| Family XVIII. CORVINAE. CROWS. GENUS III. GARRULUS, Briss. JAY. |
Next >> |

Family |
THE FLORIDA JAY. [Scrub Jay (see also Ultramarine Jay).] |
| Genus | GARRULUS FLORIDANUS, Bartram. [Aphelocoma coerulescens.] |
This beautiful and lively bird is a constant resident in the south-western
parts of Florida, from which country it seldom if ever removes to any great
distance. It is never seen in the State of Louisiana, far less in that of
Kentucky, and when CHARLES BONAPARTE asserts that it occurs in these districts,
we must believe that he has been misinformed. It is so confined to the
particular portions of Florida which it inhabits, that even on the eastern
shores of that peninsula few are to be seen. I have never observed it in any
part of Georgia, or farther to the eastward.
The flight of the Florida Jay is generally performed at a short distance
from the ground, and consists either of a single sailing sweep, as it shifts
from one tree or bush to another, or of continuous flappings, with a slightly
undulated motion, in the manner of the Magpie (Pica melanoleuca) or of the
Canada Jay (Garrulus canadensis). Its notes are softer than those of its
relative the Blue Jay (Garrulus cristatus), and are more frequently uttered.
Its motions are also more abrupt and quicker. It is seen passing from one tree
to another with expanded tail, stopping for a moment to peep at the intruder,
and hopping off to another place the next minute. It frequently descends to the
ground, along the edges of oozy or marshy places, to search for snails, of
which, together with berries of various kinds, fruits and insects, its food
consists. It is easily approached during the breeding season, but is more shy
at other times. It is a great destroyer of the eggs of small birds, as well as
of young birds, which it chases and kills by repeated blows of its bill on their
heads, after which it tears their flesh with avidity.
The Florida Jay is easily kept in a cage, where it will feed on recent or
dried fruits, such as figs, raisins, and the kernels of various nuts, and
exhibits as much gaiety as the Blue Jay does in a similar state. Like the
latter, it secures its food between its feet, and breaks it into pieces before
swallowing it, particularly the acorns of the live oak, and the snails which it
picks up among the sword palmetto. No sooner have the seeds of that plant
become black, or fully ripe, than the Florida Jay makes them almost its sole
food for a time, and wherever a patch of these troublesome plants are to be
seen, there also is the Jay to be met with. I have called the palmetto a
troublesome plant, because its long, narrow, and serrated leaves are so stiff,
and grow so close together, that it is extremely difficult to walk among them,
the more so that it usually grows in places where the foot is seldom put without
immediately sinking in the mire to a depth of several inches.
The nest of the Florida Jay is sparingly formed of dry sticks, placed
across each other, and, although of a rounded shape, is so light that the bird
is easily seen through it. It is lined with fibrous roots, placed in a circular
manner. The eggs are from four to six, of a light olive colour, marked with
irregular blackish dashes. Only one brood is raised in the season.
I had a fine opportunity of observing a pair of these birds in confinement,
in the city of New Orleans. They had been raised out of a family of five, taken
from the nest, and when I saw them had been two years in confinement. They were
in full plumage, and extremely beautiful. The male was often observed to pay
very particular attentions to the female, at the approach of spring. They were
fed upon rice, and all kinds of dried fruit. Their cage was usually opened
after dinner, when both immediately flew upon the table, fed on the almonds
which were given them, and drank claret diluted with water. Both affected to
imitate particular sounds, but in a very imperfect manner. These attempts at
mimicry probably resulted from their having been in company with parrots and
other birds. They suffered greatly when moulting, becoming almost entirely
bare, and required to be kept near the fire. The female dropped two eggs in the
cage, but never attempted to make a nest, although the requisite materials were
placed at her disposal.
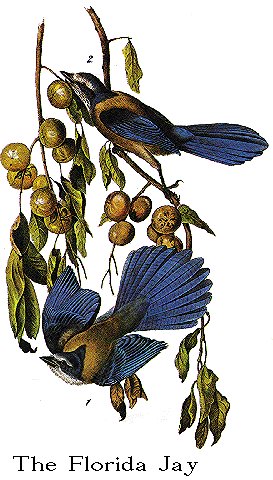
I have represented a pair of Florida Jays on a branch of the persimon tree,
ornamented with its richly coloured fruits. This tree grows to a moderate
height as well as girth. The wood is hard and compact. The leaves drop off at
an early period. The fruit, when fully ripe, is grateful to the palate. The
persimon occurs in all parts of the United States, but abounds in the low lands
of Florida and Louisiana, probably more than in any other portion of the Union.
CORVUS FLORIDANUS, Bonap. Syn., p. 58.
FLORIDA JAY, Garrulus floridanus, Bonap. Amer. Orn., vol. ii. p.
FLORIDA JAY, Nutt. Man., vol. i. p. 230.
FLORIDA JAY, Corvus floridanus, Aud. Orn. Biog., vol. i. p. 444.
Male, 11 1/4, 14.
Confined to the Floridas. Not very common. Resident.
Bill short, strong, straight, compressed, acute; upper mandible with the
dorsal outline nearly straight, the sides sloping, the edges sharp and
overlapping, the tip slightly declinate; lower mandible with the back narrow,
the sides sloping. Nostrils basal, open, covered by the reversed bristly
feathers. Head rather large, neck short, body robust. Feet of ordinary length;
tarsus about the same length as the middle toe, anteriorly scutellate,
compressed, acute behind; toes free, scutellate, the inner shorter than the
outer; claws arched, compressed, acute.
Plumage soft, blended, glossy. A tuft of reflected bristly feathers over
the nostril on each side, and several bristle-pointed feathers at the base of
the upper mandible. Wings short, third and fourth quills longest, first short.
Tail long, much rounded, of twelve rounded feathers.
Bill and feet brownish-black. Iris hazel. Upper part of the head, the
cheeks, side, and back part of the neck, the wings and tail, of a bright
purplish-azure. Back light yellowish-brown. A band of white on the forehead,
extending over the eyes. The under parts brownish-white. The upper
tail-coverts are blue, and the tail-feathers are indistinctly barred with deeper
lines.
Length 11 1/4 inches; bill along the ridge 11/12, along the gap nearly
1 1/4; tarsus 1 2/12, middle toe nearly the same.
Adult Female.
The female presents the same colours as the male, the difference in tint
being hardly perceptible.
THE PERSIMON TREE.
DIOSPYROS VIRGINIANA, Willd., Sp. Pl., vol. iv. p. 1107. Pursh, Flor.
Amer., vol. i. p. 265. Mich., Abr. Forest. de l'Amer. Sept., vol. ii.
p. 195, pl. 12.--POLYGAMIA DIOECIA, Linn.--GUAIACANAE, Juss.
Leaves ovato-oblong, acuminate, smooth, venous; petioles downy; buds
smooth. The flowers are pale yellow, and the fruits, which are of the size of a
plum, are of a globular form, and when mature, of a dull yellowish colour. The
bark of old trees is cracked, and of a dark colour. The wood is employed for
various purposes, being fine-grained, hard and durable.
| Next >> |