

|
|
3.9 Editorial MarkupHTML 4.0 introduced two tags that can help groups of authors collaborate in the development of documents and maintain some semblance of editorial and version control. The insert (<ins>) and delete (<del>) tags respectively let you either designate portions of your document's body as new or added content or designate old stuff that should be replaced. And with special attributes, you can indicate when you made the change (datetime) and a reference to a document that may explain the change (cite). 3.9.1 The <ins> and <del> TagsThe <ins> and <del> tags let authors set off portions of body contents that they intend to add to or delete from the current versions of their documents. HTML 4/XHTML-compliant browsers display the contents of the <ins> or <del> tags in some special way so that readers can quickly scan the document for the changes.
Netscape 4 and earlier versions ignore the tags, as did Internet Explorer 4 and its earlier versions. The newer versions of Internet Explorer (Versions 5 and 6) and Netscape (Version 6) use common editorial markings by underlining inserted text and striking out deleted text (Figure 3-3). Figure 3-3. Internet Explorer 6 displays <ins>- and <del>-tagged content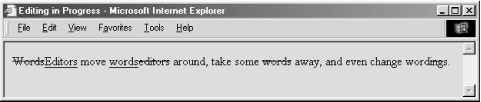 3.9.1.1 The cite attributeThe cite attribute lets you document the reasons for the insertion or deletion. Its value must be a URL that points to some other document that explains the inserted/deleted text. How cite gets treated by a browser is a question for the future. 3.9.1.2 The datetime attributeAlthough the reason for the change is important, knowing when a change was made is often more important. The datetime attribute for the <ins> and <del> tags takes a single value: a specially encoded date and time stamp. The rigorous format for the datetime value is YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssTZD. The components are:
For example: 2003-02-22T14:26Z decodes to February 22, 2003 at 2:26 P.M. Greenwich Mean Time. To specify Eastern Standard Time, the code for the same time and date is: 2003-02-22T09:26-05:00 Notice that the local time zone may change depending on where the document gets edited, whereas the universal time will stay the same. 3.9.1.3 The class, dir, event, id, lang, style, title, and events attributesThere are several nearly universal attributes for the many HTML and XHTML tags. These attributes give you a common way to identify (title) and label (id) a tag's contents for later reference or automated treatment, to change the contents' display characteristics (class, style), and to reference the language used (lang) and related direction the text should flow (dir). There are also input events that may happen in and around the tagged contents that you may react to via an on-event attribute and some programming. [Section 3.6.1.1] [Section 3.6.1.2] [Section 4.1.1.4] [Section 4.1.1.4] [Section 8.1.1] [Section 8.3] [Section 12.3.3] 3.9.2 Using Editorial MarkupThe uses of <ins> and <del> are obvious to anyone who has used a "boilerplate" document or form or has collaborated with others in the preparation of a document. For example, law firms typically have a collection of online legal documents that are specially completed for each client. Law clerks usually do the "fill in," and the final document gets reviewed by a lawyer. To highlight where the clerk made changes in the document so that they are readily evident to the reviewer, use the <ins> tag to indicate the clerk's added text and the <del> tag to mark the text that was replaced. Optionally, use the cite and datetime attributes to indicate when and why the changes were made. For example, the clerk might fill in a boilerplate document with the law firm's and representative's names, indicating the time and source for the change: The party of the first part, as represented by
<ins datetime=2002-06-22T08:30Z
cite="http://www.mull+dull.com/tom_duller.html">
Thomas Muller of Muller and Duller
</ins>
<del>[insert representation here]</del>
The editorial markup tags could also be used by editing tools to denote how documents were modified as authors make changes over a period of time. With the correct use of the cite and datetime attributes, it would be possible to recreate a version of a document from a specific point in time. |

|
|