


| Skip navigation | ||
 |
 |  |
|
|
||
Acute MI
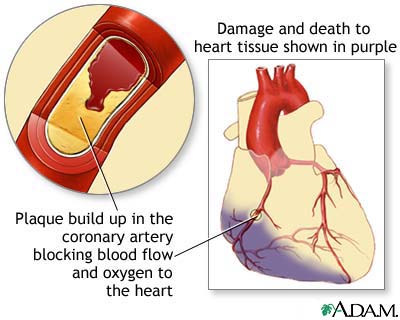
A heart attack or acute myocardial infarction (MI) occurs when one of the arteries that supplies the heart muscle becomes blocked. Blockage may be caused by spasm of the artery or by atherosclerosis with acute clot formation. The blockage results in damaged tissue and a permanent loss of contraction of this portion of the heart muscle.
Update Date: 2/20/2007 Updated by: Updated by A.D.A.M. Editorial Team: Greg Juhn, M.T.P.W., David R. Eltz, Kelli A. Stacy. Previously reviewed by Alan Berger, MD, Assistant Professor, Divisions of Cardiology and Epidemiology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN. Review provided byVeriMed Healthcare Network. (2006)

| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Page last updated: 02 January 2008 |