

|
|
Perl ReferencesThe big difference between Perl 4 and Perl 5 was the introduction of references, which made object orientation possible. You can think of references as being a kind of pointers, locators, or remote tracking devices. They are the glue spot trails sticking Perl 5 data structures together. Think of ET pointing the way home, Indiana Jones standing on the X marking the spot in Venice, or James Bond trailing Goldfinger's car with a remote tracking device. The bony finger, the X, or the beeper are all references to remote information. So how does Perl point to its own vital information? In structure, references are simple scalars holding two vital pieces of information:
These two pieces of information can be seen in Figure A-4, stored under each of our three references. The first refers to a scalar, the second to an array, and the third to a hash. Each reference holds the variable type it's referring to and its memory address. We can see this for ourselves if we create three similar references, and then print them out: $camel = "Asimov";
@camel = ("Foundation and Earth", "I, Robot", "Nightfall");
%camel = (Emperor => "Cleon",
CouncilMan => "Trevize",
Robot => "R. Daneel Olivaw");
$scalar_ref = \$camel; # References created by backslashing
$array_ref = \@camel; # the original variable.
$hash_ref = \%camel;
print $scalar_ref, " ", $array_ref, " ", $hash_ref, "\n";
Figure A-4. The glue of Perl references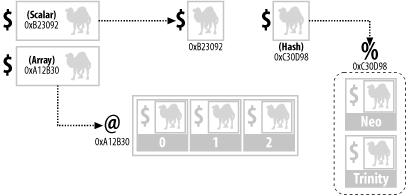 Notice that each original variable is named camel, but this causes absolutely no clash in Perl because scalars, arrays, and hashes are all different variable types, in the same way that Homer Simpson, Springfield philosopher, and Homer the Greek, Trojan chronicler, are different types of people, despite possessing the same name. When executed, the print statement shown above produced memory address traces like these: SCALAR(0x457c3f4) ARRAY(0x457f420) HASH(0x457f468) We can now take these three references and go back along their arrows, to get the original information back out again: print "SCALAR: ${$scalar_ref} \n"; # Isolate reference with braces
# then dereference with a $ symbol.
print "ARRAY: @{$array_ref} \n"; # Isolate reference with braces,
# then dereference with a @ symbol.
%copy_camel = %{$hash_ref}; # Isolate reference with braces, and then
# dereference with a % to create hash copy.
foreach $key (keys %copy_camel) {
print "HASH VALUE: $copy_camel{$key} \n"; # Get key, then value.
}
This code produces: SCALAR: Asimov ARRAY: Foundation and Earth I, Robot Nightfall HASH VALUE: Cleon HASH VALUE: Trevize HASH VALUE: R. Daneel Olivaw Arrow NotationIf you work carefully through the above code you'll see how the references are isolated by curly braces. The variable symbols, $, @, and %, are then used to dereference the data to the appropriate variable type. If this notation looks a little clumsy, relax, because you're among friends. For hashes and arrays, the arrow operator may ride to the rescue. Let's rewrite that code for the two array types: for $index (0..$#{$array_ref}) { # Work out size of array
print "ARRAY $index: $array_ref->[$index] \n"; # Drill down arrow
}
for $key (keys %{$hash_ref}) { # Work out original keys
print "HASH $key: $hash_ref->{$key} \n"; # Drill down arrow
}
The arrow operator can make life easier, because it makes the diagrammatic arrows in Figure A-4 come alive directly within the code: ARRAY 0: Foundation and Earth ARRAY 1: I, Robot ARRAY 2: Nightfall HASH Emperor: Cleon HASH CouncilMan: Trevize HASH Robot: R. Daneel Olivaw The ref OperatorReferences are simply ordinary scalars, meaning that they can be stored in both arrays and hashes. We illustrate this in Figure A-5, where from a single $binary_tree_root_ref scalar we spider through a binary tree, made up of anonymous hashes, to quickly find ROWID information. Figure A-5. Binary tree built from hashes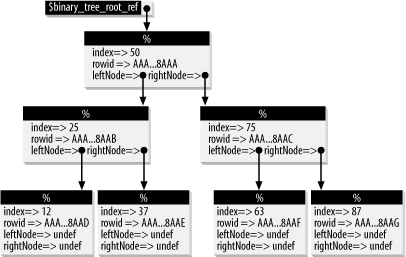 In dynamic coding like this, however, there is a problem. We're often unaware of what variable types our references are pointing to, which is information required for accurate de-referencing. The solution is then to use the ref operator. This returns the type of variable being pointed to. The main values returned by ref are detailed in Table A-4.
We can now use ref to navigate our way around any data structure held together by references, with blocks of code such as the following: if (( ref($this_ref) eq "SCALAR" ) || ( ref($this_ref) eq "REF" )) {
# This reference is either pointing to an ordinary scalar,
# or a scalar reference. Deal with accordingly...
} elsif ( ref($this_ref) eq "ARRAY" ) {
# This reference is pointing to an array...
} elsif ( ref($this_ref) eq "HASH" ) {
# Pointing to a hash...
} elsif ( not ref $this_ref ) {
# $this_ref is an ordinary scalar...
}
Anonymous Arrays and HashesIn addition to generating named arrays and hashes, we can also generate anonymous arrays and hashes in Perl. Think of an anonymous array as being like an amateur ice hockey team being created spontaneously by a group of friends on a visit to a local ice rink. There's simply no need for a team name. This ability to create unnamed arrays on the fly creates enormous dynamism within our code, and is especially good for the creation of multidimensional arrays (think of a series of wooden Russian dolls opening up to reveal more dolls inside). Here are the basics of creating anonymous arrays:
You can create anonymous hashes in the same basic way:
You can also mix and match your anonymous hash and array elements.
|

|
|