| Family XV. FRINGILLINAE. FINCHES. GENUS XVI. COCCOBORUS, Swains. SONG-GROSBEAK. |
Next >> |

Family |
THE ROSE-BREASTED GROSBEAK. [Rose-breasted Grosbeak.] |
| Genus | COCCOBORUS LUDOVICIANUS, Linn. [Pheucticus ludovicianus.] |
One year, in the month of August, I was trudging along the shores of the
Mohawk river, when night overtook me. Being little acquainted with that part of
the country, I resolved to camp where I was; the evening was calm and beautiful,
the sky sparkled with stars, which were reflected by the smooth waters, and the
deep shade of the rocks and trees of the opposite shore fell on the bosom of the
stream, while gently from afar came on the ear the muttering sound of the
cataract. My little fire was soon lighted under a rock, and, spreading out my
scanty stock of provisions, I reclined on my grassy couch. As I looked around
on the fading features of the beautiful landscape, my heart turned towards my
distant home, where my friends were doubtless wishing me, as I wished them, a
happy night and peaceful slumbers. Then were heard the barkings of the
watch-dog, and I tapped my faithful companion to prevent his answering them.
The thoughts of my worldly mission then came over my mind, and having thanked
the Creator of all for his never-failing mercy, I closed my eyes, and was
passing away into the world of dreaming existence, when suddenly there burst on
my soul the serenade of the Rose-breasted bird, so rich, so mellow, so loud in
the stillness of the night, that sleep fled from my eyelids. Never did I enjoy
music more: it thrilled through my heart, and surrounded me with an atmosphere
of bliss. One might easily have imagined that even the Owl, charmed by such
delightful music, remained reverently silent. Long after the sounds ceased did
I enjoy them, and when all had again become still, I stretched out my wearied
limbs, and gave myself up to the luxury of repose. In the morning I awoke
vigorous as ever, and prepared to continue my journey.
I have frequently observed this beautiful species, early in the month of
March, in the lower parts of Louisiana, making its way eastward; and when
residing at Henderson in Kentucky, and in Cincinnati in Ohio, I have noticed the
same circumstance. At this early period, it passes at a considerable height in
the air, and now and then alights on the tops of the tallest trees of the
forest, as if to rest awhile. While on wing it utters a clear note, but when
perched it remains silent, in an upright and rather stiff attitude. It is then
easily approached. I have followed it in its migrations into Pennsylvania, New
York, and other Eastern States, through the British provinces of New Brunswick
and Nova Scotia, as far as Newfoundland, where many breed, but I saw none in
Labrador. It is never seen in the maritime parts of Georgia, or those of the
Carolinas, but some have been procured in the mountainous portions of those
States. I have found them rather plentiful in the early part of May, along the
steep banks of the Schuykill river, twenty or thirty miles from Philadelphia,
and observed, that at that season they fed mostly on the buds of the trees,
their tender blossoms, and upon insects, which they catch on wing, making short
sallies for the purpose. I saw several in the Great Pine Forest of
Pennsylvania; but they were more abundant in New York, especially along the
banks of the beautiful river called the Mohawk. They are equally abundant along
the shores of Lakes Ontario and Erie, although I believe that the greater number
go as far as New Brunswick to breed. While on an excursion to the islands at
the entrance of the Bay of Fundy, in the beginning of May, my son shot several
which were in full song. These islands are about thirty miles distant from the
main land.
The most western place in which I found the nest of this species was within
a few miles of Cincinnati on the Ohio. It was placed in the upright forks of a
low bush, and differed so much in its composition from those which I have seen
in the Eastern States, that it greatly resembled the nest of the Blue Grosbeak
already described. The young, three in number, were ready to fly. The parents
fed them on the soft grains of wheat which they procured in a neighbouring
field, and often searched for insects in the crannies of the bark of trees, on
which they alighted sidewise, in the manner of Sparrows. This was in the end of
July. Generally, however, the nest of the Rose-breasted Grosbeak is placed on
the top branches of an alder bush, near water, and usually on the borders of
meadows or alluvial grounds. It is composed of the dried twigs of trees, mixed
with a few leaves and the bark of vines, and is lined with fibrous roots and
horse-hair. The eggs are seldom more than four, and I believe only one brood is
raised in the season. Both sexes incubate. I have found the nest and eggs, on
the 20th of May, on the borders of Cayuga Lake in the State of New York.
The flight of the Rose-breasted Grosbeak is strong, even, and as graceful
as it is sustained. When travelling southward, at the approach of autumn, or
about the 1st of September, it passes high over the forest trees, in the manner
of the King-bird and the Robin, alighting toward sunset on a tall tree, from
which it in a few minutes dives into some close thicket, where it remains during
the night. The birds travel singly at this season, as well as during spring.
I am indebted to my friend JOHN BACHMAN, for the following information
respecting this interesting Grosbeak: "One spring, I shot at a beautiful male
bird of this species, in the State of New York. It was wounded in one foot
only, and although I could not perceive any other injury afterwards, it fell
from the tree to the ground, and before it recovered itself I secured it. Not
having a cage at hand, I let it fly in the room which I had made my study.
Before an hour had elapsed, it appeared as if disposed to eat; it refused corn
and wheat, but fed heartily on bread dipped in milk. The next day it was nearly
quite gentle, and began to examine the foot injured by the shot, which was much
swollen and quite black. It began to bite off its foot at the wounded part, and
soon succeeded in cutting it quite across. It healed in a few days, and the
bird used the mutilated leg almost as well as the other, perching and resting
upon it. It required indeed some care to observe that the patient had been
injured. I procured a cage for it, to which it immediately became reconciled.
It ate all kinds of food, but preferred Indian corn meal and hempseed. It
appeared fonder of insects than birds of that genus are supposed to be, and ate
grasshoppers and crickets with peculiar relish. It would at times sit for hours
watching the flies, as these passed about it, and snatched at and often secured
such wasps as now and then approached the pieces of fruit thrown into the cage.
Very often, of fine moonshiny nights, it would tune its pipe, and sing sweetly,
but not loudly, remaining quietly perched and in the same position. Whilst
singing during the day, it was in the habit of opening its wings, and gently
raising them, somewhat in the manner of the Mocking-bird. I found it very
difficult to preserve this bird during winter, and was obliged for that purpose
to place it in a room heated by a stove to summer temperature. It was a lively
and very gentle companion of my study for nearly three years; it died of cold
the third winter. It frequently escaped from the cage, but never exhibited the
least desire to leave me, for it invariably returned to some portion of the
house at the approach of night. Its song continued about six weeks during
summer, and about two in the autumn; at all other periods it simply uttered a
faint chuck, and seemed to possess many of the ordinary habits of the Blue
Grosbeak."
The food of this beautiful bird consists of seeds of the cereal plants, of
grasses, and those of different kinds of berries, along with insects. The young
are three years in obtaining their full dress, and undergo their changes very
slowly.
Although common about the mouths of the Mississippi in spring, when on its
way northward, this species is never seen in South Carolina. When proceeding to
the Texas in April, 1837, I found it so abundant wherever we landed that
hundreds might have been procured. Both sexes were in perfect plumage. Mr.
TOWNSEND observed it on the Missouri; and Dr. T. M. BREWER informs me that he
shot a fine male at Fresh Pond, near Boston, in the summer of 1832, and knew of
two or three females killed afterwards.
In an adult male from Texas, the palate is deeply concave in the middle,
with two prominent longitudinal ridges, forming a large projection at their
meeting anteriorly; it ascends obliquely, is gradually narrowed, and beyond the
nostrils becomes horizontal, the upper mandible beneath being concave, with
three strong longitudinal ridges and four grooves; the lower mandible is very
deeply concave. The posterior aperture of the nares is 3 twelfths long,
oblongo-linear, margined with papillae. The width of the mouth is 6 twelfths.
The tongue is 5 3/4 twelfths long, emarginate and papillate at the base, convex
and fleshy above, as high as broad, horny beneath, and tapering to a point.
OEsophagus 3 inches 2 twelfths long, nearly uniformly 3 twelfths wide. Stomach
small, roundish, compressed, 1/2 inch long, and of the same breadth; its muscles
distinct and of moderate thickness, the tendons large, the epithelium thin,
tough, longitudinally rugous, and of a reddish-brown colour. The contents of
the stomach small seeds and particles of quartz. Intestine 9 1/2 inches long,
its width from 2 twelfths to 1 1/2 twelfths; coeca 1 1/2 twelfths long, 1/2
twelfth in breadth, 1 inch distant from the extremity.
Trachea 2 inches 1 twelfth long, from 1 twelfth to 1/2 twelfth in breadth;
the rings about 70, firm, considerably flattened. Bronchi of about 15 rings.
Muscles as usual in this family; the inferior laryngeal large. There are very
slender elongated salivary glands, extending to beyond the articulation of the
jaw.
Male, 7 3/4, 13.
Passes from Texas northward and eastward in great numbers. Breeds on the
Missouri, in the Middle States, Newfoundland, and Labrador. Rather common.
Migratory.
ROSE-BREASTED GROSBEAK, Loxia rosea, Wils. Amer. Orn., vol. ii. p. 135.
FRINGILLA LUDOVICIANA, Bonap. Syn., P. 113.
COCCOTHRAUSTES LUDOVICIANA, Rose-breasted Grosbeak, F. Bor. Amer., vol. i.p. 271.
ROSE-BREASTED GROSBEAK, Fringilla ludoviciana, Nutt. Man., vol. i. p. 527.
ROSE-BREASTED GROSBEAK, Fringilla ludoviciana, Aud. Orn. Biog., vol. ii.p. 166; vol. v. p. 513.
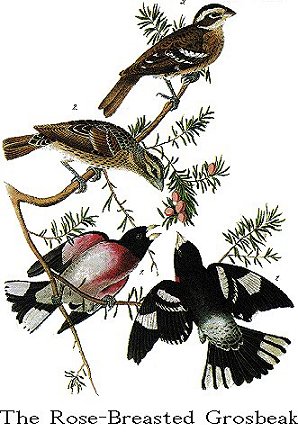
Adult Male.
Bill short, robust, bulging at the base, conical, acute; upper mandible
with its dorsal outline a little convex, the sides rounded, the edges sharp;
lower mandible with its dorsal outline also a little convex, the sides rounded,
the edges inflected; the gap-line is deflected at the base, then straight to the
end. Nostrils basal, roundish, open, partly concealed by the feathers. Head
rather large, neck short, general form robust. Legs of moderate length, rather
strong; tarsus anteriorly covered with a few scutella, the upper long,
posteriorly sharp; toes scutellate above, free, the lateral ones nearly equal;
claws slender, arched, compressed, acute, that of the hind toe not much larger.
Plumage soft and blended, but firm and elastic. Wings of moderate length,
broad, the second, third, and fourth quills longest, the secondaries rounded.
Tail longish, slightly emarginate, of twelve rounded feathers.
Bill white. Iris hazel. Feet greyish-blue. The head all round, including
the upper part of the neck, the hind neck, the back, wings, and tall, glossy
black; the first row of coverts, the tips of the secondary coverts, the basal
half of the primary quills, and the inner webs towards the end of the three
lateral tail-feathers, white, as is the rump, that part, however, being spotted
with black. Lower neck and middle of the breast of a bright carmine tint; lower
wing coverts white, tinged with carmine.
Length 7 3/4 Inches, extent of wings 13; bill along the back (7 1/2)/12,
along the edge 9/12; tarsus 11/12.
Adult Female.
The female differs greatly from the male in external appearance. The bill
brown above, paler beneath; iris hazel; feet as in the male. The general colour
of the plumage above is olivaceous-brown, spotted with brownish-black, the
central part of each feather being, of the latter colour. On the head is a
central longitudinal band of pale yellowish-grey, spotted with dark brown, then
on each side a dark brown band, and above the eye a white one; a brown band from
the bill to the eye and beyond it, and under this a whitish band. There are two
white bands on the wings as in the male, but narrower and duller. The quills
and tail are brown. The lower parts light brownish-yellow, fading behind into
white; the fore neck, breast, and sides marked with small longitudinal spots or
streaks of dark-brown. The lower wing-coverts very slightly tinged with
rose-colour.
Young Male in autumn.
After the first moult, the young male resembles the female, but already
shews the rosy tints both on the breast and on the under wing-coverts.
Young in first plumage.
In this state also the young resemble the female.
THE GROUND HEMLOCK.
TAXUS CANADENSIS, Willd. Sp. Pl., vol, iv. p. 856. Pursch, Flor. Amer.
Sept., vol. ii. p. 647.--DIAECIA MONADELPHIA.--CONIFERAE, Juss.
The ground hemlock, or Canadian yew, is abundant on the declivities of the
mountains from Maryland to Maine. It is a low tree, or rather bush, often
almost prostrate, and frequently hanging from the rocks. The leaves are linear,
distichous, revolute at the margin. The berries, which are oblong or globular,
and of a pale red colour, are eatable.
| Next >> |