
Sacred Texts Taoism Index Previous Next

1. He who understands the conditions of Life does not strive after what is of no use to life; and he who understands the conditions of Destiny does not strive after what is beyond the reach of knowledge. In nourishing the body it is necessary to have beforehand the things (appropriate to its support) 2; but there are cases where there is a superabundance of such things, and yet the body is not nourished'. In order to have life it is necessary that it do not have left the body; but there are cases when the body has not been left by it, and yet the life has perished 3.
When life comes, it cannot be declined; when it goes, it cannot be detained. Alas! the men of the world think that to nourish the body is sufficient to preserve life; and when such nourishment is not sufficient to preserve the life, what can be done in the world that will be sufficient? Though (all that men can do) will be insufficient, yet there are things which they feel they ought to do, and they do not try to avoid doing them. For those who wish to
avoid caring for the body, their best plan is to abandon the world. Abandoning the world, they are free from its entanglements. Free from its entanglements, their (minds) are correct and their (temperament) is equable. Thus correct and equable, they succeed in securing a renewal of life, as some have done 1. In securing a renewal of life, they are not far from the True (Secret of their being). But how is it sufficient to abandon worldly affairs? and how is it sufficient to forget the (business of) life? Through the renouncing of (worldly) affairs, the body has no more toil; through forgetting the (business of) life, the vital power suffers no diminution. When the body is completed and the vital power is restored (to its original vigour), the man is one with Heaven. Heaven and Earth are the father and mother of all things. It is by their union that the body is formed; it is by their separation that a (new) beginning is brought about. When the body and vital power suffer no diminution, we have what may be called the transference of power. From the vital force there comes another more vital, and man returns to be the assistant of Heaven.
2. My master 2 Lieh-dze 2 asked Yin, (the warden) of the gate 2, saying, 'The perfect man walks under
water without encountering any obstruction, treads on fire without being burned, and walks on high above all things without any fear; let me ask how he attains to do this 1?' The warden Yin replied, 'It is by his keeping of the pure breath (of life); it is not to be described as an achievement of his skill or daring. Sit down, and I will explain it to you. Whatever has form, semblance, sound, and colour is a thing; how can one thing come to be different from another? But it is not competent for any of these things to reach to what preceded them all;--they are but (form and) visibility. But (the perfect man) attains to be (as it were) without form, and beyond the capability of being transformed. Now when one attains to this and carries it out to the highest degree, how can other things come into his way to stop him? He will occupy the place assigned to him without going beyond it, and lie concealed in the clue which has no end. He will study with delight the process which gives their beginning and ending to all things. By gathering his nature into a unity, by nourishing his vital power, by concentrating his virtue, lie will penetrate to the making of things. In this condition, with his heavenly constitution kept entire, and with no crevice in his spirit, how can things enter (and disturb his serenity)?
'Take the case of a drunken man falling from his carriage;--though he may suffer injury, he will not
die. His bones and joints are the same as those of other men, but the injury which he receives is different:--his spirit is entire. He knew nothing about his getting into the carriage, and knew nothing about his falling from it. The thought of death or life, or of any alarm or affright, does not enter his breast; and therefore he encounters danger without any shrinking from it. Completely under the influence of the liquor he has drunk, it is thus with him;--how much more would it be so, if he were under the influence of his Heavenly constitution! The sagely man is kept hid in his Heavenly constitution, and therefore nothing can injure him.
'A man in the pursuit of vengeance would not break the (sword) Mo-yê or Yü-kiang (which had done the deed); nor would one, however easily made wrathful, wreak his resentment on the fallen brick. In this way all under heaven there would be peace, without the disorder of assaults and fighting, without the punishments of death and slaughter:--such would be the issue of the course (which I have described). If the disposition that is of human origin be not developed, but that which is the gift of Heaven, the development of the latter will produce goodness, while that of the former would produce hurt. If the latter were not wearied of, and the former not slighted, the people would be brought nearly to their True nature.'
3. When Kung-nî was on his way to Khû, as he issued from a forest, he saw a hunchback receiving cicadas (on the point of a rod), as if he were picking them up with his hand 1. 'You are clever!' said he
to the man. 'Is there any method in it?' The hunchback replied, 'There is. For five or six months, I practised with two pellets, till they never fell down, and then I only failed with a small fraction 1 of the cicadas (which I tried to catch). Having succeeded in the same way with three (pellets), I missed only one cicada in ten. Having succeeded with five, I caught the cicadas as if I were gathering them. My body is to me no more than the stump of a broken trunk, and my shoulder no more than the branch of a rotten tree. Great as heaven and earth are, and multitudinous as things are, I take no notice of them, but only of the wings of my cicadas; neither turning nor inclining to one side. I would not for them all exchange the wings of my cicadas;--how should I not succeed in taking them?' Confucius looked round, and said to his disciples, "Where the will is not diverted from its object, the spirit is concentrated;"--this might have been spoken of this hunchback gentleman.'
4. Yen Yüan asked Kung-nî, saying, 'When 1 was crossing the gulf of Khang-shän 2, the ferryman handled the boat like a spirit. I asked him whether such management of a boat could be learned, and he replied, "It may. Good swimmers can learn it quickly; but as for divers, without having seen a boat, they can manage it at once." He did not
directly tell me what I asked;--I venture to ask you what he meant.' Kung-nî replied, 'Good swimmers acquire the ability quickly;--they forget the water (and its dangers). As to those who are able to dive, and without having seen a boat are able to manage it at once, they look on the watery gulf as if it were a hill-side, and the upsetting of a boat as the going back of a carriage. Such upsettings and goings back have occurred before them multitudes of times, and have not seriously affected their minds. Wherever they go, they feel at ease on their occurrence.
'He who is contending for a piece of earthenware puts forth all his skill 1. If the prize be a buckle of brass, he shoots timorously; if it be for an article of gold, he shoots as if he were blind. The skill of the archer is the same in all the cases; but (in the two latter cases) he is under the influence of solicitude, and looks on the external prize as most important. All who attach importance to what is external show stupidity in themselves.'
5. Thien Khâi-kih 2 was having an interview with duke Wei of Kâu 2, who said to him, 'I have heard that (your master) Kû Hsin 2 has studied the subject of Life. What have you, good Sir, heard from him about it in your intercourse with him?' Thien Khâi-kih replied, 'In my waiting on him in the courtyard with my broom, what should I have heard from my master?' Duke Wei said, 'Do not put the question off, Mr. Thien; I wish to hear what
you have to say.' Khâi-kih then replied, 'I have heard my master say that they who skilfully nourish their life are like shepherds, who whip up the sheep that they see lagging behind 1.' 'What did he mean?' asked the duke. The reply was, 'In Lû there was a Shan Pâo, who lived among the rocks, and drank only water. He would not share with the people in their toils and the benefits springing from them; and though he was now in his seventieth year, he had still the complexion of a child. Unfortunately he encountered a hungry tiger, which killed and ate him. There was also a Kang Î, who hung up a screen at his lofty door, and to whom all the people hurried (to pay their respects) 2. In his fortieth year, he fell ill of a fever and died. (Of these two men), Pho nourished his inner man, and a tiger ate his outer; while I nourished his outer man, and disease attacked his inner. Both of them neglected whipping up their lagging sheep.'
Kung-nî said, 'A man should not retire and hide himself; he should not push forward and display himself; he should be like the decayed tree which stands in the centre of the ground. Where these three conditions are fulfilled, the name will reach its greatest height. When people fear the dangers of a path, if one man in ten be killed, then fathers and sons, elder brothers and younger, warn one another that they must not go out on a journey without a large number of retainers;--and is it not a mark of wisdom to do so? But there are dangers which
men incur on the mats of their beds, and in eating and drinking; and when no warning is given against them;--is it not a mark of error 1?'
6. The officer of Prayer 2 in his dark and square-cut robes goes to the pig-pen, and thus counsels the pigs, 'Why should you shrink from dying? I will for three months feed you on grain. Then for ten days I will fast, and keep vigil for three days, after which I will put down the mats of white grass, and lay your shoulders and rumps on the carved stand;--will not this suit you?' If he had spoken from the standpoint of the pigs, he would have said, 'The better plan will be to feed us with our bran and chaff, and leave us in our pen.' When consulting for himself, he preferred to enjoy, while he lived, his carriage and cap of office, and after death to be borne to the grave on the ornamented carriage, with the canopy over his coffin. Consulting for the pigs, he did not think of these things, but for himself he would have chosen them. Why did he think so differently (for himself and) for the pigs 3?
7. (Once), when duke Hwan 4 was hunting by a marsh, with Kwan Kung 5 driving the carriage, he saw a ghost. Laying his hand on that of Kwan
Kung, he said to him, 'Do you see anything, Father Kung?' 'Your servant sees nothing,' was the reply. The duke then returned, talking incoherently and becoming ill, so that for several days he did not go out. Among the officers of Khî there was a Hwang-dze Kâo-âo 1, who said to the duke, 'Your Grace is injuring yourself; how could a ghost injure you? When a paroxysm of irritation is dispersed, and the breath does not return (to the body), what remains in the body is not sufficient for its wants. When it ascends and does not descend, the patient becomes accessible to gusts of anger. When it descends and does not ascend, he loses his memory of things. When it neither ascends nor descends, but remains about the heart in the centre of the body, it makes him ill.' The duke said, 'Yes, but are there ghostly sprites 2?' The officer replied, 'There are about mountain tarns there is the Lî; about furnaces, the Khieh; about the dust-heaps inside the door, the Lei-thing. In low-lying places in the north-east, the Pei-a and Wa-lung leap about, and in similar places in the north-west there dwells the Yî-yang. About rivers there is the Wang-hsiang; about mounds, the Hsin; about hills, the Khwei; about wilds, the Fang-hwang; about marshes, the Wei-tho.' 'Let me ask what is the Wei-tho like?' asked the duke. Hwang-dze said, 'It is the size of the
nave of a chariot wheel, and the length of the shaft. It wears a purple robe and a red cap. It dislikes the rumbling noise of chariot wheels, and, when it hears it, it puts both its hands to its head and stands up. He who sees it is likely to become the leader of all the other princes.' Duke Hwan burst out laughing and said, 'This was what I saw.' On this he put his robes and cap to rights, and made Hwang-dze sit with him. Before the day was done, his illness was quite gone, he knew not how.
8. Kî Hsing-dze was rearing a fighting-cock for the king 1. Being asked after ten days if the bird were ready, he said, 'Not yet; he is still vain and quarrelsome, and relies on his own vigour.' Being asked the same after other ten days, he said, 'Not yet; he still responds to the crow and the appearance of another bird.' After ten days more, he replied, 'Not yet. He still looks angrily, and is full of spirit.' When a fourth ten days had passed, he replied to the question, 'Nearly so. Though another cock crows, it makes no change in him. To look at him, you would say he was a cock of wood. His quality is complete. No other cock will dare to meet him, but will run from him.'
9. Confucius was looking at the cataract near the gorge of Lü 2, which fell a height of 240 cubits, and
the spray of which floated a distance of forty lî, (producing a turbulence) in which no tortoise, gavial, fish, or turtle could play. He saw, however, an old man swimming about in it, as if he had sustained Some great calamity, and wished to end his life. Confucius made his disciples hasten along the stream to rescue the man; and by the time they had gone several hundred paces, he was walking along singing, with his hair dishevelled, and enjoying himself at the foot of the embankment. Confucius followed and asked him, saying, 'I thought you were a sprite; but, when I look closely at you, I see that you are a man. Let me ask if you have any particular way of treading the water.' The man said, 'No, I have no particular way. I began (to learn the art) at the very earliest time; as I grew up, it became my nature to practise it; and my success in it is now as sure as fate. I enter and go down with the water in the very centre of its whirl, and come up again with it when it whirls the other way. I follow the way of the water, and do nothing contrary to it of myself;--this is how I tread it.' Confucius said, 'What do you mean by saying that you began to learn the art at the very earliest time; that as you grew up, it became your nature to practise it, and that your success in it now is as sure as fate?' The man replied, 'I was born among these hills and lived contented among them;--that was why I say that I have trod this water from my earliest time. I grew up by it, and have been happy treading it;--that is why I said that to tread it had become natural to me. I know not how I do it, and yet I do it;--that is why I say that my success is as sure as fate.'
10. Khing, the Worker in Rottlera 1 wood, carved a bell-stand 2, and when it was completed, all who saw it were astonished as if it were the work of spirits. The marquis of Lû went to see it, and asked by what art he had succeeded in producing it. 'Your subject is but a mechanic,' was the reply; 'what art should I be possessed of? Nevertheless, there is one thing (which I will mention), When your servant had undertaken to make the bell-stand, I did not venture to waste any of my power, and felt it necessary to fast in order to compose my mind. After fasting for three days, I did not presume to think of any congratulation, reward, rank, or emolument (which I might obtain by the execution of my task); after fasting five days, I did not presume to think of the condemnation or commendation (which it would produce), or of the skill or want of skill (which it might display). At the end of the seven days, I had forgotten all about myself;--my four limbs and my whole person. By this time the thought of your Grace's court (for which I was to make the thing) had passed away; everything that could divert my mind from exclusive devotion to the exercise of my skill had disappeared. Then I went into the forest, and looked at the natural forms of the trees. When I saw one of a perfect form, then the figure of the bell-stand rose up to my view, and I applied my hand to the work. Had
I not met with such a tree, I must have abandoned the object; but my Heaven-given faculty and the Heaven-given qualities of the wood were concentrated on it. So it was that my spirit was thus engaged in the production of the bell-stand.'
11. Tung-yê Kî 1 was introduced to duke Kwang 2 to exhibit his driving. His horses went forwards and backwards with the straightness of a line, and wheeled to the right and the left with the exactness of a circle. The duke thought that the lines and circles could not be surpassed if they were woven with silken strings, and told him to make a hundred circuits on the same lines. On the road Yen Ho 3 met the equipage, and on entering (the palace), and seeing the duke, he said, 'Kî's horses will break down,' but the duke was silent, and gave him no reply. After a little the horses did come back, having broken down; and the duke then said,' How did you know that it would be so?' Yen Ho said, 'The horses were exhausted, and he was still urging them on. It was this which made me say that they would break down.'
12. The artisan Shui 4 made things round (and square) more exactly than if he had used the circle
and square. The operation of his fingers on (the forms of) things was like the transformations of them (in nature), and required no application of his mind; and so his Intelligence 1 was entire and encountered no resistance.
13. To be unthought of by the foot that wears it is the fitness of a shoe; to be unthought of by the waist is the fitness of a girdle. When one's wisdom does not think of the right or the wrong (of a question under discussion), that shows the suitability of the mind (for the question); when one is conscious of no inward change, or outward attraction, that shows the mastery of affairs. He who perceives at once the fitness, and never loses the sense of it, has the fitness that forgets all about what is fitting.
14. There was a Sun Hsiû 2 who went to the door of Dze-pien Khing-dze, and said to him in a strange perturbed way, 'When I lived in my village, no one took notice of me, but all said that I did not cultivate (my fields); in a time of trouble and attack, no one took notice of me, but all said that I had no courage. But that I did not cultivate my fields, was really because I never met with a good year; and that I did not do service for our ruler, was because I did not meet with the suitable opportunity to do so. I have been sent about my business by the villagers, and am driven away by the registrars of the district;--what is my crime? O Heaven! how is it that I have met with such a fate?'
Pien-dze 1 said to him, 'Have you not heard how the perfect man deals with himself? He forgets that be has a liver and gall. He takes no thought of his ears and eyes. He seems lost and aimless beyond the dust and dirt of the world, and enjoys himself at ease in occupations untroubled by the affairs of business. He may be described as acting and yet not relying on what he does, as being superior and yet not using his superiority to exercise any control. But now you would make a display of your wisdom to astonish the ignorant; you would cultivate your person to make the inferiority of others more apparent; you seek to shine as if you were carrying the sun and moon in your hands. That you are complete in your bodily frame, and possess all its nine openings; that you have not met with any calamity in the middle of your course, such as deafness, blindness, or lameness, and can still take your place as a man among other men;--in all this you are fortunate. What leisure have you to murmur against Heaven? Go away, Sir.'
Sun-dze on this went out, and Pien-dze went inside. Having sitten down, after a little time he looked up to heaven, and sighed. His disciples asked him why he sighed, and he said to them, 'Hsiû came to me a little while ago, and I told him the characteristics of the perfect man. I am afraid he will be frightened, and get into a state of perplexity.' His disciples said, 'Not so. If what he said was right, and what you
said was wrong, the wrong will certainly not be able to perplex the right. If what he said was wrong, and what you said was right, it was just because he was perplexed that he came to you. What was your fault in dealing with him as you did?' Pien-dze said, 'Not so. Formerly a bird came, and took up its seat in the suburbs of Lû 1. The ruler of Lû was pleased with it, and provided an ox, a sheep, and a pig to feast it, causing also the Kiû-shâo to be performed to delight it. But the bird began to be sad, looked dazed, and did not venture to eat or drink. This was what is called "Nourishing a bird, as you would nourish yourself." He who would nourish a bird as a bird should be nourished should let it perch in a deep forest, or let it float on a river or lake, or let it find its food naturally and undisturbed on the level dry ground. Now Hsiû (came to me), a man of slender intelligence, and slight information, and I told him of the characteristics of the perfect man, it was like using a carriage and horses to convey a mouse, or trying to delight a quail with the music of bells and drums;--could the creatures help being frightened?'
11:1 See vol. xxxix, pp. 150, 151.
11:2 Wealth will supply abundantly the things that are necessary and fit for the nourishment of the body, but sudden death may render them unavailing.
11:3 That is, the higher fife of the spirit has perished.
12:1 I think I have caught the meaning. The phrase signifying 'the renewal of life' has been used to translate 'being born again' in John's Gospel, ch. 3.
12:2 We find here Lieh-dze (whose name has already occurred several times) in communication with the warden Yin, who was a contemporary of Lâo-dze, and we must refer him therefore to the sixth century B.C. He could not therefore be contemporary with our author, and yet the three characters of the text mean 'My Master, Lieh-dze;' and the whole of the paragraph is found in Lieh-dze's second Book (4a-5a) with a good many variants in the text. p. 13 The gate was at the passage leading from the Royal Domain of those days into the great feudal territory of Zin;--from the north-west of the present province of Ho-nan into Shen-hsî.
13:1 Lieh-dze puts an absurd question to the warden, which is replied to at length, and unsatisfactorily. We need not discuss either the question or the answer in this place.
14:1 This paragraph is also found with variations in Lieh-dze, p. 15 Bk. II (9a). The dexterity of the hunchback in catching the cicadas will remind some readers of the account given by the butcher in Book III of his dexterity in cutting up his oxen.
15:1 The names of two small weights, used anciently for 'a fraction,' 'a small proportion.'
15:2 This is another paragraph common both to our author and Lieh-dze, but in neither is there any intimation of the place.
16:1 I think this is the meaning.
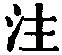 is defined by
is defined by
 , 'to compete for anything by archery.'
, 'to compete for anything by archery.'
16:2 We have no information about who these personages and the others below were, and I have missed the story, if it be in Lieh-dze. The duke, it will be seen, had the appanage of Kâu.
17:1 Pay more attention to any part of their culture which they are neglecting.
17:2 It served its purpose there, but had not been put in its place with any special object.
18:1 This may seem to nourish the body, but in reality injures the life.
18:2 Who had the charge also of the sacrifices.
18:3 Lin Hsî-hung says that the story shows the many troubles that arise from not renouncing the world. Ensnared by the world, men sacrifice for it their higher life, and are not so wise as pigs are for their life. The short paragraph bristles with difficulties.
18:4 The first of the leading chieftains among the princes; B.C. 683-642.
18:5 His chief minister.
19:1 An officer introduced here for the occasion, by surname Hwang, and designation Kâo-âo. The Dze simply = Mr.
19:2 The commentators have a deal to say about the folklore of the various sprites mentioned. 'The whole shows that ghostly sprites are the fruit of a disordered mind.' It is a touch of nature that the prince recovers as soon as he knows that the ghost he had seen was of good presage.
20:1 According to the Lieh-dze version of this story (Bk. II, 17b) the king was king Hsüan, B.C. 827-782. The trainer's rule seems to have been that his bird should meet its antagonist, with all its vigour complete and undisturbed, and not wishing to fight.
20:2 I think that there are two versions of this story in Lieh-dze. In Bk. VIII (4b, 5a), it appears that Confucius was on his way from Wei to Lû, when he stopped his carriage or cart at this spot to view the cataract, and the incident occurred, and he took the opportunity to give the lesson to his disciples.
22:1 The Dze or rottlera was and is a very famous tree, called 'the king of trees,' from its stately appearance and the excellence of its timber.
22:2 The 'bell-stand' is celebrated in the Shih King, III, i, Ode 8. A complete peal consisted of twelve bells, suspended in two tiers one above the other.
23:1 Ki would be the name of the charioteer, a gentleman of La, called Tung-yê, 'eastern country,' I suppose from the situation of his estate.
23:2 Duke Kwang would be the marquis Thung of Lû, B.C. 693-662.
23:3 Yen Ho was probably the chief of the Yen family at the time. A scion of it, Yen Hui, afterwards became the favourite disciple of Confucius. He could hardly be the same Yen Ho who is mentioned in Bk. IV, par. 5. Ki has had, and still has, his representatives in every country.
23:4 Shui is mentioned in the Shû King, V, xxii, 19, as a famous maker of arrows. Some carry him back to the time of Shun.
24:1 Literally, 'Tower of intelligence,'--a Tâoistic name for the mind.
24:2 A weakling, of whom we know only what we read here.
25:1 This must have been a man of more note. We find him here with a school of disciples in his house, and sought out for counsel by men like Sun Hsiû.
26:1 Compare par. 5, Bk. XVIII.