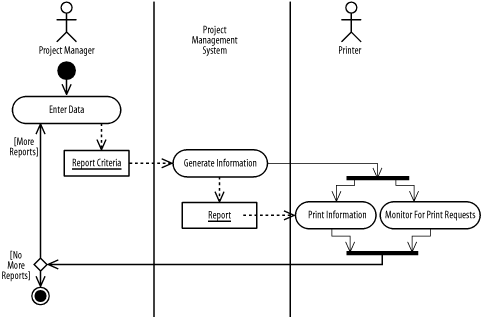
8.5 Concurrency
Concurrency involves selecting
multiple
transitions simultaneously. For example, while the printer is
printing a report, the printer must also monitor for other incoming
print requests.
In the UML, concurrency is shown using a short heavy bar. If a bar
has one incoming transition and two or more outgoing transitions, it
indicates that all outgoing transitions occur once the incoming
transition
occurs. This is called
splitting of control. If a bar has two or more
incoming transitions and one outgoing transition, it indicates that
all incoming transitions must occur
before the outgoing transition
occurs. This is called synchronization of
control. Figure 8-8 shows that the
printer uses concurrency to print a report using the
Print Information action state,
and to monitor for other incoming print requests while handling the
current request using the Monitor
for Print
Requests action state. Once both of these action
states have completed, a project manager may choose to print more
reports.
|
