| [ Team LiB ] |
|
16.1 The Overall DesignYou will actually build two independent applications (a desktop application and an ASP.NET application) tied together by a back-end database. Specifically, you'll create a desktop application that obtains data from Amazon.com and stores it in a table in a SQL Server database, and then you'll display that data in your ASP.NET application.[1]
The SQL Server Database is very simple. It is named AmazonSalesRanks and consists of a single table, BookInfo, as shown in Figure 16-2. Figure 16-2. The BookInfo table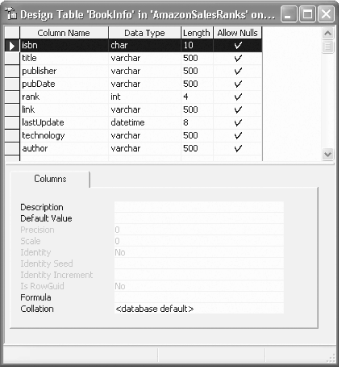
The design is fairly straightforward: the screen-scraper desktop application (SalesRankDB.sln) obtains the data on all of the books that compete in the C#, ASP.NET and VB.NET arenas, and saves them to the table. Each book has a unique ISBN, and may or may not have associated information about the publisher, publication date, etc. The rank is the relative sales rank on Amazon at the time the information is gathered. To facilitate the display, each entry is marked for a particular technology, one of "ASPNET," "CSharp" or "VBNET." The ASP.NET application used to display the results will be unchanged in each version of this program, but the desktop application will be shown with three different iterations. The first iteration is a screen-scraper application that obtains data for each ISBN for books in each category. The list of ISBNs is stored in a set of XML files. The second iteration is a web services client that replaces the screen scraper mechanism with calls to the Amazon service, searching for each book by ISBN based on the same XML files. Finally, the third iteration is a web services client that utilizes the Amazon web service to search for all books based on a keyword (and thus dispenses with the list of ISBNs). |
| [ Team LiB ] |
|