Audio: 16k, 8k and slides
- A slideshow showing Dr. Metcalf's solar water pasteurization projects in Africa
- An interview with Bob Metcalf discussing food safety and solar water pasteurization
- Pasteurization of Naturally Contaminated Water with Solar Energy - Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Feb. 1984, p. 223-228
- Recent Advances in Solar Water Pasteurization
- Solar Cooking Archive page on solar water pasteurization
- Colilert
- The Solar Puddle - Dale Andreatta
- Petrifilm is available from Arrow Scientific
- Construction plans for a simple solar water pasteurizer
- The Solar Kangaroo water pasteurizer
- July 2006: Compound parabolic concentrators for solar water heat pasteurizaion: numerical simulation - David Denkenberger
- July 2006: A comparative study of brackish water desalination using indigenously-prepared solar desalination unit - Rizwan Raza
- March 2007: Major development in drinking water testing technology - International Aid & Trade
Audio and video Edit
Edit
See this article in our foreign language wikis Edit
Edit
- Voyez cet article dans le wiki en français: Pasteurisation de l'eau
- Vea este artículo en el wiki en español: Un Pasteurizador de Agua Sencillo