


| Skip navigation | ||
 |
 |  |
|
|
||
Sentinel node biopsy
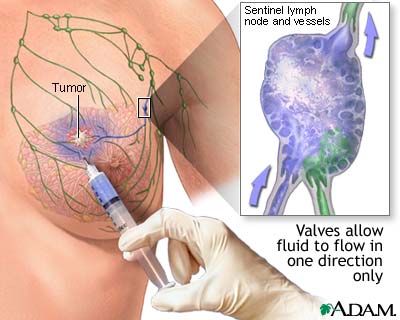
Sentinel node biopsy is a technique which helps determine if a cancer has spread (metastasized), or is contained locally. When a cancer has been detected, often the next step is to find the lymph node closest to the tumor site and retrieve it for analysis. The concept of the "sentinel" node, or the first node to drain the area of the cancer, allows a more accurate staging of the cancer, and leaves unaffected nodes behind to continue the important job of draining fluids. The procedure involves the injection of a dye (sometimes mildly radioactive) to pinpoint the lymph node which is closest to the cancer site. Sentinel node biopsy is used to stage many kinds of cancer, including lung and skin (melanoma).
Update Date: 9/14/2006 Updated by: Stephen Grund, M.D. Ph.D., Chief of Hematology/Oncology and Director of the George Bray Cancer Center at New Britain General Hospital, New Britain, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.

| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Page last updated: 02 January 2008 |