

|
|
7.2 Ordered ListsUse an ordered list when the sequence of the list items is important. A list of instructions is a good example, as are tables of contents and lists of document footnotes or endnotes. 7.2.1 The <ol> TagThe typical browser formats the contents of an ordered list just like an unordered list, except that the items are numbered instead of bulleted. The numbering starts at one and is incremented by one for each successive ordered list element tagged with <li>. [<li>]
HTML 3.2 introduced a number of features that provide a wide variety of ordered lists. You can change the start value of the list and select any of five different numbering styles. Here is a sample XHTML ordered list: <h3>Pickled Kumquats</h3> Here's an easy way to make a delicious batch of pickled 'quats: <ol> <li>Rinse 50 pounds of fresh kumquats</li> <li>Bring eight gallons white vinegar to rolling boil</li> <li>Add kumquats gradually, keeping vinegar boiling</li> <li>Boil for one hour, or until kumquats are tender</li> <li>Place in sealed jars and enjoy!</li> </ol> Netscape renders the example as shown in Figure 7-2. Figure 7-2. An ordered list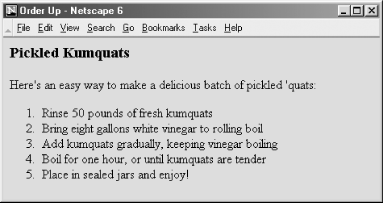 7.2.1.1 The start attributeNormally, browsers automatically number ordered list items beginning with the Arabic numeral 1. The start attribute for the <ol> tag lets you change that beginning value. To start numbering a list at 5, for example: <ol start=5> <li> This is item number 5.</li> <li> This is number six!</li> <li> And so forth...</li> </ol> 7.2.1.2 The type attributeBy default, browsers number ordered list items with a sequence of Arabic numerals. Besides being able to start the sequence at some number other than 1, you can use the type attribute with the <ol> tag to change the numbering style itself. The attribute may have a value of A for numbering with capital letters, a for numbering with lowercase letters, I for capital Roman numerals, i for lowercase Roman numerals, or 1 for common Arabic numerals. (See Table 7-1.)
The start and type attribute extensions work in tandem. The start attribute sets the starting value of the item integer counter at the beginning of an ordered list. The type attribute sets the actual numbering style. For example, the following ordered list starts numbering items at 8, but because the style of numbering is set to i, the first number is the lowercase Roman numeral "viii." Subsequent items are numbered with the same style, and each value is incremented by 1, as shown in this HTML example, and rendered as shown in Figure 7-3:[1]
<ol start=8 type="i"> <li> This is the Roman number 8. <li> The numerals increment by 1. <li> And so forth... </ol> Figure 7-3. The start and type attributes work in tandem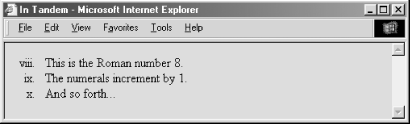 The type and value of individual items in a list can be different from those of the list as a whole, described in Section 7.3.1. As mentioned earlier, the start and type attributes are deprecated in HTML 4 and XHTML. Consider using style sheets instead. 7.2.1.3 Compact ordered listsLike the <ul> tag, the <ol> tag has an optional compact attribute that is deprecated in the HTML 4 and XHTML standards. Unless you absolutely need to use it, don't. 7.2.1.4 The class, dir, id, lang, event, style, and title attributesThese attributes are applicable with ordered lists, too; their effects are identical to those for unordered lists. [Section 7.1.1.3] [Section 7.1.1.4] [Section 7.1.1.5] [Section 7.1.1.6] |

|
|