
Sacred Texts Taoism Index Previous

1. The time of the autumnal floods was come, and the hundred streams were all discharging themselves into the Ho. Its current was greatly swollen 2, so that across its channel from bank to bank one could not distinguish an ox from a horse. On this the (Spirit-) earl of the Ho 3 laughed with delight, thinking that all the beauty of the world was to be found in his charge. Along the course of the river he walked east till he came to the North Sea, over which he looked, with his face to the east, without being able to see where its waters began. Then he began to turn his face round, looked across the expanse, (as if he were) confronting Zo 3, and said with a sigh, 'What the vulgar saying expresses about him who has learned a hundred points (of the Tâo), and thinks that there is no one equal to himself, was surely spoken of me. And moreover, I have heard
parties making little of the knowledge of Kung-nî and the righteousness of Po-î, and at first I did not believe them. Now I behold the all-but-boundless extent (of your realms). If I had not come to your gate, I should have been in danger (of continuing in my ignorance), and been laughed at for long in the schools of our great System 1.'
Zo, (the Spirit-lord) of the Northern Sea, said, 'A frog in a well cannot be talked with about the sea;--he is confined to the limits of his hole. An insect of the summer cannot be talked with about ice;--it knows nothing beyond its own season. A scholar of limited views cannot be talked with about the Tâo;--he is bound by the teaching (which he has received). Now you have come forth from between your banks, and beheld the great sea. You have come to know your own ignorance and inferiority, and are in the way of being fitted to be talked with about great principles. Of all the waters under heaven there are none so great as the sea. A myriad streams flow into it without ceasing, and yet it is not filled; and afterwards 2 it discharges them (also) without ceasing, and yet it is not emptied. In spring and in autumn it undergoes no change; it takes no notice of floods or of drought. Its superiority over such streams even as the Kiang and the
[paragraph continues] Ho cannot be told by measures or numbers; and that I have never, notwithstanding this, made much of myself, is because I compare my own bodily form with (the greatness of) heaven and earth, and (remember that) I have received my breath from the Yin and Yang. Between heaven and earth I am but as a small stone or a small tree on a great hill. So long as I see myself to be thus small, how should I make much of myself? I estimate all within the four seas, compared with the space between heaven and earth, to be not so large as that occupied by a pile of stones in a large marsh! I estimate our Middle States, compared with the space between the four seas, to be smaller than a single little grain of rice in a great granary! When we would set forth the number of things (in existence), we speak of them as myriads; and man is only one of them. Men occupy all the nine provinces; but of all whose life is maintained by grain-food, wherever boats and carriages reach, men form only one portion. Thus, compared with the myriads of things, they are not equal to a single fine hair on the body of a horse. Within this range are comprehended all (the territories) which the five Tîs received in succession from one another; all which the royal founders of the three dynasties contended for; all which excited the anxiety of Benevolent men; and all which men in office have toiled for. Po-î was accounted famous for declining (to share in its government), and Kung-nî was accounted great because of the lessons which he addressed to it. They acted as they did, making much of themselves;--therein like you who a little time ago did so of yourself because of your (volume of) water!'
2. The earl of the Ho said, 'Well then, may I consider heaven and earth as (the ideal of) what is great, and the point of a hair as that of what is small?' Zo of the Northern Sea replied, 'No. The (different) capacities of things are illimitable; time never stops, (but is always moving on); man's lot is ever changing; the end and the beginning of things never occur (twice) in the same way. Therefore men of great wisdom, looking at things far off or near at hand, do not think them insignificant for being small, nor much of them for being great:--knowing how capacities differ illimitably. They appeal with intelligence to things of ancient and recent occurrence, without being troubled by the remoteness of the former, or standing on tiptoe to lay hold of the latter:--knowing that time never stops in its course. They examine with discrimination (cases of) fulness and of want, not overjoyed by success, nor disheartened by failure:--knowing the inconstancy of man's lot. They know the plain and quiet path (in which things proceed), therefore they are not overjoyed to live, nor count it a calamity to die: the end and the beginning of things never occurring (twice) in the same way.
'We must reckon that what men know is not so much as what they do not know, and that the time since they were born is not so long as that which elapsed before they were born. When they take that which is most small and try to fill with it the dimensions of what is most great, this leads to error and confusion, and they cannot attain their end. Looking at the subject in this way, how can you know that the point of a hair is sufficient to determine the minuteness of what is most small, or that
heaven and earth are sufficient to complete the dimensions of what is most large?'
3. The earl of the Ho said, 'The disputers of the world all say, "That which is most minute has no bodily form; and that which is most great cannot be encompassed;"--is this really the truth?' Zo of the Northern Sea replied, 'When from the standpoint of what is small we look at what is great, we do not take it all in; when from the standpoint of what is great we look at what is small, we do not see it clearly. Now the subtile essence is smallness in its extreme degree; and the vast mass is greatness in its largest form. Different as they are, each has its suitability,--according to their several conditions. But the subtile and the gross both presuppose that they have a bodily form. Where there is no bodily form, there is no longer a possibility of numerical division; where it is not possible to encompass a mass, there is no longer a possibility of numerical estimate. What can be discoursed about in words is the grossness of things; what can be reached in idea is the subtilty of things. What cannot be discoursed about in words, and what cannot be reached by nice discrimination of thought, has nothing to do either with subtilty or grossness.
'Therefore while the actions of the Great Man are not directed to injure men, he does not plume himself on his benevolence and kindness; while his movements are not made with a view to gain, he does not consider the menials of a family as mean; while he does not strive after property and wealth, he does not plume himself on declining them; while he does not borrow the help of others to accomplish his affairs, he does not plume himself on supporting
himself by his own strength, nor does he despise those who in their greed do what is mean; while he differs in his conduct from the vulgar, he does not plume himself on being so different from them; while it is his desire to follow the multitude, he does not despise the glib-tongued flatterers. The rank and emoluments of the world furnish no stimulus to him, nor does he reckon its punishments and shame to be a disgrace. He knows that the right and the wrong can (often) not be distinguished, and that what is small and what is great can (often) not be defined. I have heard it said, "The Man of Tâo does not become distinguished; the greatest virtue is unsuccessful; the Great Man has no thought of self;"--to so great a degree may the lot be restricted.'
4. The earl of the Ho said, 'Whether the subject be what is external in things, or what is internal, how do we come to make a distinction between them as noble and mean, and as great or small?' Zo of the Northern Sea replied, 'When we look at them in the light of the Tâo, they are neither noble nor mean. Looking at them in themselves, each thinks itself noble, and despises others. Looking at them in the light of common opinion, their being noble or mean does not depend on themselves. Looking at them in their differences from one another, if we call those great which are greater than others, there is nothing that is not great, and in the same way there is nothing that is not small. We shall (thus) know that heaven and earth is but (as) a grain of the smallest rice, and that the point of a hair is (as) a mound or a mountain;--such is the view given of them by their relative size. Looking
at them from the services they render, allowing to everything the service which it does, there is not one which is not serviceable; and, extending the consideration to what it does not do, there is not one which is not unserviceable. We know (for instance) that East and West are opposed to each other, and yet that the one cannot be without (suggesting the idea of) the other;--(thus) their share of mutual service is determined. Looking at them with respect to their tendencies, if we approve of what they approve, then there is no one who may not be approved of; and, if we condemn what they condemn, there is no one who may not be condemned. There are the cases of Yâo and Kieh, each of whom approved of his own course, and condemned the other;--such is the view arising from the consideration of tendency and aim.
'Formerly Yâo and Shun resigned (their thrones), and yet each continued to be Tî; Kih-khwâi 1 resigned (his marquisate) which led to his ruin. Thang and Wû contended (for the sovereignty), and each became king; the duke of Pâi 2 contended (for Khû), which led to his extinction. Looking at the subject from these examples of striving by force and of resigning, and from the conduct of Yâo (on the one hand) and of Kieh (on the other), we see that there is a time for noble acting, and a time for
mean;--these characteristics are subject to no regular rule.
5. 'A battering ram may be used against the wall of a city, but it cannot be employed to stop up a hole;--the uses of implements are different. The (horses) Khih-kî and Hwâ-liû 1 could in one day gallop 1000 lî, but for catching rats they were not equal to a wild dog or a weasel;--the gifts of creatures are different. The white horned owl collects its fleas in the night-time, and can discern the point of a hair, but in bright day it stares with its eyes and cannot see a mound or a hill;--the natures of creatures are different.
'Hence the sayings, "Shall we not follow and honour the right, and have nothing to do with the wrong? shall we not follow and honour those who secure good government, and have nothing to do with those who produce disorder?" show a want of acquaintance with the principles of Heaven and Earth, and with the different qualities of things. It is like following and honouring Heaven and taking no account of Earth; it is like following and honouring the Yin and taking no account of the Yang. It is clear that such a course cannot be pursued. Yet notwithstanding they go on talking so:--if they are not stupid, they are visionaries. The Tî sovereigns resigned their thrones to others in one way, and the rulers of the three dynasties transmitted their thrones to their successors in another. He who acts differently from the requirements of his time and contrary to its custom is called an usurper; he who complies with the time
and follows the common practice is said to be righteous. Hold your peace, O earl of the Ho. How should you know what constitutes being noble and being mean, or who are the small and who the great?'
6. The earl of the Ho said, 'Very well. But what am I to do? and what am I not to do? How am I to be guided after all in regard to what I accept or reject, and what I pursue or put away from me?' Zo of the Northern Sea replied, 'From the standpoint of the Tâo, what is noble? and what is mean? These expressions are but the different extremes of the average level. Do not keep pertinaciously to your own ideas, which put you in such opposition to the Tâo. What are few? and what are many? These are denominations which we employ in thanking (donors) and dispensing gifts. Do not study to be uniform in doing so;--it only shows how different you are from the Tâo. Be severe and strict, like the ruler of a state who does not selfishly bestow his favours. Be scrupulous, yet gentle, like the tutelary spirit of the land, when sacrifice is offered to him who does not bestow his blessing selfishly. Be large-minded like space, whose four terminating points are illimitable, and form no particular enclosures. Hold all things in your love, favouring and supporting none specially. This is called being without any local or partial regard; all things are equally regarded; there is no long or short among them.
'There is no end or beginning to the Tâo. Things indeed die and are born, not reaching a perfect state which can be relied on. Now there is emptiness, and now fulness;--they do not continue in one form. The years cannot be reproduced; time
cannot be arrested. Decay and growth, fulness and emptiness, when they end, begin again. It is thus that we describe the method of great righteousness, and discourse about the principle pervading all things. The life of things is like the hurrying and galloping along of a horse. With every movement there is a change; with every moment there is an alteration. What should you be doing? what should you not be doing? You have only to be allowing this course of natural transformation to be going on.'
7. The earl of the Ho said, 'What then is there so valuable in the Tâo?' Zo of the Northern Sea replied, 'He who knows the Tâo, is sure to be well acquainted with the principles (that appear in the procedures of things). Acquainted with (those) principles, he is sure to understand how to regulate his conduct in all varying circumstances. Having that understanding, he will not allow things to injure himself. Fire cannot burn him who is (so) perfect in virtue, nor water drown him; neither cold nor heat can affect him injuriously; neither bird nor beast can hurt him. This does not mean that he is indifferent to these things; it means that he discriminates between where he may safely rest and where he will be in peril; that he is tranquil equally in calamity and happiness; that he is careful what he avoids and what he approaches;--so that nothing can injure him. Hence it is said, "What is heavenly is internal; what is human is external." The virtue (of man) is in what is Heavenly. If you know the operation of what is Heavenly and what is Human, you will have your root in what is Heavenly and your position in Virtue. You will bend or stretch
(only) after the (necessary) hesitation; you will have returned to the essential, and may be pronounced to have reached perfection.'
'What do you mean,' pursued the earl, 'by the Heavenly, and by the Human?' Zo replied, 'Oxen and horses have four feet;--that is what I call their Heavenly (constitution). When horses' heads are haltered, and the noses of oxen are pierced, that is what I call (the doing of) Man. Hence it is said, "Do not by the Human (doing) extinguish the Heavenly (constitution); do not for your (Human) purpose extinguish the appointment (of Heaven); do not bury your (proper) fame in (such) a pursuit of it; carefully guard (the Way) and do not lose it:--this is what I call reverting to your True (Nature)."'
8. The khwei 1 desires to be like 2 the millipede 1; the millipede to be like the serpent; the serpent like the wind; the wind to be like the eye; and the eye to be like the mind 3.
The khwei said to the millipede, 'With my one leg I hop about, and can hardly manage to go along. Now you have a myriad feet which you can employ; how is it that you are so abundantly furnished?' The millipede said, 'It is not so. Have you not seen one ejecting saliva? The largest portion of it is like a pearl, while the smaller portions fall down like a shower of mist in innumerable
drops. Now I put in motion the springs set in me by Heaven, without knowing how I do so.'
The millipede said to the serpent, 'I go along by means of my multitude of feet; and yet how is it that I do not go so fast as you who have no feet at all?' The serpent replied, 'How can the method of moving by the springs set in us by Heaven be changed? How could I make use of feet?'
The serpent said to the wind, 'I get along by moving my backbone and ribs, thus appearing to have some (bodily) means of progression. But now you, Sir, rise with a blustering force in the North Sea, and go on in the same way to the South Sea;--seemingly without any such means. How does it take place?' The wind said, 'Yes. With such a blustering force I rise in the North Sea and go on to the: South Sea. But you can point to me, and therein are superior to me, as you are also in treading on me. Yet notwithstanding, it is only I who can break great trees, and blow down great houses. Therefore he whom all that are small cannot overcome is a great overcomer. But it is only he who is the sagely man 1 that is the Great Conqueror (of all).'
9. When Confucius was travelling in Khwang 2,
some people of Sung (once) surrounded him (with a hostile intention) several ranks deep; but he kept singing to his lute without stopping. Dze-lû came in, and saw him, and said, 'How is it, Master, that you are so pleased?' Confucius said, 'Come here, and I will tell you. I have tried to avoid being reduced to such a strait for a long time; and that I have not escaped shows that it was so appointed for me. I have sought to find a ruler that would employ me for a long time, and that I have not found one, shows the character of the time. Under Yâo and Shun there was no one in the kingdom reduced to straits like mine; and it was not by their sagacity that men succeeded as they did. Under Kieh and Kâu no (good and able man) in the kingdom found his way to employment; and it was not for (want of) sagacity that they failed to do so. It was simply owing to the times and their character.
2. People that do business on the water do not shrink from meeting iguanodons and dragons;--that is the courage of fishermen. Those who do business on land do not shrink from meeting rhinoceroses and tigers;--that is the courage of hunters. When men see the sharp weapons crossed before them, and look on death as going home;--that is the courage of the determined soldier. When he knows that his strait is determined for him, and that the employment of him by a ruler depends on the character of the time, and then meeting with great distress is yet not afraid;-that is the courage of the sagely man. Wait, my good Yû, and you will see what there is determined for me in my lot.' A little afterwards, the leader of the armed men approached and took his leave, saying, 'We thought you were
Yang Hû 1, and therefore surrounded you. Now we see our mistake.' (With this) he begged to take his leave, and withdrew.
10. Kung-sun Lung 2 asked Mâu of Wei 3, saying, 'When I was young, I learned the teachings of the former kings; and when I was grown up, I became proficient in the practice of benevolence and righteousness. I brought together the views that agreed and disagreed; I considered the questions about hardness and whiteness 4; I set forth what was to be affirmed and what was not, and what was allowable and what was not; I studied painfully the various schools of thought, and made myself master of the reasonings of all their masters. I thought that I had reached a good understanding of every subject; but now that I have heard the words of Kwang-dze, they throw me into a flutter of surprise. I do not know whether it be that I do not come up to him in the power of discussion, or that my knowledge is not equal to his. But now I do not feel able to open my mouth, and venture to ask you what course I should pursue.' Kung-dze Mâu leant forward on his stool, drew a long breath, looked up to heaven, smiled, and
said, 'Have you not heard of the frog of the dilapidated well, and how it said to the turtle of the Eastern Sea, "How I enjoy myself? I leap upon the parapet of this well. I enter, and having by means of the projections formed by the fragments of the broken tiles of the lining proceeded to the water, I draw my legs together, keep my chin up, (and strike out). When I have got to the mud, I dive till my feet are lost in it. Then turning round, I see that of the shrimps, crabs, and tadpoles there is not one that can do like me. Moreover, when one has entire command of all the water in the gully, and hesitates to go forward, it is the greatest pleasure to enjoy one's self here in this dilapidated well 1;--why do not you, Master, often come and enter, and see it for yourself? "The turtle of the Eastern Sea (was then proceeding to go forward), but before he had put in his left foot, he found his right knee caught and held fast. On this he hesitated, drew back, and told (the frog) all about the sea, saying, "A distance of a thousand lî is not sufficient to express its extent, nor would (a line of) eight thousand cubits be equal to sound its depth. In the time of Yü, for nine years out of ten the flooded land (all drained into it), and its water was not sensibly increased; and in the time of Thang for seven years out of eight there was a drought, but the rocks on the shore (saw) no diminution of the water because of it. Thus it is that no change is produced in its waters by any cause operating for a short time or a long, and that they do not advance nor recede for any addition or subtraction, whether great or small; and this is the great pleasure afforded by the Eastern Sea." When
the frog of the dilapidated well heard this, he was amazed and terror-struck, and lost himself in surprise.
'And moreover, when you, who have not wisdom enough to know where the discussions about what is right and what is wrong should end, still desire to see through the words of Kwang-dze, that is like employing a mosquito to carry a mountain on its back, or a millipede 1 to gallop as fast as the Ho runs;--tasks to which both the insects are sure to be unequal. Still further, when you, who have not wisdom enough to know the words employed in discussing very mysterious subjects, yet hasten to show your sharpness of speech on any occasion that may occur, is not this being like the frog of the dilapidated well?
'And that (Kwang-dze) now plants his foot on the Yellow Springs (below the earth), and anon rises to the height of the Empyrean. Without any regard to south and north, with freedom he launches out in every direction, and is lost in the unfathomable. Without any regard to east and west, starting from what is abysmally obscure, he comes back to what is grandly intelligible. (All the while), you, Sir, in amazement, search for his views to examine them, and grope among them for matter for discussion;--this is just like peeping at the heavens through a tube, or aiming at the earth with an awl; are not both the implements too small for the purpose? Go your ways, Sir.
'And have you not heard of the young learners of
Shâu-ling 1, and how they did in Han-tan? Before they had acquired what they might have done in that capital, they had forgotten what they had learned to do in their old city, and were marched back to it on their hands and knees. If now you do not go away, you will forget your old acquirements, and fail in your profession.'
Kung-sun Lung gaped on the speaker, and could not shut his mouth, and his tongue clave to its roof. He slank away and ran off.
11. Kwang-dze was (once) fishing in the river Phû 2, when the king of Khû 3 sent two great officers to him, with the message, 'I wish to trouble you with the charge of all within my territories.' Kwang-dze kept on holding his rod without looking round, and said, 'I have heard that in Khû there is a spirit-like tortoise-shell, the wearer of which died 3000 years ago 4, and which the king keeps, in his ancestral temple, in a hamper covered with a cloth. Was it better for the tortoise to die, and leave its shell to be thus honoured? Or would it have been better for it to live, and keep on dragging its tail through the mud?' The two officers said, 'It would have been better for it to live, and draw its tail after it over the mud 5.' 'Go your ways. I will keep on drawing my tail after me through the mud.'
12. Hui-dze being a minister of state in Liang 1, Kwang-dze went to see him. Some one had told Hui-dze that Kwang-dze was come with a wish to supersede him in his office, on which he was afraid, and instituted a search for the stranger all over the kingdom for three days and three nights. (After this) Kwang-dze went and saw him, and said, 'There is in the south a bird, called "the Young Phoenix 2;"--do you know it? Starting from the South Sea, it flies to the Northern; never resting but on the bignonia 3, never eating but the fruit of the melia azederach 4, and never drinking but from the purest springs. An owl, which had got a putrid rat, (once), when a phoenix went passing overhead, looked up to it and gave an angry scream. Do you wish now, in your possession of the kingdom of Liang, to frighten me with a similar scream?'
13. Kwang-dze and Hui-dze were walking on the dam over the Hâo 5, when the former said, 'These thryssas come out, and play about at their ease;--that is the enjoyment of fishes.' The other said, 'You are not a fish; how do you know what
constitutes the enjoyment of fishes 1?' Kwang-dze rejoined, 'You are not I. How do you know that I do not know what constitutes the enjoyment of fishes?' Hui-dze said, 'I am not you; and though indeed I do not fully know you, you certainly are not a fish, and (the argument) is complete against your knowing what constitutes the happiness of fishes.' Kwang-dze replied, 'Let us keep to your original question. You said to me, "How do you know what constitutes the enjoyment of fishes?" You knew that I knew it, and yet you put your question to me;--well, I know it (from our enjoying ourselves together) over the Hâo.'
374:2
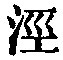 here perhaps means 'turbid.' It has nothing to do with the river King.
here perhaps means 'turbid.' It has nothing to do with the river King.
374:3 See Mayers's Manual, p. 54. Our author adopts the common beliefs or superstitions of his time, and after his fashion puts his own reasonings into the mouths of these mythological personages. It is more difficult to collect the legends about Zo of the sea, or of the Northern Sea. See the Khang-hsî Thesaurus under
 .
.
375:1 Thus the Confucian learning and its worthies were to the system of the Tâo only as the waters of the Ho to the great sea.
375:2 I have translated here as if the reading were
 which is given by Lin Hsî-kung. The correct reading, however, so far as depends on editions and dictionaries, is
which is given by Lin Hsî-kung. The correct reading, however, so far as depends on editions and dictionaries, is
 ; which is explained in the Khang-hsî dictionary as 'a great Rock in Fû-sang on the East,' against which the water of the sea collects, and is all evaporated!
; which is explained in the Khang-hsî dictionary as 'a great Rock in Fû-sang on the East,' against which the water of the sea collects, and is all evaporated!
380:1 See Mencius II, ii, ch. 8, and I, ii, chaps. 10, 11, with the notes.
 is probably a mistake for
is probably a mistake for
 .
.
380:2 See the last narrative but one in the Zo Khwan, under the sixteenth year of duke Âi of Lû,--the year in which Confucius died. 'The duke of Pâi' was merely the chief of a district of Khû; but rebelling against the Ruler of the State, he was defeated, and strangled himself.
381:1 Two of king Mu's team of eight famous steeds.
384:1 The khwei is 'a sort of dragon (it may be, a worm) with one foot.' The hsien has many feet; one account calls it 'a centipede.'
384:2 Such is the meaning of the lin or lien. The best commentators explain it by hsien (###), 'to covet and desire.'
384:3 Compare Book I, par. 3, towards the end.
385:1 The sagely man is 'the True man,' who embodies the Tâo. The Tâo has given to the khwei, the millipede, the serpent, and it may be said also to the wind, their means of progression and action. Nothing is said of the eye and the mind;--it was not necessary to dwell on the Tâo in them.
385:2 See Confucian Analects, IX, v and XI, xxii. Our author's account of this event is his own, constructed by him to convey his own Tâoistic lessons.
387:1 No doubt the Yang Ho of Analects XVII, i.
387:2 The grandson (Kung-sun) of one of the rulers of Kâo (one of the three states into which the great state of Zin had been broken up). He has come down to us as a philosophic sophist, whose views it is not easy to define. See Mayers's Manual, p. 288, and Book XXXIII, par. 7.
387:3 Wei was another of the divisions of Zin, and Mâu was one of the sons of its ruler at this time, a great admirer, evidently, of Kwang-dze, and more than a match for the sophist Lung.
387:4 Holding, it is supposed, that 'the attributes of material objects, such as hardness and colour, are separate existences:'--so Mayers, after Wylie.
388:1 A passage difficult to construe.
389:1 A different character from that for a millipede in the last paragraph;--a Shang Kü, evidently some small insect, but we cannot tell what.
390:1 A city of Kâo, as Han-tan was its capital. Of the incident referred to, I have not been able to learn anything. The 'were marched' gives my idea of what it may have been.
390:2 A river, which still gives its name to Phû-kâu, department Khao-kâu, Shan-tung.
390:3 Probably king Wei, B. C. 339-330.
390:4 A good antiquity for Khû!
390:5 ? A species of Testudo Serpentina, such as is often seen on pieces of Japanese lacquer-ware.
391:1 Another name for Wei, so called from its capital;--in the present department of Khâi-fäng.
391:2 So the critics explain the name. Williams thinks the bird may be 'the argus pheasant,' or 'a variety of the peacock.' But what the bird was does not affect the meaning of our author's reference to it.
391:3 One of the Eleococcae, the Dryandra Cordifolia of Thunberg.
391:4 All the editions I have seen give
 here, which makes no sense. The character should doubtless be
here, which makes no sense. The character should doubtless be
 , with the meaning which I have given; and not 'bamboo,' which is found in the critics. It is also called 'the Pride of India.'
, with the meaning which I have given; and not 'bamboo,' which is found in the critics. It is also called 'the Pride of India.'
391:5 A river in the department and district of Fung-yang, An-hui.
392:1 Surely a captious question. We infer the feelings of other creatures from their demonstrations.