


| Skip navigation | ||
 |
 |  |
|
|
||
Nervous system
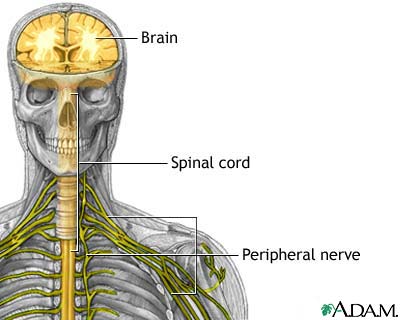
Peripheral Neuropathy is not a distinct disease, but the manifestation of many conditions that damage the peripheral nerves (nervous tissue other than the brain and spinal cord). Symptoms depend on whether sensory nerves (the nerves that transmit sensory information from the body to the brain and spinal cord) or motor nerves (the nerves that transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the body) are affected. If the sensory nerves are damaged, sensation may be diminished, lacking or abnormal. Damaged motor nerves impair movement or function. Peripheral neuropathy may be caused by direct or indirect injury, or by a systemic cause such as a metabolic disorder.
Update Date: 8/7/2006 Updated by: Daniel Kantor, M.D., Director of the Comprehensive MS Center, Neuroscience Institute, University of Florida Health Science Center, Jacksonville, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.

| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Page last updated: 02 January 2008 |